
In 2020, China unexpectedly laid claim to the Sakteng Wildlife Sanctuary, a biodiverse region in eastern Bhutan, during a Global Environment Facility (GEF) meeting. This marked the first time the sanctuary was included in territorial discussions, surprising Bhutan and the international community. The sanctuary, spanning approximately 750 square kilometers, is home to unique flora and fauna, including the red panda and, according to local lore, the yeti.
Bhutan rejected China’s claim, emphasizing that Sakteng has always been an integral part of its territory and was never previously disputed in the 24 rounds of boundary talks between the two nations. Analysts view this sudden claim as part of China’s broader strategy to assert its influence in the Himalayan region, potentially pressuring Bhutan and its ally, India. The dispute has raised concerns about regional stability, conservation efforts, and the sanctity of protected areas.
Strategic Significance of Sakteng
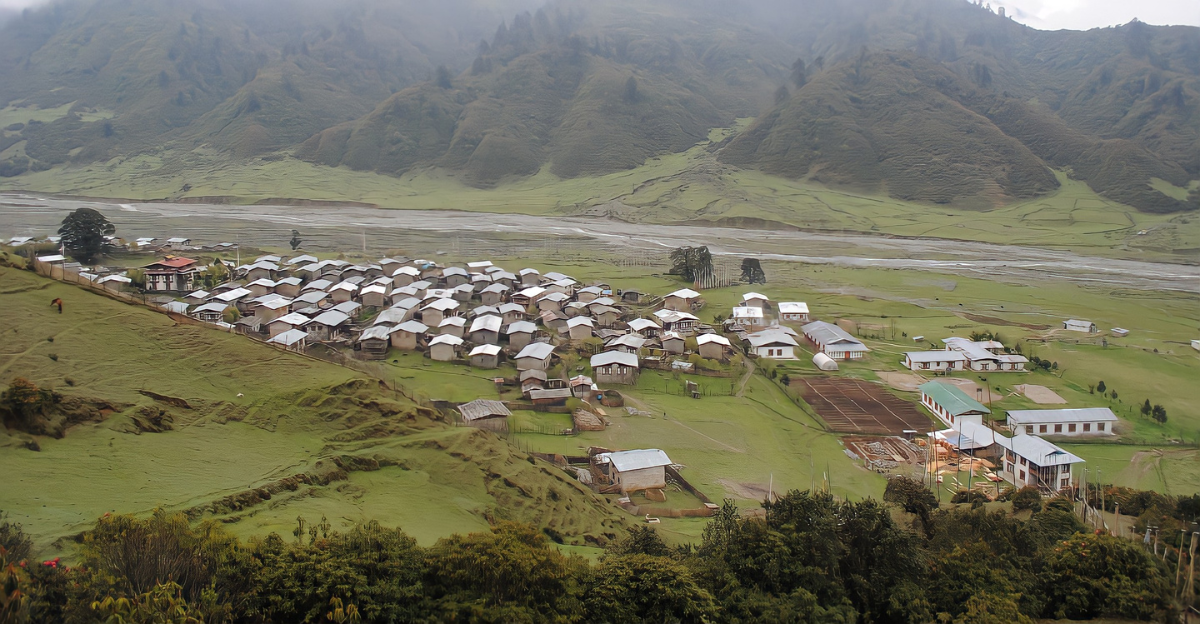

Sakteng’s location is not only ecologically important but also strategically significant. Situated near the tri-junction of Bhutan, India, and China, control over this area could provide strategic advantages, especially concerning the Siliguri Corridor, a narrow stretch connecting India’s northeastern states to the rest of the country.
Some experts perceive China’s claim over Sakteng as an attempt to gain leverage over India and Bhutan, potentially altering the balance of power in the region.
Bhutan’s Stance and International Reactions

