
Wisconsin’s picturesque lakes are cherished for their serene beauty and recreational opportunities. However, beneath these tranquil waters lurk certain creatures that pose risks to unsuspecting swimmers and anglers. While encounters are rare, awareness of these inhabitants is crucial for ensuring safety during aquatic activities.
The Worst Of All
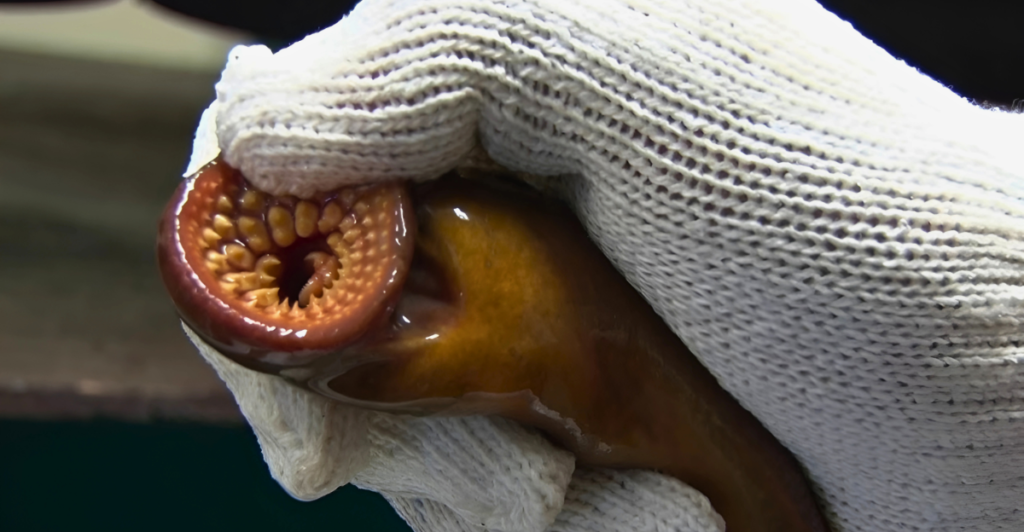
Let’s look at four of the most dangerous creatures found in Wisconsin’s lakes: the Landshark, sea lamprey, snakehead fish and lake sturgeon. Understanding their behaviors, habitats, and potential threats can help lake-goers take necessary precautions and appreciate the delicate balance of these freshwater ecosystems.
The Mythical Landshark

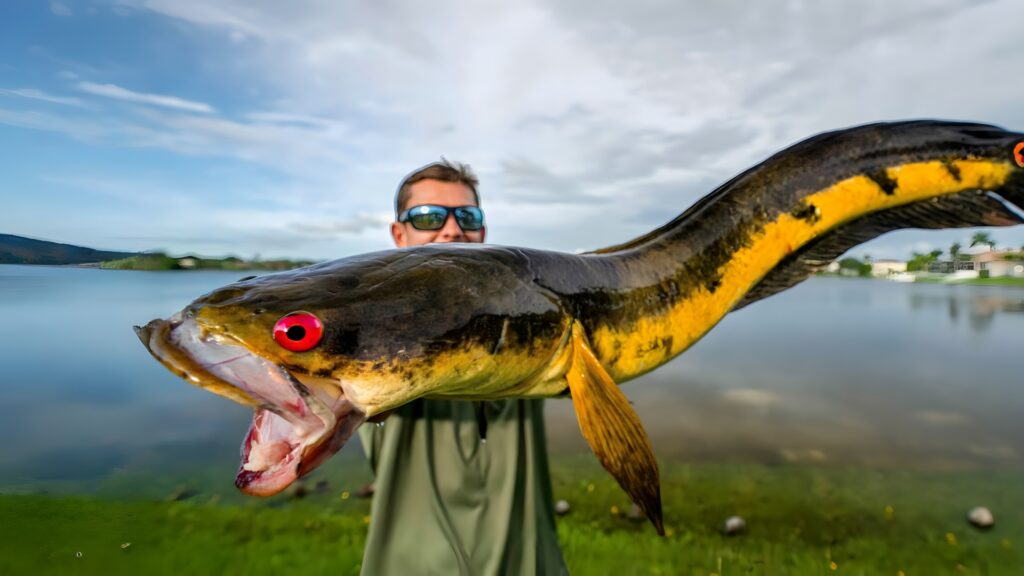
The term “landshark” often conjures images of mythical creatures; however, in Wisconsin, it refers to the colloquial name for the bowfin fish. This ancient species, known for its aggressive behavior, inhabits the shallow waters of many Midwestern lakes. While not typically dangerous to humans, their sharp teeth and powerful jaws can cause injury if mishandled.
