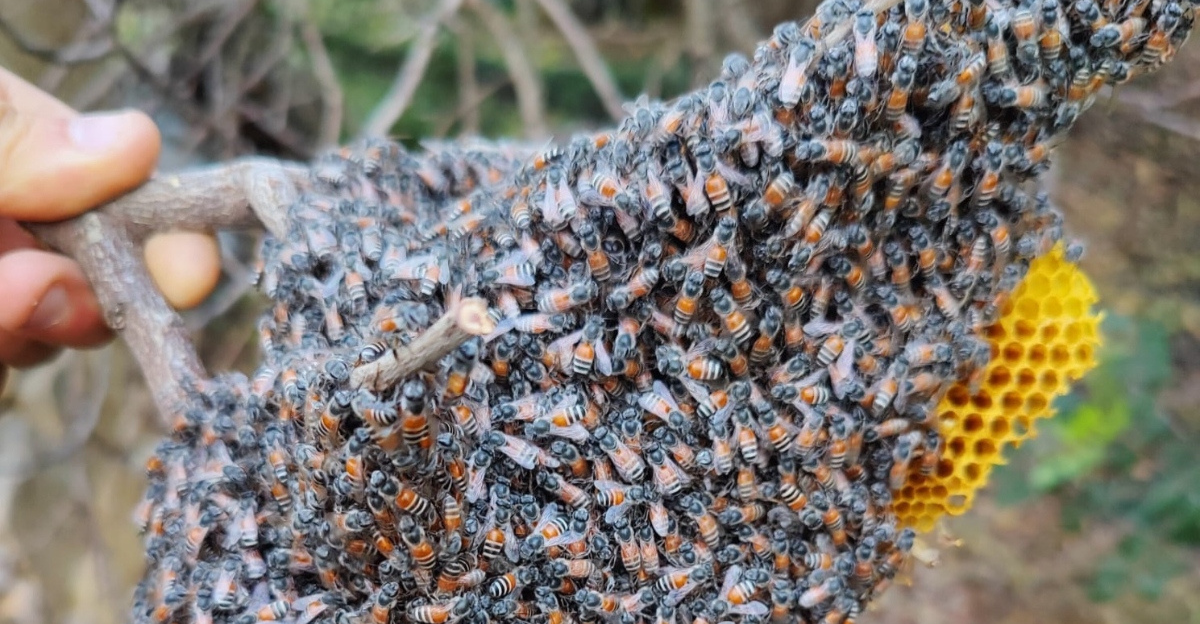

It should be no surprise that when researchers find a bee native to Asia in Europe, some questions will be raised. This red dwarf honeybee, also known as Apis florea, was found in Malta for the first time. This raises significant concerns about the potential impact on native bee populations and ecosystems.
Background of Apis Florea
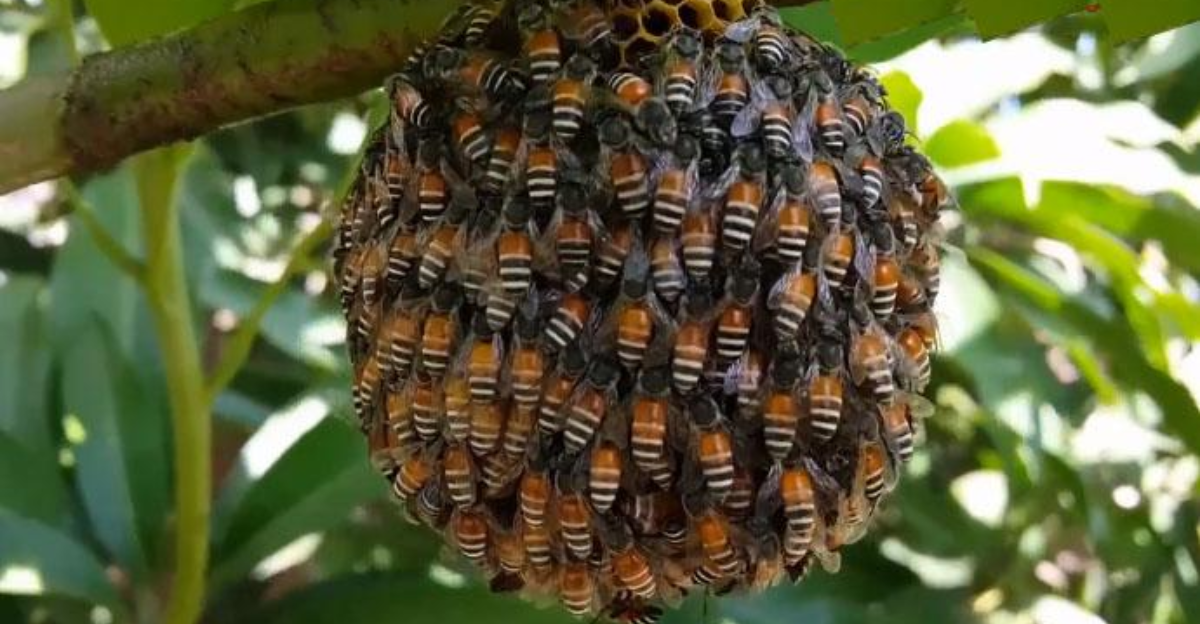

