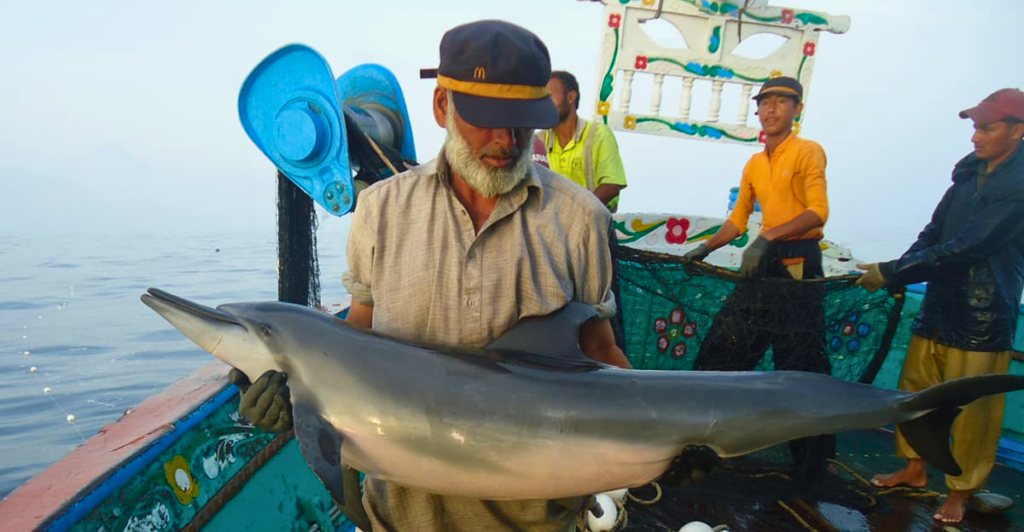

In a historic step toward protecting marine life, the United States this week agreed to ban the imports of seafood linked with the deadly bycatch of dolphins, whales, and other marine mammals. The decision follows a settlement agreement reached by the U.S. Court of International Trade and is a major step toward the enforcement of long-overlooked provisions of the Marine Mammal Protection Act. The ban, which will go into effect on January 1, 2026, aims to protect threatened species and level the playing field for American fishers who comply with stricter domestic standards.
Background of the Ban

The ban results from a lawsuit filed by the Animal Welfare Institute, the Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC), and the Center for Biological Diversity, represented by Anderson & Kreiger LLP. The suit targeted the U.S. Department of Commerce, National Marine Fisheries Service, Department of the Treasury, and Department of Homeland Security. This legal action was required to ensure that U.S. standards for protecting marine mammals from bycatch in foreign fisheries were enforced.
Purpose of the Ban
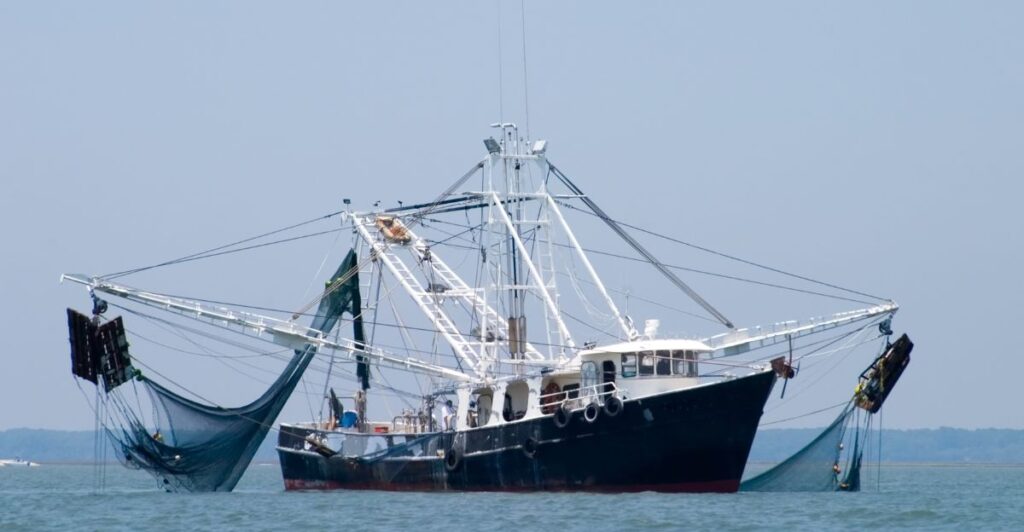