Anglers occasionally encounter bowfins due to their voracious feeding habits. It’s essential to handle them with care to avoid bites. Despite their intimidating appearance, bowfins play a vital role in maintaining the ecological balance by controlling populations of smaller fish species.
Sea Lamprey: The Vampire Fish
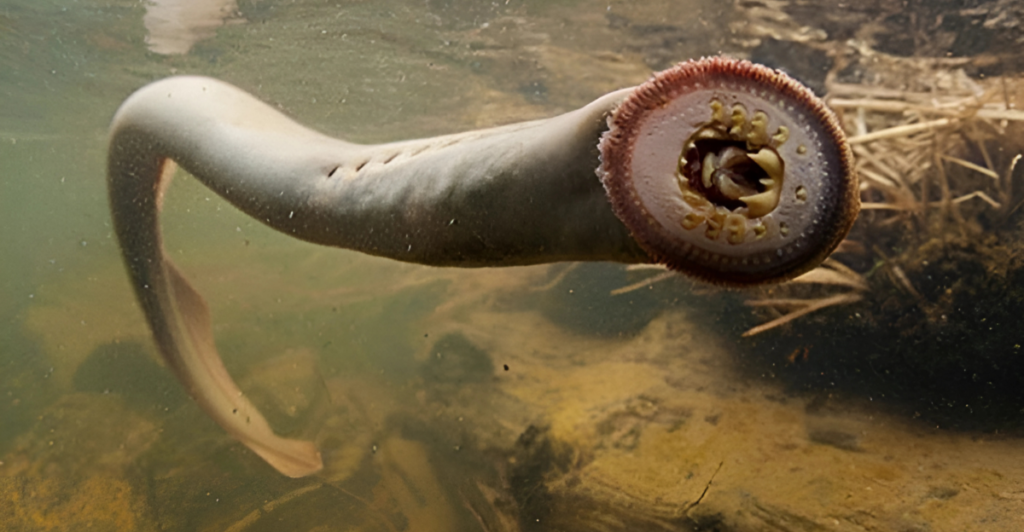

The sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus), often dubbed the “vampire fish,” is an invasive, eel-like parasite that has significantly impacted the Great Lakes region, including Wisconsin’s waters. Originating from the Atlantic Ocean, they entered the Great Lakes through man-made shipping canals in the early 20th century. Their presence has led to substantial declines in native fish populations, as they attach to host fish, extracting blood and bodily fluids, often resulting in the host’s death.
Measuring up to 18 inches in length, sea lampreys are identifiable by their jawless, suction-cup mouths lined with sharp teeth. They primarily inhabit deep lake waters but migrate to shallow streams to spawn. While they pose minimal direct threat to humans due to their preference for deep waters, their impact on the aquatic ecosystem indirectly affects recreational and commercial fishing industries.
