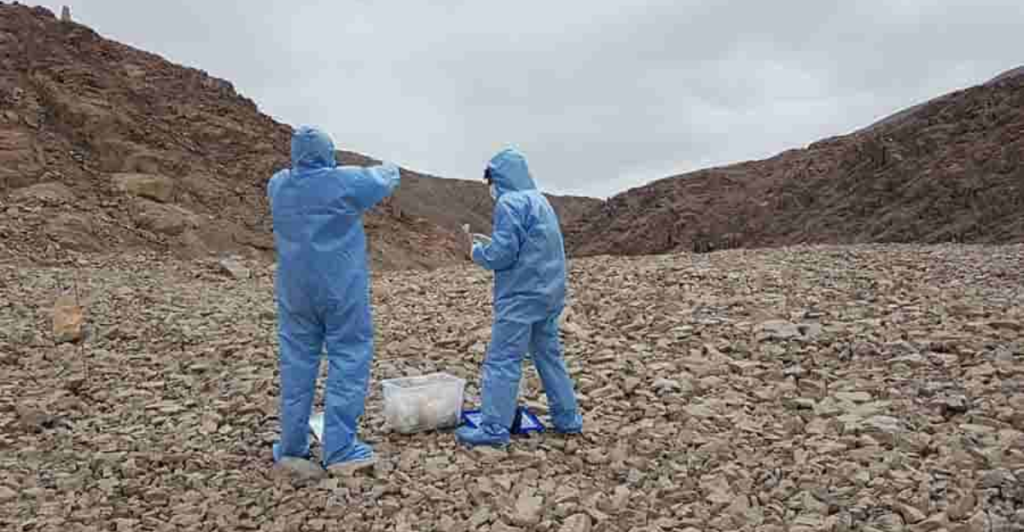

In a groundbreaking revelation, scientists have uncovered a hidden world teeming with life beneath one of the planet’s most unforgiving environments. The Atacama Desert in Chile, known as the driest place on Earth, has long been thought of as barren and inhospitable. However, new research has revealed a vibrant ecosystem thriving just below the surface, challenging our understanding of life in extreme conditions.
A Decade-Long Quest for Answers
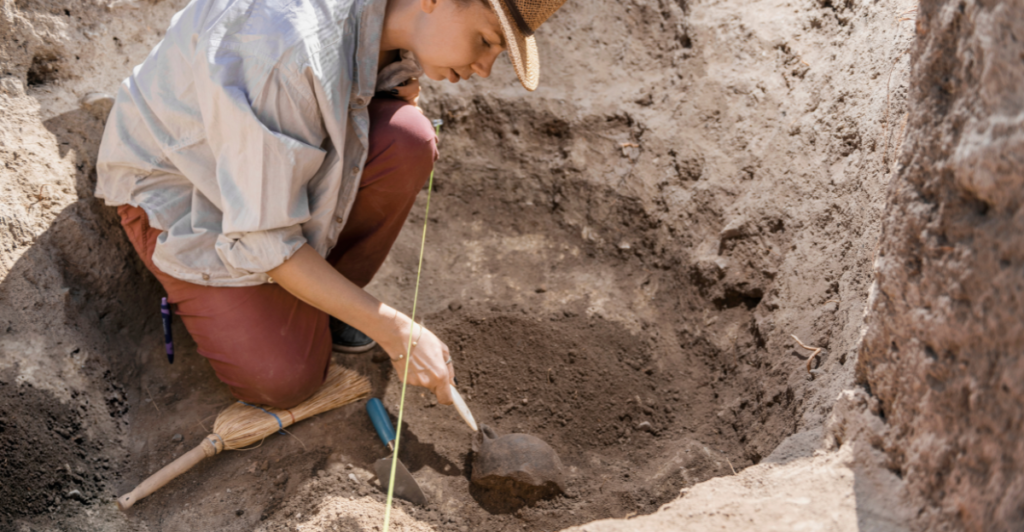

The discovery is the result of a ten-year collaborative effort between international scientists specializing in microbiology, geology, and environmental science. Led by Dr. Elena Morales of the University of Santiago, the team employed advanced imaging technology and drilling techniques to explore beneath the desert’s parched surface. “We were prepared to find traces of ancient life, not a living ecosystem,” said Dr. Morales. “What we’ve uncovered is beyond our wildest expectations.”
The Subterranean Ecosystem

Beneath the surface lies a labyrinth of interconnected chambers filled with microscopic organisms. These extremophiles, as they are known, have adapted to the harsh environment by extracting nutrients from minerals and surviving on minuscule amounts of water vapor. This underground biosphere is sustained by geothermal energy, a phenomenon rarely observed in such arid regions.
Unique Microbial Communities
The organisms found are unlike anything seen before. DNA analysis has revealed hundreds of new microbial species, many of which belong to previously unidentified genetic lineages. “These microbes have evolved unique mechanisms to endure extreme dryness, high salinity, and intense solar radiation,” explained Dr. Anwar Patel, a microbiologist on the team. “Their survival strategies could hold the key to understanding life on other planets.”
Implications for Astrobiology

