
For millions of years, Earth’s tectonic plates have orchestrated the planet’s geological drama, shaping continents and influencing ocean currents. The extraordinary rediscovery of the Pontus plate — a massive tectonic structure believed lost to subduction around 20 million years ago, marks a seismic shift in our understanding. The discovery, detailed in Gondwana Research, has implications not just for geological history; it’s also a potential game-changer for how we interpret the evolution of ecosystems across the Western Pacific. The implications are vast, from re-assessing previous climate models to recovering the migratory habits of ancient species.
The Tethyan-Panthalassa Divide and Junction Region
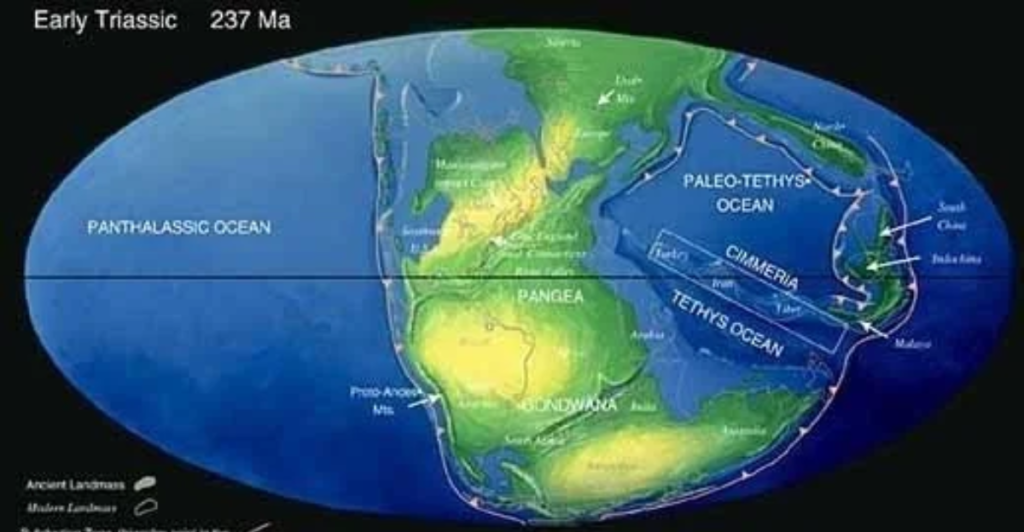
Understanding Earth’s ancient plate tectonic realms is important for grasping its significance. The Tethyan realm, nestled within Pangea, featured east-west subduction zones.
At the same time, the Panthalassa realm was undergoing radial subduction. The “Junction Region” where these met, extending from Australia to Eurasia, was a hotbed of tectonic complexity. Pontus existed in this region and made connections that contributed to the geological landscape.
The disappearance of plates such as Pontus complicates the reconstruction picture, yet its impact is clear. By examining these remnants embedded in mountain ranges, scientists can reconstruct the planet’s geologic history and the forces driving plate movements.
A Colossus Rediscovered: The Pontus Plate
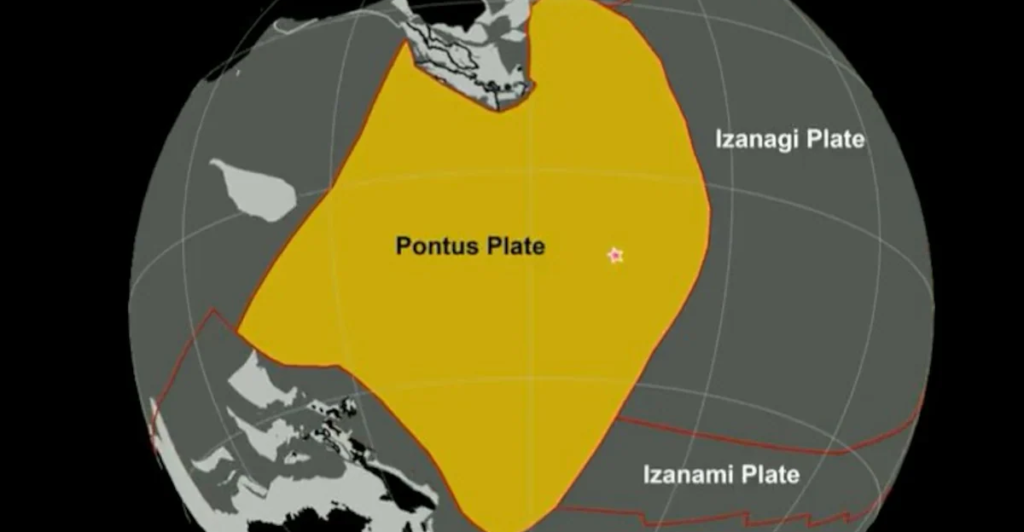
The Pontus plate, an ancient seismic force spanning 15 million square miles—a quarter of the Pacific Ocean—was long thought to be a geological ghost, completely wiped out by subduction.
However, a new study led by Dr. Suzanna Van de Lagemaat of Utrecht University confirms its existence and lasting influence. Fossils in oceanic rock formations known as the ”relics of Pontus” tell their complex story, using advanced computer modeling, reveals its complex history.
Seismic signals and solid geological evidence confirm that the plate existed until around 20 million years ago, making its rediscovery a crucial piece in the tectonic puzzle.
Piecing Together the Puzzle
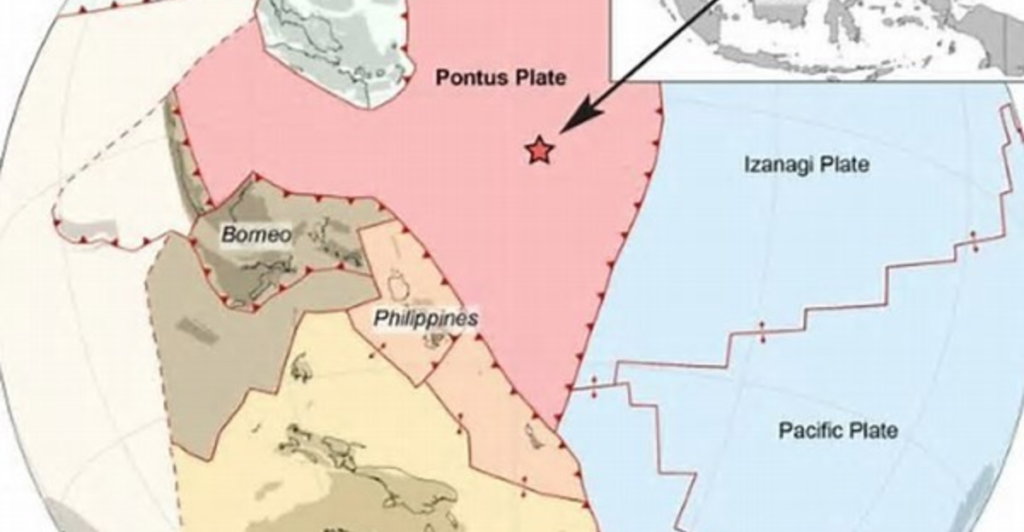
Unlocking the secrets of the Pontus plate required careful geological forensics. Van de Lagemaat and her team studied mountain belts in Japan, Borneo, the Philippines, New Guinea, and New Zealand.
These regions, which were part of a geologically complex zone, contained remnants of long-lost oceanic crust, like pieces of a jigsaw puzzle. A breakthrough in northern Borneo initially appeared to be an established plate fragment, but magnetic signatures indicated an origin much farther north. This indicated that these rocks were fragments of a different yet undiscovered plate.
Redefining Subduction Zones and Mantle Dynamics
Pontus’ discovery provides important insights into subduction zones, the places where one tectonic plate slides under another. These zones aren’t just geological graveyards; they drive mantle convection, the engine of Earth’s internal heating and material transport.
The history of Pontus refines our models of plate interaction and evolution in the Western Pacific. Seismic imaging also corroborates this, exposing ancient plate remnants buried under the Earth’s mantle 300 million years ago. This confirms a theory of a massive subduction zone along the western edge of the Pacific.
Impact on Ocean Currents and Climate