Hard To Detect
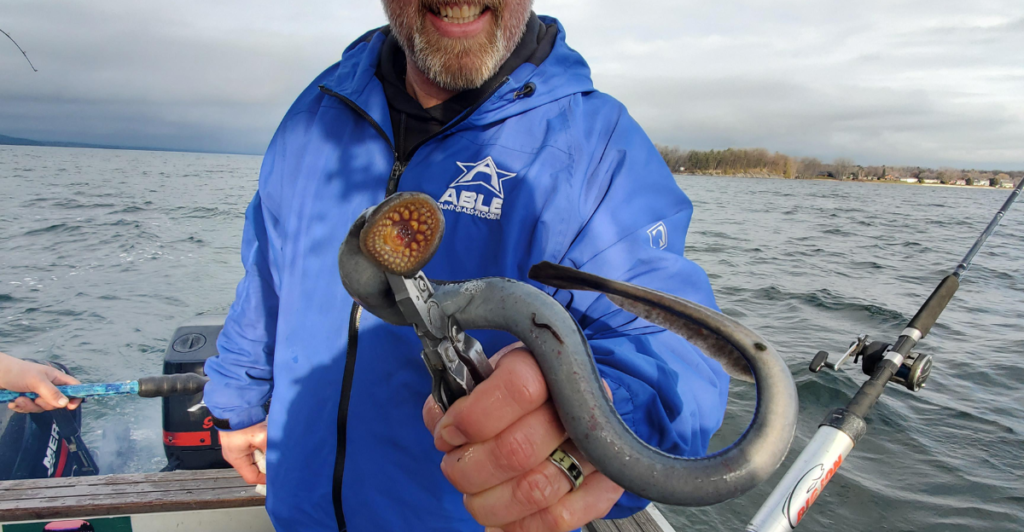

Efforts to control sea lamprey populations have been ongoing, with agencies implementing measures such as chemical lampricides and barriers to prevent their spread. These initiatives have seen some success, reducing their numbers and allowing native fish populations to recover. However, continuous monitoring and management are essential to maintain the ecological balance in Wisconsin’s lakes.
Snakehead Fish: The Invasive Predator
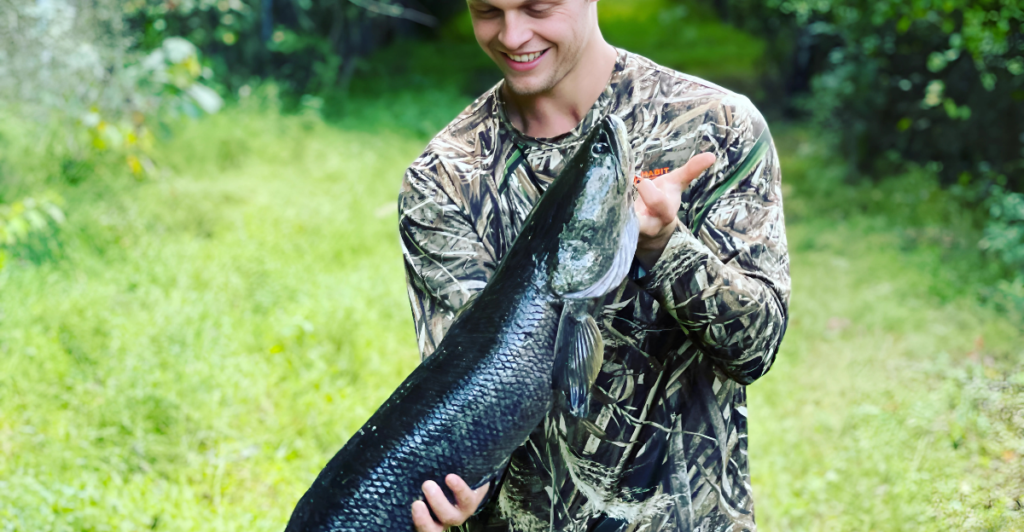

Snakehead fish, native to parts of Africa and Asia, have become a concerning invasive species in North American waters, including those in Wisconsin. Known for their aggressive predatory behavior, they can disrupt local ecosystems by preying on native fish and competing for resources. Their ability to breathe air and survive on land for short periods further aids their spread across various water bodies.