Bhutan has rejected China’s claims over the Sakteng Wildlife Sanctuary, stating that the area has always been integral to its sovereign territory. This marks a rare challenge to Bhutan’s borders, which have traditionally seen limited dispute. India, Bhutan’s close ally, has voiced its support, especially relevant given its ongoing border tensions with China.
The claim has drawn international concern, spotlighting the complexity of territorial disputes and emphasizing the need to uphold established borders and international agreements to ensure regional peace and stability.
Environmental Implications of Territorial Disputes
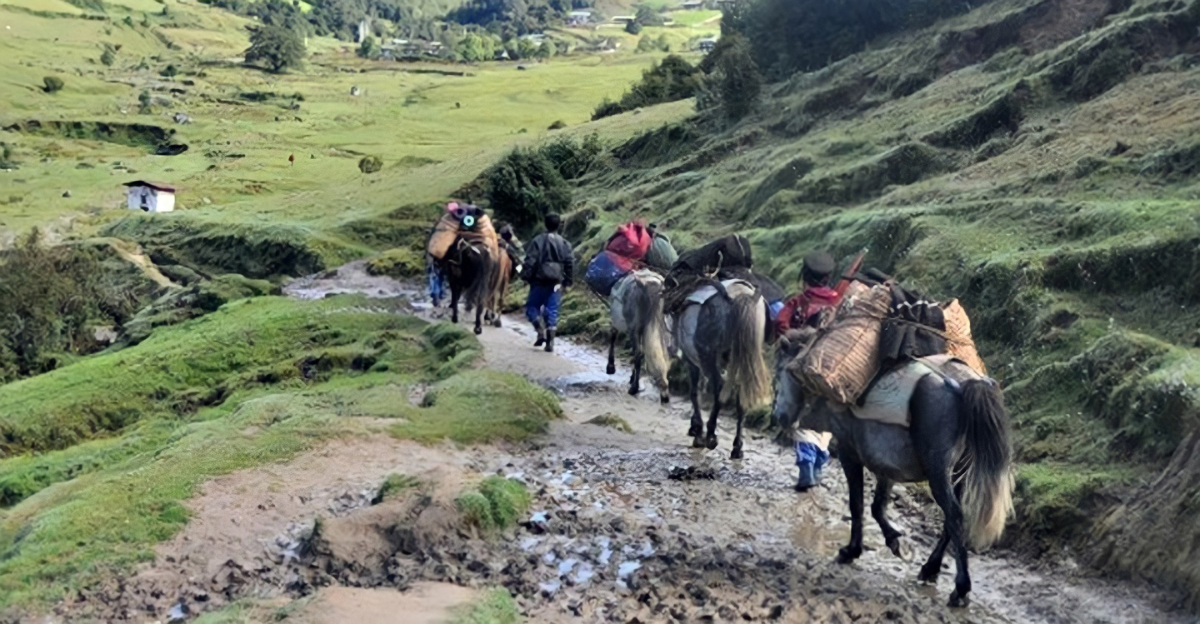

Territorial disputes like the one over Sakteng can significantly undermine conservation efforts. When protected areas become geopolitical flashpoints, they may face administrative neglect, diminished funding, and increased encroachment, all threatening biodiversity. The lack of clear jurisdiction hampers long-term planning, scientific research, and sustainable management.
This uncertainty puts endangered species and fragile ecosystems at heightened risk. Effective conservation requires political stability, international cooperation, and clearly defined boundaries to ensure that environmental goals are not sacrificed amid diplomatic tensions.
China’s Broader Territorial Assertions
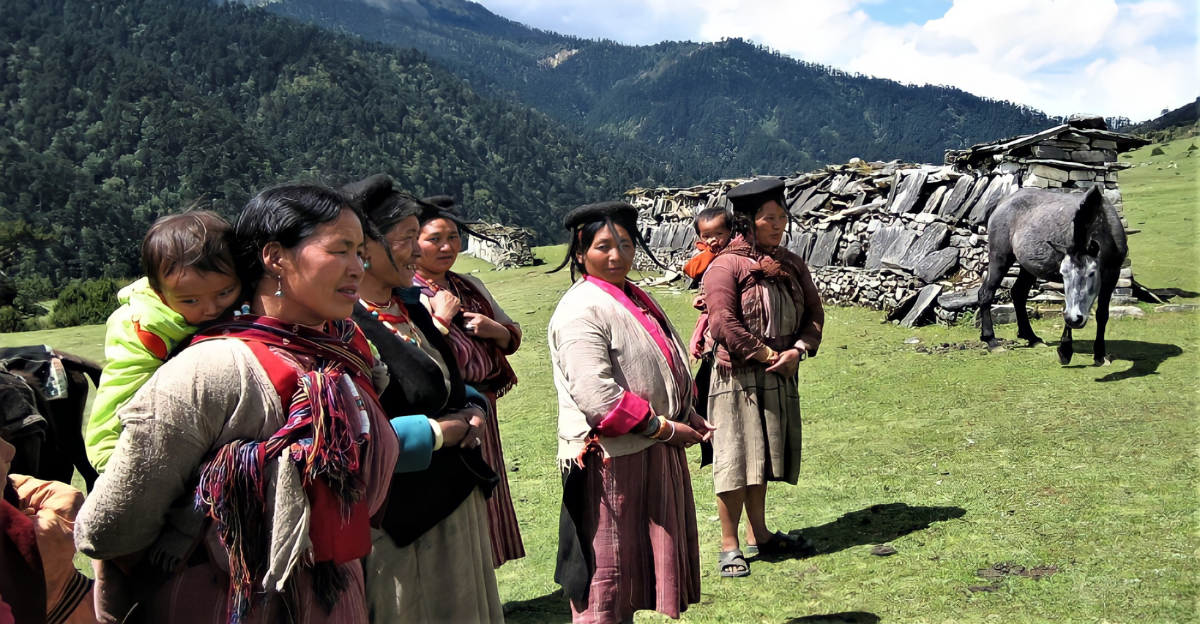

