
Recent studies reveal that plants absorb approximately 31% more carbon dioxide (CO₂) than previously estimated. This significant finding enhances our understanding of the global carbon cycle and highlights the crucial role of vegetation in mitigating climate change. The increased CO₂ uptake by plants underscores the importance of preserving and restoring natural ecosystems to combat rising atmospheric carbon levels.
Understanding Terrestrial Gross Primary Production (GPP)

Terrestrial Gross Primary Production (GPP) refers to the total CO₂ that land plants capture through photosynthesis. This process is fundamental to life on Earth, as it forms the basis of the food chain and regulates atmospheric CO₂ levels. Accurate assessments of GPP are essential for predicting climate change impacts and formulating effective environmental policies.
The Role of Carbonyl Sulfide in Measuring Photosynthesis

Scientists have utilized carbonyl sulfide (OCS), a trace gas absorbed by plants alongside CO₂, to estimate photosynthetic activity. OCS is a reliable proxy because, unlike CO₂, plants do not emit it back into the atmosphere. This allows for more precise measurements of CO₂ uptake and enhances the accuracy of global GPP estimates.
Implications for Climate Modeling

The revised understanding of plant CO₂ absorption necessitates updates to climate models, which previously underestimated terrestrial ecosystems’ capacity to sequester carbon. Incorporating these findings will improve predictions of future atmospheric CO₂ concentrations and inform strategies for mitigating climate change through natural carbon sinks.
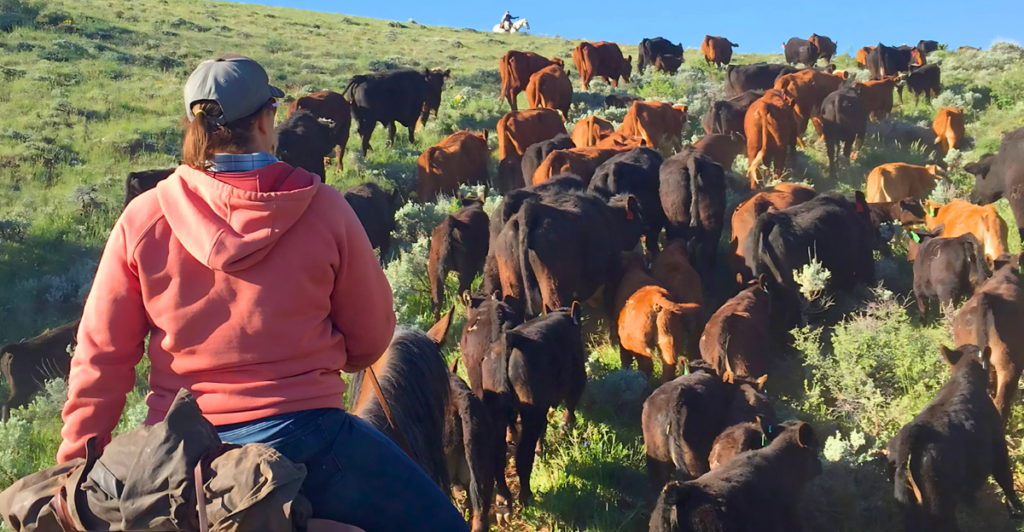
Introduction to Regenerative Ranching
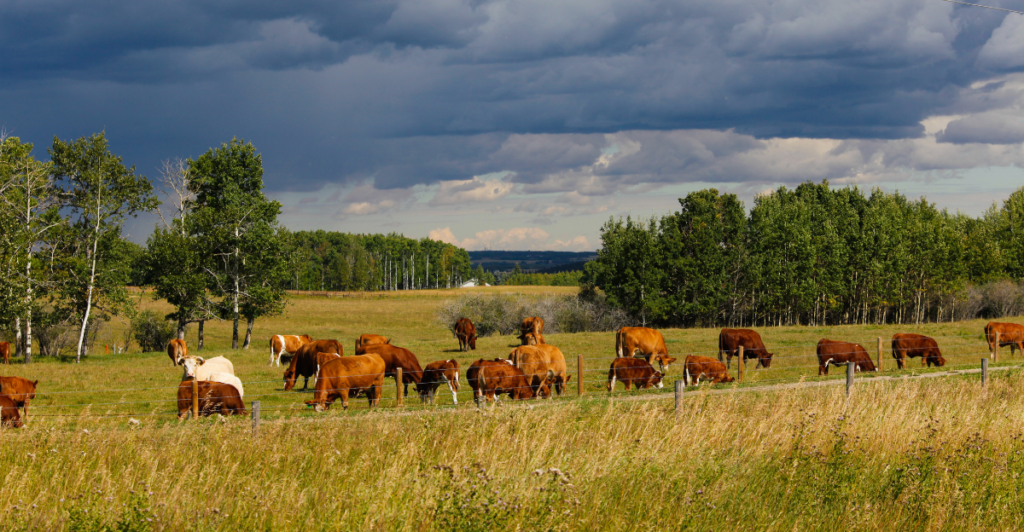

