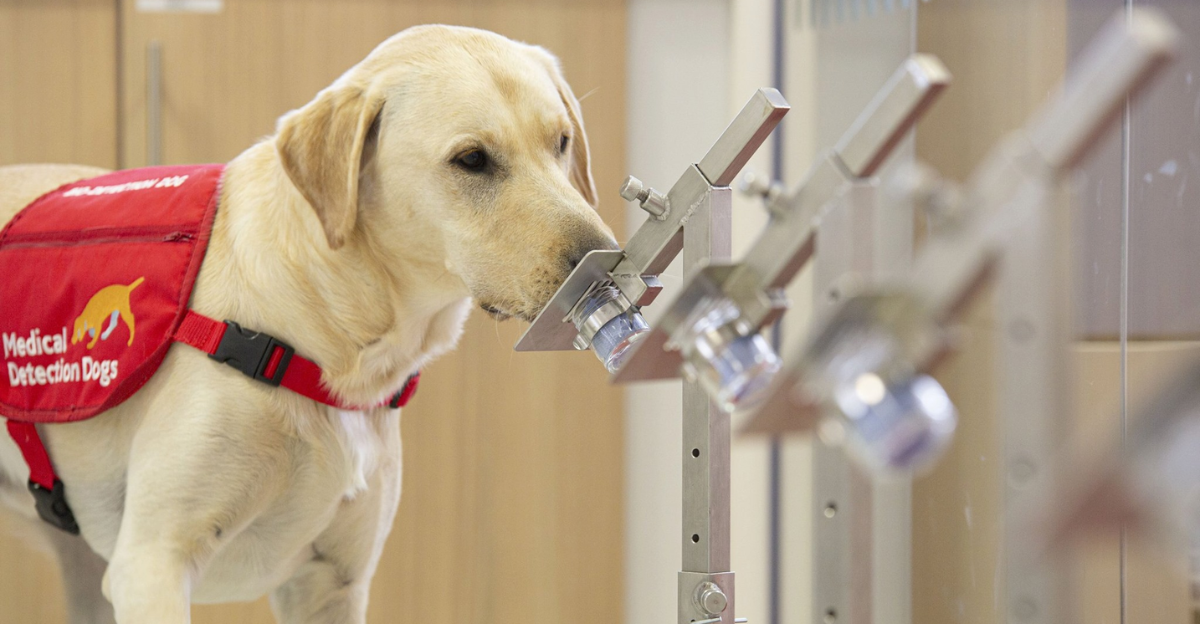

In a futuristic fusion of nature and technology, researchers have unveiled a novel method for early cancer detection that pairs the unparalleled olfactory abilities of dogs with advanced artificial intelligence (AI). This innovative approach has demonstrated remarkable accuracy, identifying multiple cancer types through non-invasive means. The implications of this development could revolutionize cancer screening protocols, offering a promising avenue for early diagnosis and treatment.
Sniffing Out The Solution
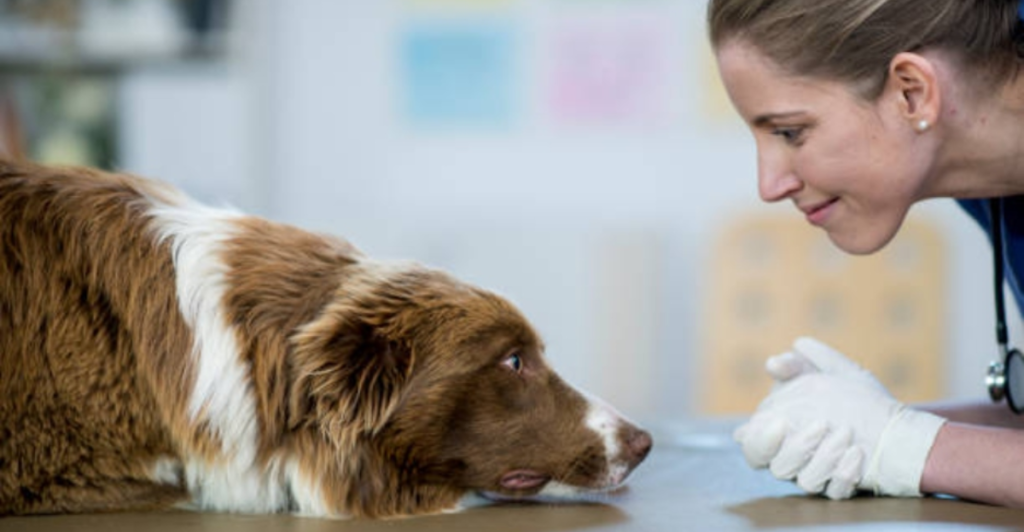