These bees are extremely adaptable and can survive in most climates. They travel in swarms and migrate after nectar flows. Their reproductive rate is incredibly high, which makes them a concerning invasive species. Unlike the Western Honey Bee, they make a lot less honey, producing only between 300 and 450 grams of honey per colony.
Habitat Expansion and Climate Change

One of the main reasons this species has changed its location is climate change. Although they are highly adaptable to climate changes, certain areas are just more favorable than others, especially concerning nectar flow.
Discovery in Malta
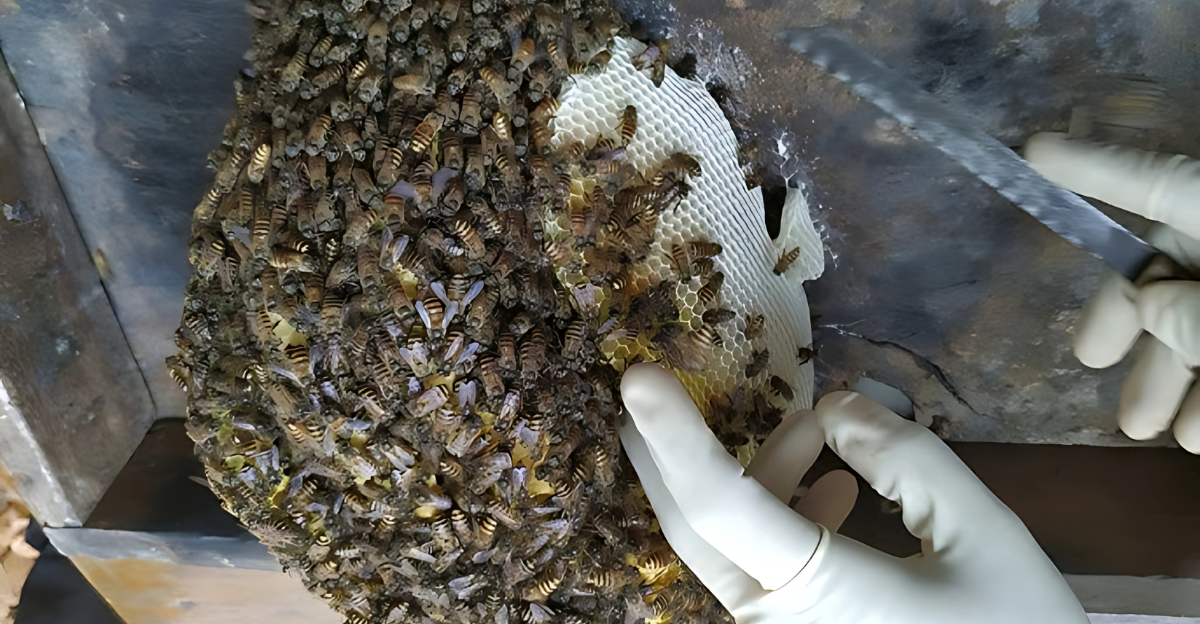

