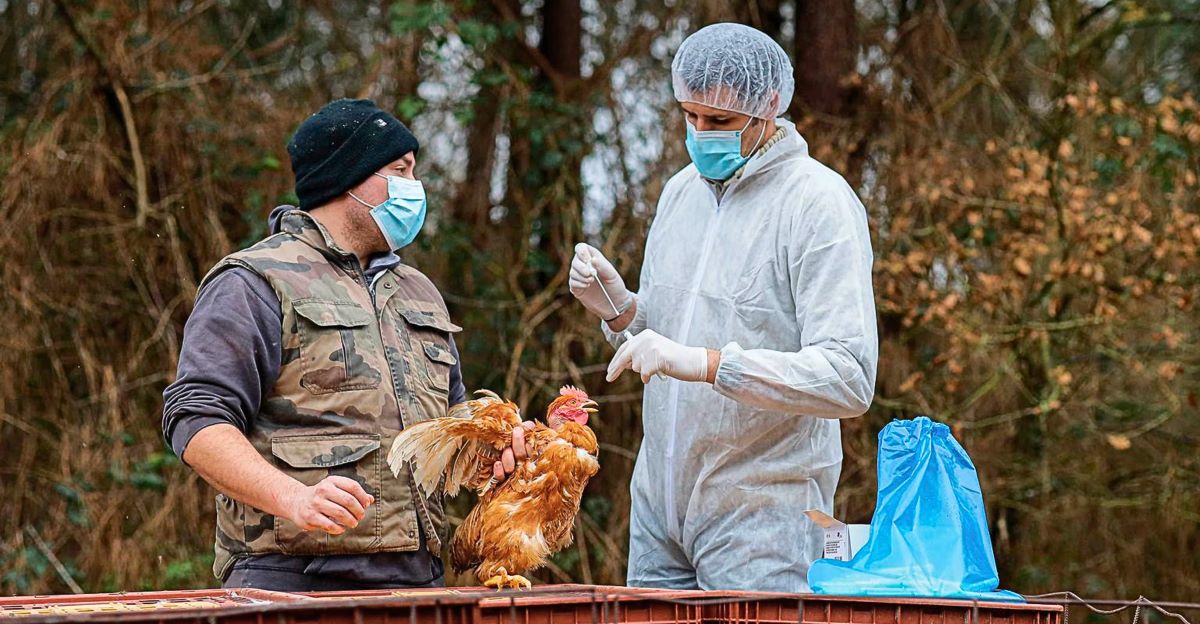

Avian influenza, commonly known as bird flu, is a viral infection that primarily affects bird species but can occasionally infect humans and other animals. The H5N1 strain, in particular, has caused significant outbreaks globally, leading to substantial economic losses in the poultry industry. Transmission to humans is rare but can occur through direct contact with infected birds or contaminated environments. Understanding the nature of bird flu is crucial for implementing effective prevention and control measures.
Economic Impact of Bird Flu on the Poultry Industry

Bird flu outbreaks have devastating effects on the poultry sector. In the United States, the 2015 H5N2 outbreak led to the culling of over 43 million birds across 15 states, causing egg prices to surge by 120% in the Midwest. Similarly, South Africa’s ostrich farming hub, Oudtshoorn, faced severe economic challenges due to H5N2 outbreaks, resulting in the loss of thousands of birds and significant revenue declines.
Inflation and Rising Food Prices
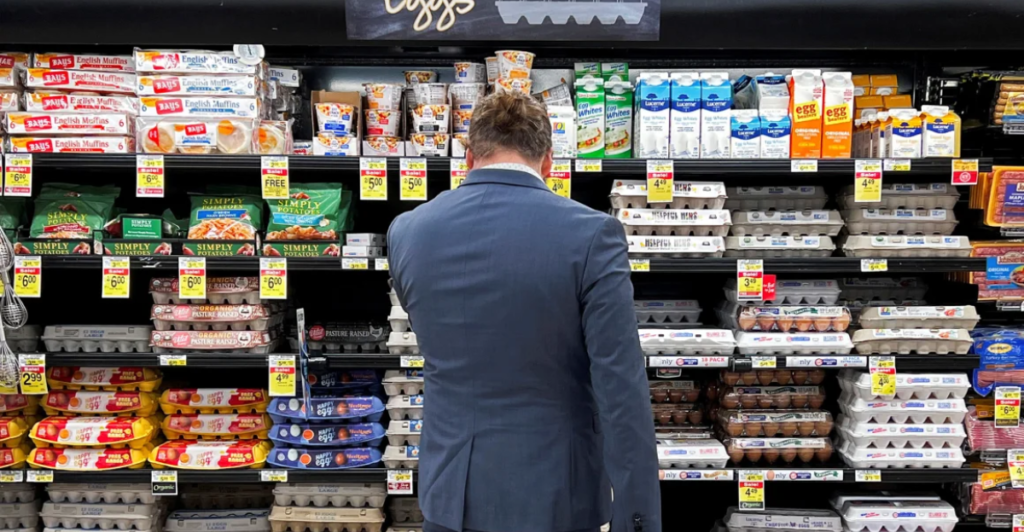

