
The most recent wildfires in L.A. caused countless destruction of both human infrastucture and wildlife. Researchers have started to look into the cause for the destruction, and evidence is pointing them towards factors like the drought, winds, and dry conditions.
Hotter, Drier Conditions
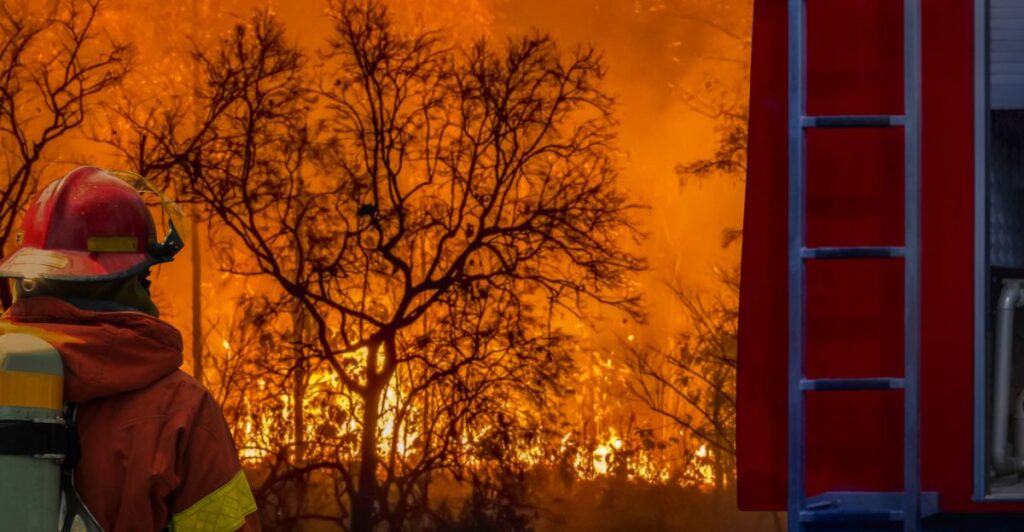

Climate change seems to be creating the conditions that are perfect for the L.A. wildfires. Researchers found that the heat conditions that caused the fires were about 35% more likely due to climate change, leaving the area with less rain and drier vegetation.
The Role of Fossil Fuels

The biggest contributor to global warming by humans is the burning of fossil fuels like coal, which provides electricity for most of the world. With the earth heating up, weather events become more extreme, which leads to the perfect conditions associated with wildfires. Moving away from fossil fuels will slow down global warming a significant amount.
Santa Ana Winds

Southern California is no stranger to the Santa Ana winds, which have the potential to help spread the wildfires a great deal. They played a role in the most recent fires, which spread far and wide as more dry vegetation caught fire.
Increased Likelihood
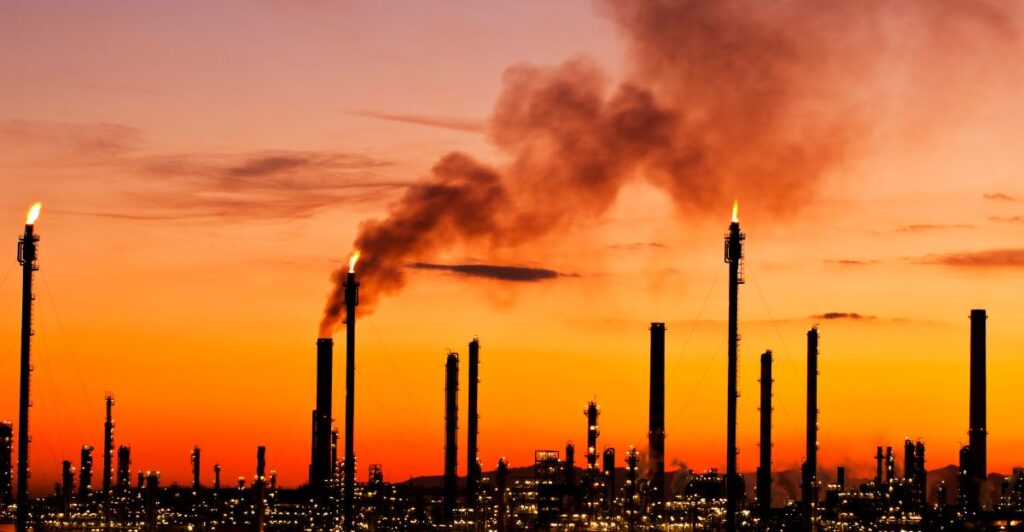