China’s claim over Sakteng is emblematic of a broader pattern of territorial assertions across Asia. In recent years, Beijing has escalated border disputes with neighboring countries such as India, Nepal, and the Philippines. These contested regions often hold strategic or economic importance, including access to trade routes, natural resources, or military vantage points.
Analysts suggest that these actions reflect China’s growing regional ambitions. The Sakteng claim, while unprecedented in Bhutan, fits a larger strategy of reinforcing control over borderlands, increasing diplomatic pressure, and testing the resolve of smaller neighboring nations.
Conservation Amidst Geopolitical Tensions

The intersection of conservation and geopolitics presents complex challenges. Protected areas like Sakteng are designed to safeguard biodiversity and promote ecological research, yet their integrity can be threatened when territorial disputes arise. Political tensions can disrupt conservation funding, management, and enforcement, undermining environmental goals.
To maintain the sanctuary’s ecological value, nations must cooperate across borders and prioritize environmental protection. Separating conservation from geopolitical conflict ensures long-term preservation of unique ecosystems and fosters global environmental stewardship.
The Role of International Organizations

International organizations are pivotal in balancing geopolitics with conservation. The United Nations fosters diplomatic dialogue between nations in conflict through its peacebuilding and environmental programs. The Global Environment Facility (GEF), which funds biodiversity and climate initiatives, also supports conservation in disputed regions.
These institutions provide critical funding and offer platforms for negotiation and cooperation. Their neutral stance and global influence help uphold environmental priorities, even in tense political landscapes where sovereignty and strategy often take precedence.
Importance of Clear Demarcation

Clear and mutually agreed-upon borders are essential to preventing territorial disputes, especially in environmentally sensitive areas. When boundaries are ambiguous or contested, tensions can escalate, disrupting conservation efforts and undermining regional cooperation. Protected areas, such as wildlife sanctuaries, require stability and transparent governance to ensure effective management.
Diplomatic negotiations focusing on mutual respect and international law are vital for establishing precise demarcations. Such clarity helps safeguard biodiversity, fosters peaceful coexistence, and promotes long-term ecological sustainability in regions shared by multiple nations.
Potential for Regional Cooperation

Despite ongoing tensions, there remains meaningful potential for regional cooperation in conservation efforts. Neighboring countries, such as Bhutan, China, and India, can work together on transboundary protected areas and ecological zones that span national borders. These initiatives can help protect shared biodiversity, mitigate habitat fragmentation, and enhance environmental resilience.
Beyond ecological benefits, such collaboration fosters trust, improves diplomatic dialogue, and encourages peaceful coexistence. Joint conservation projects can act as a neutral ground, allowing countries to engage on non-political terms and reinforce mutual respect for territorial sovereignty and shared environmental responsibilities.
The Path Forward

Resolving the Sakteng Wildlife Sanctuary dispute demands a balanced approach grounded in diplomacy, international law, and conservation ethics. Dialogue, not confrontation, must remain the primary tool for resolving territorial tensions. Upholding Bhutan’s sovereignty while ensuring the protection of this ecologically rich sanctuary is essential for long-term peace and environmental stability.
International bodies can play a constructive role by mediating talks, encouraging transparency, and supporting cross-border conservation efforts. As geopolitical interests continue to grow, so does the responsibility to protect shared natural heritage for future generations through peaceful, cooperative means.
Explore more of our trending stories and hit Follow to keep them coming to your feed!
Don’t miss out on more stories like this! Hit the Follow button at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest news. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!