The ripple effects of bird flu extend to consumers through increased food prices. For instance, a recent bird flu outbreak led to a 10.4% jump in egg prices in February 2025, with large white eggs reaching $8.15 per dozen. This surge contributes to broader food inflation, affecting household budgets and prompting concerns about food affordability.
Breaker Eggs: A Niche Market Affected

Breaker eggs, or liquid eggs used in processed foods, are also impacted by avian influenza. The 2022 outbreak led to skyrocketing prices for breaker eggs, affecting the food industry’s supply chain and production costs. This niche market’s volatility underscores the far-reaching consequences of bird flu on various food sectors.
Farm Animal Protection Laws: Balancing Welfare and Disease Control
Bird flu outbreaks often necessitate stringent measures, including mass culling infected and at-risk poultry populations. While these actions are essential for disease control, they raise ethical questions about animal welfare and the adequacy of existing farm animal protection laws. The balance between safeguarding public health and ensuring the humane treatment of animals remains a complex and evolving issue.
Ventilation Shutdown: A Controversial Culling Method
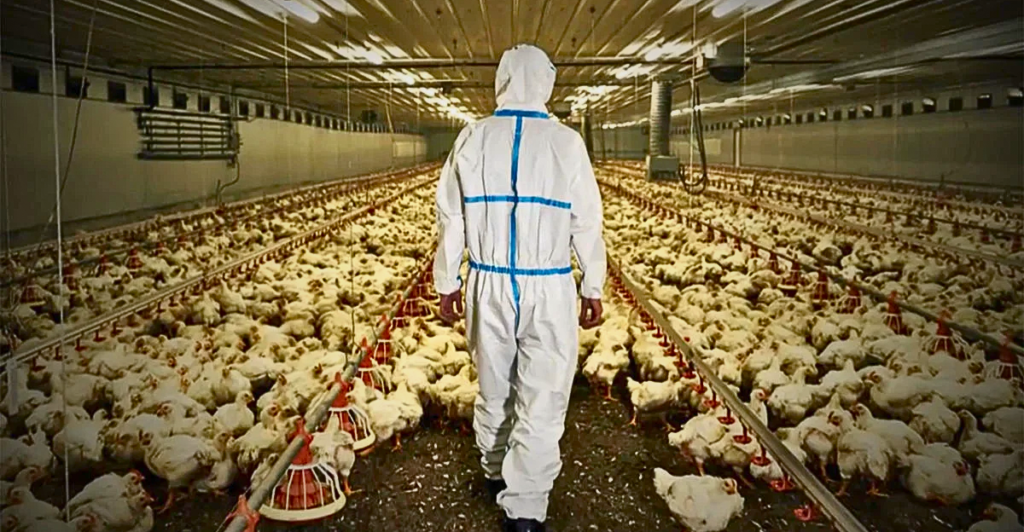

