
Throughout Earth’s history, life has faced catastrophic events that have led to species’ rapid and widespread extinction. These events, known as mass extinctions, are characterized by the loss of at least 75% of species within a geologically short period, typically less than 2.8 million years. There have been five such mass extinctions, each profoundly altering the course of evolution and reshaping the diversity of life on our planet.
Ordovician-Silurian Extinction
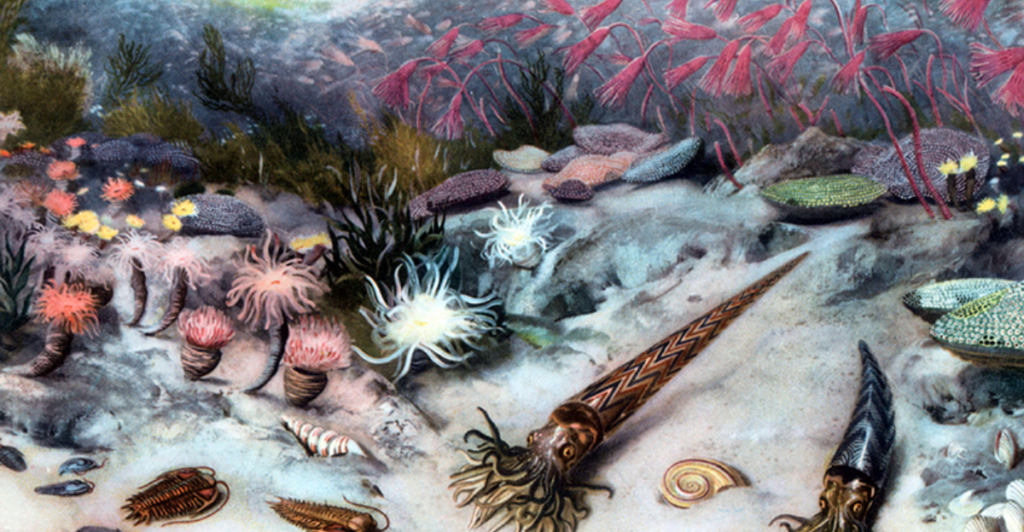

The Ordovician-Silurian Extinction, which happened approximately 445 million years ago, led to the extinction of about 86% of all species, primarily affecting small marine organisms. Scientists believe this was caused by temperatures plummeting, causing huge glaciers to form that drastically affected sea levels.
Devonian Extinction
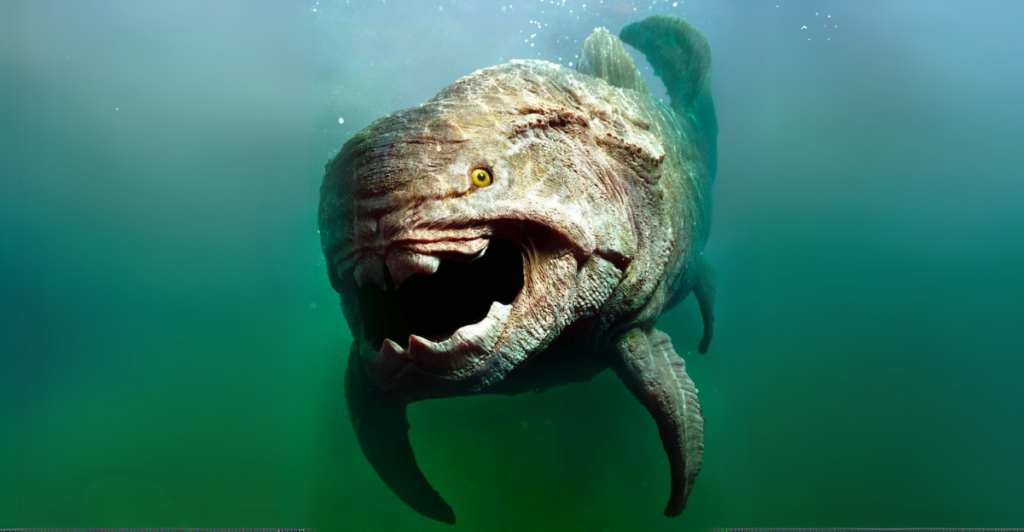

