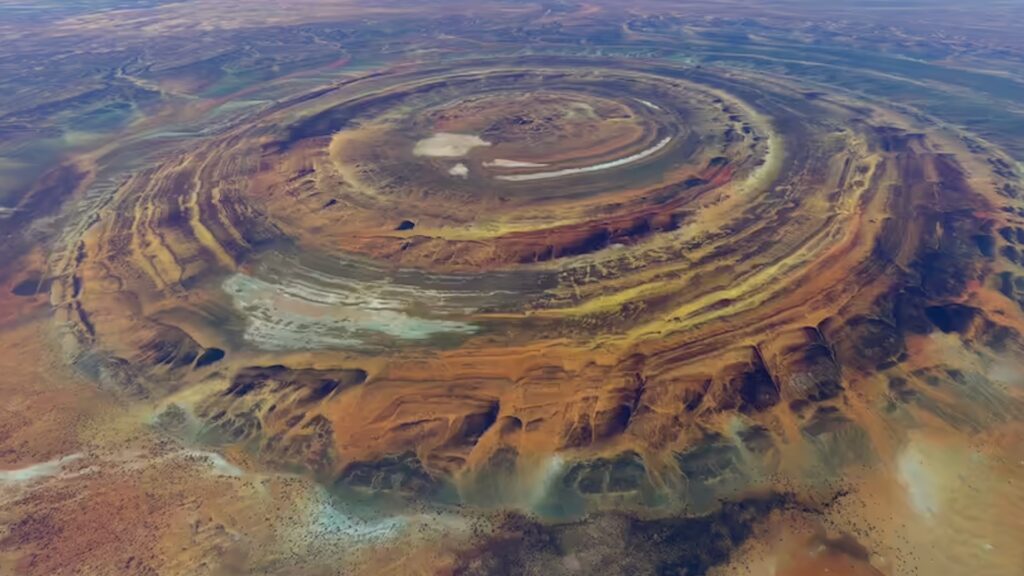

The Richat Structure, commonly known as the Eye of the Sahara, is a remarkable geological formation located in the western Sahara Desert of Mauritania. This massive structure, measuring approximately 50 kilometers (31 miles) in diameter, has intrigued scientists and adventurers alike for centuries. Its distinctive circular shape and vibrant concentric rings resemble a giant eye, making it an iconic landmark visible even from space. The local Arabic name, “Guelb er Richât,” translates to “the eye of the Richat,” reflecting its striking appearance.
What Created the Eye of the Sahara?

The formation of the Eye of the Sahara has been a subject of fascination and speculation. Initially thought to be an impact crater, further geological studies revealed that it is actually an eroded geological dome. This dome was created by volcanic activity that uplifted sedimentary layers over millions of years. The current structure is a result of complex geological processes involving erosion by wind and water, which have shaped its unique appearance.
Geological Composition
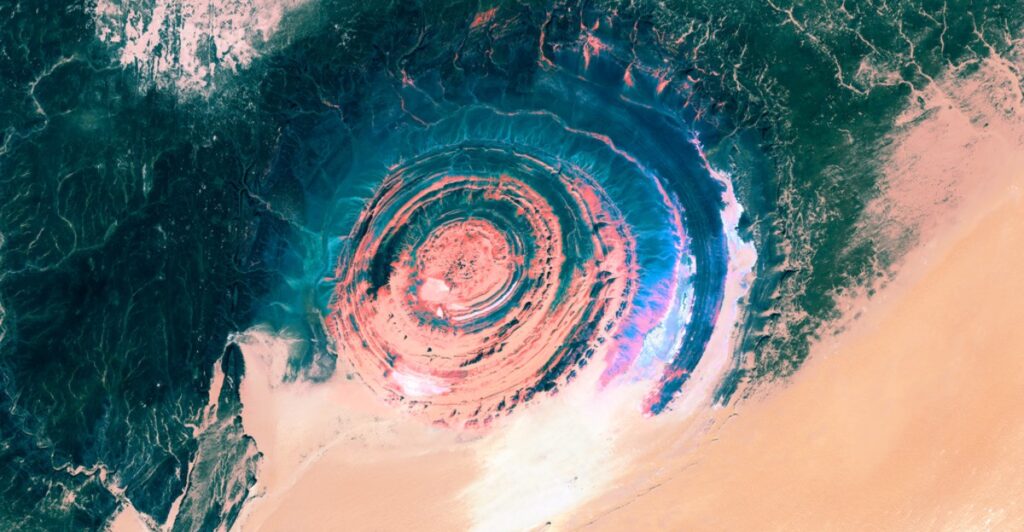

