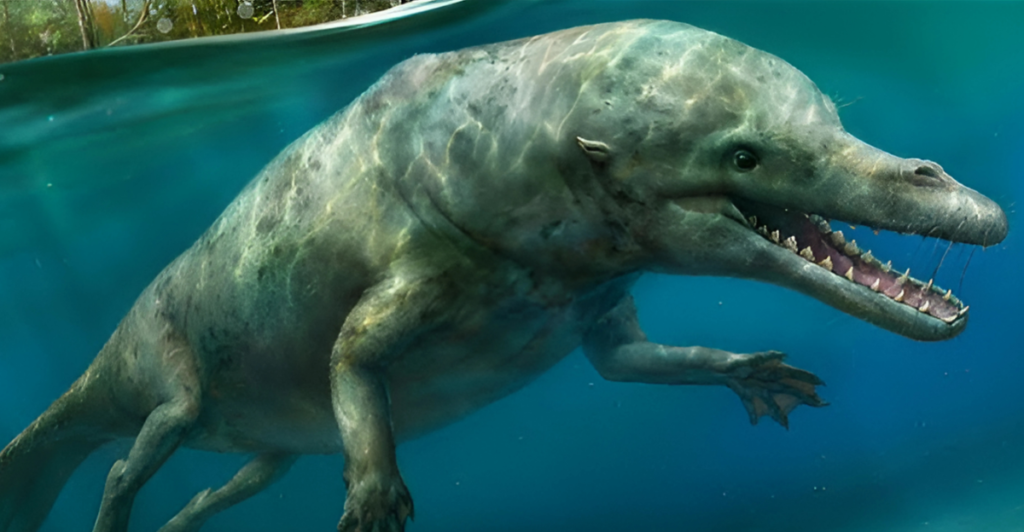

In the 1990s, scientists unearthed fossils of an unusual creature named Pakicetus. This animal, dating back over 50 million years, is a fascinating link between modern whales and their land-dwelling ancestors. Resembling a wolf with features adapted for aquatic life, Pakicetus provides compelling evidence of whales’ evolutionary journey from land mammals to the ocean giants we know today. Its discovery transformed our understanding of whale ancestry and evolution.
Meet Pakicetus
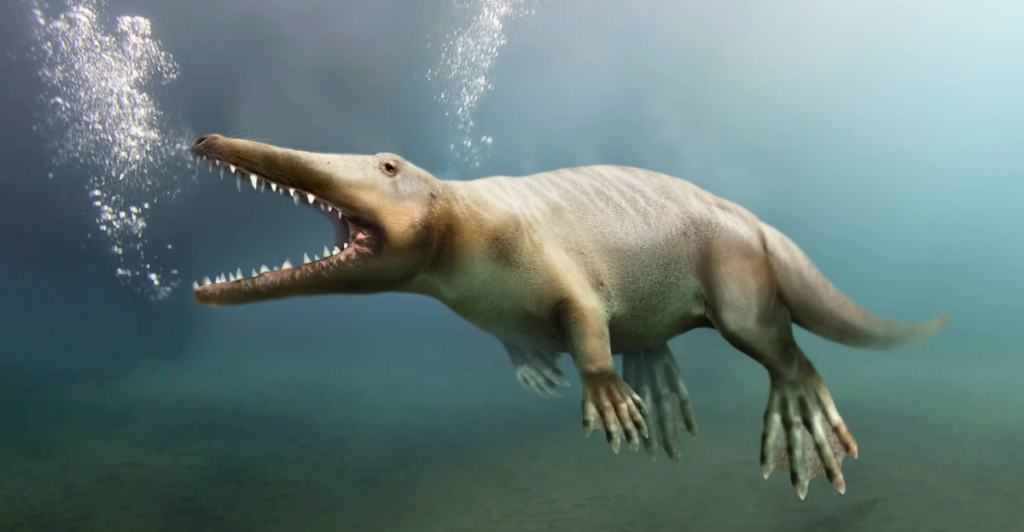