A colony of over 2,000 Apis florea bees was discovered in Malta, specifically on a tree branch. DNA testing confirmed the species, and the colony was promptly removed to prevent further spread. However, there are concerns that some bees may have escaped to establish new colonies elsewhere.
Potential Impact on Native Bees
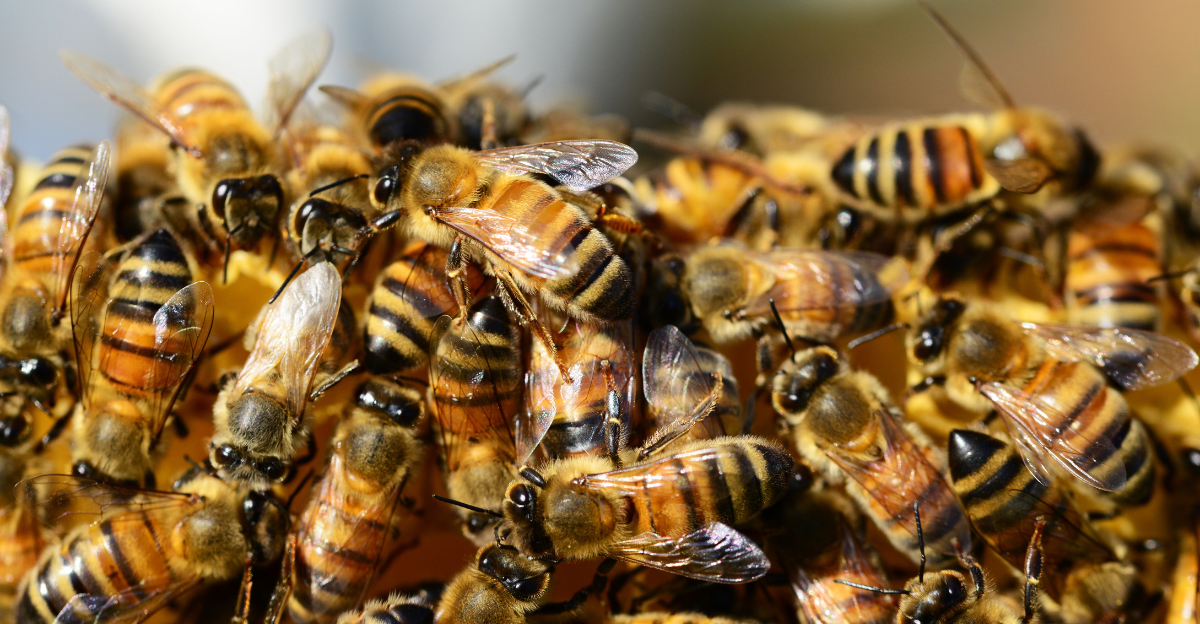

Having an invasive species in the area puts native bees at serious risk regarding population decline, as these bees are already under pressure from habitat loss and pesticide use. They could also carry diseases the native species have little resistance to, causing an even greater risk.
Disease Transmission Risks

Having these invasive bees in the area raises alarming concerns about the diseases they can transmit to the native species. These include viruses, mites, and parasitic fungi, which could further weaken European bees already struggling with diseases like Varroa destructor.
Ecological Consequences
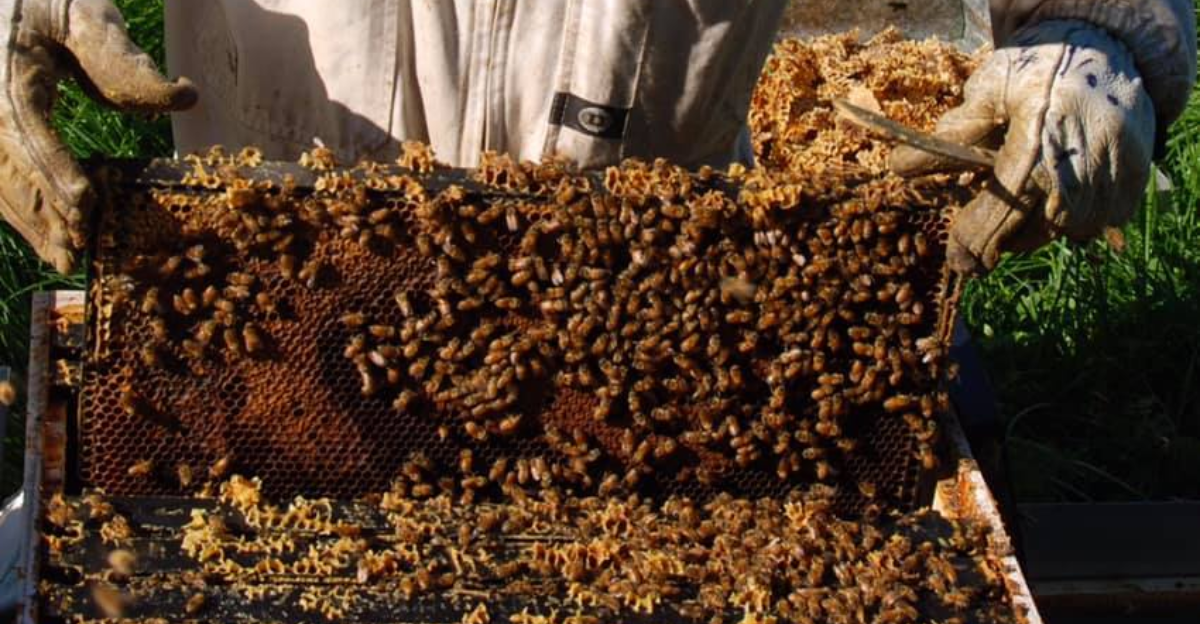