The Eye of the Sahara consists primarily of sedimentary rocks, including sandstone and limestone, arranged in concentric rings. The outermost rings are composed of harder igneous rocks, while the softer inner layers have eroded more rapidly. This differential erosion has contributed to the formation’s striking visual characteristics, allowing scientists to study the geological history recorded in these rock layers.
Erosion Processes

Erosion has played a significant role in shaping the Richat Structure. Over millions of years, wind and water have sculpted the dome, exposing different rock types and creating its distinctive circular shape. The varying erosion rates between harder and softer rock layers have led to the formation of ridges and valleys that characterize this geological wonder.
Scientific Significance
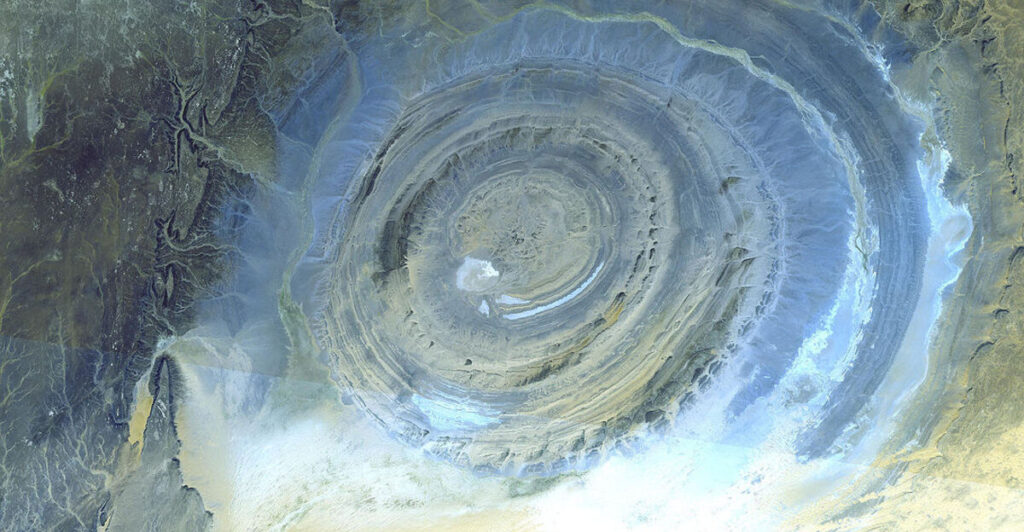

The Richat Structure is not only visually captivating but also scientifically significant. It provides valuable insights into Earth’s geological processes, including tectonic forces and magmatic activity. The presence of sedimentary layers offers evidence of ancient environments and climatic conditions that existed long before the Sahara became a desert.
Evidence of Early Human Activity

Archaeological findings suggest that the area surrounding the Eye of the Sahara may have been inhabited by early hominids such as Homo erectus or Homo heidelbergensis. Discoveries of Acheulean tools indicate that early humans utilized this region for hunting and perhaps temporary habitation, adding another layer of intrigue to this geological marvel.
Wildlife in the Region
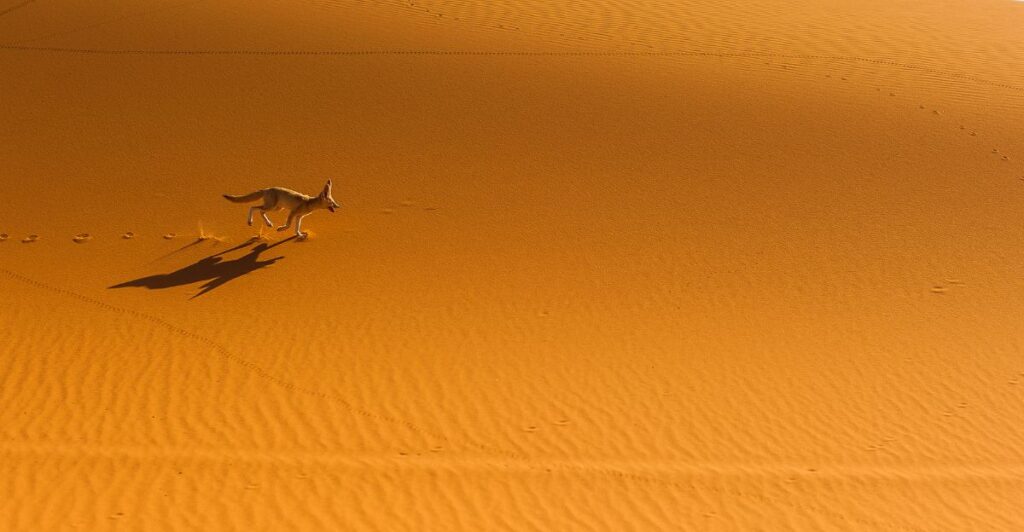