As global warming increases, the chance of wildfires will only go up. The most recent chances went up 35%, but in future they may go up much more unless climate change can be slowed or other preventative measures like controlled fires are carried out.
Longer Fire Season
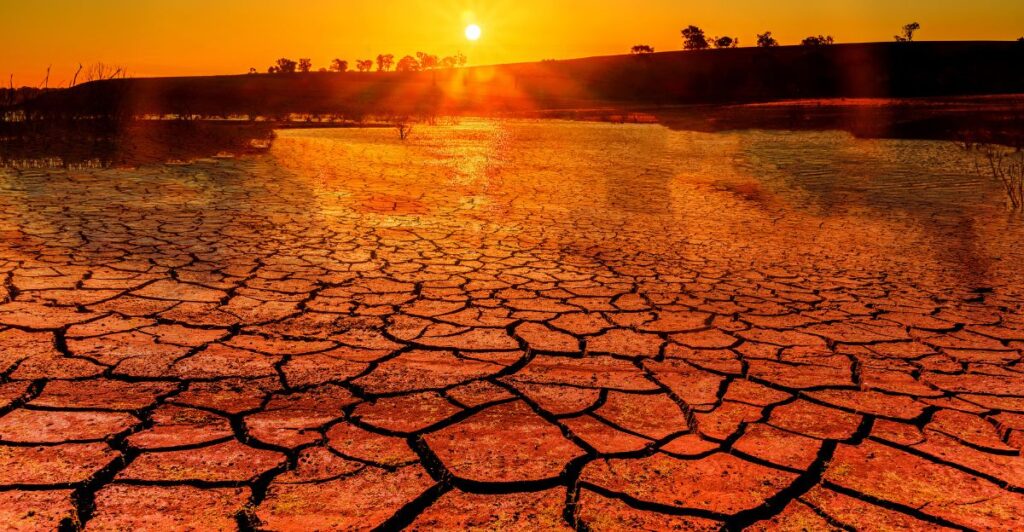

The effects of the industrial age on the climate are evident, with dry seasons in Los Angeles lasting nearly a month longer than they used to. This is directly linked to human-induced global warming through industrial pollution. The region is now over two times more likely to experience a dry winter compared to before the industrial era.
Hydroclimate Whiplash
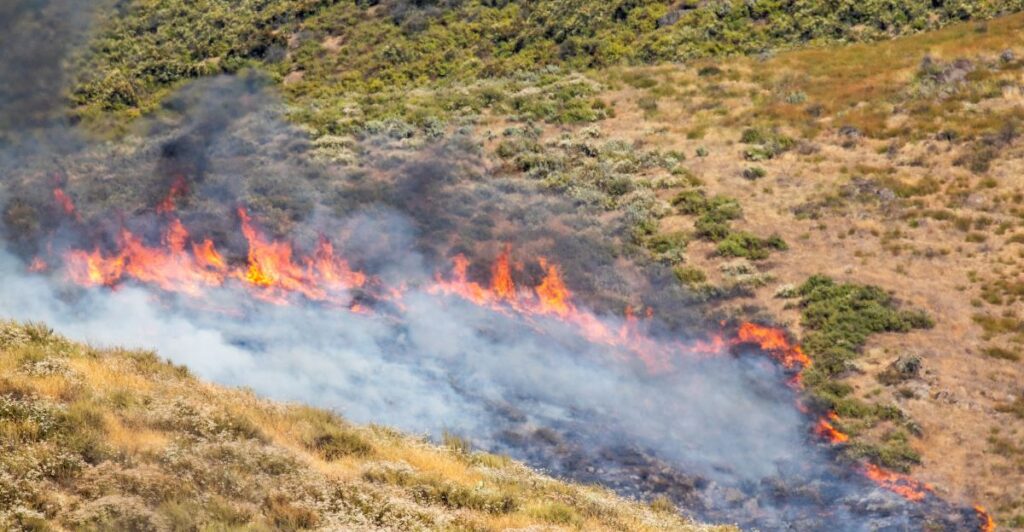