These fish can grow up to three feet in length and are characterized by their elongated bodies and sharp teeth. They inhabit shallow, vegetated areas of lakes and rivers, making them more likely to come into contact with humans during recreational activities. While snakeheads are not known to attack humans unprovoked, their presence can significantly impact local biodiversity and fishing practices.
What The Law Says
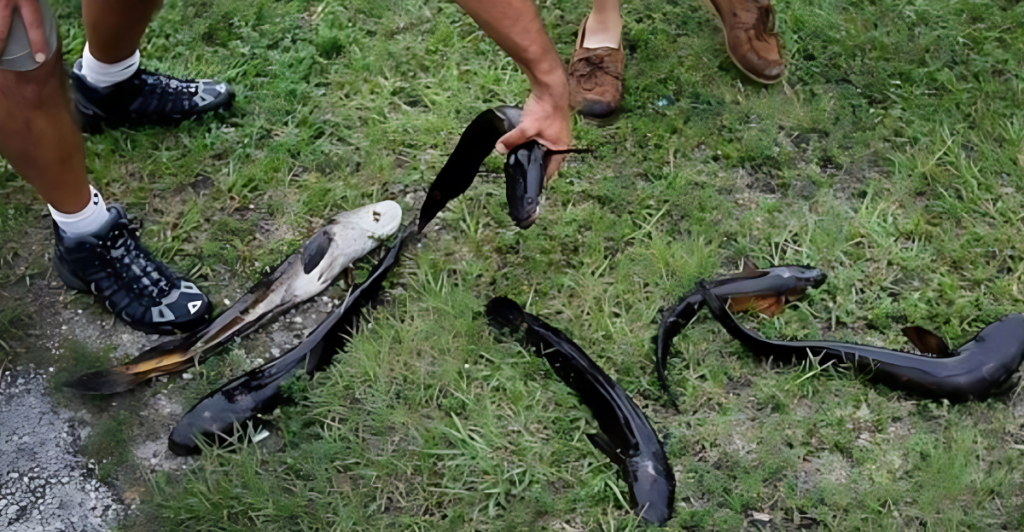

The Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (DNR) has issued advisories to help prevent the spread of snakehead fish. Anglers are encouraged to report any sightings and avoid releasing caught snakeheads back into the water. Public awareness and adherence to these guidelines are crucial in managing this invasive species and protecting Wisconsin’s aquatic ecosystems.
Lake Sturgeon: Gentle Giants with Potential Risks
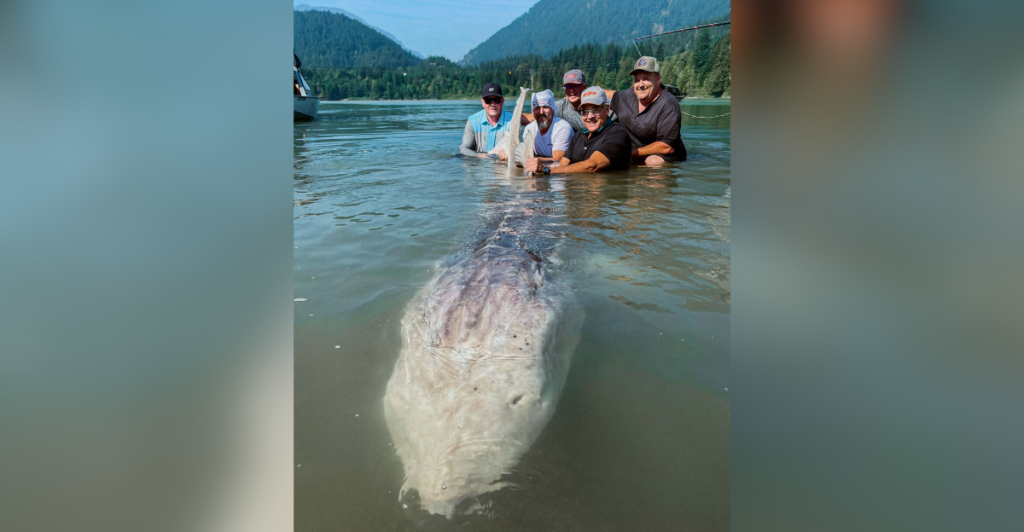

Lake sturgeon (Acipenser fulvescens) are ancient, bottom-dwelling fish native to Wisconsin’s lakes and rivers. These gentle giants can live for over a century and grow up to seven feet long, weighing more than 200 pounds. Despite their size and prehistoric appearance, they are generally harmless to humans and play a vital role in the aquatic ecosystem.