Despite its harsh desert environment, the area around the Richat Structure supports a variety of wildlife adapted to arid conditions. Species such as gazelles, desert foxes, and various birds can be found here. These animals have evolved unique survival strategies to thrive in extreme temperatures and limited water availability.
Cultural Impact
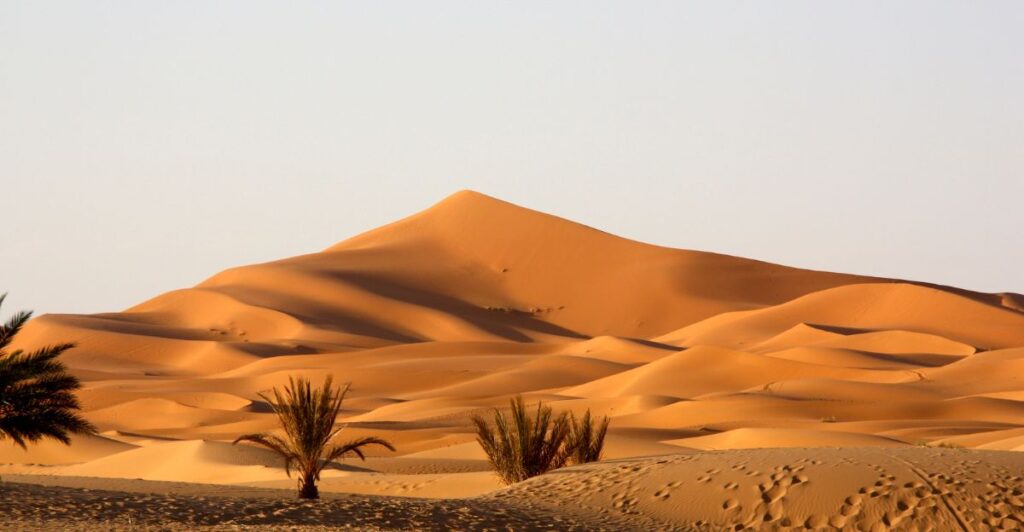

The Eye of the Sahara has captured the imagination of many cultures throughout history. Its unique shape has inspired myths and legends, including theories linking it to Atlantis. This cultural significance adds to its allure as a destination for explorers and tourists seeking to uncover its mysteries.
Modern Exploration
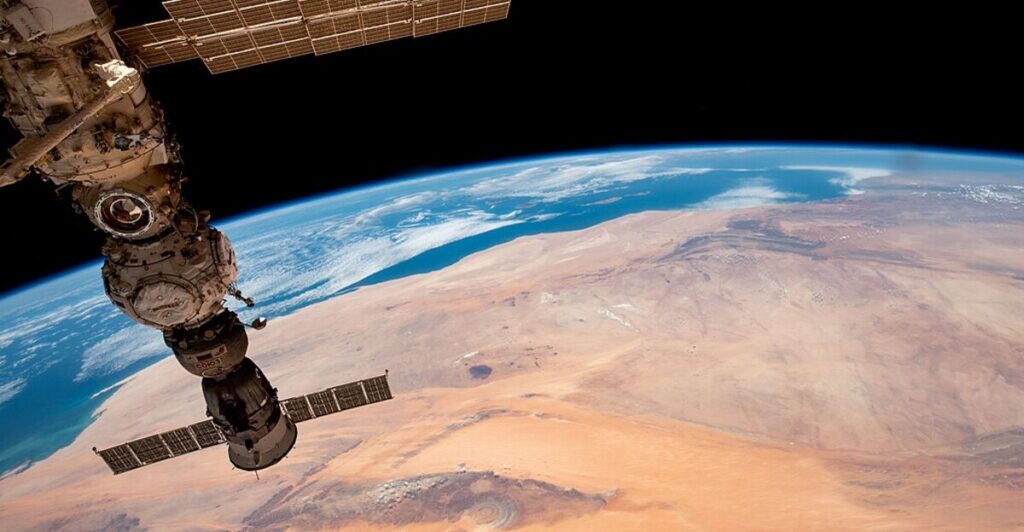