Global warming also introduces drastic shifts of wet seasons into dry ones. More rainfall in the winter means that more vegetation can flourish before the harsh and dry summer, which becomes fuel for wildfires. This sudden shift in seasons is called hydroclimate whiplash.
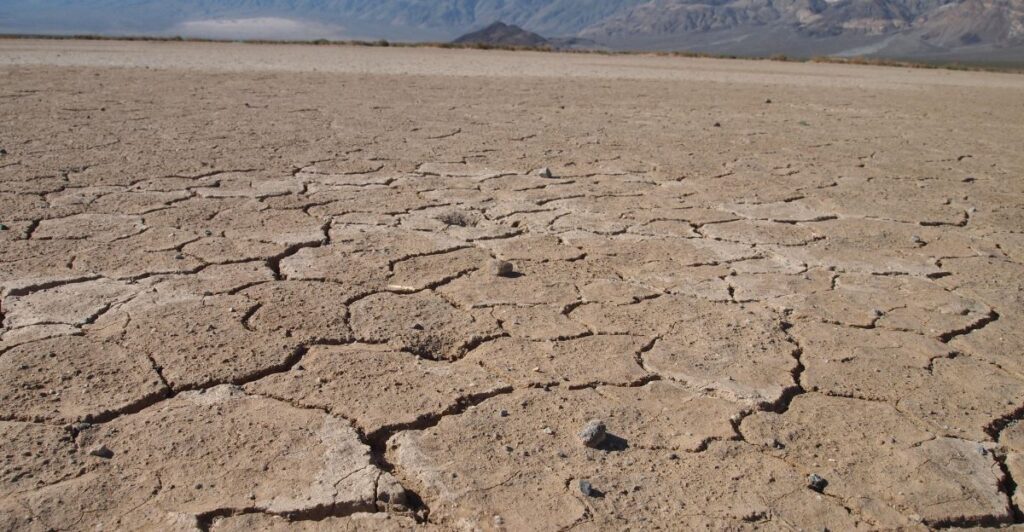
Impact on Rainfall
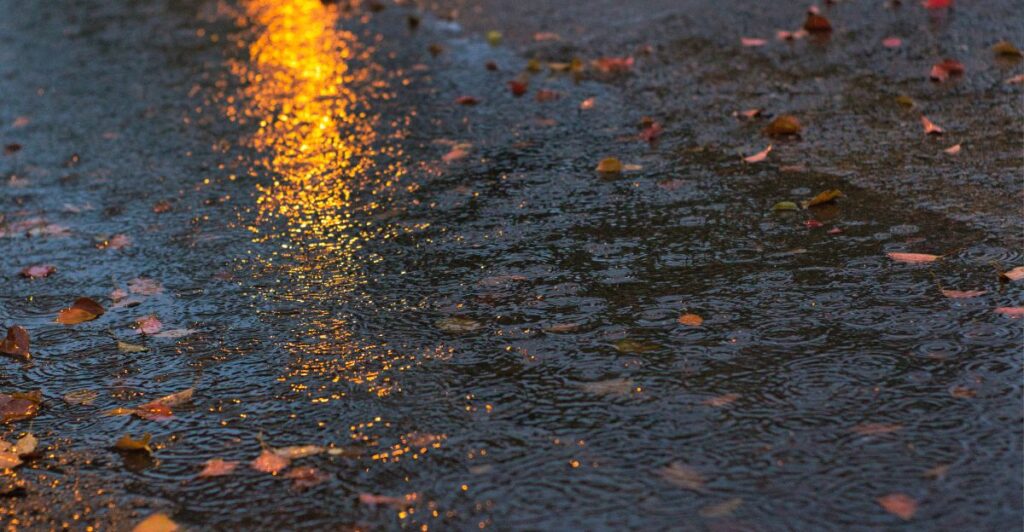