Approximately 365 million years ago, around 75% of species, including many tropical marine species, went extinct during the Devonian Extinction. We don’t know what exactly triggered the extinction event, but during this time, the Earth underwent many environmental changes, such as global warming and cooling, a rise and fall of sea levels, and a reduction in oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Permian-Triassic Extinction
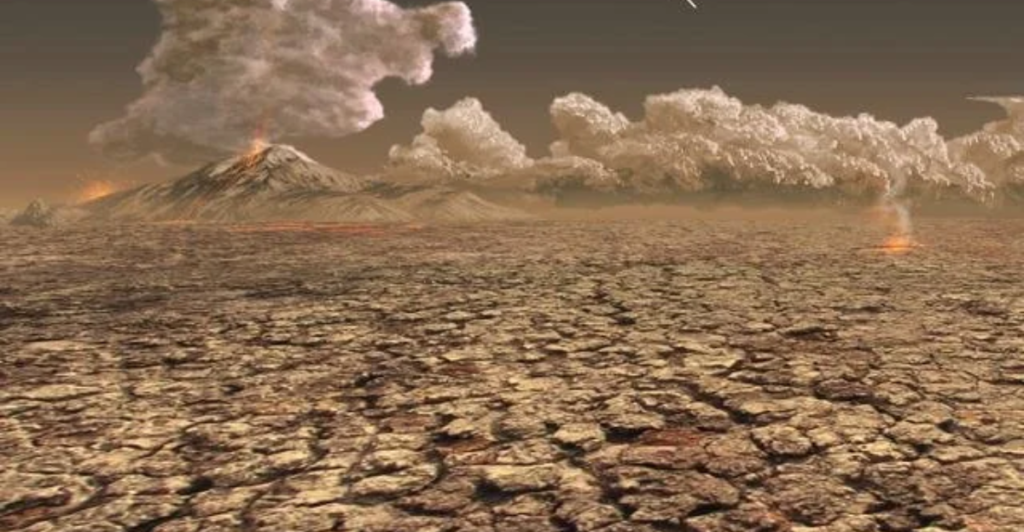

Known as the largest mass extinction event in Earth’s history, the Permian-Triassic Extinction resulted in the loss of about 90% of species, including many vertebrates. This happened approximately 250 million years ago when intense volcanic activity in Siberia caused global warming. Large amounts of carbon dioxide were released into the Earth’s atmosphere, causing a greenhouse effect that heated up the planet. According to the Sam Noble Museum in Oklahoma, the oceans absorbed a significant amount of carbon dioxide, poisoning marine invertebrates.
Triassic-Jurassic Extinction
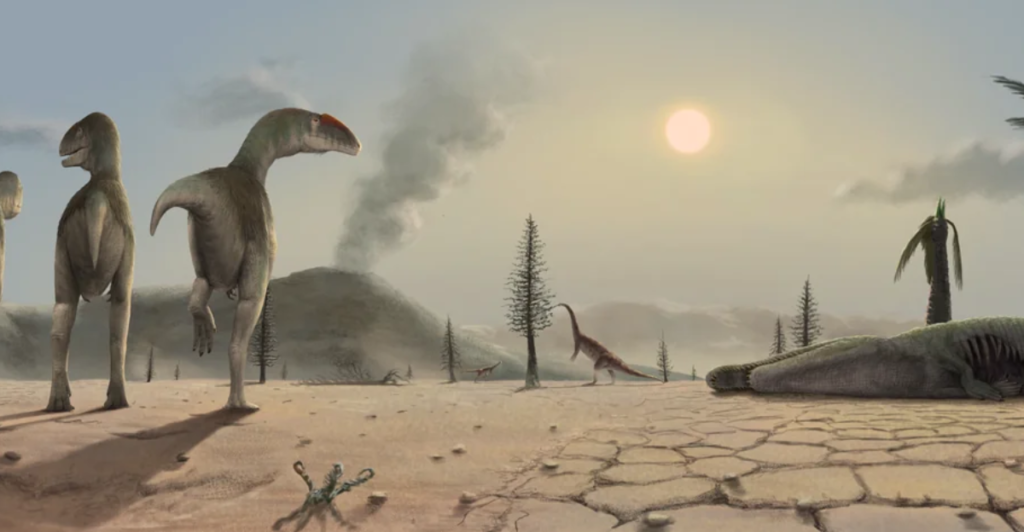

