
Climate change is driving the spread of infectious diseases into northern regions previously unaffected. Rising temperatures and shifting precipitation patterns create hospitable environments for disease vectors like mosquitoes, ticks, and pathogens like fungi. This expansion poses new health risks to populations unaccustomed to these diseases. For instance, mosquitoes have been detected as far north as Shetland, Scotland, for the first time, raising concerns about the potential introduction of mosquito-borne illnesses in these areas.
Similarly, dangerous fungi like Aspergillus fumigatus are projected to expand their range by 77% by 2100, potentially exposing millions more to infections. These developments underscore the urgent need for enhanced surveillance, public health preparedness, and research into climate-sensitive diseases.
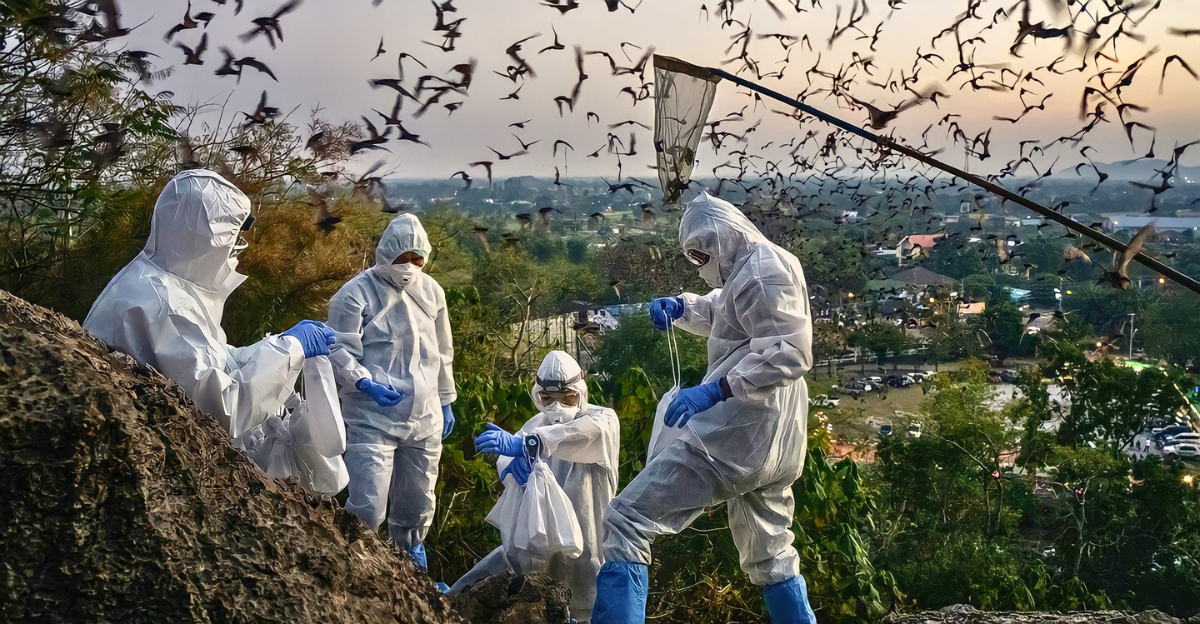
Mosquitoes Migrating Northward
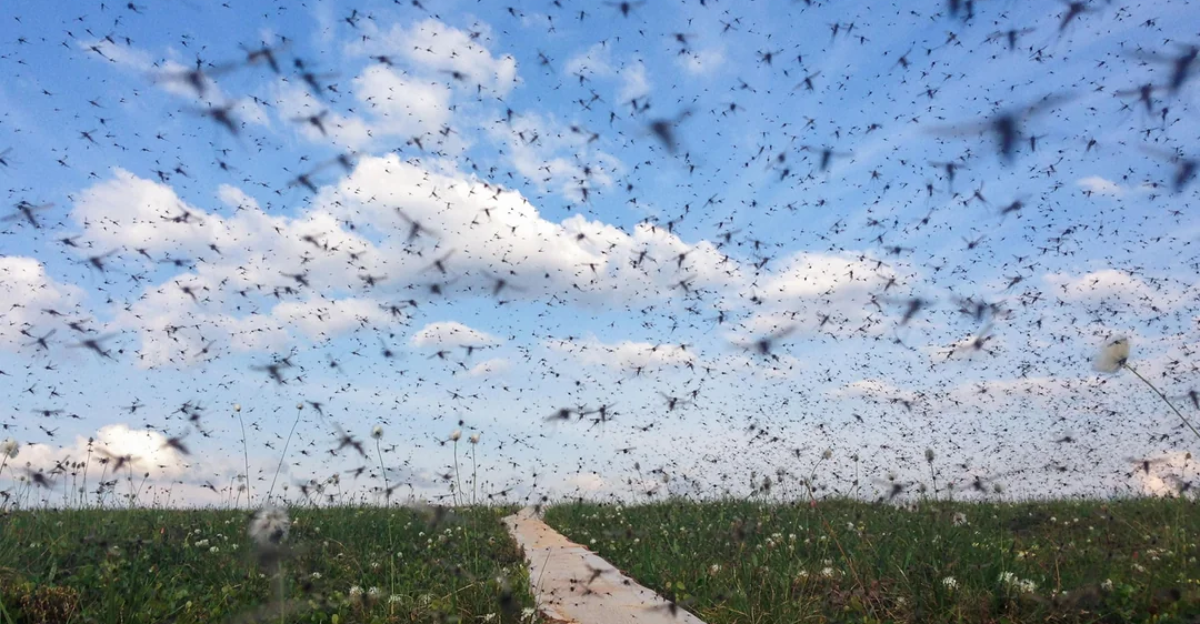

