
California is well known for its seismic activity that goes below the surface, and for years, there have been warnings of a megaquake that might happen. With scientists predicting a magnitude 8 or higher quake within the next 30 years, the urgency to prepare has never been greater. This potential disaster stems from the complex interplay of tectonic plates and fault lines, particularly the infamous San Andreas Fault.
“For the average citizen, it’s nothing more than a reminder that this is earthquake country and big earthquakes can occur anywhere in the state,” says Ned Field, a USGS seismologist and lead author of the report.
Understanding the San Andreas Fault
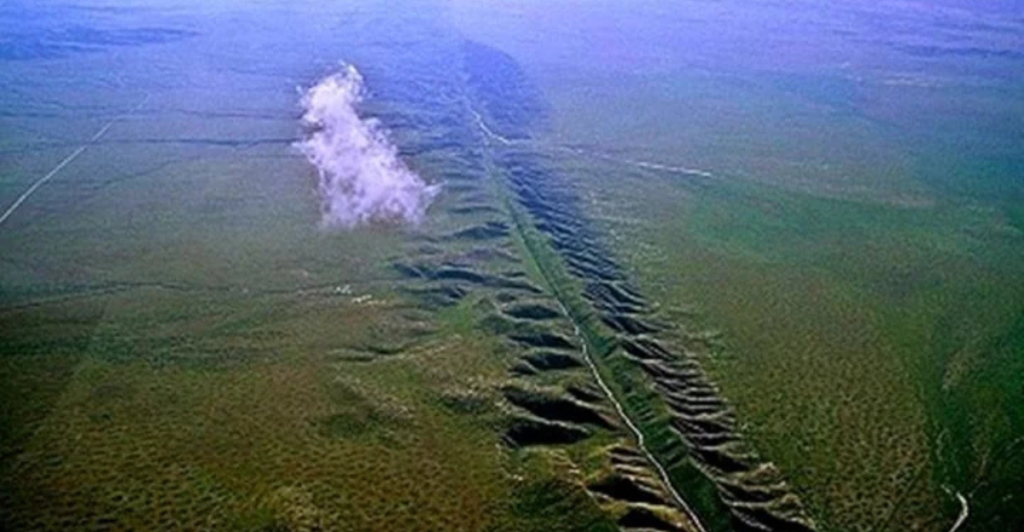

The San Andreas Fault remains the most significant seismic threat to California. Stretching from central California to the Salton Sea near the U.S.-Mexico border, this fault has not ruptured in over three centuries, making it “locked and loaded” for a major quake. Geological studies highlight critical structures within the fault, such as the Durmid ladder structure, which could amplify seismic energy, increasing the odds of a magnitude 7 or greater earthquake.
This fault serves as the dynamic boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate, where the plates slide past each other at an average rate of 20–35 millimeters per year. This fault has been responsible for quakes as powerful as magnitude 8.1.
The Science Behind Megaquakes
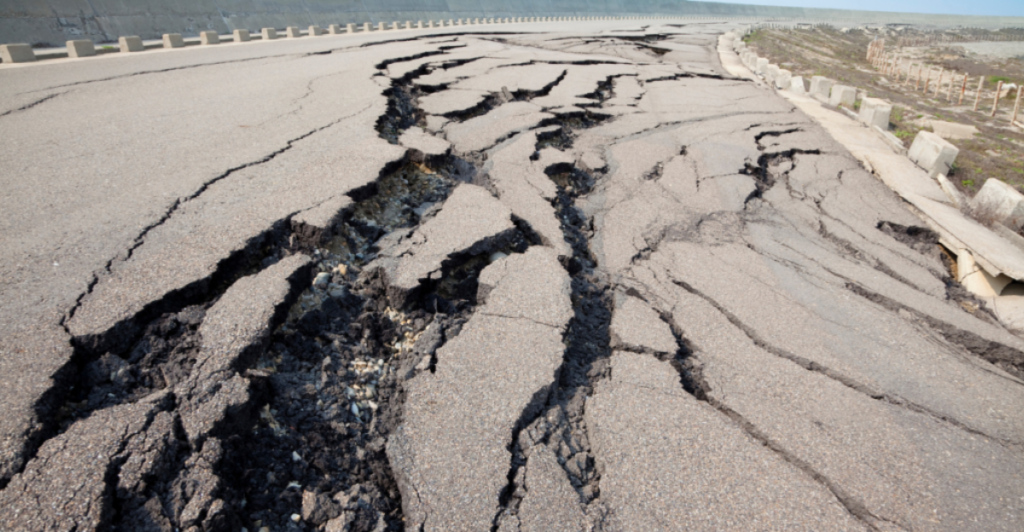

Megaquakes occur when immense tectonic pressure is released along fault lines. In California, this pressure builds as the Pacific and North American plates grind against each other. Scientists have identified over 300 faults crisscrossing the state, many of which could contribute to a cascading rupture event.