The Triassic-Jurassic Extinction, which occurred approximately 201 million years ago, led to the extinction of about 76% of all marine and terrestrial species. Scientists believe this mass extinction occurred because of massive volcanic activity that released large amounts of carbon dioxide, which caused climate change and devastated life on Earth.
Cretaceous-Paleogene Extinction
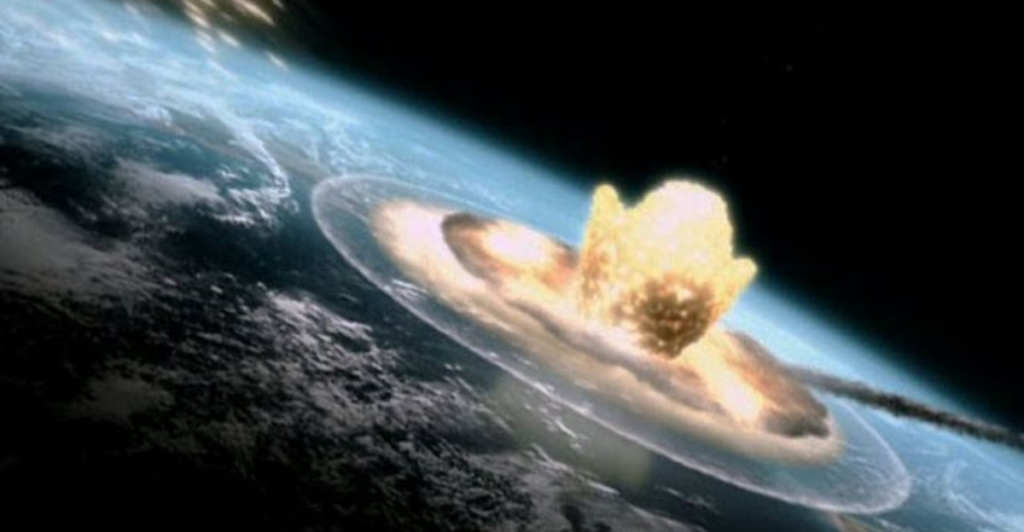

Approximately 65 million years ago, the Cretaceous-Paleogene Extinction led to the demise of 75% of species, including the non-avian dinosaurs. This extinction was caused by the Chicxulub asteroid that slammed into Earth. The impact released an enormous amount of energy, causing shockwaves, tsunamis, and a massive ejection of debris into the atmosphere. The impact ejected vast amounts of dust, sulfur, and soot into the atmosphere, which blocked sunlight and led to a phenomenon known as an “impact winter.”
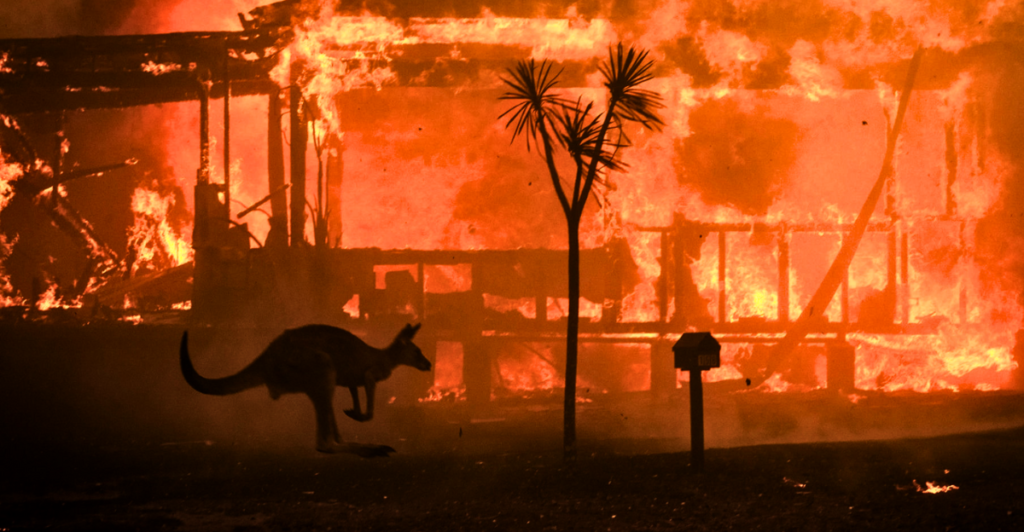
A Potential Sixth Mass Extinction