Ventilation shutdown (VSD) depopulates poultry facilities during severe outbreaks by cutting off airflow, leading to heat stress and suffocation. Critics argue that VSD is inhumane, prompting debates within the veterinary community and among animal rights advocates about its ethical implications and the need for more humane alternatives.
Vaccination Strategies: Pros and Cons
Vaccinating poultry against bird flu could mitigate the impact of outbreaks and stabilize egg prices. However, concerns about vaccine efficacy, potential trade restrictions, and the logistics of mass vaccination programs have made some countries, like the United States, hesitant to adopt this strategy widely. Ongoing research aims to address these challenges and assess the feasibility of vaccination as a preventive measure.
Impact on Specific Regions: The Case of Oudtshoorn
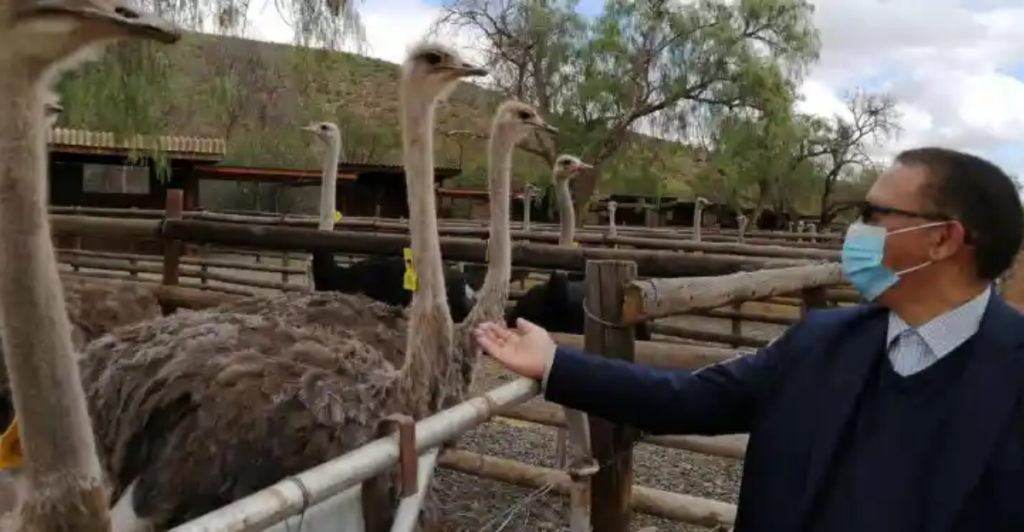

Oudtshoorn, South Africa’s ostrich farming capital, has faced multiple bird flu outbreaks, leading to significant economic losses and job cuts. The 2011 H5N2 outbreak resulted in the culling of 38,000 ostriches and a ban on South African ostrich meat exports to the European Union, highlighting the vulnerability of regions dependent on poultry farming.
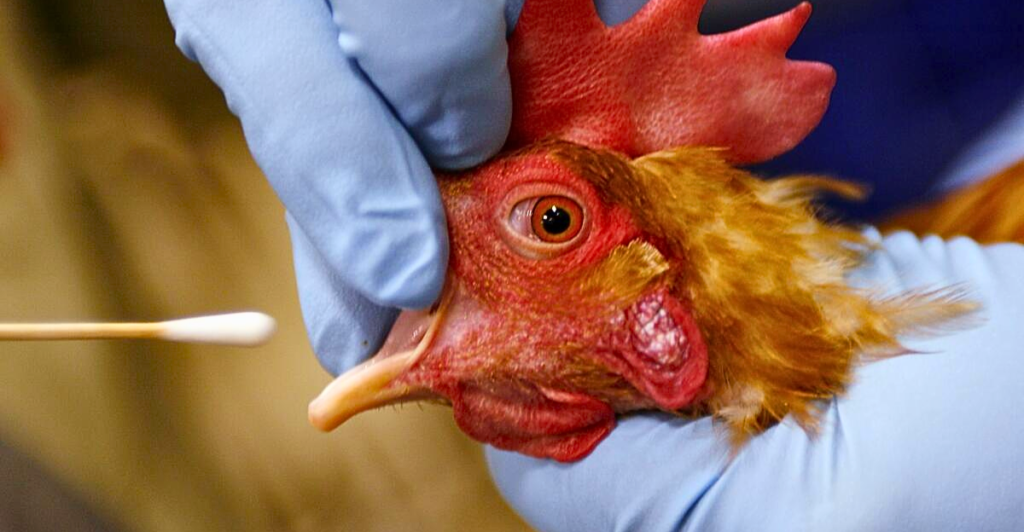
Human Health Risks and Monitoring
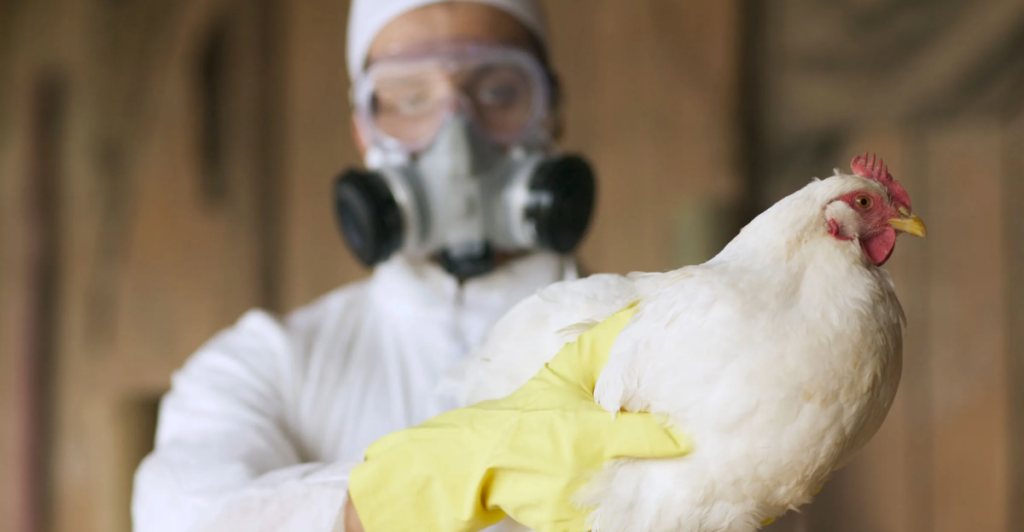