Native bees do much more than fly around and produce honey; they help pollinate the ecosystem and keep habitats thriving. When these invasive species enter the ecosystem, they can affect its delicate balance and damage crops and ecosystem resilience.
Management and Eradication Efforts
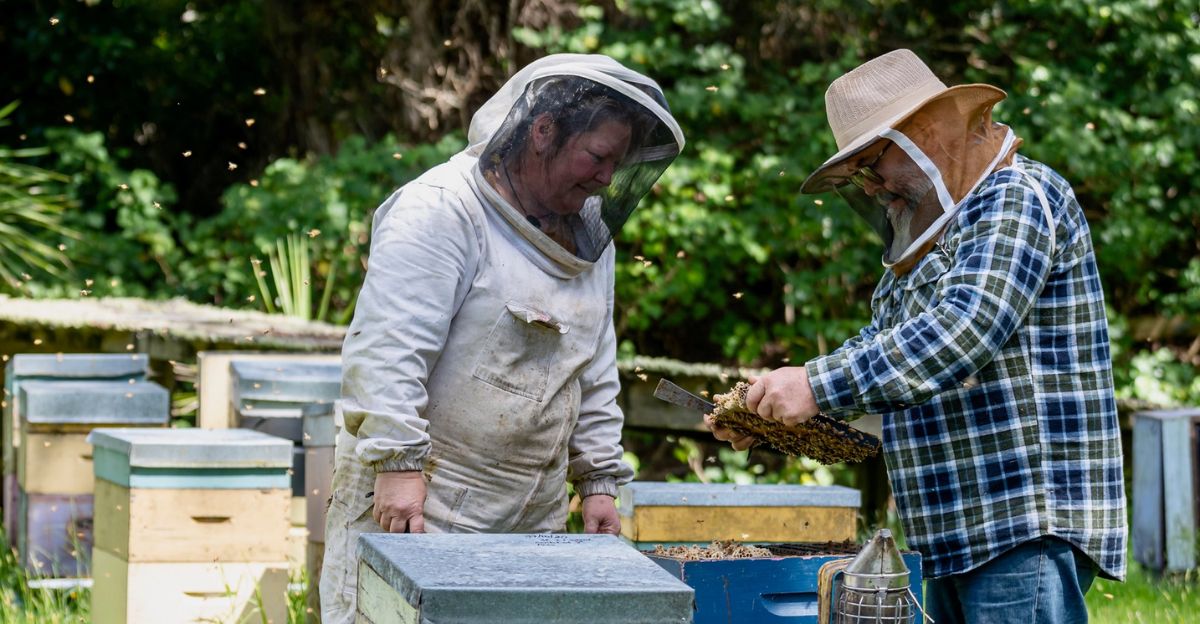

