
Waterfalls captivate with their awe-inspiring beauty, yet one of Earth’s greatest wonders lies hidden beneath the ocean. The Denmark Strait cataract, the world’s largest waterfall, remains unseen, plunging to astonishing depths under the Denmark Strait, a narrow passage between Iceland and Greenland. This natural marvel reveals the incredible power and mystery of the planet’s underwater landscapes.
The Unseen Giant
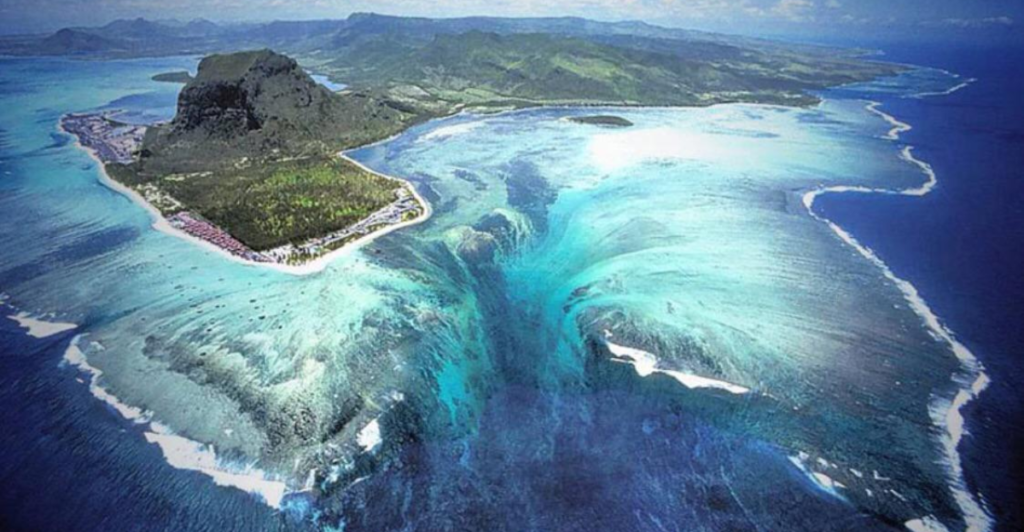

The Denmark Strait cataract is a waterfall like no other, hidden deep beneath the waves. Spanning an incredible height of 11,500 feet, it dwarfs Angel Falls, the world’s tallest land-based waterfall, which measures 3,212 feet. Its sheer scale makes it a remarkable yet invisible wonder of nature.
A Spectacle of Scale
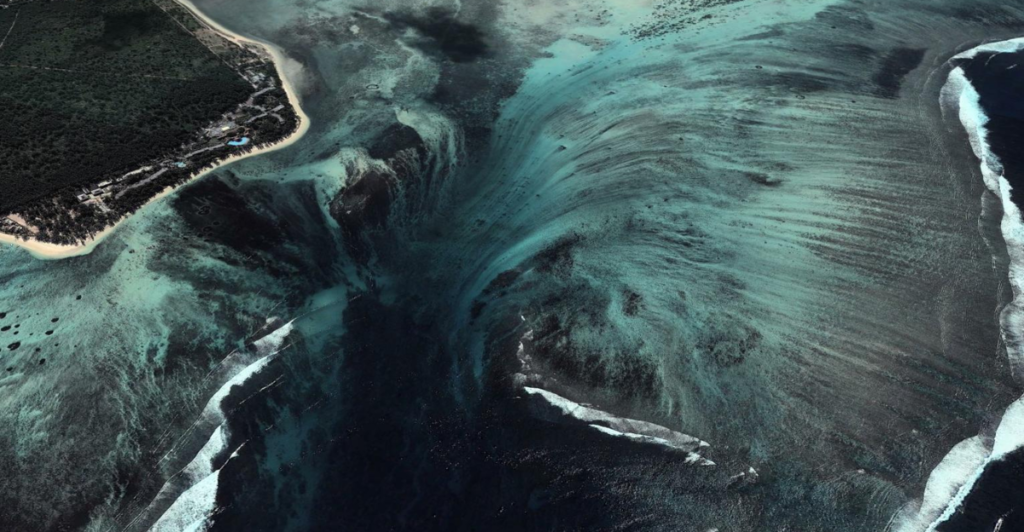

This underwater cascade carries an extraordinary 175 million cubic feet of water per second—2,000 times the volume of Niagara Falls. Its towering height and massive flow are made even more impressive by its concealment, hidden under thousands of feet of ocean.
How It Was Formed