Rainfall has a significant impact on wildfires, as droughts create the perfect conditions for wildfires. With rainfall being hard to come by in current months, it puts the landscape at a greater risk of another wildfire. The lack of rainfall used to mostly be between October and April, although recently, a drier winter is more likely to happen.
Climate Change and Burned Areas
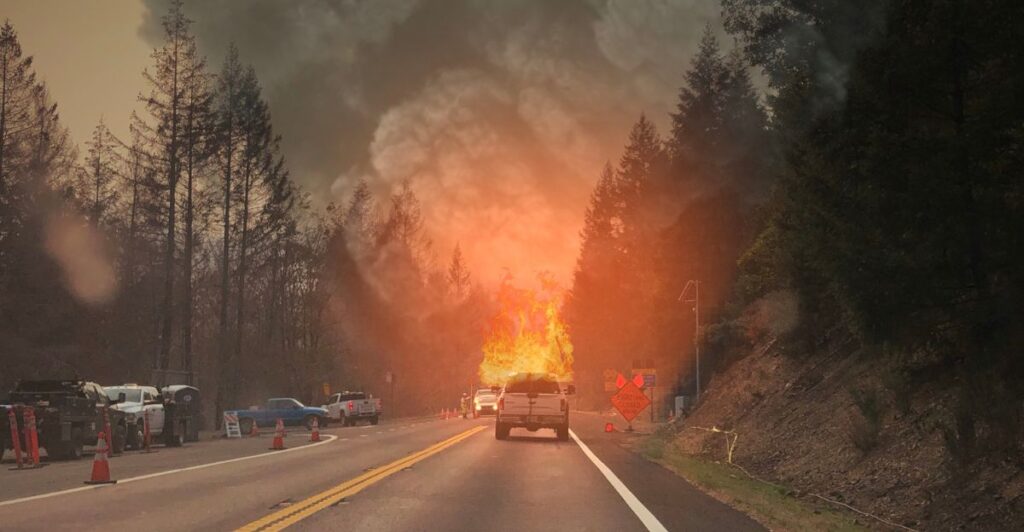

Researchers have already linked the climate emergency to a large increase in burned areas in California since the 1970s. The situation is only expected to worsen in the years to come. Climate change has increased the frequency, duration, and area affected by wildfires.
Habitat Destruction
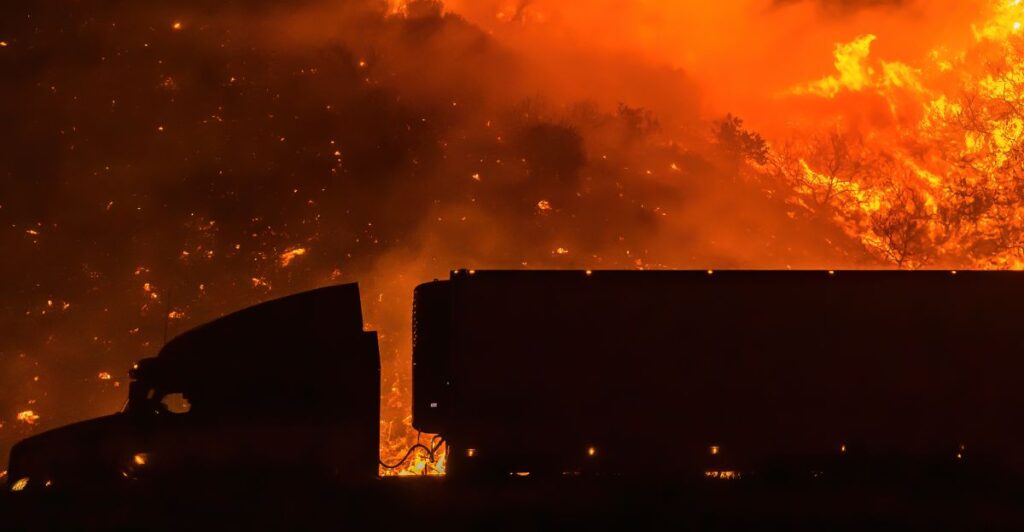

