
A23a, the world’s largest iceberg, might collide with South Georgia, a British Overseas Territory. This huge ice formation threatens wildlife in the region, especially seals and penguins. Scientists are observing its course.
Size and Origin
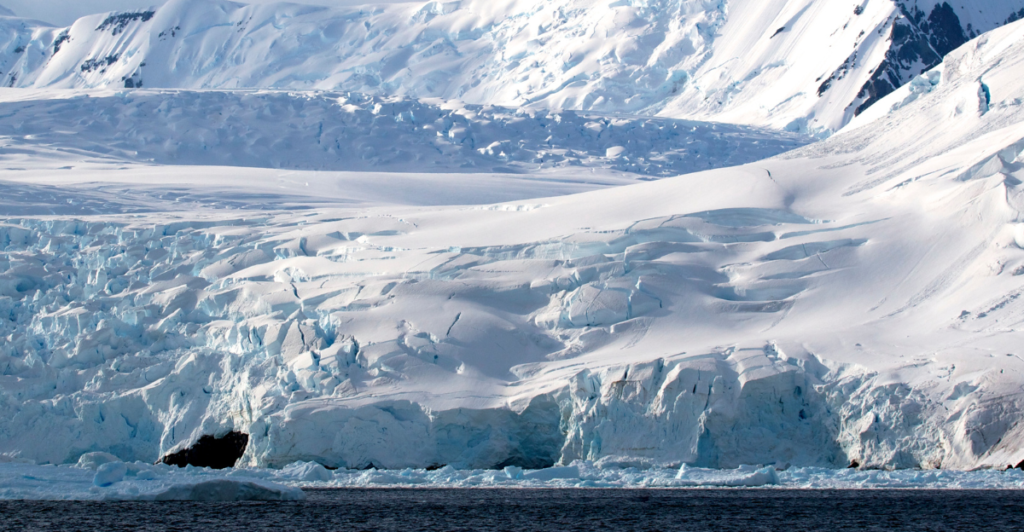

A23a is approximately 3,500 square kilometers. The iceberg is larger than Rhode Island. It has remained entrapped at the bottom of the sea for over three decades. It emerged from the Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf in Antarctica in 1986. In 2020, it began its journey northward.
Current Location

A23a is now, as of late January 2025, approximately 173 miles (280 kilometers) away from South Georgia. Researchers are observing its movement as it floats with ocean currents, which could change its course significantly. It may move toward the island’s shallow continental shelf.
Possible Effect on Wildlife

A23a’s potential collision with South Georgia may interfere with feeding grounds for millions of wildlife locally. About 1.3 million pairs of Chinstrap penguins and approximately 5 million seals may be affected. Icebergs have had a history of detrimental effects on animals in the area, affecting access to their food source.
Dynamics of Icebergs

Large icebergs like A23a behave unpredictably. Either they lock onto the continental shelf or they drift into deeper waters. The current trajectory suggests that in two to four weeks, A23a may ‘dock’ onto the continental shelf, but where exactly is anybody’s guess.
Historical Context

A23a is not the first iceberg that has threatened the South Georgia ecosystem. Previous icebergs have caused fatalities amongst penguin chicks and seal pups by blocking their feeding routes. If grounding occurs, the ecological impact may be evident for years.
Monitoring Efforts

A23a’s movements are being monitored by scientists from different organizations, including the British Antarctic Survey. They are using satellite imagery to predict its behavior and potential impacts on local wildlife and shipping routes.
Climate Change Considerations

While climate change did not cause the formation of A23a, it certainly does play a role in how icebergs move. Warmer ocean water may increase melting and create unstable ice formations. It may also lead to iceberg sections breaking off and falling into the ocean, (this is called calving), more frequently.
Scientific Research Opportunities

Scientists are analyzing how water from such an enormous iceberg affects ocean chemistry and the marine ecosystem.
Local Community Concerns

Local fishermen and residents of South Georgia are worried that the iceberg could affect their livelihoods. Icebergs may be hazardous to shipping vessels and fishing. They could also make access to valuable fishing grounds more difficult.
The Role of Ocean Currents

Ocean currents will determine the fate of A23a, either carrying it away from South Georgia or pushing it to its grounding on the continental shelf. Understanding these currents is essential in predicting future movements.
Future Predictions

According to experts, A23a is likely to become a common feature in the waters around South Georgia. Given its size and mass, it can be seen from far distances. This makes apparent the continuous changes at the poles due to climate dynamics.
A Colossal Climate Wake-Up Call

The journey of iceberg A23a serves as a reminder of the delicate balance in marine ecosystems and the challenges posed by climate change. While scientists continue to monitor this colossal iceberg, its impact on wildlife and the environment in South Georgia is significant.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them appearing in your feed
Massive Underwater Volcano Off U.S. Coast Shows Signs of 2025 Eruption
“There Will Be Eruptions”: Concerns Mount as Yellowstone Supervolcano Activity Shifts
The 10 Largest Sharks Ever Known to Roam the Seas
DNA Shows Woolly Mammoths Roamed Mainland North America Until 5,000 Years Ago
References:
Reference 1
Reference 2
This article first appeared here
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