The Denmark Strait cataract owes its existence to geological events during the last ice age, 17,500 to 11,500 years ago. As glaciers shaped the seafloor, they created the conditions necessary for this massive underwater phenomenon to form.
The Science Behind the Flow

The cataract is naturally created by the interaction of cold, dense water from the Nordic Seas and warmer water from the Irminger Sea. The colder water sinks below the warmer water, creating a powerful downward flow over the ocean floor.
A Hidden Journey Downward

The series of cascading underwater waterfalls begins 2,000 feet below the surface and drops to a depth of 10,000 feet at the southern tip of Greenland. Despite its immense scale, this natural wonder is entirely hidden from view.
Beyond Human Eyes

Unlike land-based waterfalls, the Denmark Strait cataract cannot be seen from above or even from space. It can only be detected through advanced mapping technologies that measure water temperature and salinity.
The Role of Ocean Currents

This underwater cascade is an integral part of the Atlantic-wide ocean circulation system. It helps regulate the movement of cold and warm water currents, playing a critical role in maintaining the Earth’s climate balance.
Slow Yet Mighty

Although the water plunges from staggering heights, its flow is surprisingly slow. It moves at just 1.6 feet per second, a stark contrast to Niagara Falls, where water rushes at 100 feet per second. This slow pace belies the cataract’s immense power.
Other Underwater Waterfalls

While other underwater waterfalls exist, none compare to the Denmark Strait cataract in size or scale. These phenomena result from a combination of temperature, salinity, tides, and oceanic circulation patterns.
A Glimpse of Arctic Serenity

At the surface, the Denmark Strait offers typical Arctic conditions—calm, icy waters under sunny skies. Yet, beneath this serene exterior lies one of the most extraordinary natural formations on Earth.
Insights from Experts

Marine scientists emphasize the slow, almost imperceptible movement of the Denmark Strait cataract. According to experts, standing on the ocean floor near the waterfall would reveal a vast yet subtle flow, a testament to the quiet force of underwater currents.
A Marvel of Nature
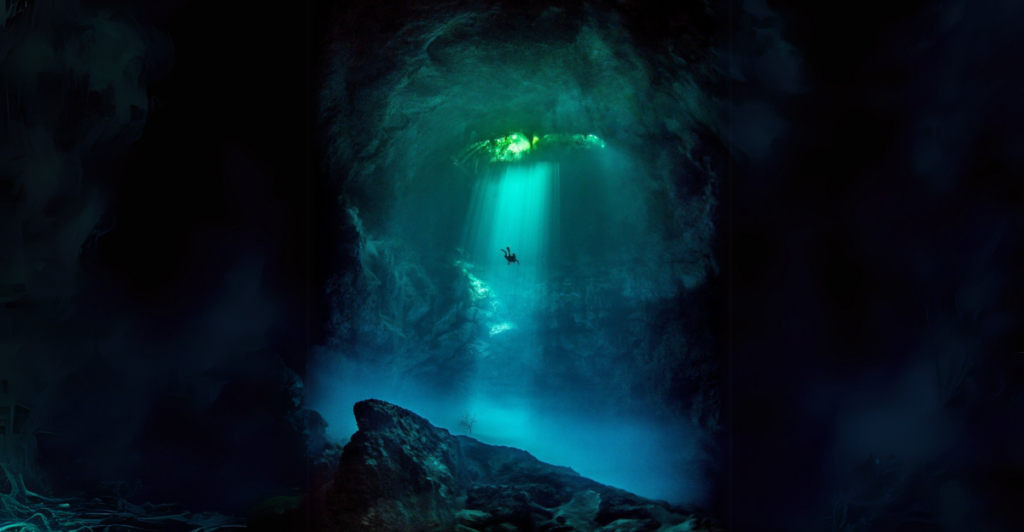

Though unseen and unreachable, the Denmark Strait cataract is a testament to the planet’s hidden wonders. Its immense scale, critical role in ocean circulation, and mysterious beauty remind us of the vast and unexplored marvels beneath the ocean’s surface.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them appearing in your feed
Colossal American Impact Crater Found—Three Times Bigger Than the Grand Canyon
Deepest Hole On Earth Permanently Sealed After 2 Billion Year Old Discovery
Waterfall Found To Shelter One Of Earth’s Nine Eternal Flames
Scientists Confirm Underwater Megastructure Isn’t Natural
References:
Denmark Strait Cataract: World’s Largest Underwater Waterfall Discovered
The world’s largest waterfall hidden 6,600 feet tall underwater amazes scientists
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







