
Electric vehicles (EVs) are widely celebrated for their potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. However, producing EV batteries necessitates the extraction of critical minerals such as lithium, nickel, and cobalt, which poses significant environmental challenges. Mining activities associated with these minerals have been linked to deforestation, habitat destruction, and pollution, adversely affecting wildlife and ecosystems.
For instance, nickel mining in Indonesia has led to extensive deforestation and water pollution, disrupting local communities and biodiversity. Similarly, lithium extraction in Chile’s salt flats has depleted water resources, impacting the environment and indigenous populations. These examples highlight the complex trade-offs in the transition to electric mobility, emphasizing the need for a holistic approach that considers both climate benefits and ecological consequences.
Lithium Extraction: Water Scarcity and Ecosystem Disruption
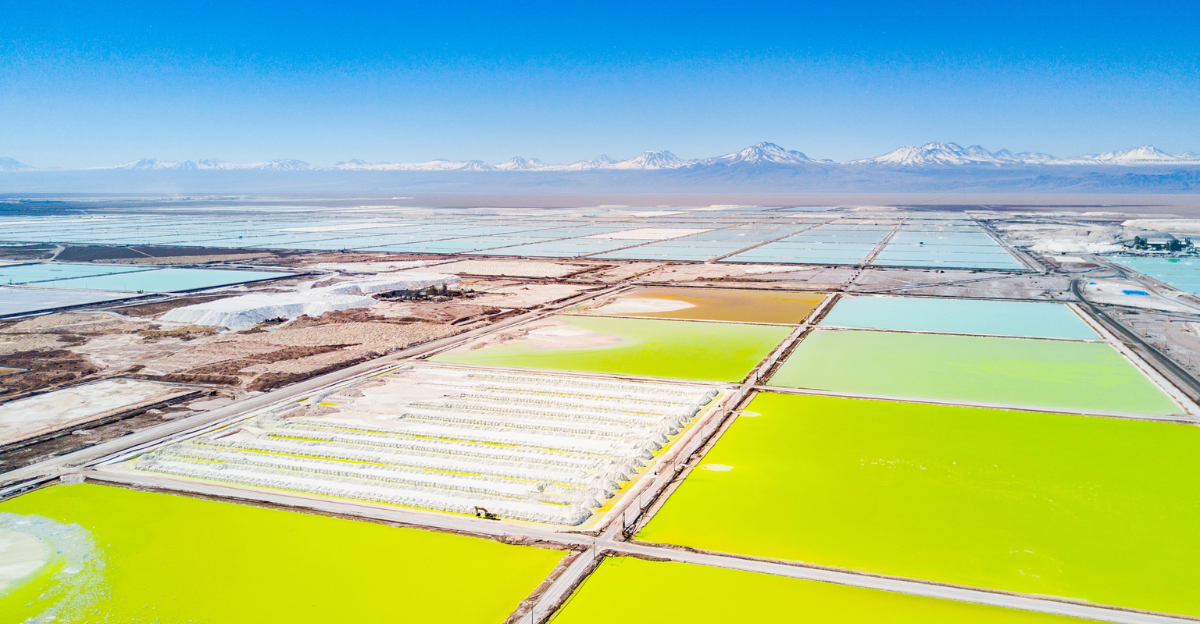

Lithium, a key component in EV batteries, is predominantly extracted from brine deposits in arid regions like Chile’s Atacama Desert. This process involves pumping large volumes of brine to the surface, leading to significant water consumption. The depletion of water resources threatens local ecosystems and the livelihoods of indigenous communities reliant on these water sources. The environmental impact of lithium mining underscores the need for sustainable extraction methods that minimize water usage and ecological disruption.
Nickel Mining: Deforestation and Pollution in Indonesia