Recently, scientists have raised concerns about a potential sixth mass extinction driven primarily by human activities. Unlike previous events caused by natural phenomena, the current decline in biodiversity is attributed to factors such as habitat destruction, overexploitation of resources, pollution, and climate change. These activities have accelerated the rate of species extinction far beyond the natural background rate.
The Evidence
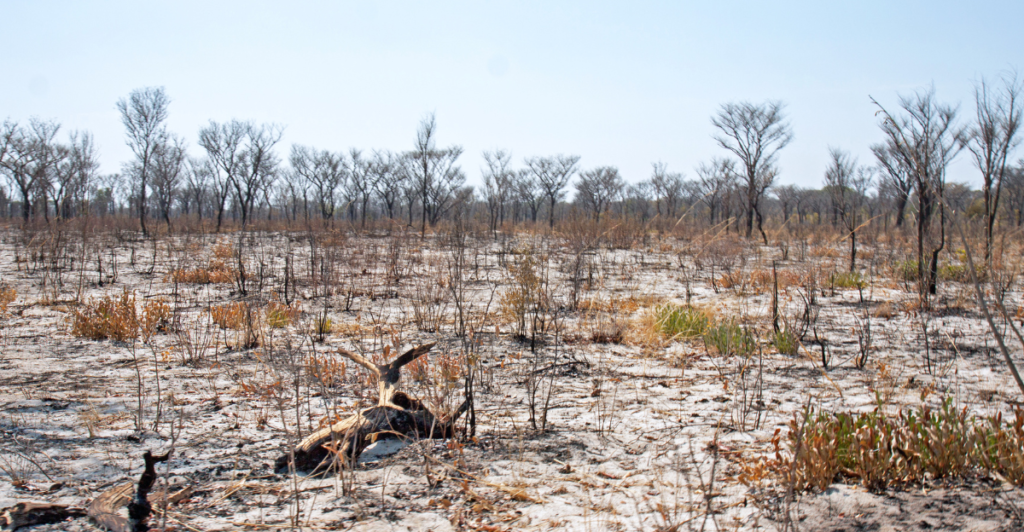

Evidence of this ongoing extinction is supported by the dramatic decline in wildlife populations worldwide. According to the World Wildlife Fund, wildlife populations have declined by 69% since 1970, indicating a rapid loss of biodiversity.
Human Activities
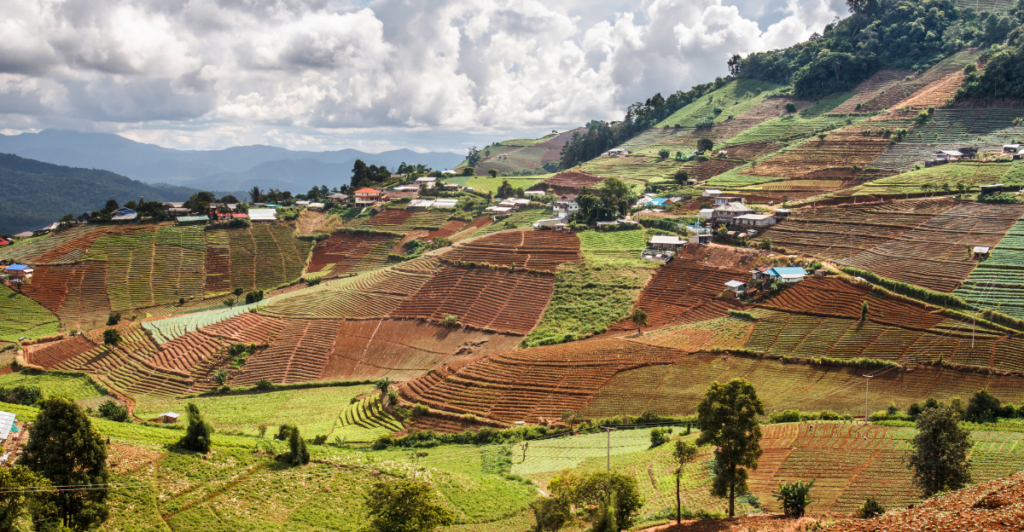