In recent years, advances in satellite imagery have facilitated new explorations of the Richat Structure. Scientists can now study this geological wonder from space, gaining insights into its formation and evolution over time. This modern approach complements traditional field studies and enhances our understanding of this remarkable site.
Tourism Potential
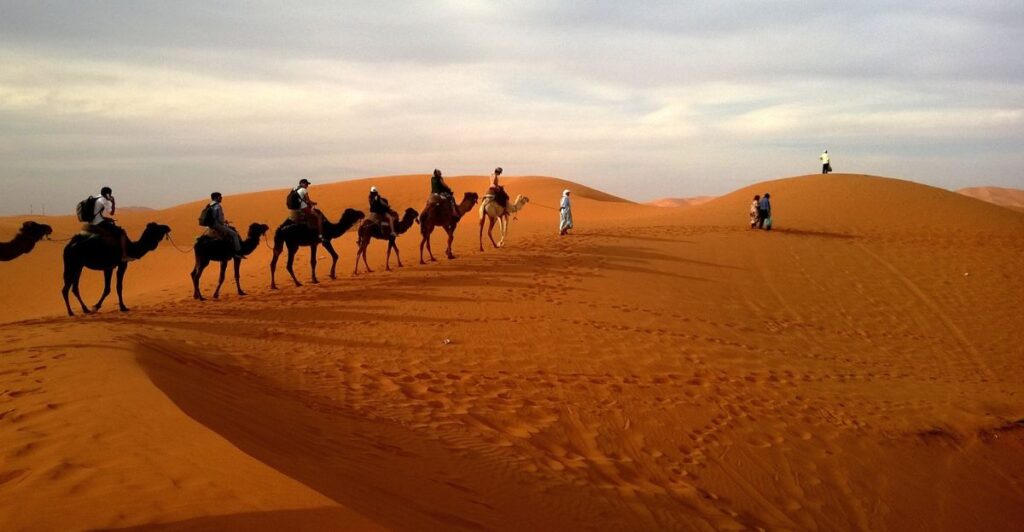

Although tourism to the Richat Structure is limited due to its remote location in the Sahara Desert, those who venture there are rewarded with breathtaking views and a sense of adventure. The journey to this natural wonder offers visitors a chance to experience one of Earth’s most unique geological formations firsthand.
Challenges to Access
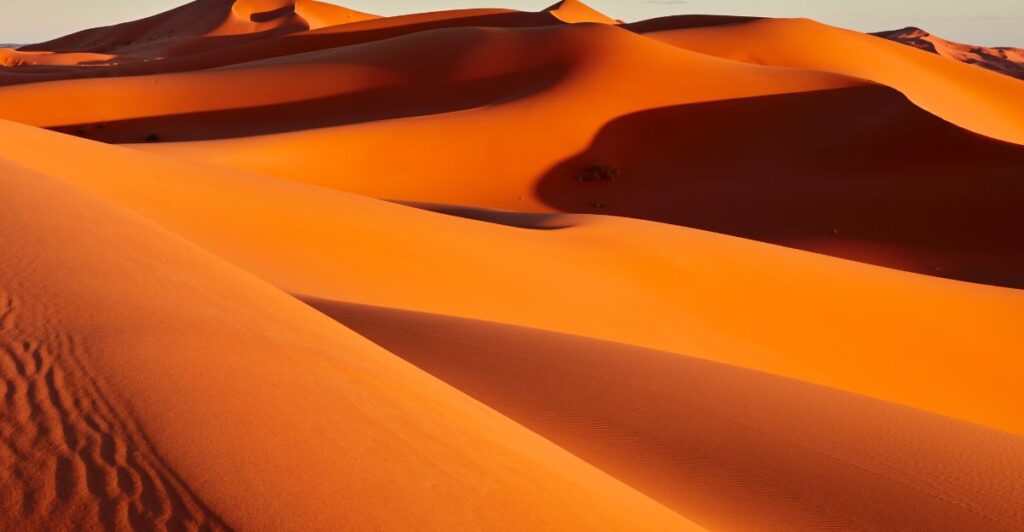