However, their sheer size can pose unintentional risks. There have been instances where sturgeon have leaped out of the water, potentially injuring boaters or swimmers. Such occurrences are rare but can be dangerous due to the fish’s substantial mass and strength.
Saving The Sturgeon
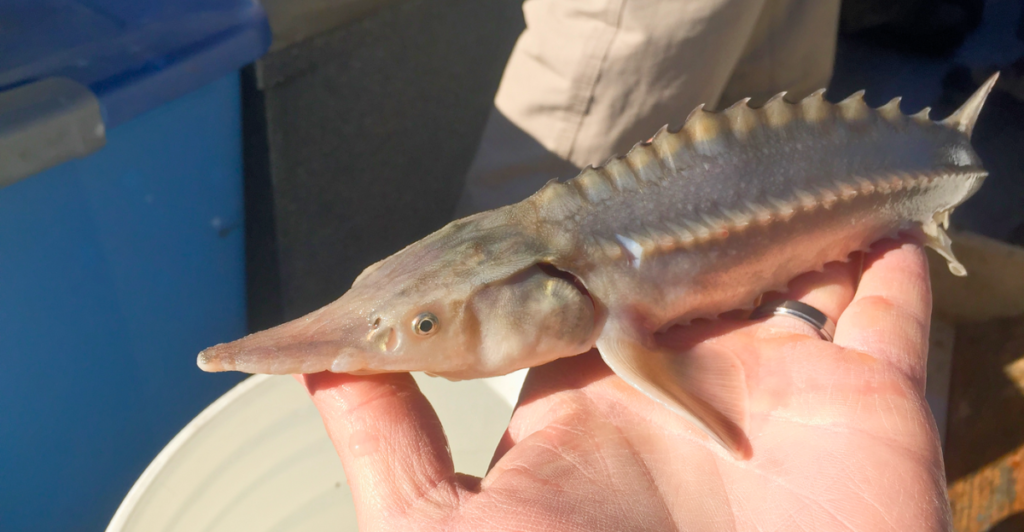

Conservation efforts have been instrumental in protecting lake sturgeon populations, which faced significant declines due to overfishing and habitat loss. Today, regulated fishing seasons and habitat restoration projects have contributed to a gradual recovery of this species, ensuring that they remain a part of Wisconsin’s natural heritage.