The wildfires have caused significant habitat destruction, impacting local ecosystems. Wildfires are a natural part of the local ecosystem, with some species even depending on it. However, the increased frequency and intensity of these fires are disrupting these ecosystems.
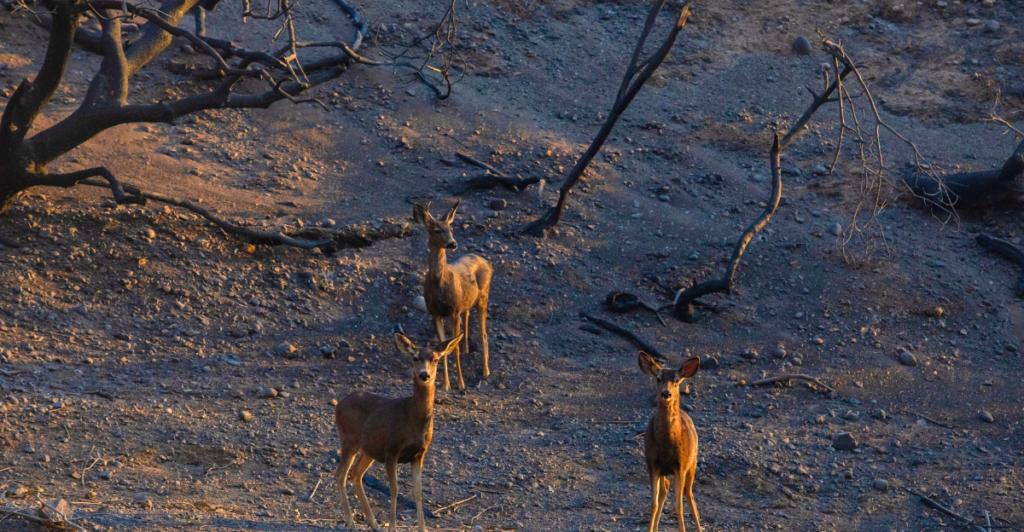
Threats To Wildlife
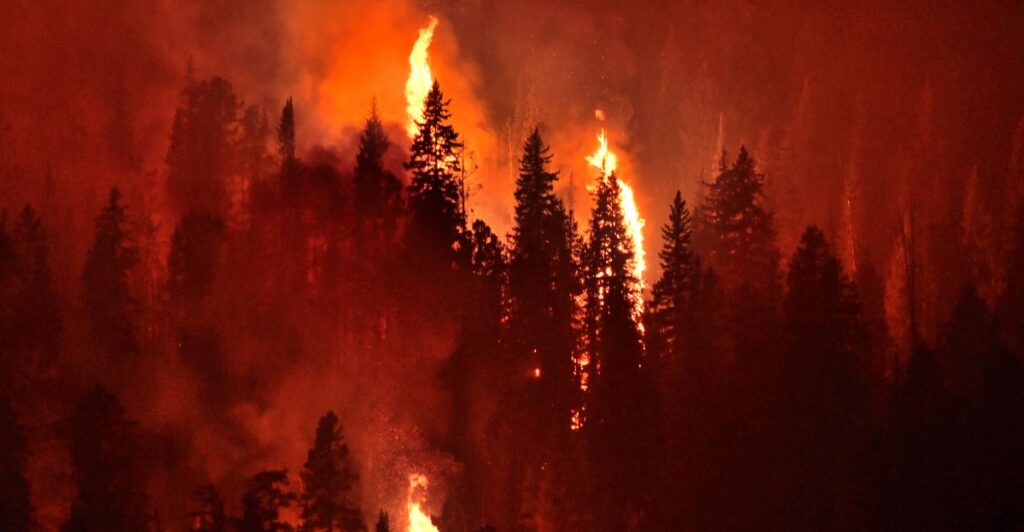