Recent studies have highlighted the potential of this bio-AI hybrid system. By analyzing breath samples from patients, trained canines, assisted by AI, have successfully detected the presence of cancer with impressive precision. This method not only underscores the synergy between biological instincts and machine learning but also paves the way for more accessible and efficient cancer screening solutions.
The Canine Contributors: Mars, Moon, and Pluto
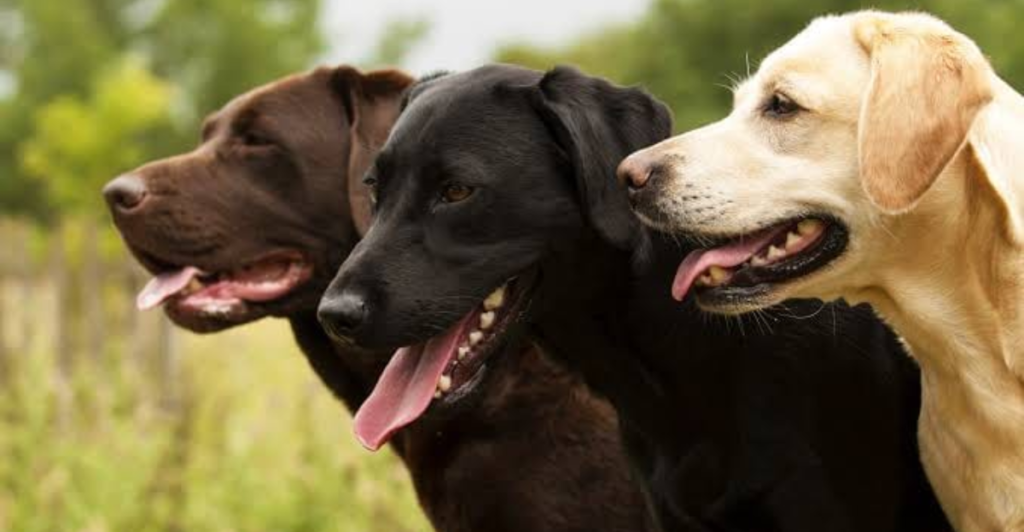

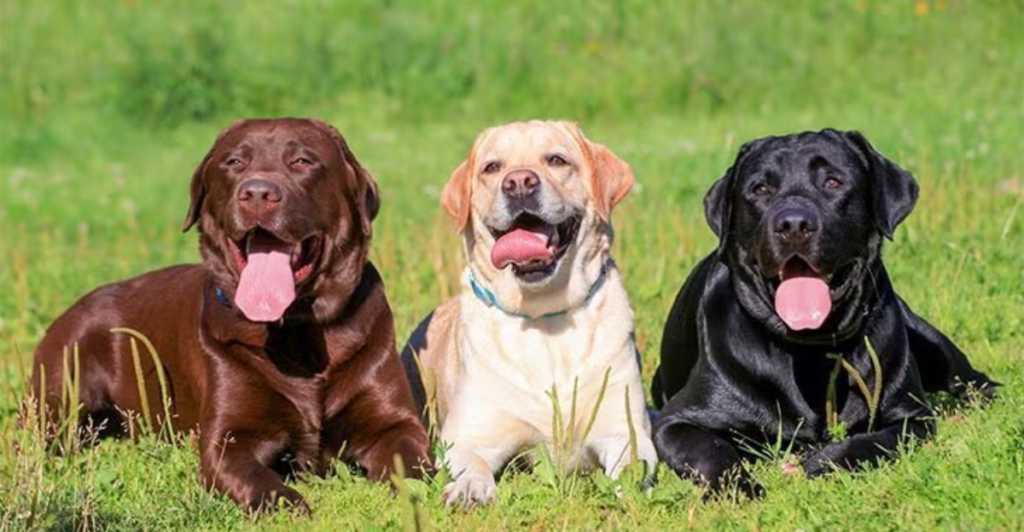
Central to this pioneering research are three exceptional dogs: Mars, Moon, and Pluto. These canines have been meticulously trained to identify specific volatile organic compounds (VOCs) associated with cancer, which are present in human breath. Their acute sense of smell enables them to detect these compounds at minute concentrations, a feat beyond current technological capabilities.
The training regimen for these dogs is rigorous and comprehensive. They undergo extensive conditioning to recognize the unique scent profiles of various cancers, ensuring high accuracy in detection. Their contributions are invaluable, serving as the biological foundation upon which the AI algorithms build.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence
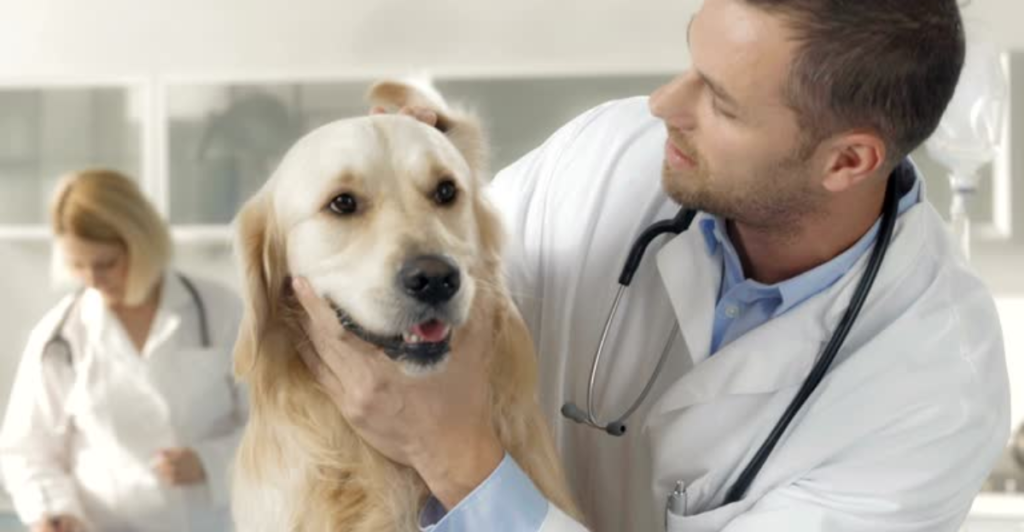