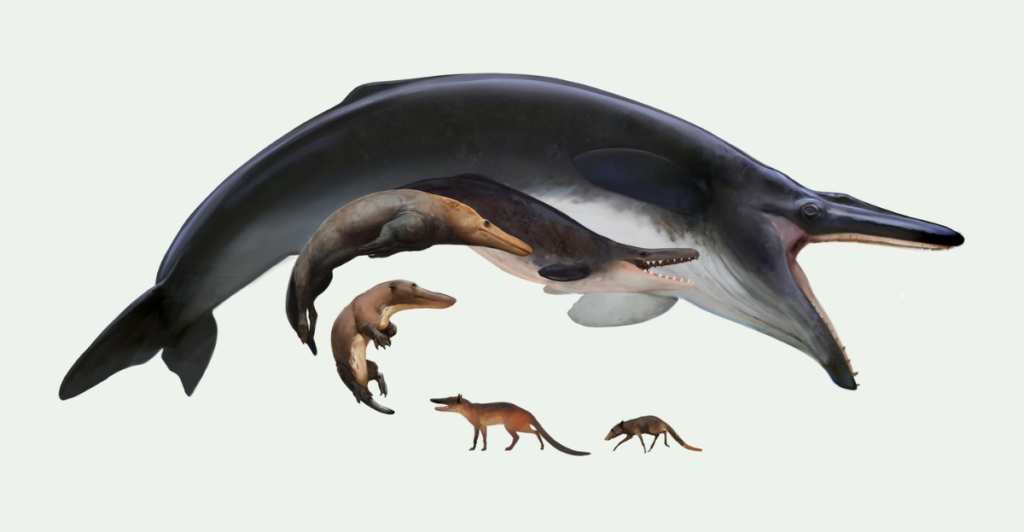
Pakicetus was a small, four-legged mammal that lived near rivers and streams. Measuring about the size of a modern wolf, it had long limbs for running but also exhibited features suited for swimming. Fossils reveal that its ears were adapted to hear both underwater and on land, a critical clue to its dual-environment lifestyle. This adaptability marked the early stages of whale evolution’s transition from land to sea.
The Unique Skull of Pakicetus
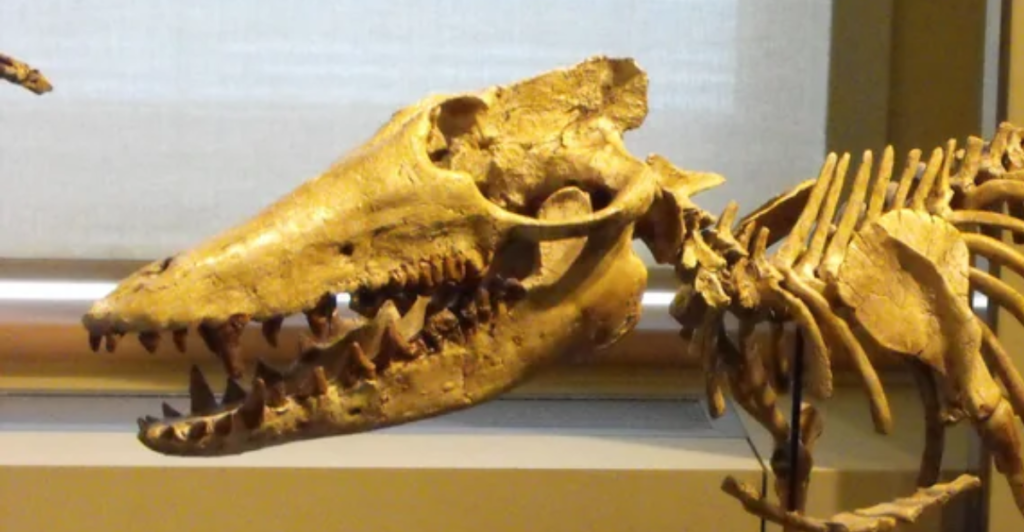