Eradication needs to be immediate to keep the risk at bay. Authorities are urged to monitor for further sightings and take action promptly to prevent the establishment of new colonies.
Conservation Strategies
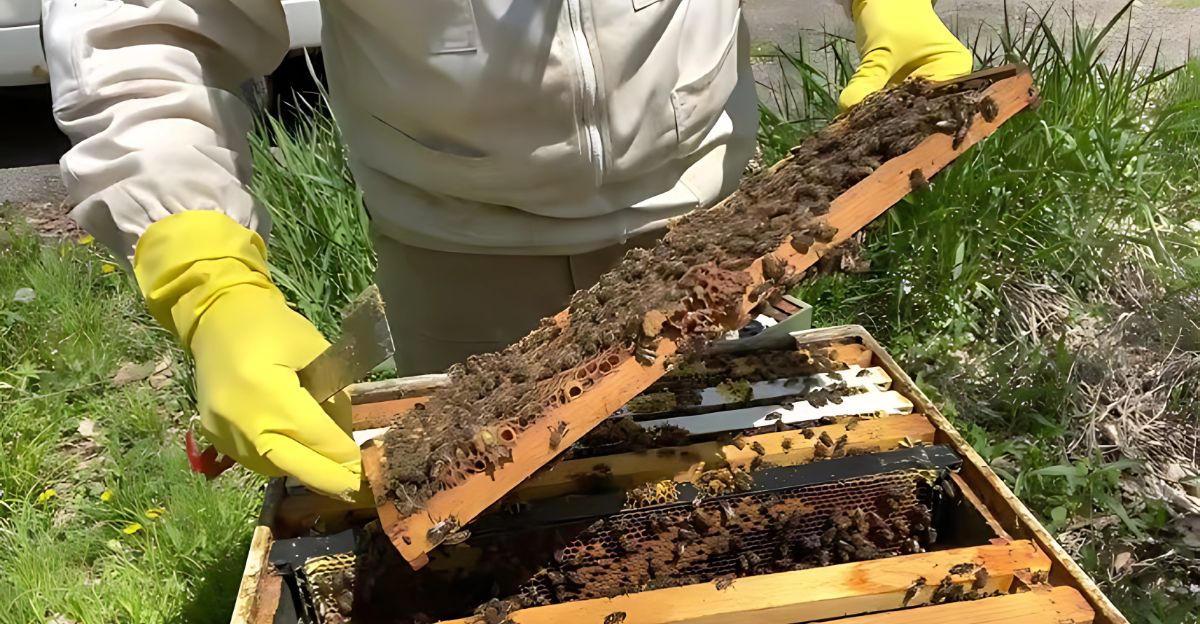

Native bees play a bigger role in maintaining the ecosystem than most people realize. Because of this, it’s extremely important to focus on conservation efforts to help keep these bees safe. Some of those strategies include preserving habitats and reducing pesticide use.
Human Activities and Species Movement

It’s suspected that this invasive species found its way to Malta on a cargo ship. They were found in the region of a major cargo hub; if that’s the case, we will most likely see these bees popping up in different areas of the world.
Future Risks and Projections
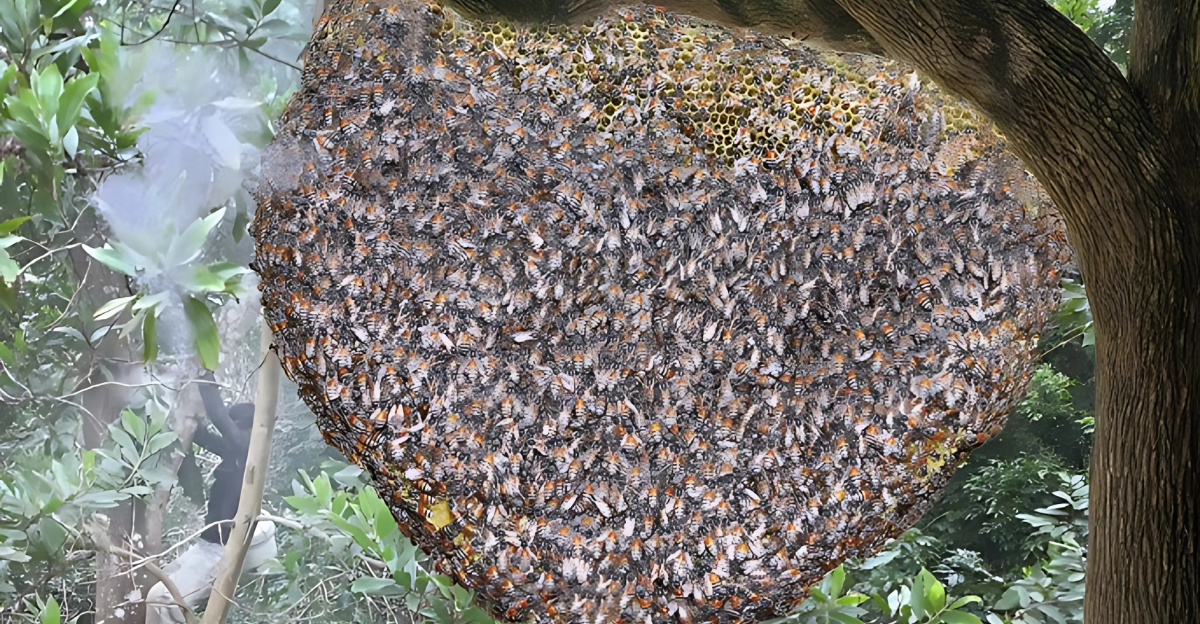