The policy’s primary purpose is protecting whales, dolphins, and seals from becoming ensnared in fishing nets used in foreign waters. This ensures that foreign fisheries follow the same standards imposed on U.S. fishers, who are already required to operate under strict regulations in domestic waters. This move not only protects marine mammals but will also benefit U.S. fishermen by creating a fair market environment.
Impact on Marine Mammals
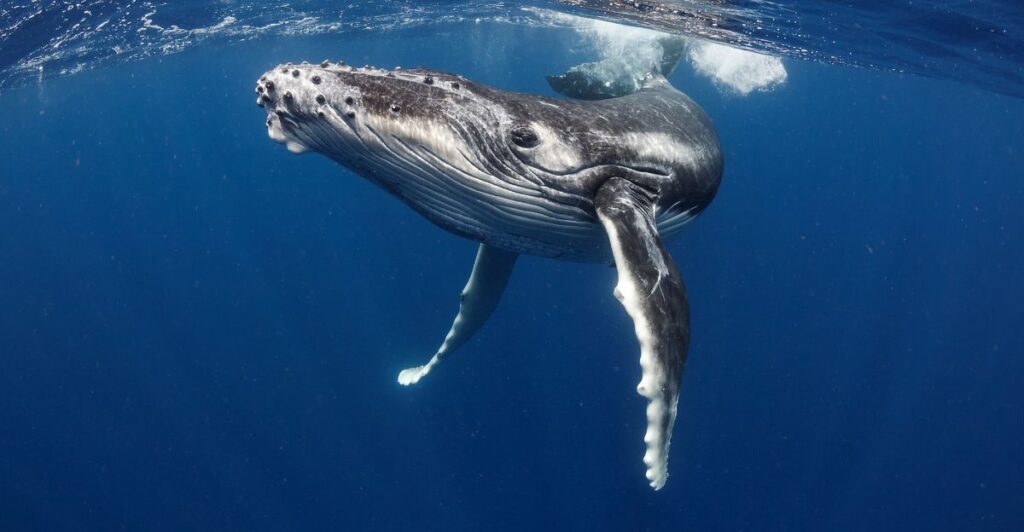

Bycatch kills more than 650,000 marine mammals, including whales, dolphins, and seals, every year worldwide. This unintentional capture is the greatest conservation threat to marine mammals globally. The ban is intended to decrease these numbers by imposing more stringent standards on foreign fisheries that export to the United States.
Bycatch: Biggest Threat to Conservation
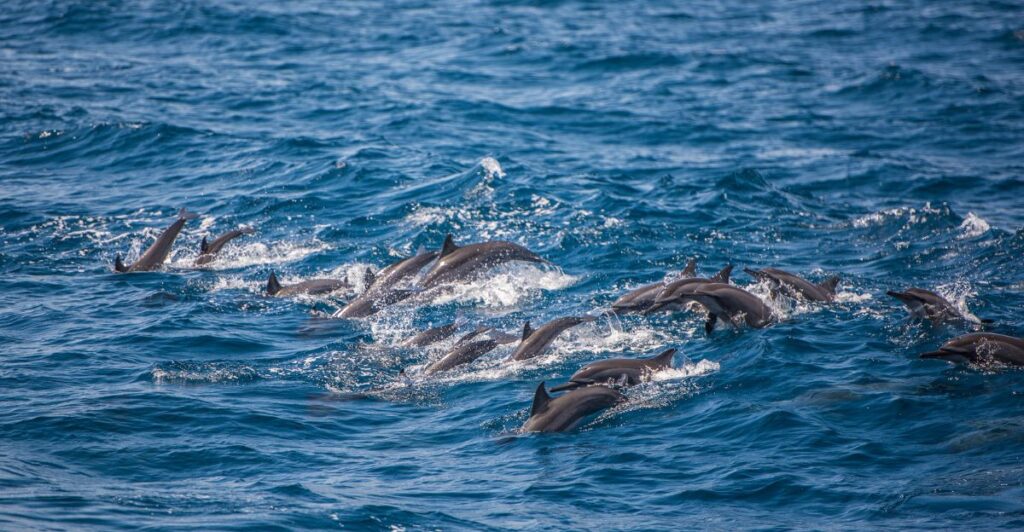