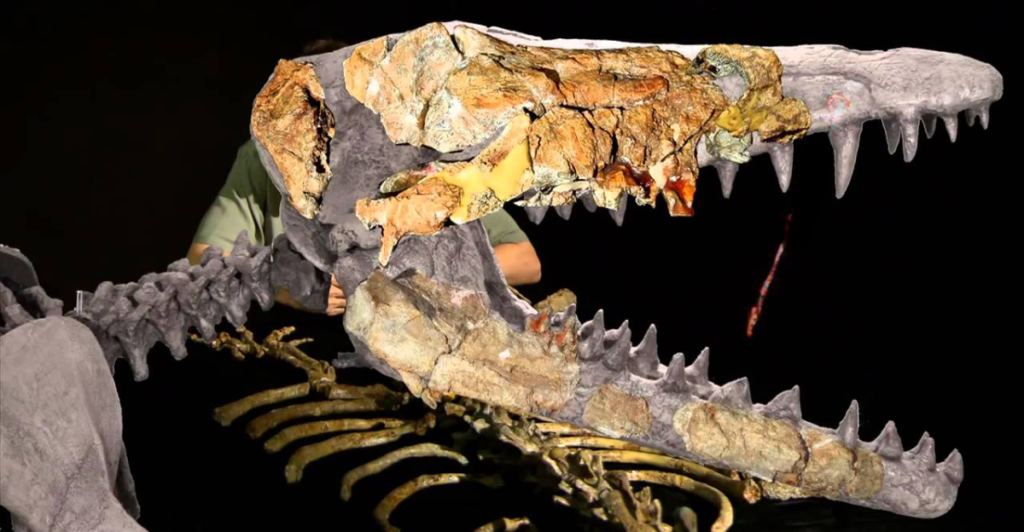
One of the most striking features of Pakicetus is its skull. The shape and structure closely resemble early whales, particularly in the ear region. Its auditory bulla, a bony structure housing the ear bones, is distinctly similar to modern whales, enabling underwater hearing. This characteristic directly links to cetaceans, supporting the theory that whales evolved from terrestrial ancestors like Pakicetus.
A Semi-Aquatic Lifestyle
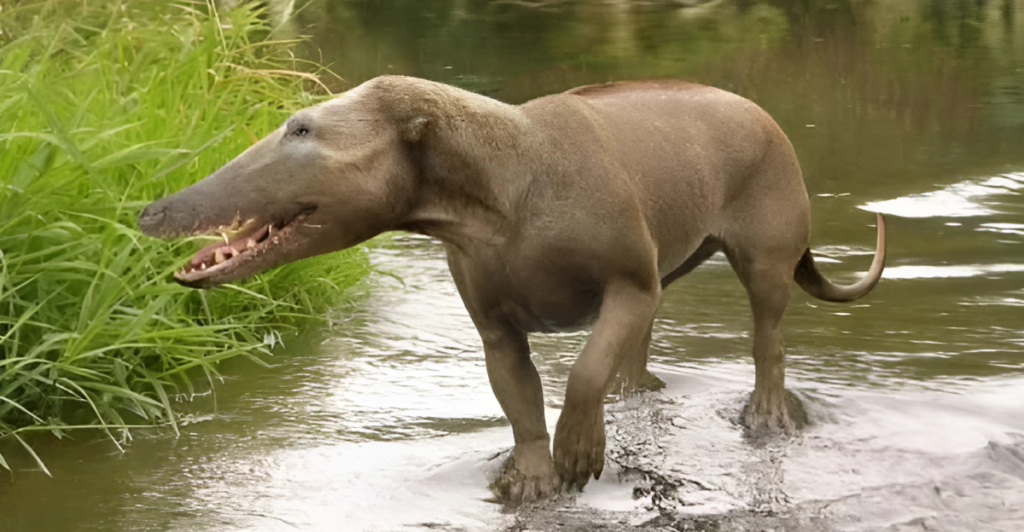

While Pakicetus primarily lived on land, it likely spent significant time in water. Its long, powerful limbs suggest it was an adept runner, but its teeth and jaw structure indicate it hunted fish in shallow waters. This dual lifestyle highlights its transitional role in evolution. Over time, its descendants became increasingly adapted to aquatic environments, marking the gradual shift from land mammals to ocean dwellers.
Descendants of Pakicetus
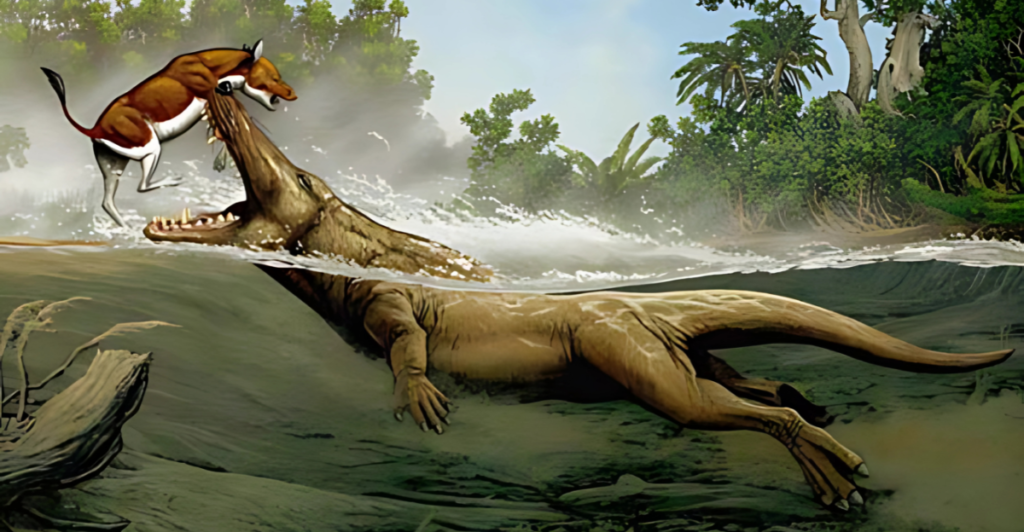