Watch Out
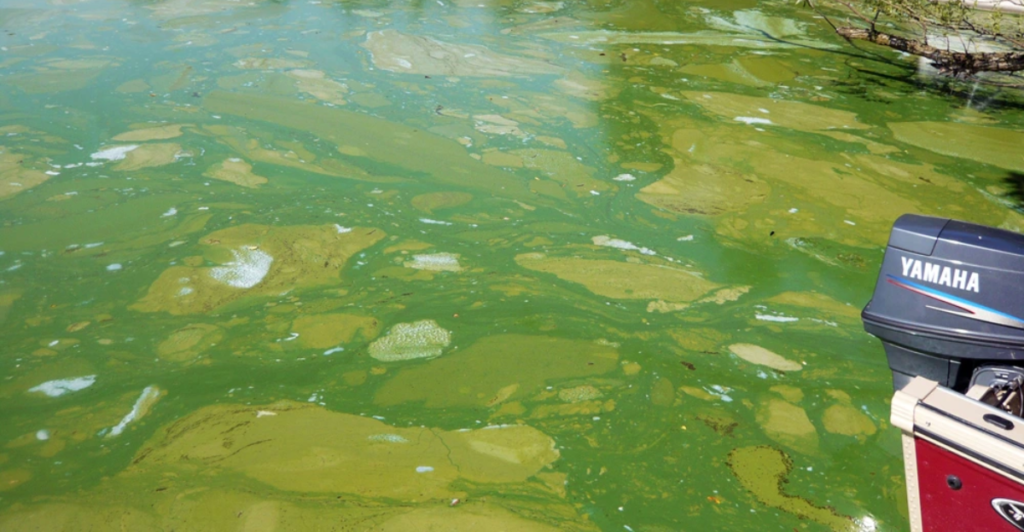

In Wisconsin, approximately 90% of recreation-related impairments of lakes and reservoirs are due to blooms of blue-green algae. Exposure to these toxins can cause symptoms ranging from skin irritation to more severe gastrointestinal and neurological issues. Pets are particularly vulnerable, with several cases of animal fatalities reported following contact with contaminated water.
Check The Stats
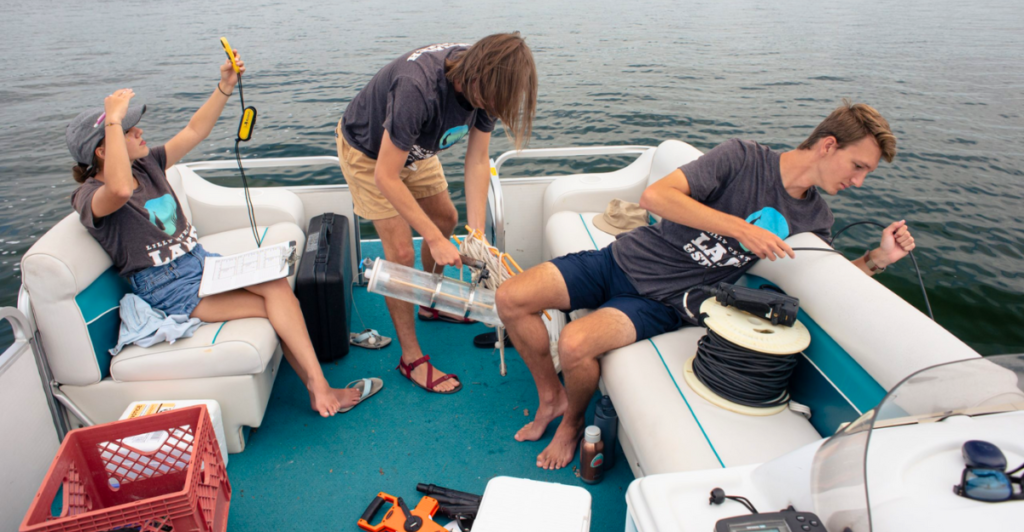

To mitigate the risks associated with HABs, the Wisconsin DNR monitors water quality and issues advisories when high toxin levels are detected. Lake visitors are advised to avoid contact with water that appears discolored or has a noticeable surface scum. Staying informed about current water conditions and adhering to public health advisories can help prevent exposure to these invisible threats.