Indonesia’s rich nickel reserves have attracted extensive mining operations to meet the growing demand for EV batteries. However, these activities have resulted in the clearing of vast forested areas, leading to habitat loss for numerous species and contributing to climate change. Additionally, mining processes have polluted waterways, adversely affecting marine life and the health of local communities. The environmental degradation caused by nickel mining calls for stricter regulations and more sustainable practices to protect Indonesia’s biodiversity.
Cobalt Extraction: Human Rights and Environmental Concerns
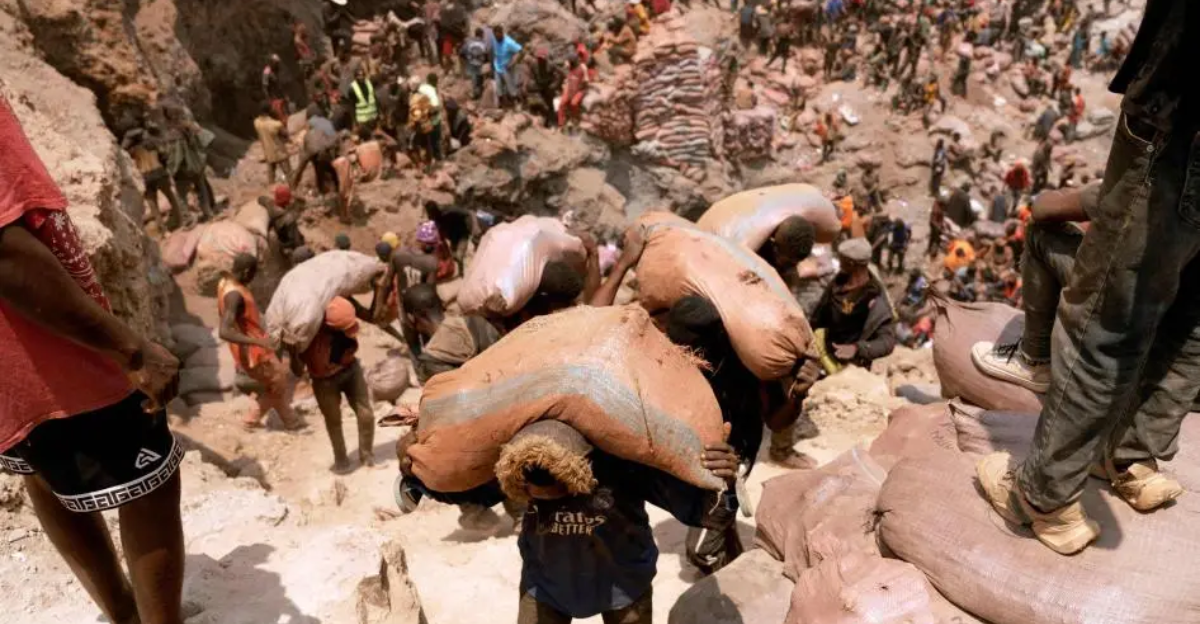

The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) supplies a significant portion of the world’s cobalt, which is essential for EV batteries. Cobalt mining in the DRC has been associated with severe environmental degradation, including soil erosion and water contamination, which harm local ecosystems and agriculture. Moreover, the industry faces criticism for human rights abuses, including child labor and unsafe working conditions. Addressing these issues requires comprehensive reforms and ethical sourcing standards to ensure that cobalt extraction does not come at the expense of human welfare and environmental integrity.
Impact on Indigenous Communities: The Case of the Hongana Manyawa
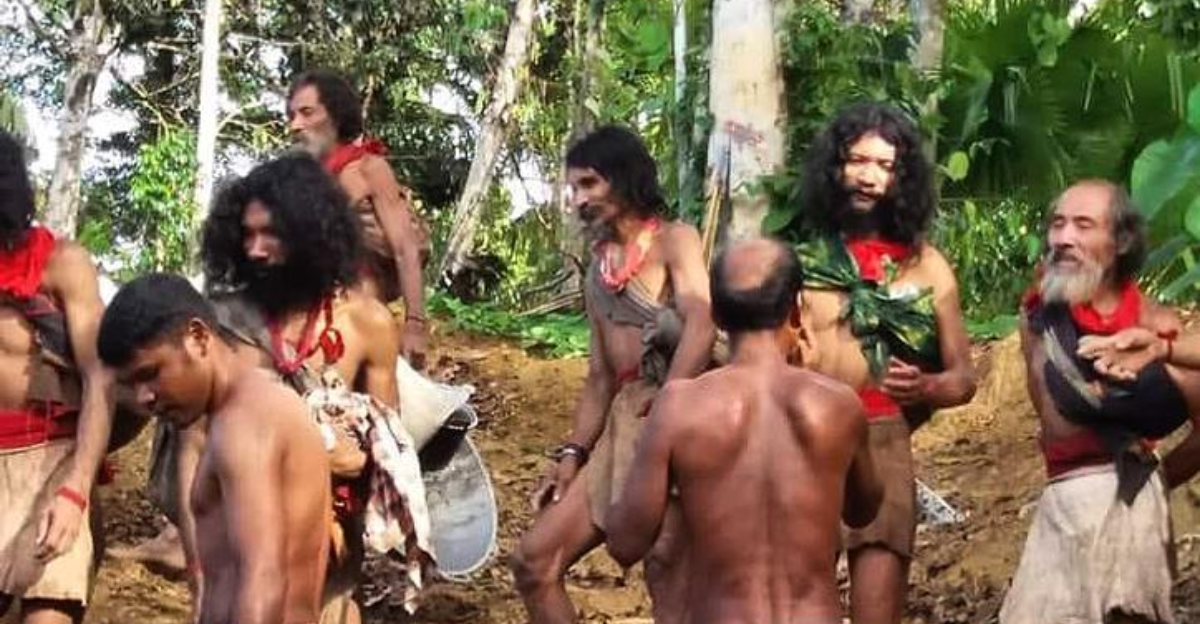