The Los Angeles wildfires pose immediate and severe threats to wildlife. Animals face direct mortality from the flames, which can be especially devastating for slower-moving creatures. Smoke inhalation causes respiratory issues, and the overall stress of fleeing the fires weakens animals, making them more vulnerable.
Habitat Loss and Displacement
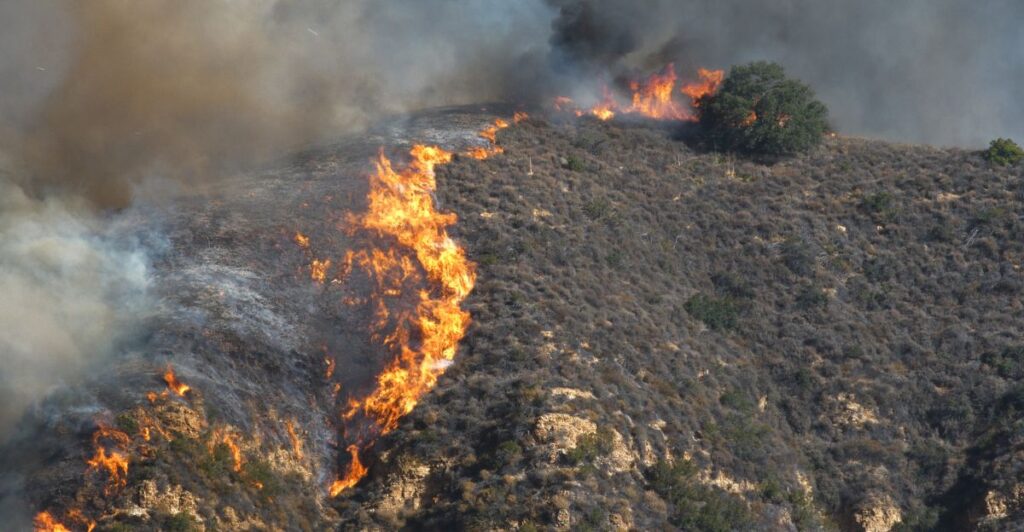

Wildfires destroy critical habitats and food sources, displacing animals and disrupting ecosystems. Mountain lions, for example, avoid burned areas after fires, increasing the size of their range to find food and risking encounters with humans. The loss of cover makes hunting difficult, potentially leading to starvation.
Vulnerable Species
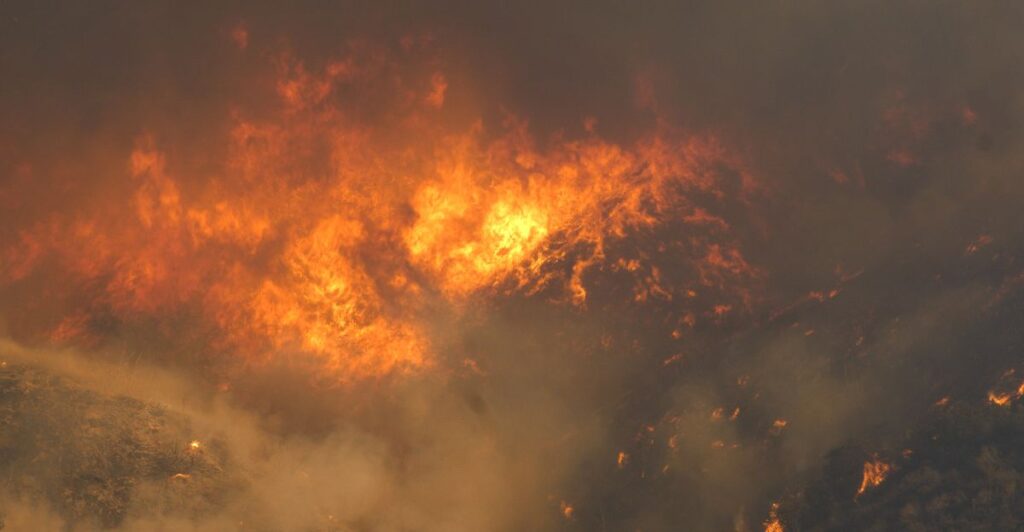

Certain species are particularly vulnerable to the effects of wildfires. Slow-moving animals like snails and salamanders struggle to escape the flames. Nocturnal animals forced to move during the day face increased risks. Animals that require specific habitats and those with young are also highly susceptible. The loss of overwintering sites for monarch butterflies is a harsh blow in a year with already low returns.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them appearing in your feed
The Real Cause Behind Los Angeles’ Devastating Wildfires
Rescue Efforts in Full Swing as Animals Face Wildfire Threats in California
The War on Cows Is Over—And Green Extremists Have Lost
There Will Be Eruptions”: Concerns Mount as Yellowstone Supervolcano Activity Shifts
References:
Reference 1
This article first appeared here
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