Reaching the Eye of the Sahara presents logistical challenges due to its isolation in a vast desert landscape. Travelers must navigate difficult terrain and extreme weather conditions, making it essential to plan carefully for any expedition to this extraordinary site.
Environmental Considerations
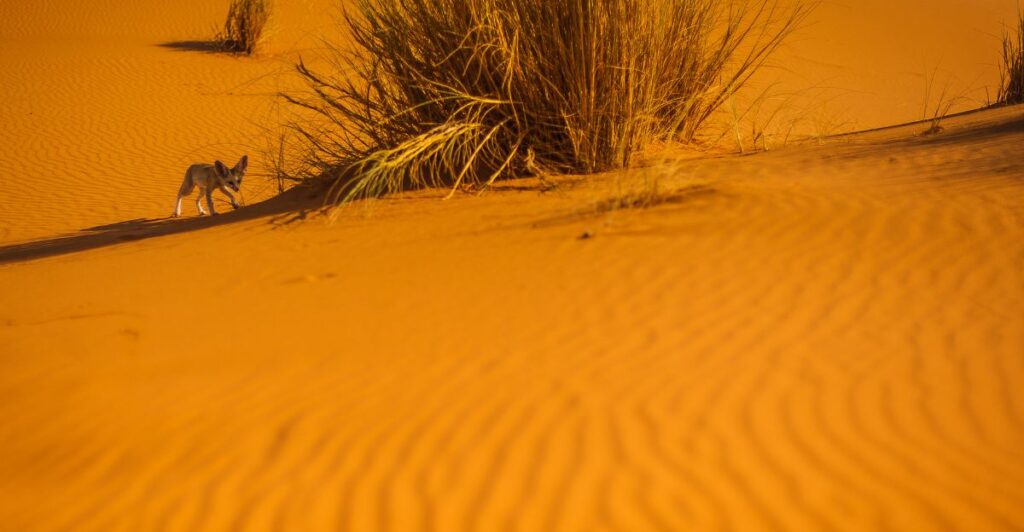

As interest in exploring the Richat Structure grows, it is crucial to consider environmental impacts on this fragile ecosystem. Sustainable tourism practices can help preserve both the geological integrity and wildlife habitats surrounding this natural wonder for future generations.
Nature’s Incredible Power
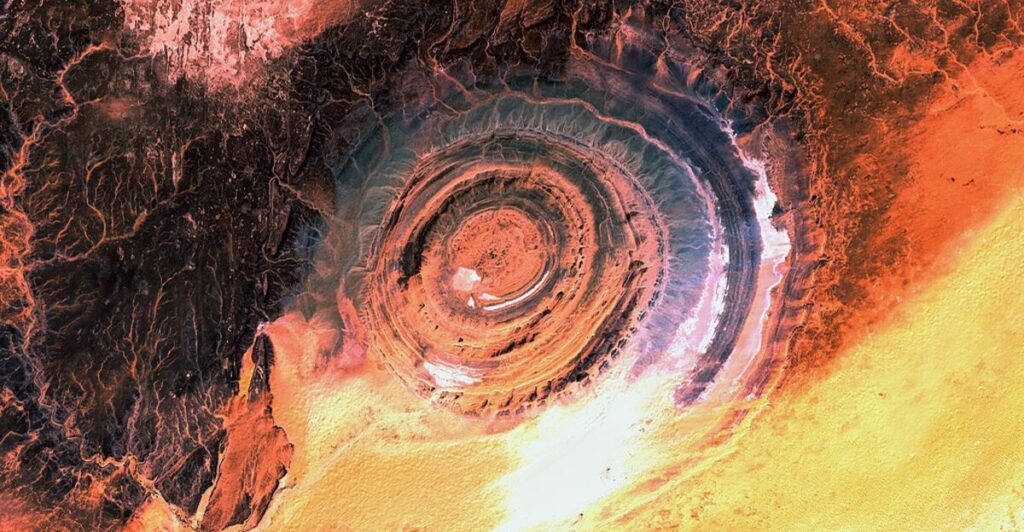

The Eye of the Sahara stands as a testament to Earth’s dynamic geological history and continues to inspire curiosity among scientists and adventurers alike. Its unique formation offers valuable insights into past environments while reminding us of nature’s incredible power to shape our planet over millions of years. As exploration continues, its scientific significance and cultural impact will undoubtedly endure in our collective consciousness.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them appearing in your feed
Diamond Dust Could Reverse Climate Change—But at a $175 Trillion Cost
Scientists Discover New Ecosystem in Antarctic Lake Hidden Beneath the Ice
There Will Be Eruptions”: Concerns Mount as Yellowstone Supervolcano Activity Shifts
The War on Cows Is Over—And Green Extremists Have Lost
References:
Reference 1
Reference 2
Reference 3
This article first appeared here
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