Take Care Of The Environment
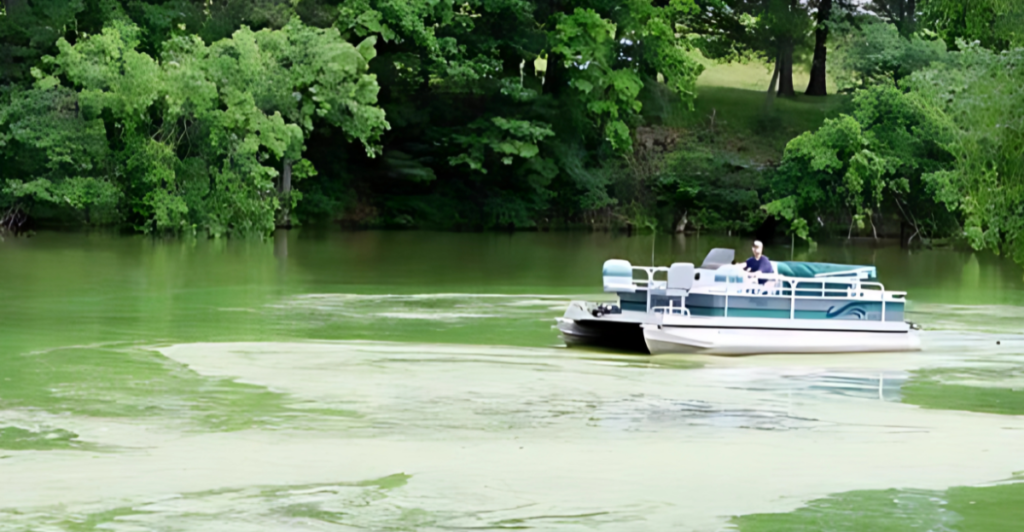

While Wisconsin’s lakes offer abundant recreational opportunities, it’s essential to remain aware of the potential dangers that certain creatures and environmental conditions may present. Understanding the behaviors and habitats of species like the sea lamprey, snakehead fish, lake sturgeon, and recognizing the signs of harmful algal blooms can significantly enhance safety for all lake-goers.
Do Your Research
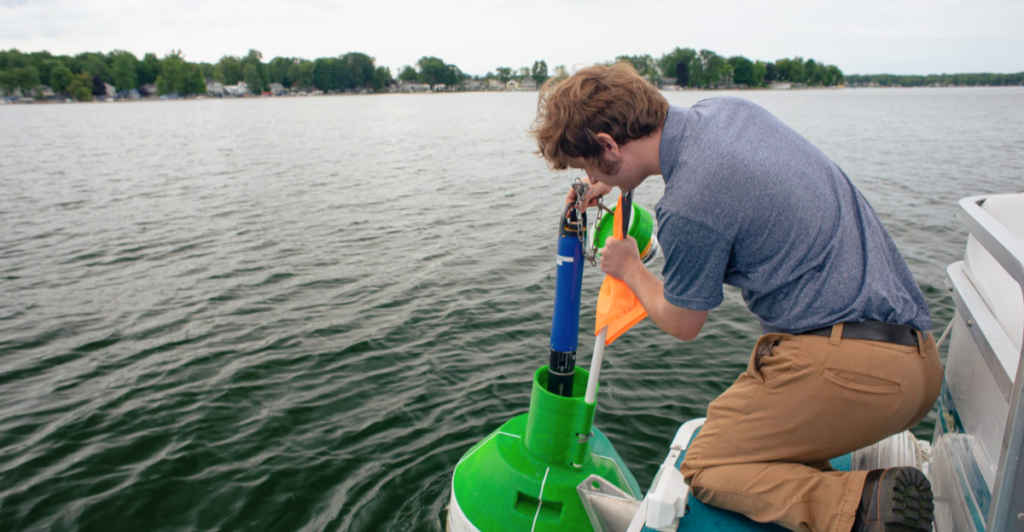

By staying informed and following guidelines set forth by environmental and wildlife agencies, individuals can continue to enjoy the natural beauty and resources of Wisconsin’s lakes while minimizing risks. Ongoing conservation and management efforts are vital in preserving these ecosystems, ensuring they remain safe and vibrant for future generations.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them appearing in your feed.

Meet the Massive Crocodiles That Make Their Homes 40 Feet Underground
Lake Shasta’s Remarkable Recovery From Drought Captured in Stunning Images
12 Mysterious Underwater Forests Lurking Beneath Lakes
12 High-Altitude Lakes Protecting Rare Aquatic Life in the U.S.
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