Recent studies have highlighted how slow slip events, gradual movements along the plate interface, may precede these quakes, offering potential clues for prediction. Factors like seafloor topography and subducted features, such as seamounts, can also influence the magnitude and spread of seismic ruptures.
What Scientists Are Predicting
These warnings have been coming and going for the past few years, but the timeline has moved to the next 30 years. The U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) has increased the probability of such a catastrophic event from 4.7% to 7%, mainly due to new insights into how interconnected fault systems can rupture simultaneously, releasing massive seismic energy. This quake would produce exponentially more energy than the devastating 1994 Northridge earthquake and could have far-reaching impacts on California’s ecosystems and infrastructure.
While smaller earthquakes frequently occur, experts emphasize that these interconnected fault ruptures could trigger a rare and destructive megaquake, highlighting the urgency of refining these prediction methods to prepare for the situation. “As we’ve added more and more faults based on new science in California, we’ve discovered it’s an interconnected fault system,” Field said.
Impacts on California’s Ecosystems
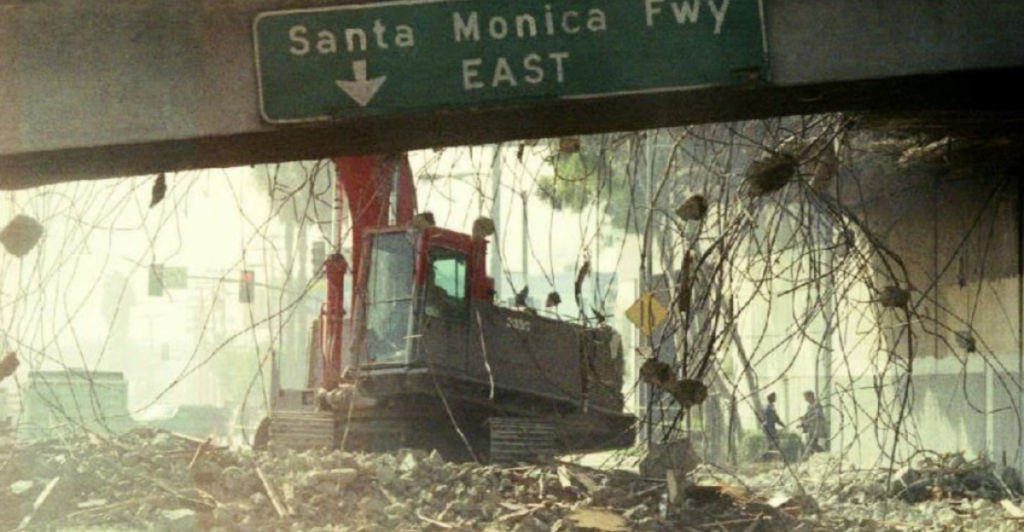

A quake this big could drastically alter landscapes, as seen in past events like the 2010 Chile earthquake, where coastal ecosystems experienced significant shifts due to land-level changes and tsunamis. In California, coastal habitats may face submersion or uplift, disrupting intertidal species and vegetation patterns. Inland ecosystems could also suffer from ruptured water systems, leading to drought-like conditions that threaten plant and animal life.