Agriculture is considered the primary driver of global deforestation, accounting for nearly 90% of forest loss. It also consumes about 70% of the world’s freshwater supply, drastically transforming natural habitats and endangering the species that rely on them. The climate crisis worsens these issues, leading to prolonged droughts, stronger and more frequent storms, and other environmental disruptions that make ecosystems increasingly unlivable for many forms of wildlife.
An Unprecedented Pace
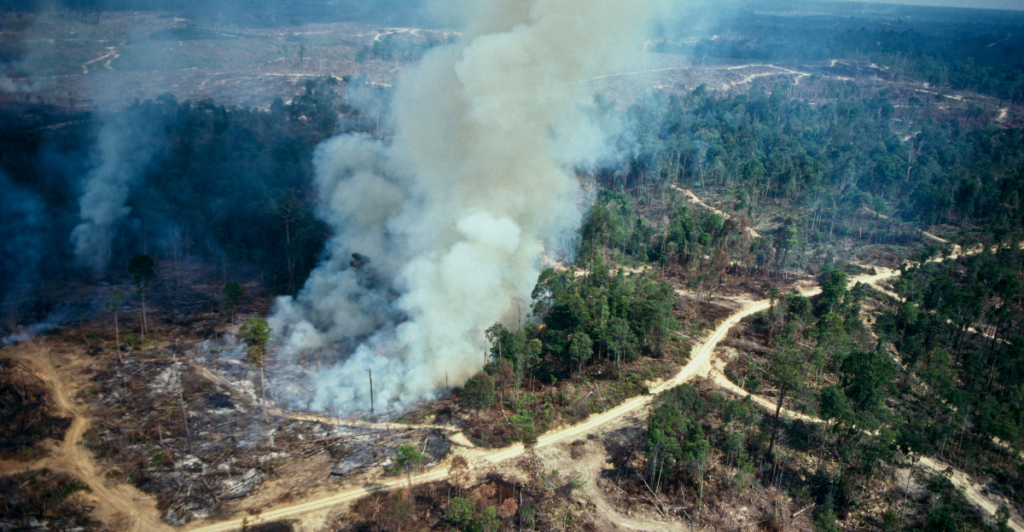

Unlike previous mass extinctions that unfolded over thousands or millions of years, the current biodiversity crisis is occurring at an unprecedented pace. This rapid decline poses significant risks to the natural world and human societies that depend on healthy ecosystems for services such as pollination, water purification, and climate regulation.
Global Efforts

Addressing the drivers of the sixth mass extinction requires comprehensive global efforts. Strategies include implementing sustainable land and water use practices, reducing greenhouse gas emissions to mitigate climate change, and protecting critical habitats by establishing conservation areas.
Proactive Measures

While Earth has experienced five mass extinctions due to natural causes, the potential sixth mass extinction is unique in being driven by human activities. Recognizing the urgency of this crisis and taking proactive measures can help preserve the planet’s biodiversity and ensure the resilience of ecosystems upon which all life depends.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them appearing in your feed
Dinosaurs Discovered to Defy a 150-Year-Old Scientific Rule
Earth’s Third Form Of Life Discovered—And It’s Reshaping Power Generation As We Know It
Meet the Massive Crocodiles That Make Their Homes 40 Feet Underground
The ‘Dragon Head’ Hominid Discovery in China Challenging the Out of Africa Theory
References:
Reference 1
Reference 2
Reference 3
This article first appeared here
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