In Indonesia, the uncontacted Hongana Manyawa people face existential threats due to nickel mining encroaching upon their ancestral lands. The expansion of mining activities has led to habitat destruction and poses risks of forced displacement, endangering their traditional way of life. This situation highlights the broader issue of indigenous rights being compromised when pursuing mineral resources for EV production. Protecting these communities requires enforcing legal frameworks that recognize and uphold their land rights and cultural heritage.
Biodiversity at Risk: The Karachi Fish in Chile
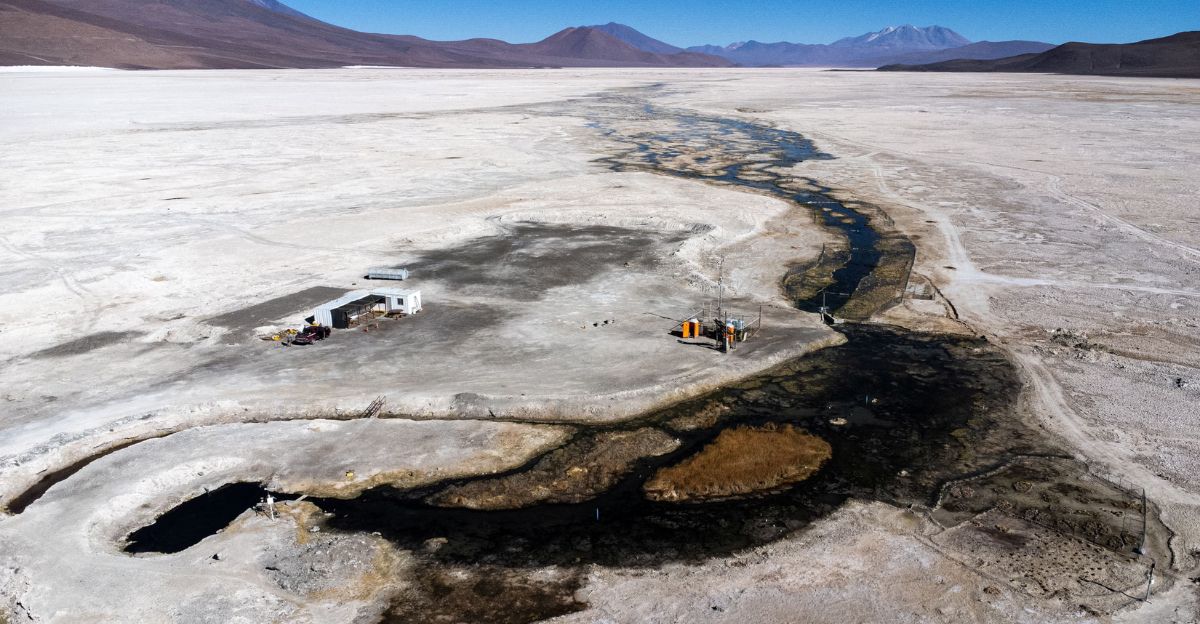