Pakicetus belongs to the cetaceans group, which includes modern whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Its descendants include semi-aquatic creatures like Ambulocetus (“walking whale”) and Rodhocetus. These animals show progressive adaptations to aquatic life, such as webbed feet and streamlined bodies. By tracing these evolutionary steps, scientists can piece together the fascinating journey from land-dwelling mammals to fully aquatic whales.
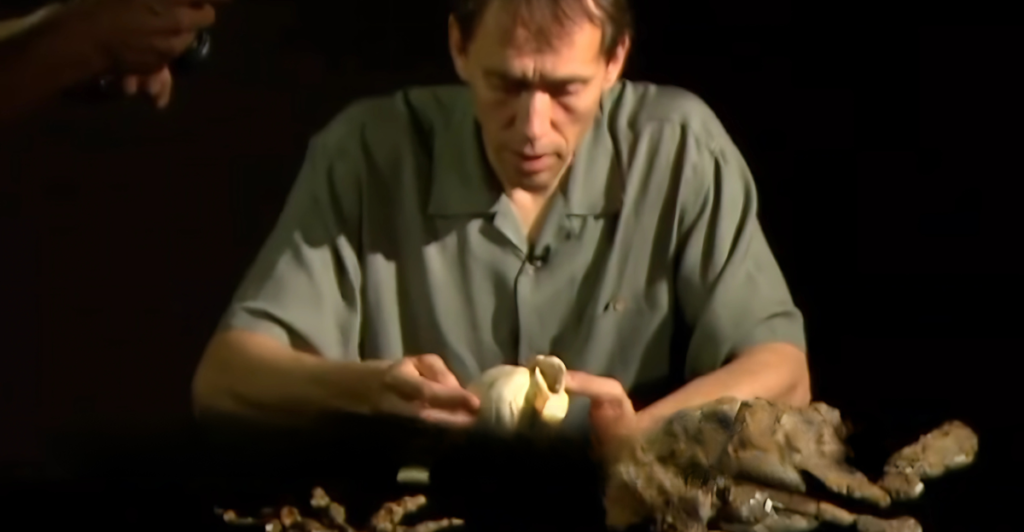
How Fossils Tell the Story
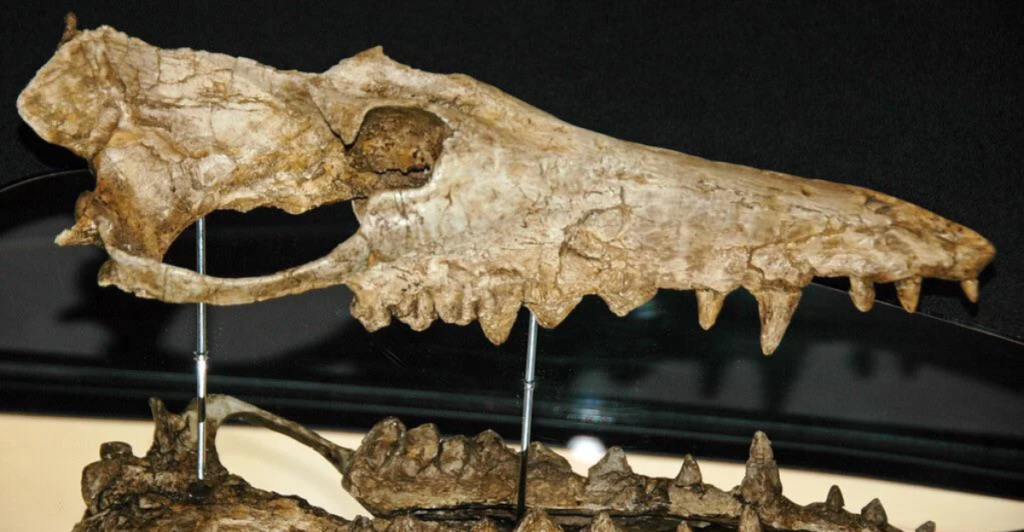