The northward migration of mosquitoes is a tangible indicator of climate change’s impact on disease dynamics. Warmer temperatures and altered precipitation patterns have enabled mosquito species to survive and reproduce in previously inhospitable northern climates. In the UK, a study by the University of Glasgow confirmed the presence of mosquitoes in Shetland, marking their furthest north reach.
This shift raises concerns about the potential spread of mosquito-borne diseases like West Nile virus and dengue fever into new regions. Public health authorities are urged to monitor these changes closely and implement vector control measures to mitigate risks.
Fungal Threats on the Rise

Fungal pathogens are emerging as significant health threats in the context of climate change. Species like Aspergillus fumigatus and Aspergillus flavus thrive in warmer, humid conditions, increasing prevalence in northern regions. These fungi can cause severe respiratory infections, particularly in immunocompromised individuals.
A study predicts that A. fumigatus could expand its range by 77% by 2100, potentially affecting an additional 9 million people in Europe alone. The rise in antifungal resistance further complicates treatment, highlighting the need for improved diagnostics and therapeutics.
Arctic Warming and Disease Emergence
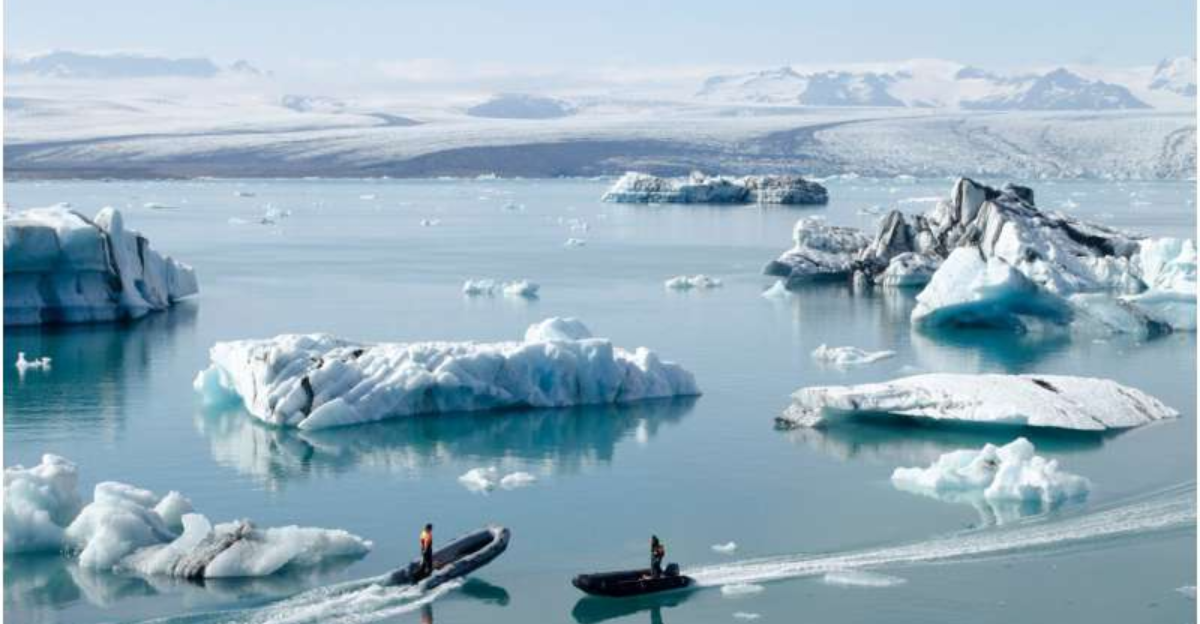