Chile’s Ascotan salt flat is home to the “Karachi” fish, a species uniquely adapted to its harsh environment. Proposed lithium mining projects in the area threaten the survival of this rare fish by altering its habitat and water quality. The potential loss of the Karachi fish exemplifies how mining for EV materials can endanger endemic species and disrupt delicate ecological balances. Conservation efforts must prioritize the protection of such species when considering mining developments.
Deforestation Linked to Mining Activities
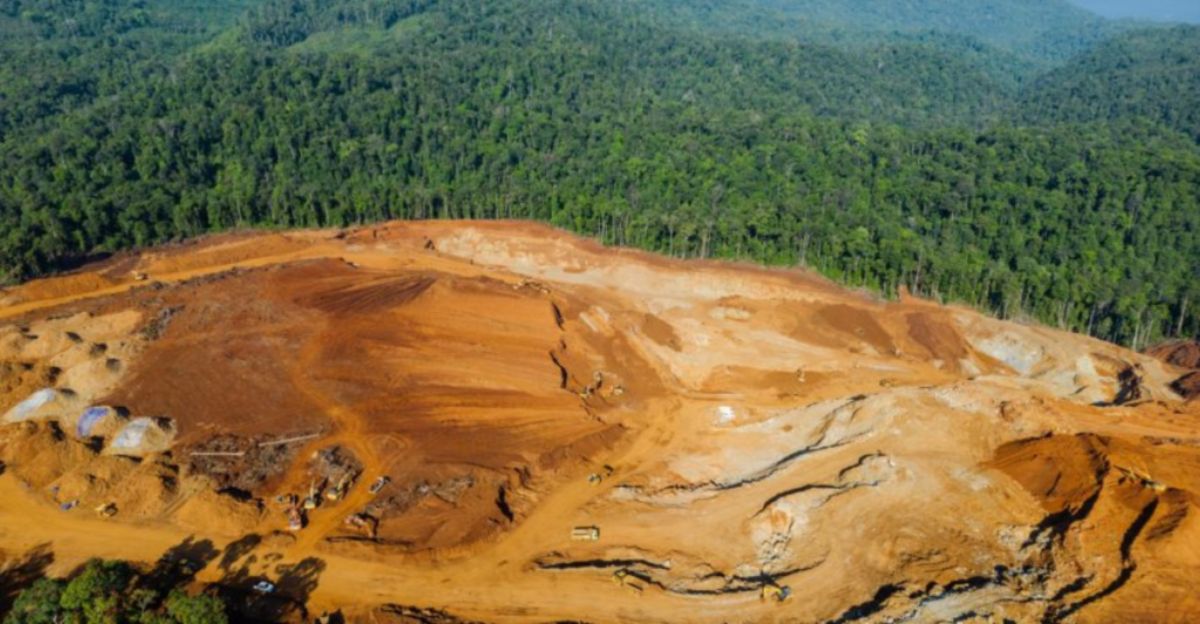

Mining operations for minerals like lithium and nickel have contributed to significant deforestation globally. Between 2001 and 2020, nearly 1.4 million hectares of tree cover were lost due to mining-related activities, impacting critical carbon sinks and exacerbating climate change. Countries such as Indonesia and Brazil have experienced substantial forest loss, highlighting the need for sustainable land-use practices and reforestation initiatives to mitigate the environmental impact of mining.
Environmental Risks of Battery Production Facilities
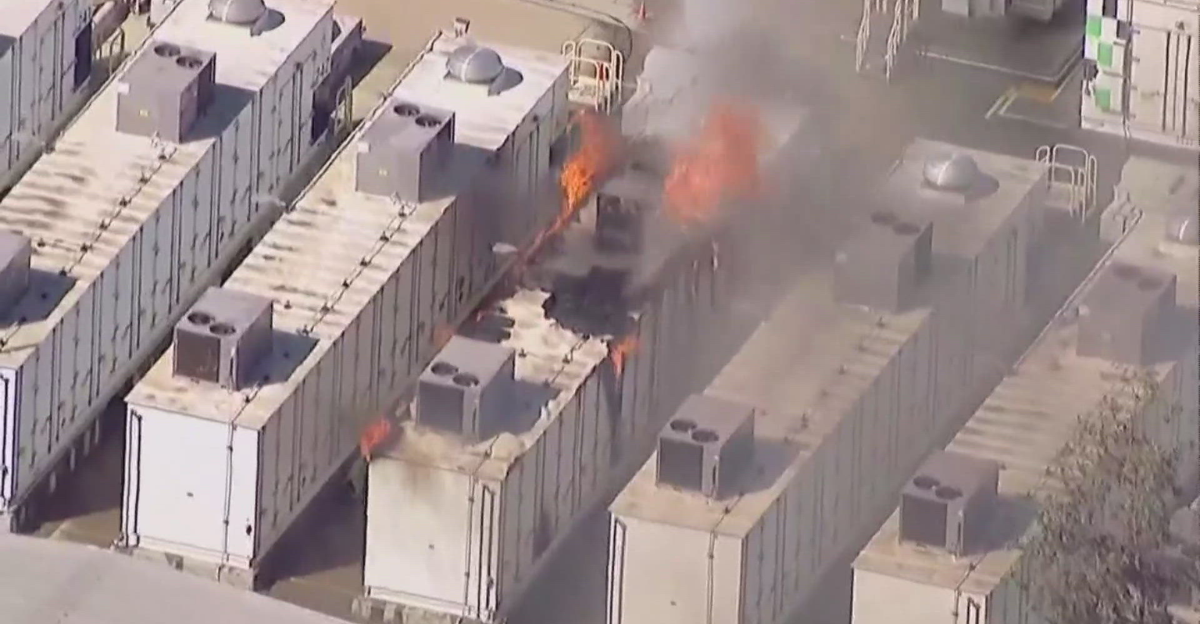