While the dogs’ olfactory skills are extraordinary, the integration of AI enhances the system’s overall effectiveness. AI algorithms analyze the behavioral responses of the canines during the detection process, interpreting subtle cues that may indicate the presence of cancer. This analysis allows for a more nuanced understanding of the dogs’ findings, leading to improved diagnostic accuracy.
Moreover, AI facilitates the processing of large datasets, enabling the system to learn and adapt over time. As more data is collected, the AI becomes increasingly proficient at identifying patterns associated with different cancer types, thereby refining the detection process and reducing the likelihood of false positives or negatives.
The Rainbow Study: A Milestone in Cancer Detection

The efficacy of this combined approach was recently demonstrated in a study known as the Rainbow Study. Published in Scientific Reports on November 15, 2024, the research involved a double-blind trial with 1,386 participants. The results were compelling, with the canine-AI duo achieving a 94% success rate in detecting four types of cancer: breast, lung, colorectal, and prostate.
Trusting An Animals Instincts
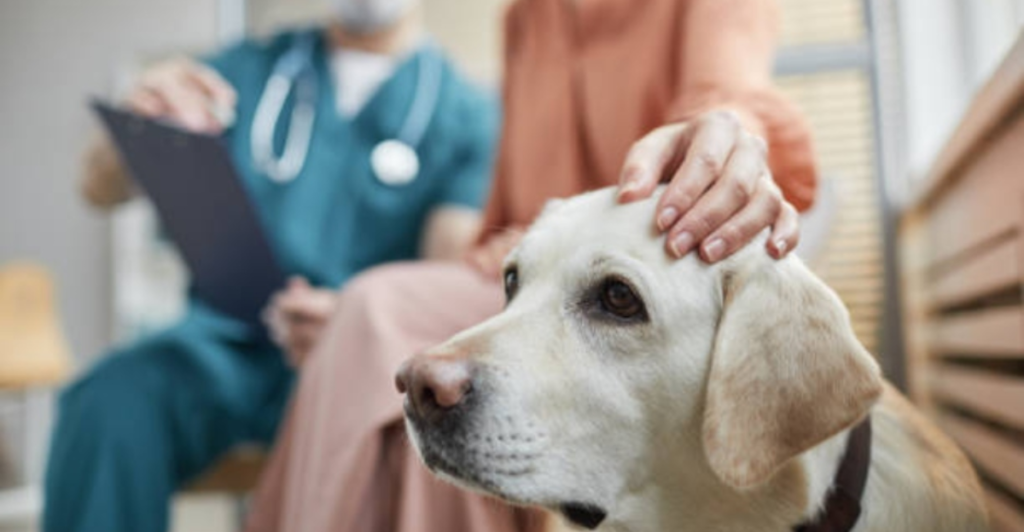

This high level of accuracy underscores the potential of the bio-AI hybrid system as a reliable tool for early cancer detection. The study’s findings suggest that this method could complement existing screening techniques, providing a non-invasive, efficient, and cost-effective alternative for identifying cancer in its early stages.
Mechanism of Detection