The Arctic is experiencing rapid warming, leading to ecological changes that facilitate the emergence and spread of infectious diseases. Melting permafrost and increased human activity in the region allow pathogens to infect new hosts.
Diseases such as brucellosis and tularemia, previously rare in the Arctic, are becoming more prevalent. These developments pose risks to indigenous populations and wildlife, necessitating comprehensive surveillance and public health strategies tailored to the unique challenges of the Arctic environment.
Migratory Birds and Tick-Borne Diseases
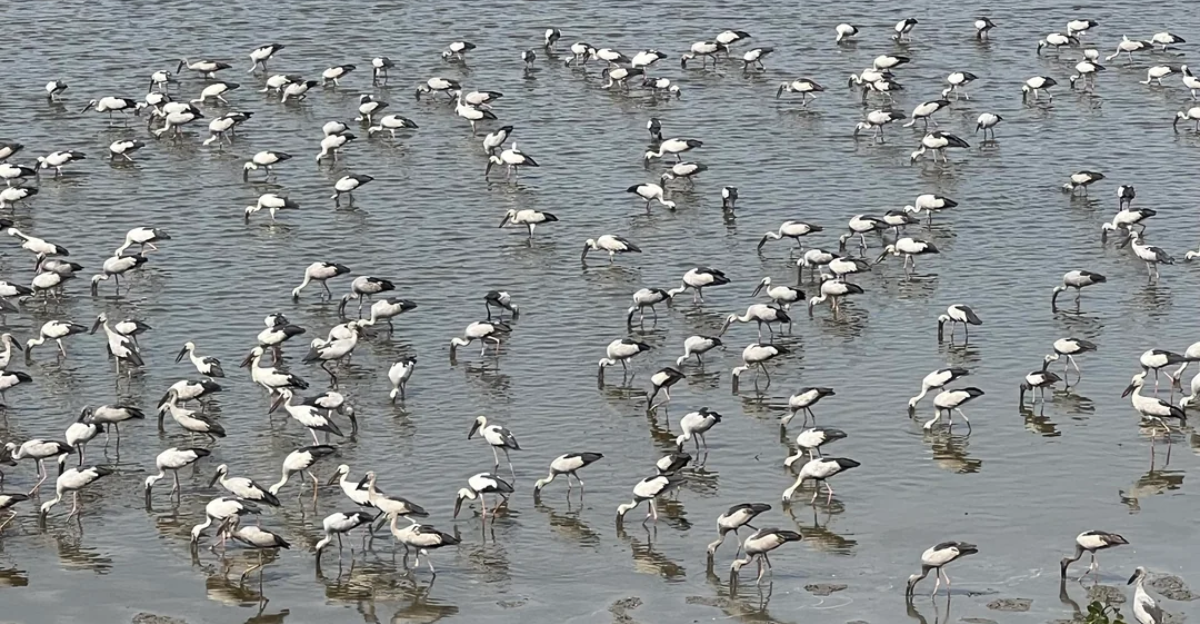