Beyond mining, the manufacturing and storage of lithium-ion batteries pose environmental risks. For example, a fire at a battery storage facility in California led to elevated levels of toxic metals like manganese, cobalt, and nickel in nearby wetlands. Such incidents highlight the need for stringent safety protocols and environmental monitoring to prevent contamination and protect surrounding ecosystems.
Recycling and Sustainable Sourcing Initiatives

Addressing the environmental challenges associated with EV production requires a focus on recycling and sustainable sourcing of battery materials. Innovators like Megan O’Connor have developed technologies to extract and refine critical metals from electronic waste, reducing the need for new mining and minimizing environmental impact. Investing in such technologies and establishing robust recycling systems can help create a more sustainable supply chain for EV batteries.
Balancing Climate Goals with Ecological Preservation
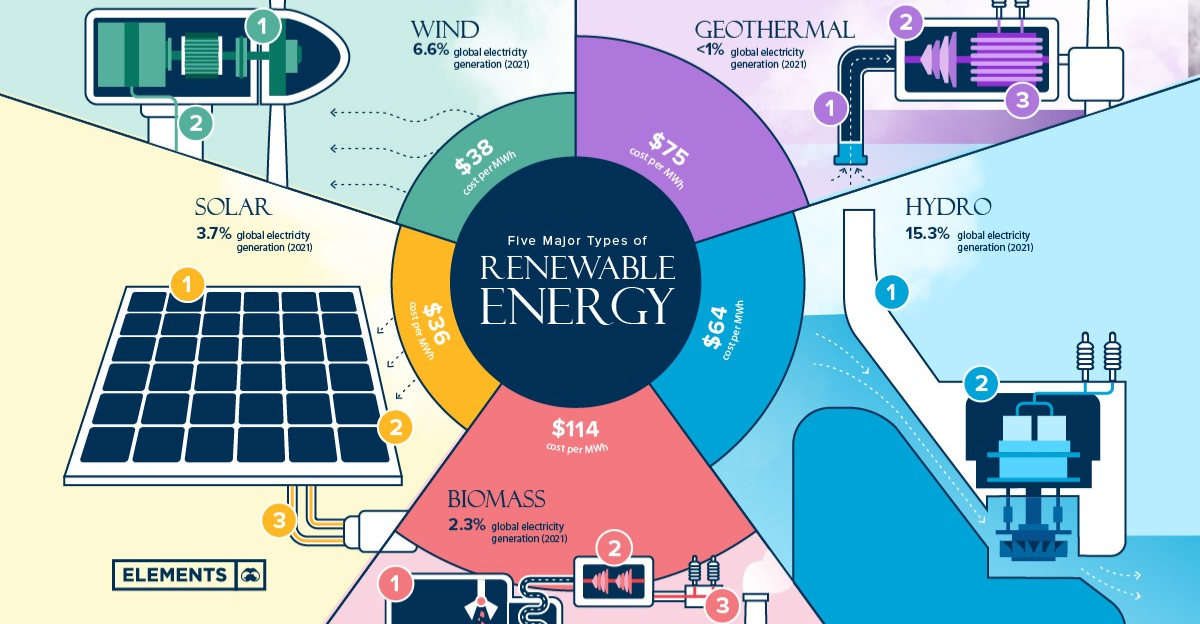
While EVs offer a pathway to reduce carbon emissions, balancing climate objectives with preserving ecosystems and biodiversity is crucial. This balance involves implementing stricter environmental regulations for mining, promoting ethical labor practices, investing in recycling technologies, and developing alternative battery materials that are less environmentally taxing. A holistic approach ensures that the transition to green energy does not inadvertently cause ecological harm.
The Path Forward: Sustainable Practices in EV Production

To mitigate the environmental impact of EVs, stakeholders must adopt sustainable practices across the entire production lifecycle. This includes responsible mining with minimal ecological disruption, robust recycling programs, and continuous research into alternative materials. By prioritizing sustainability, the automotive industry can contribute to climate change mitigation without compromising the health of the
Explore more of our trending stories and hit Follow to keep them coming to your feed!
Don’t miss out on more stories like this! Hit the Follow button at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest news. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!