Conversely, fires ignited by damaged gas pipelines and electrical infrastructure could devastate forests and grasslands, while pollutants from ruptured industrial facilities may contaminate soil and waterways.
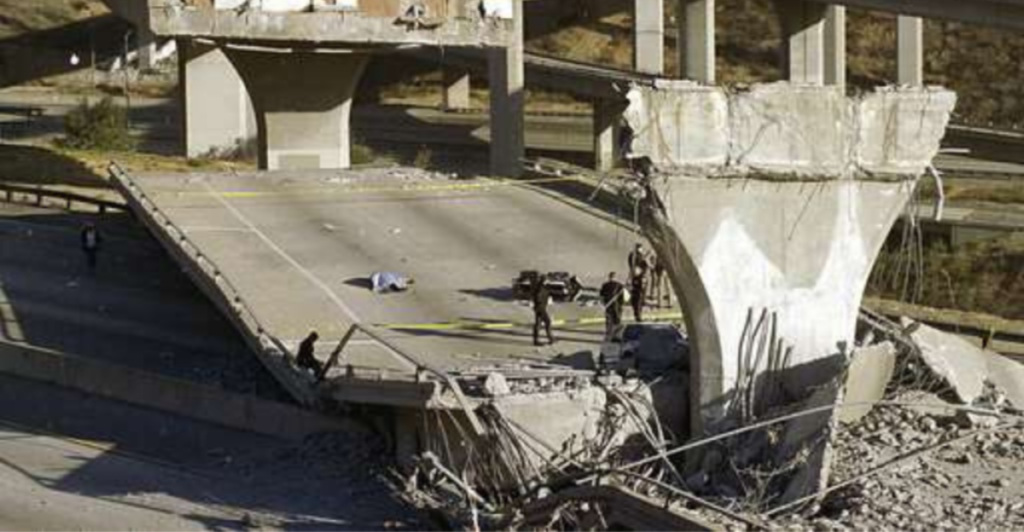
Threats to Infrastructure
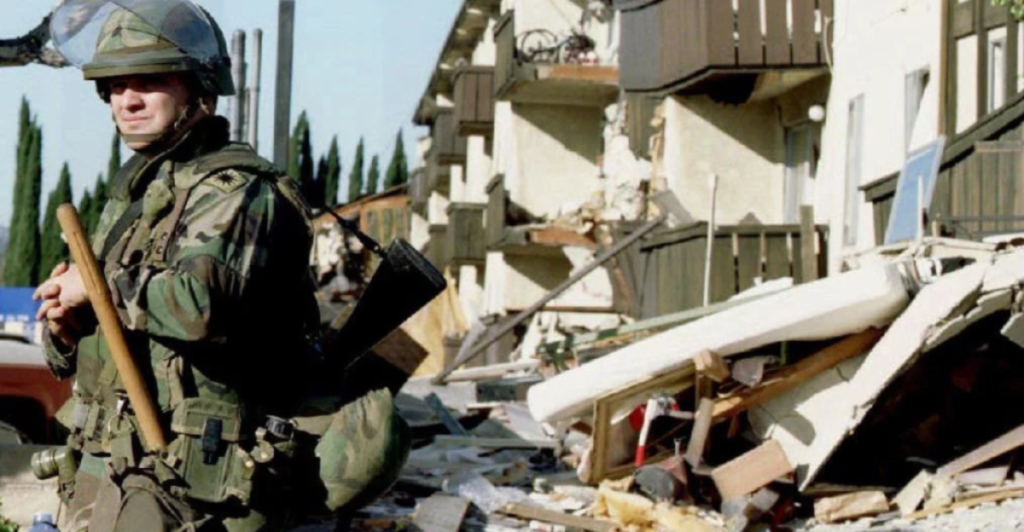

An earthquake this big can lead to major infrastructure damage that can take years to repair. Vital utilities such as electricity, water, and gas could be severely damaged, with ruptured pipelines potentially causing explosions and fires, especially in vulnerable areas like the Cajon Pass. Transportation networks, including highways, bridges, and rail systems like BART, could face extensive damage, leaving commuters stranded and businesses paralyzed.