Scientists warn that Apis florea in Malta may not be an isolated incident. The Mediterranean climate is conducive to the survival of these bees, and rising temperatures will only increase their chances of establishing themselves in Europe.
Public Awareness and Action

It’s important to make the public aware of these bees’ risk to the environment. Helping them identify and report potential sightings of invasive species can help wildlife officials eradicate them.
The Urgent Need for Vigilance
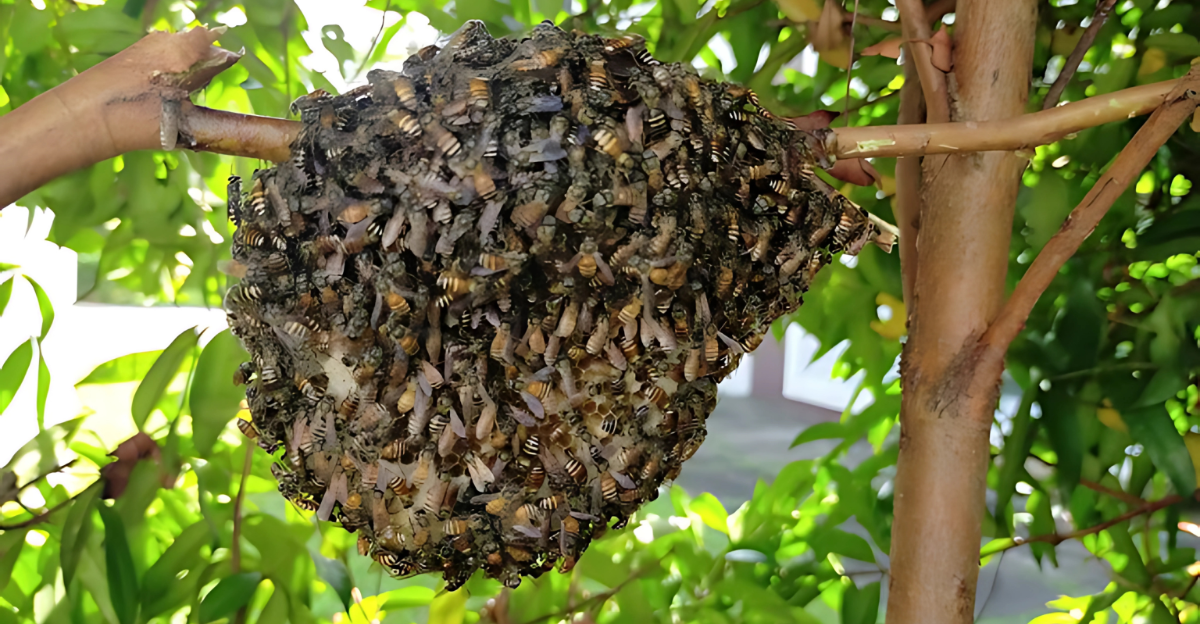

The arrival of Apis florea in Europe is a stark reminder of the urgent need for vigilance in the face of invasive species. As the climate continues to change, it is essential to monitor and manage the spread of non-native species to protect biodiversity and ecological balance.
Explore more of our trending stories and hit Follow to keep them coming to your feed!
Don’t miss out on more stories like this! Hit the Follow button at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest news. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!