Climate change alters bird migratory patterns, which can carry ticks and associated pathogens over long distances. As birds move into new areas due to shifting climates, they introduce ticks into regions where they were previously absent.
This can lead to the establishment of tick populations and the spread of diseases like Lyme disease and tick-borne encephalitis in northern locales. Monitoring bird migration and tick distribution is essential for predicting and preventing outbreaks of tick-borne illnesses.
Vector-Borne Diseases Expanding Their Reach
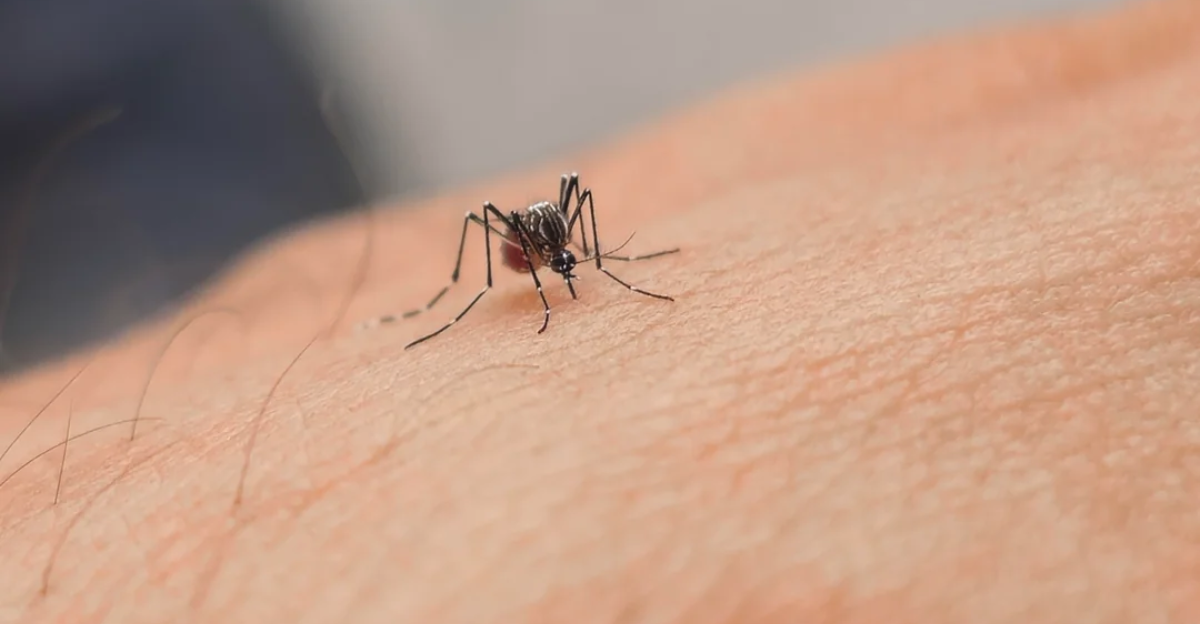
Vector-borne diseases are increasingly encroaching upon northern regions as climate change alters habitats and extends the active seasons of vectors. Once confined to tropical areas, dengue fever, chikungunya, and Zika virus are now reported in temperate zones.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) notes that climate factors significantly influence the distribution and prevalence of these diseases. Enhanced vector surveillance and public education are critical components of disease prevention strategies.
Food Security Threatened by Fungal Contamination
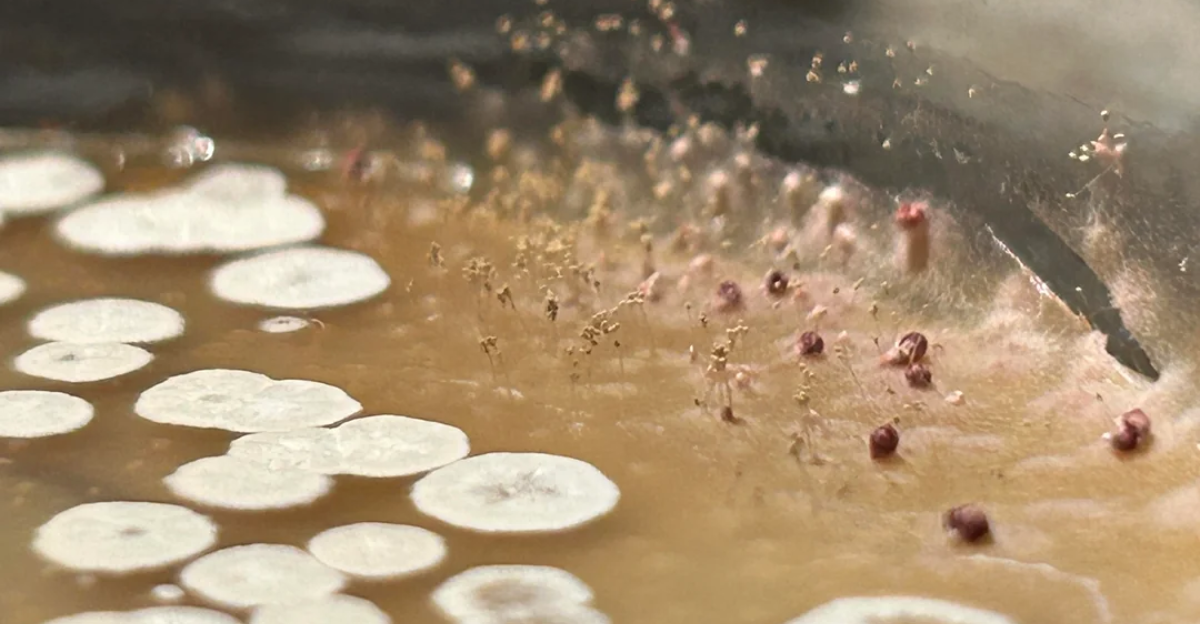