The findings have profound implications for the search for extraterrestrial life. Scientists believe that the conditions beneath the Atacama Desert closely resemble those on Mars and other celestial bodies. “If life can thrive here, it raises the possibility of similar ecosystems existing on Mars or Europa, where subsurface environments could harbor life,” said Dr. Patel.
Revolutionary Techniques in Exploration

The discovery was made possible through state-of-the-art technology, including ground-penetrating radar and nano-drilling equipment. These tools allowed scientists to map subterranean structures and extract samples without disturbing the fragile ecosystem. “This is a perfect example of how technological advancements are enabling us to explore previously inaccessible parts of our planet,” said Dr. Morales.
A Challenge to Existing Theories

The existence of such a complex ecosystem challenges long-held theories about the limits of life. “We’ve always assumed that liquid water in significant amounts is a prerequisite for life, but these findings suggest otherwise,” said Dr. Patel. This has prompted a reevaluation of biological models and a renewed interest in studying extreme environments on Earth.
Environmental Significance

The discovery also highlights the importance of protecting extreme environments, which often serve as natural laboratories for scientific research. “The Atacama Desert is not just a barren wasteland; it’s a treasure trove of biological and geological marvels,” said Dr. Morales. The team is now advocating for stricter conservation measures to preserve this unique ecosystem.
Potential Applications in Biotechnology

The extremophiles discovered beneath the Atacama may have practical applications in biotechnology. Their ability to survive extreme conditions could lead to innovations in fields such as medicine, agriculture, and environmental remediation. “We’re only beginning to understand the potential of these organisms,” said Dr. Patel. “Their enzymes and metabolic pathways could revolutionize various industries.”
Local and Global Impact

The discovery has captured the imagination of scientists and the public alike. For the local community in Chile, it has brought renewed attention to the Atacama Desert’s scientific and cultural significance. Globally, it has sparked discussions about the importance of investing in exploratory science and preserving natural habitats.
Unanswered Questions

Despite the groundbreaking nature of the discovery, many questions remain. How did these organisms evolve? What role do they play in the larger ecosystem? And could they interact with surface life in any meaningful way? Dr. Morales and her team are already planning follow-up studies to explore these mysteries.
A Catalyst for Future Exploration

The success of this mission is expected to inspire similar investigations in other extreme environments, from the frozen tundra of Antarctica to the boiling springs of Yellowstone. “This is just the beginning,” said Dr. Morales. “Our planet still has so many secrets waiting to be uncovered.”
A New Chapter in Science
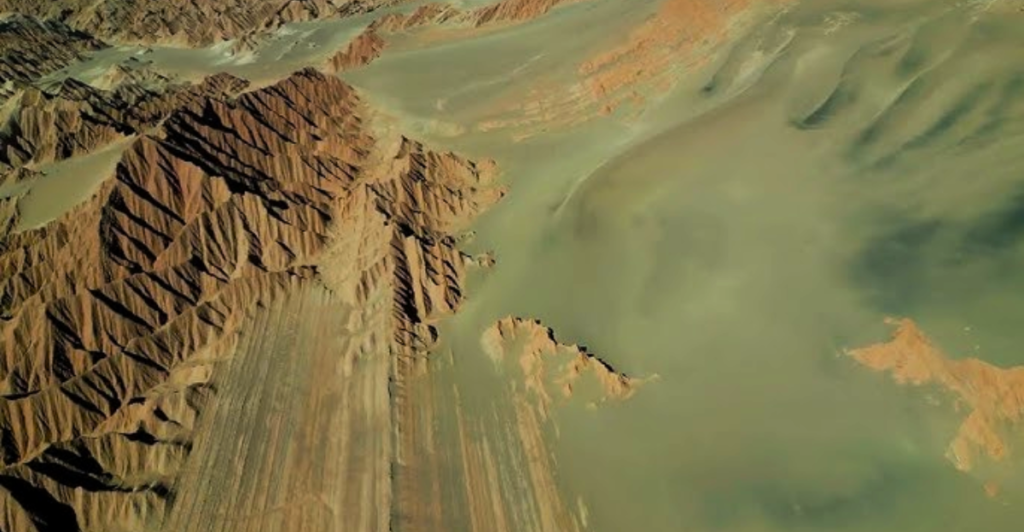

The discovery of a thriving ecosystem beneath the Atacama Desert is a testament to the resilience of life and the power of human curiosity. As scientists continue to study this hidden world, they are not only rewriting the rules of biology but also broadening our understanding of what it means to be alive. This remarkable find serves as a reminder that even in the most unlikely places, life finds a way.
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