The fossil record is a critical tool for understanding whale evolution. Fossils of Pakicetus were first discovered in Pakistan and preserved in sediments from ancient riverbeds. These remains, including skulls and limb bones, provide invaluable clues about its lifestyle and adaptations. Paleontologists meticulously compare these fossils with modern whales to reconstruct the evolutionary timeline, highlighting the pivotal role of Pakicetus in this journey.
The Importance of Transitional Forms
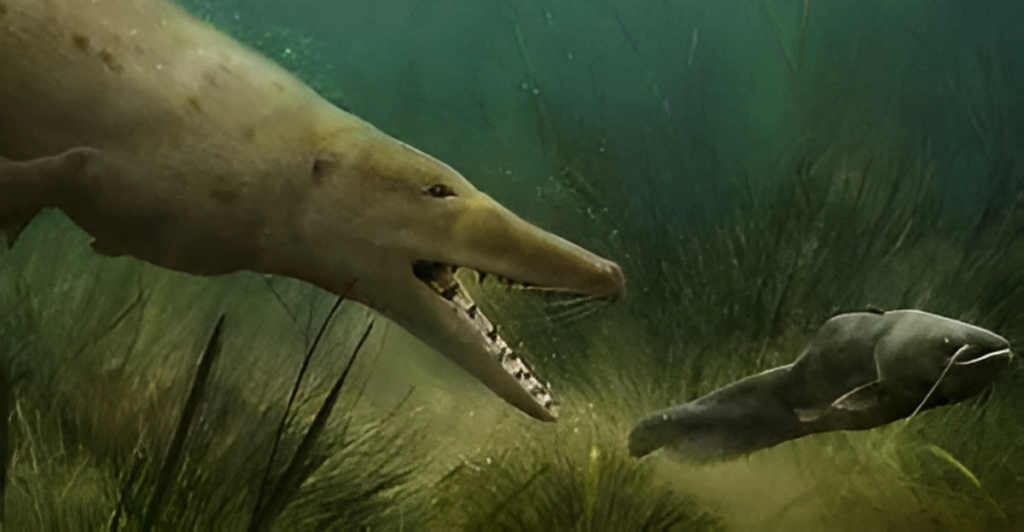

Transitional forms like Pakicetus are essential for understanding evolution. They bridge the gap between two seemingly unrelated groups, land mammals and whales. Without these “missing links,” the story of how whales adapted to life in water would remain incomplete. Fossils like those of Pakicetus illuminate the past and inspire further exploration into the mysteries of evolution.
Why Did Whales Leave the Land?
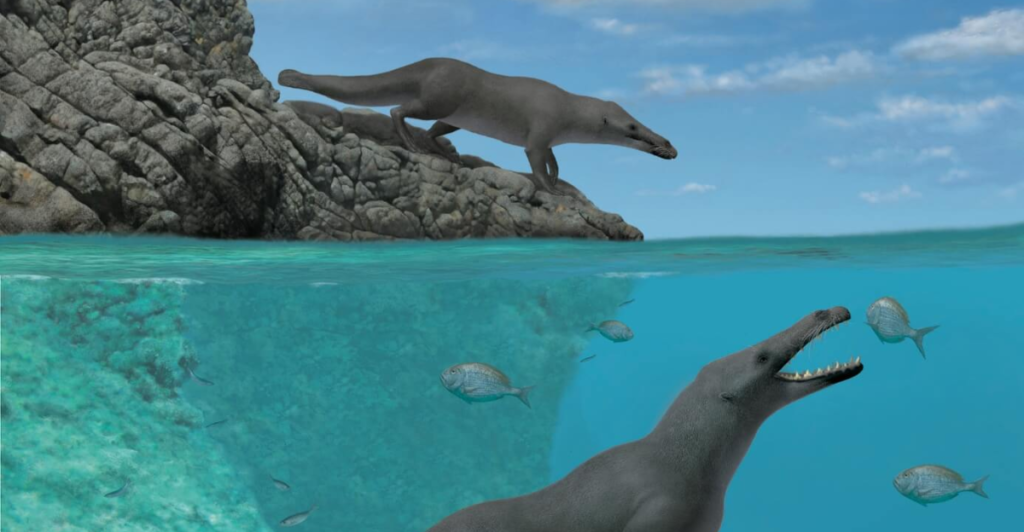