While bird flu primarily affects birds, certain strains like H5N1 can infect humans, leading to severe respiratory illnesses. Human cases are rare and typically linked to direct contact with infected poultry. Continuous monitoring and biosecurity measures are essential to prevent potential zoonotic transmission and ensure public health safety.
Global Trade Implications

Bird flu outbreaks can lead to international trade restrictions on poultry products from affected regions. For example, the 2011 outbreak in South Africa prompted the European Union to ban imports of South African ostrich meat, causing substantial revenue losses. Such trade barriers underscore the importance of effective disease management in maintaining market access.
Consumer Behavior and Market Dynamics

Rising egg prices due to bird flu outbreaks influence consumer behavior, leading to decreased demand and shifts toward alternative protein sources. Producers may also adjust production levels in response to market signals, affecting the poultry industry’s overall supply chain and pricing dynamics.
Governmental Responses and Policies
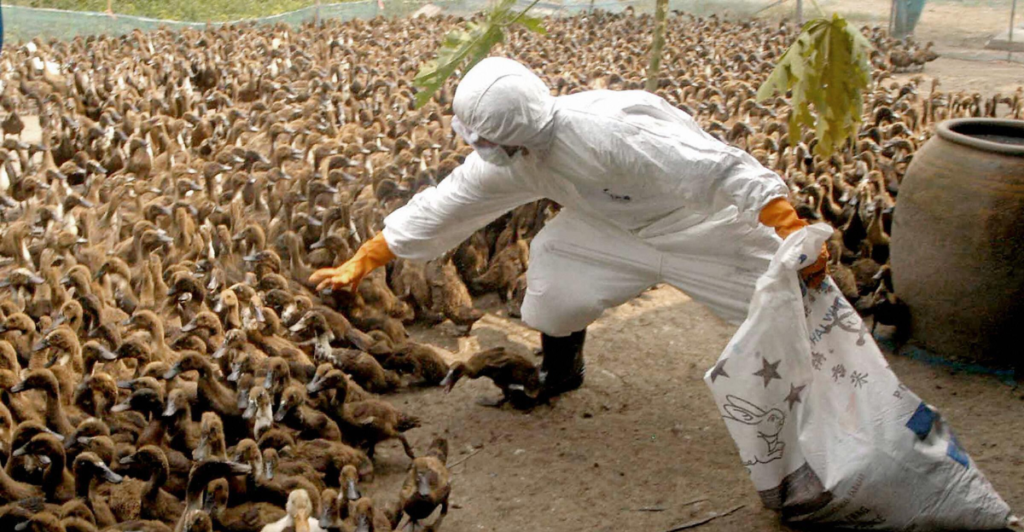

Governments play a crucial role in managing bird flu outbreaks through policies like culling infected flocks, compensating farmers, and implementing trade restrictions. Balancing these measures with animal welfare considerations and economic impacts requires careful planning and stakeholder engagement to ensure effective and ethical responses.
Future Outlook: Preparedness and Prevention

Enhancing biosecurity measures, investing in research for effective vaccines, and developing rapid response strategies are vital for mitigating the impact of future bird flu outbreaks. Collaborative efforts among governments, industry stakeholders, and international organizations are essential to protect animal and human health while ensuring economic stability in the poultry sector.
Explore more of our trending stories and hit Follow to keep them coming to your feed!

Don’t miss out on more stories like this! Hit the Follow button at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest news. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!