Climate-induced shifts in fungal populations affect human health directly and threaten food security. Fungi like Aspergillus flavus produce aflatoxins, which contaminate crops and pose serious health risks, including liver cancer. As these fungi expand into new agricultural regions due to warming temperatures, the risk of crop contamination increases.
This necessitates the development of robust agricultural practices and monitoring systems to ensure food safety in the face of changing fungal distributions.
Challenges in Disease Surveillance and Response

The northward spread of diseases presents challenges for surveillance, and healthcare systems are unaccustomed to these illnesses. Lack of awareness among healthcare providers can lead to misdiagnosis or delayed treatment.
Moreover, limited infrastructure in remote northern regions hampers effective disease monitoring and response. Investing in healthcare training, diagnostic capabilities, and public health infrastructure is essential to address these emerging threats effectively.
Importance of Interdisciplinary Approaches

Addressing the health impacts of climate change requires interdisciplinary collaboration among climatologists, ecologists, epidemiologists, and public health officials. Understanding the complex interactions between environmental changes and disease dynamics is crucial for developing effective mitigation and adaptation strategies.
Integrating traditional ecological knowledge, particularly from indigenous communities, can also enhance the effectiveness of public health interventions in northern regions.
Preparing for a Changing Disease Landscape

Proactive measures are necessary to prepare for the evolving landscape of infectious diseases driven by climate change. This includes investing in research to understand disease ecology, developing early warning systems, and implementing public health campaigns to raise awareness.
Policymakers must prioritize climate adaptation strategies, incorporating health considerations to protect vulnerable populations in northern regions. By anticipating changes and strengthening healthcare systems, societies can better manage the risks associated with the northward spread of infectious diseases.
Explore more of our trending stories and hit Follow to keep them coming to your feed!

Don’t miss out on more stories like this! Hit the Follow button at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest news. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!