The detection process hinges on the identification of VOCs emitted by cancerous cells. Patients provide breath samples, which are then presented to the trained dogs. Upon detecting the scent of cancer, the dogs exhibit specific behavioral responses, such as sitting or pawing, which are monitored and analyzed by the AI system.
Digital Dogs
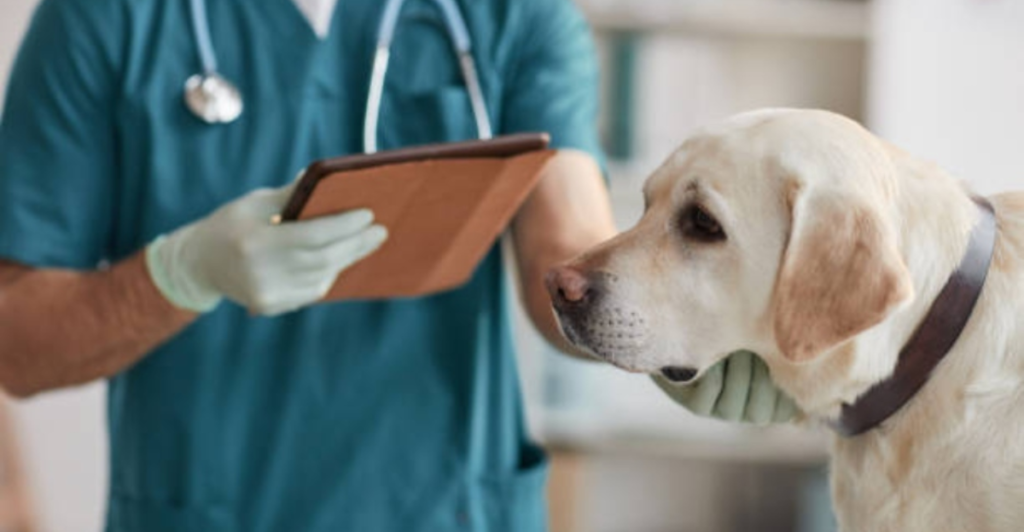

The AI component plays a crucial role in interpreting these behaviors, assessing factors such as the duration and intensity of the dogs’ responses. By combining the dogs’ natural detection abilities with AI analysis, the system achieves a level of sensitivity and specificity that surpasses traditional screening methods.
Advantages Over Traditional Screening Methods

Traditional cancer screening methods often involve invasive procedures, exposure to radiation, or reliance on imaging technologies that may not detect early-stage cancers. In contrast, the canine-AI hybrid approach offers a non-invasive alternative that can identify cancer at an earlier stage, potentially improving patient outcomes.
Additionally, this method is cost-effective and accessible, requiring minimal infrastructure compared to conventional screening techniques. The use of breath samples eliminates the need for complex medical equipment, making it feasible to implement in a variety of healthcare settings, including those with limited resources.
Challenges and Considerations

Despite its promise, the integration of canine olfaction and AI in cancer detection presents certain challenges. The training and maintenance of detection dogs require significant time and resources. Ensuring consistency in the dogs’ performance is essential, as factors such as fatigue or distractions can affect their accuracy.
Moreover, the AI algorithms must be continually updated and validated to maintain their effectiveness. This necessitates ongoing data collection and analysis, as well as collaboration between experts in fields such as veterinary science, oncology, and computer science.
Future Directions For The Dogs

Building on the success of the Rainbow Study, researchers are exploring ways to expand and refine the bio-AI hybrid system. This includes training dogs to detect a broader range of cancers and other diseases, as well as enhancing the AI algorithms to improve their interpretative capabilities.
There is also interest in developing portable devices that can replicate the dogs’ olfactory detection abilities, potentially allowing for widespread screening without the need for trained canines. Such advancements could further democratize access to early cancer detection, particularly in underserved communities.
Ethical and Societal Implications

The deployment of this technology raises important ethical and societal considerations. The welfare of the detection dogs must be prioritized, ensuring they are treated humanely and not subjected to undue stress. Additionally, the use of AI in medical diagnostics necessitates careful oversight to prevent biases and ensure patient privacy.
Public acceptance of this unconventional screening method is another factor to consider. Educational initiatives may be required to inform patients and healthcare providers about the benefits and limitations of the bio-AI hybrid system, fostering trust and encouraging adoption.
Animals In Science

The collaboration between trained canines and artificial intelligence represents a remarkable convergence of natural and technological capabilities. By harnessing the dogs’ acute sense of smell and the analytical power of AI, this innovative approach offers a promising new avenue for early cancer detection.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them appearing in your feed
Scientists Are Bringing Back The Wooly Mammoth
Scientists Are Exploring The De-Extinction Of Woolly Mammoths And It’s Closer Than We Think
Polar Vortex Will Drop Temperatures By 30 Degrees In These States
Bobcats Are Making a Comeback—And They Might Be Protecting Us From Disease
References:
Reference 1
Reference 2
This article first appeared here
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