The shift from land to water likely stemmed from ecological pressures and abundant marine resources. As ancient land mammals like Pakicetus ventured into rivers and oceans for food, their bodies gradually adapted to aquatic life. Over millions of years, traits such as powerful tails, flippers, and streamlined bodies emerged, enabling their descendants to thrive in marine environments and eventually dominate ocean ecosystems.
Comparing Pakicetus to Modern Whales

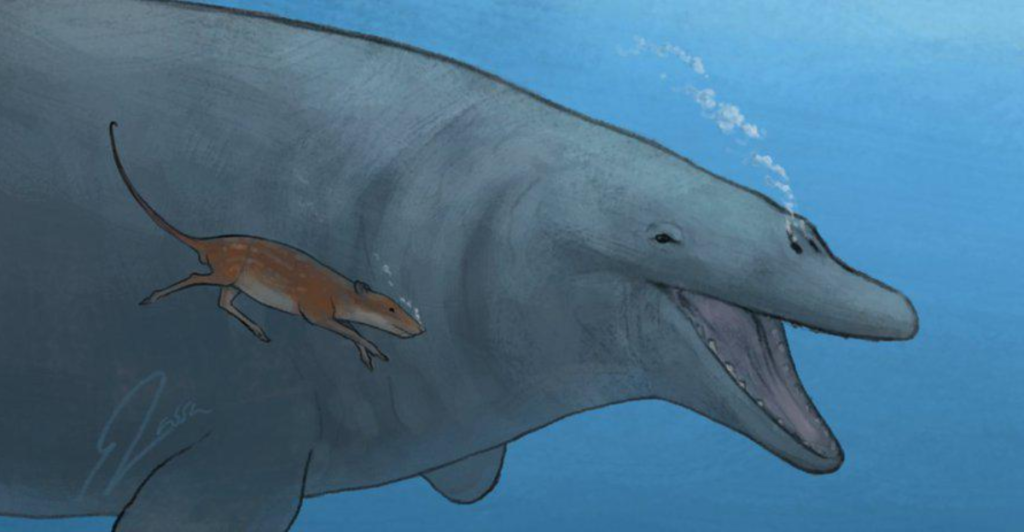
Although Pakicetus looks drastically different from modern whales, they share surprising similarities. Both have specialized ear structures for underwater hearing and similar dental patterns. However, Pakicetus retained four legs, while whales evolved flippers and tail flukes. These changes highlight the dramatic transformations over millions of years, emphasizing the adaptability of life in response to changing environments.
The Role of Genetics

Genetic studies confirm the connection between Pakicetus and modern whales. DNA evidence links whales to a group of hoofed mammals called artiodactyls, which includes hippos. Hippos are whales’ closest living relatives, sharing a common ancestor with Pakicetus. This genetic connection further solidifies the evolutionary link between terrestrial mammals and oceanic cetaceans.
What This Means for Evolutionary Science
The discovery of Pakicetus and its significance demonstrates the power of evolutionary science. It shows how life adapts over time, responding to environmental changes and opportunities. By studying these transitions, scientists gain insights into the interconnectedness of all life on Earth. Understanding Pakicetus helps bridge gaps in the evolutionary story, offering a clearer picture of our planet’s biological history.
Fascination with Whale Evolution

The story of Pakicetus captivates both scientists and the public. It reminds us how much there is to discover about Earth’s past. Each piece of evidence adds depth to the narrative of whale evolution, from fossils to genetics. This knowledge enriches our appreciation for the complexity of life and inspires further exploration into the origins of other species.
The Legacy of Pakicetus

Pakicetus may no longer roam the Earth, but its legacy remains in every whale swimming today. This small, semi-aquatic creature represents the humble beginnings of some of the planet’s largest animals. By understanding Pakicetus, we celebrate the wonder of evolution and the enduring connections between land and sea, past and present, reminding us of the shared history that unites all living creatures.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them appearing in your feed

Meet the Massive Crocodiles That Make Their Homes 40 Feet Underground
12 Colossal Prehistoric Beasts That Predate Dinosaurs
11 Prehistoric Animals We’re Glad Are Extinct
Nature’s Ancient Survivors: 10 Prehistoric Creatures Still Roaming Earth Today
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