Bycatch is an industry term for marine life that gets caught accidentally by commercial fish. It results in death for many marine mammals either through drowning or injuries sustained during entanglement. Those who escape often leave with lingering injuries, like cuts and broken bones or amputations, and may die weeks or months later.
Legal Framework
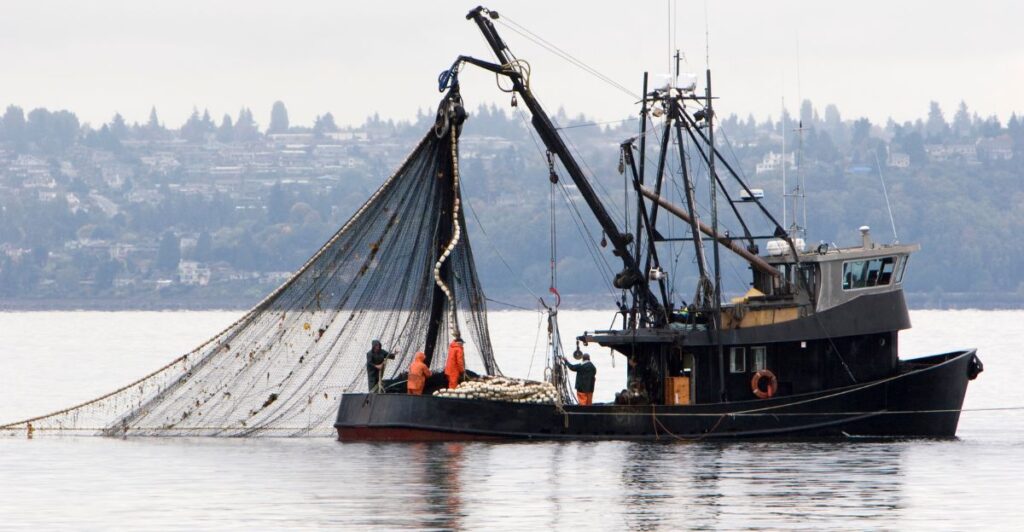

The United States Marine Mammal Protection Act, passed in 1972, prohibits the import of seafood from countries that don’t meet United States standards for reducing marine mammal bycatch. However, compliance with this provision was largely ignored until recent efforts to develop a formal process for identifying non-compliant fisheries.
Enforcement Delays

Despite creating a process in 2016 to help identify fisheries that did not meet the regulations and subject them to import bans, the U.S. government delayed imposing any bans. The recent settlement is a major step toward enforcing these standards and protecting marine mammals.
Conservation Groups’ Role

Conservation groups played a crucial role in pushing for this ban. The Animal Welfare Institute, NRDC, and Center for Biological Diversity were instrumental in filing the lawsuit, which resulted in the settlement. Their efforts highlight the importance of legal action in driving environmental policy.
Economic Impact

The U.S. is the planet’s biggest seafood importer, importing more than $25.5 billion worth of seafood every year. About 80% of seafood consumed in the U.S. is imported, much of it from China, Norway, Ecuador, Chile, and India. The ban would have a significant impact on these economies if they fail to meet U.S. standards.
Global Implications

The ban is expected to have global ramifications, as countries that export seafood to the U.S. will have to adopt more stringent measures to avoid marine mammals bycatch. This could drive significant changes in international fishing policies and practices.
Consumer Confidence
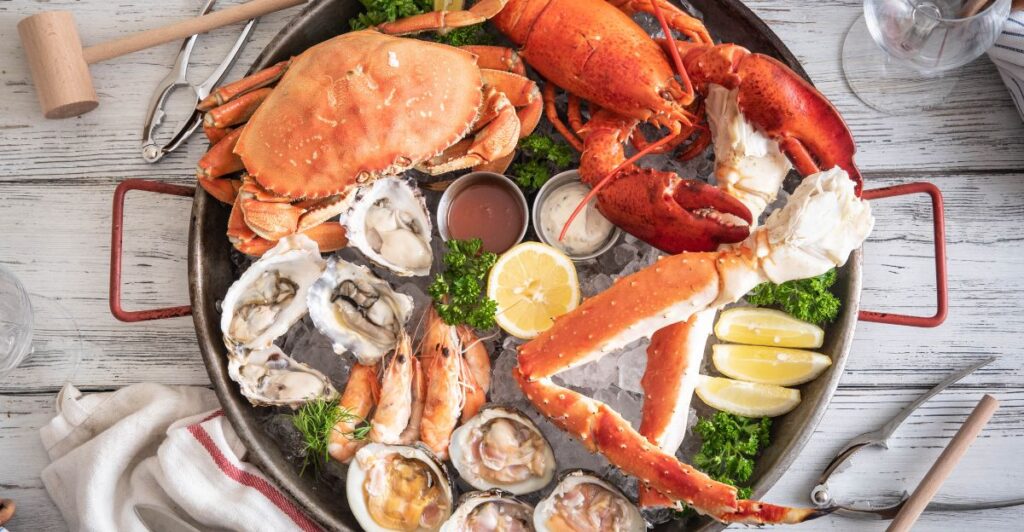