Communication networks are also at risk, as cell towers and power-dependent equipment could fail during prolonged outages, hampering emergency responses. Many buildings, especially older ones, will sustain irreversible damage that will take years, if ever, to repair. “For a tall building or a large bridge, this might be bad news because they’re more vulnerable to large earthquakes,” Field said. “If you’re concerned about your own home, I would say, for the most part, this is probably good news because you’re probably more vulnerable to having moderate-sized earthquakes than larger ones.”
Preparedness Measures
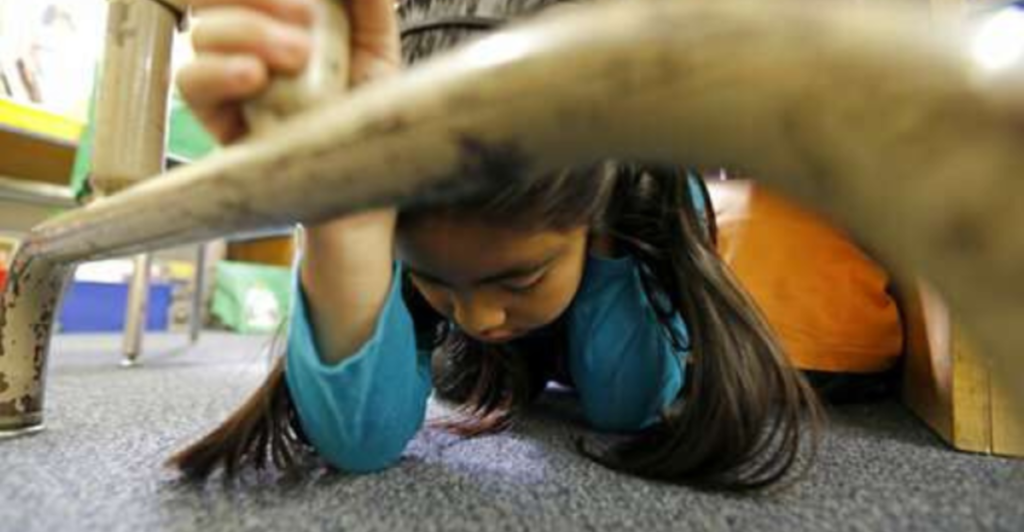

No one can ever be truly prepared for a tragedy this big, but some efforts can be made to make the aftermath easier to manage. Statewide initiatives, such as the California Earthquake Early Warning Program, provide residents with critical seconds of advance notice through ShakeAlerts, which are automatically sent to mobile devices. Cities like Los Angeles have implemented resilience programs mandating retrofitting of vulnerable buildings and securing essential infrastructure.
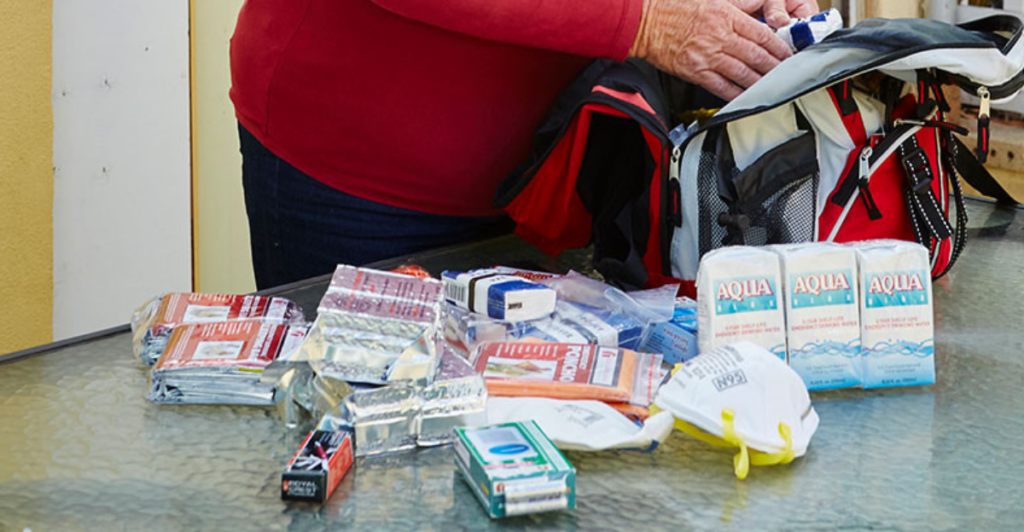
At the individual level, preparedness includes assembling emergency kits with supplies for at least three weeks, creating family communication plans, and securing heavy furniture to prevent injuries. “Building codes, earthquake insurance products, emergency plans, and other risk-mitigation efforts will be updated accordingly,” he added.