The presence and subsequent subduction of a plate as large as Pontus would have dramatically modified oceanic currents in the area. Such changes, in turn, would have had dramatic effects on the planet’s climate, particularly altering the temperature distribution of temperature and precipitation across the continents.
Reconstructing these ancient ocean currents, considering Pontus’s influence, is fundamental for refining paleoclimate models. These models are critical for understanding natural climate variability and predicting future climate scenarios.
Ecosystem Evolutions & BioGeography

Pontus’s tectonic movements directly affected the life of the Western Pacific. Continents drifted and formed new corridors and barriers for species dispersal.
This would have inspired unique evolutionary trends, resulting in the diversification of plant life and wildlife in the geographically separated areas. Pontus’s existence suggests re-examining the fossil record, potentially revealing how geological events shaped species’ migratory routes and evolutionary adaptations.
The Rise and Fall of Island Arcs

Pontus interacted with other plates, creating and destroying many island arcs. Such arcs act as bridges for species crossing wide oceanic expanses.
The geological instability that would have accompanied these arcs, propelled by Pontus’s movements, would have generated dynamic environments where both speciation and extinction would occur. Understanding the life cycles of such island arcs is essential for interpreting the region’s biodiversity patterns.
Revisiting Fossil Records and Evolutionary Timelines

The accepted timelines for species evolution in the Western Pacific must be re-evaluated in light of Pontus’s impact. The plate’s presence might explain some of the anomalies in the fossil record, including the abrupt emergence or extinction of certain species.
Molecular clock studies, which estimate rates of evolution, should be recalibrated to match geological events triggered by Pontus. The multidisciplinary nature of geology and biology represents a critical component for achieving a more complete view of evolutionary history in the area.
A New Lens on Earth’s Dynamic Past

The rediscovery of the Pontus plate is more than just a geological revelation; it is a catalyst for the rewriting of the ecological history of the Western Pacific.
By integrating this new knowledge into paleoclimate models, biogeographic studies, and evolutionary timelines gives us a more nuanced understanding of Earth’s dynamic past.
This highlights the interconnectedness of geological forces and biological evolution. Ongoing research that combines geological and biological viewpoints could yield even more profound insights into our planet’s intricate past.
Explore more of our trending stories and hit Follow to keep them coming to your feed!

Don’t miss out on more stories like this! Hit the Follow button at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest news. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!