The move is also expected to instill more consumer confidence about the seafood they buy. Knowing that their seafood does not contribute to the needless killing of whales and dolphins can also bolster consumer trust in the U.S. seafood market.
Future of Marine Conservation
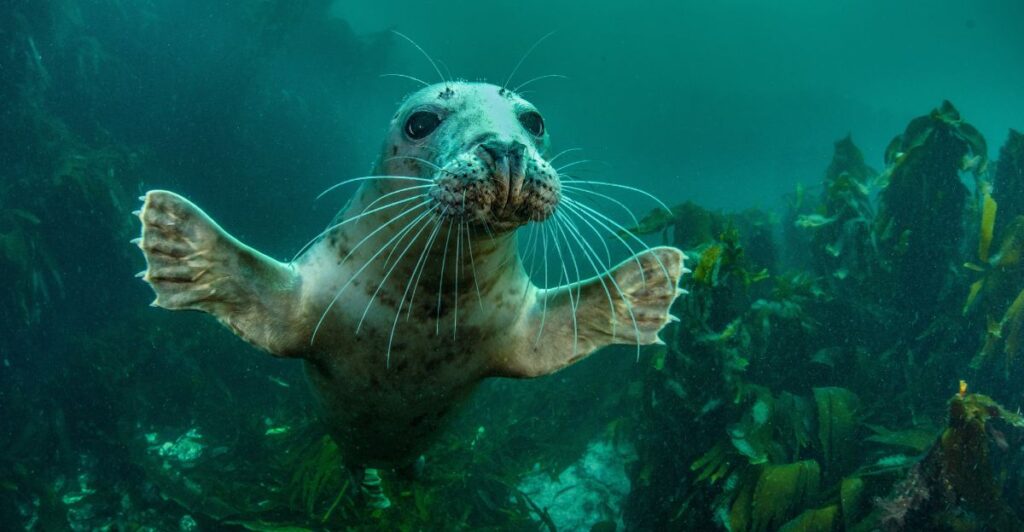

The agreement paves the way for future marine conservation efforts. The U.S. can use its market influence to put pressure on other countries to adopt stronger protections for marine wildlife. This could lead to a broader shift in global fishing practices and policies.
A Huge Step for Marine Conservation
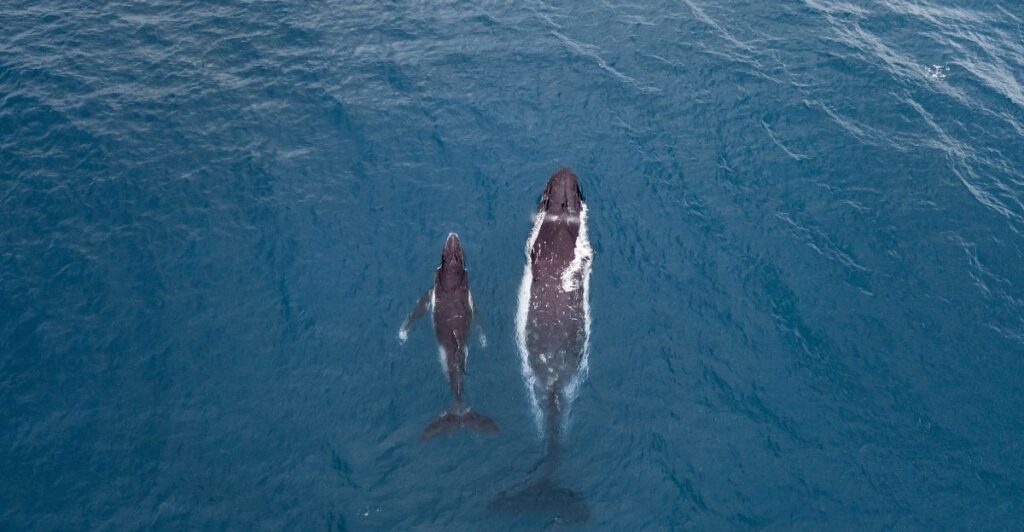

Overall, the United States ban on seafood imports associated with marine mammal bycatch represents a huge step forward for marine conservation. It also protects endangered species and promotes fair competition among fisheries. As the world’s largest seafood importer, the U.S. has the capacity to lead global change in fishing practices and set a new precedent for protecting marine mammals.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them in your feed
Concerns Mount as Largest Dolphin Pod Ever Recorded Headed For California
Scientists Have Returned to the Wild a Prehistoric Bird Thought to Be Extinct
The Most Expensive Dog Breeds in 2025 – Are They Worth the Price?
Yes, You Can Blame Climate Change for the LA Wildfires and Their Habitat Destruction
References:
Reference 1
Reference 2
Reference 3
This article first appeared here
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