The Role of Scientific Research

Research is one of the most important aspects of monitoring seismic activity and any potential threats associated with it. Advances in earthquake science, such as the use of supercomputers to simulate 800,000 years of seismic history, allow researchers to pinpoint risks and predict ground shaking patterns with unprecedented accuracy. These simulations help refine building codes and structural designs to enhance resilience against large-scale earthquakes.
Collaborative efforts between institutions like UCLA and organizations such as FEMA also ensure that scientific findings translate into actionable measures, including hazard mapping and emergency response planning.
Creating Public Awareness
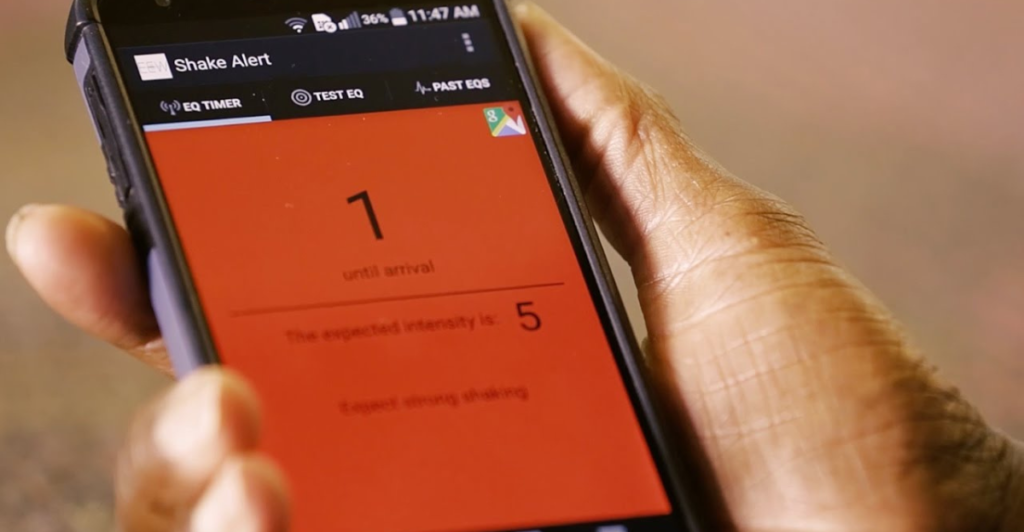
Keeping the public informed is the best way to ensure they stay on top of potential threats. Sure, you might hear the same things for a few years, but when push comes to shove, knowing is better than being caught off-guard. Campaigns like “Don’t Get Caught Off Guard” by the California Governor’s Office of Emergency Services (Cal OES) leverage digital, social media, and broadcast advertising to educate the public about life-saving tools such as the MyShake App and Wireless Emergency Alerts (WEA).
Multilingual outreach efforts target diverse communities, while partnerships with schools, businesses, and civic organizations amplify the message across the state.
Staying Vigilant

Everyone is responsible for staying informed and knowing what to do when the situation calls for it. Regular participation in drills like the Great ShakeOut reinforces these practices and keeps communities prepared. By staying informed about seismic hazards and actively engaging in preparedness efforts, Californians can reduce the impact of a major earthquake and enhance community resilience.
Explore more of our trending stories and hit Follow to keep them coming to your feed!

Don’t miss out on more stories like this! Hit the Follow button at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest news. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!