Regenerative ranching is an agricultural approach that focuses on restoring soil health, enhancing biodiversity, and increasing carbon sequestration. By implementing practices such as rotational grazing and integrating diverse plant species, regenerative ranching aims to create sustainable and resilient farming systems that benefit both the environment and agricultural productivity.
Principles of Regenerative Ranching

Key principles of regenerative ranching include minimizing soil disturbance, maintaining continuous plant cover, promoting plant diversity, and integrating livestock into farming systems. These practices work synergistically to improve soil structure, increase water retention, and enhance the land’s capacity to sequester carbon, contributing to climate change mitigation.
Benefits of Rotational Grazing

Rotational grazing involves dividing pastureland into multiple sections and allowing livestock to graze one area at a time while others recover. This method prevents overgrazing, promotes uniform manure distribution, and encourages diverse plant growth. As a result, soil fertility is enhanced, and the ecosystem’s ability to capture and store CO₂ is increased.
Silvopastoral Systems: Integrating Trees and Livestock

Silvopastoral systems combine trees, forage plants, and livestock on the same land. This integration supports biodiversity, provides shade and animal shelter, and enhances carbon sequestration through increased biomass. Implementing silvopastoral practices can lead to more sustainable and productive ranching operations.
Case Study: Sustainable Ranching in Bolivia
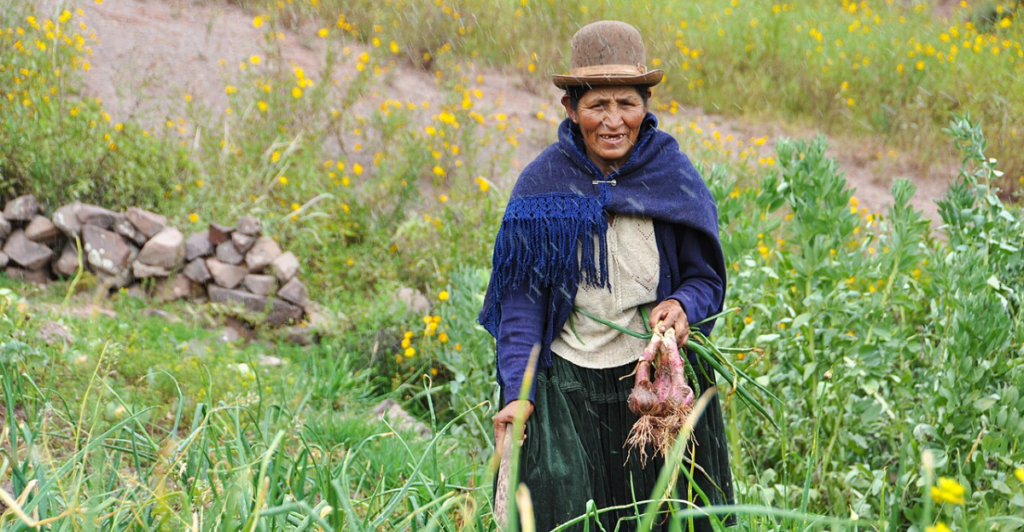

In Bolivia, some ranchers are adopting sustainable practices to combat deforestation and land degradation. These ranchers aim to prolong land usability and increase productivity by rotating cattle and diversifying pastures. Such methods contribute to environmental conservation while supporting the livelihoods of local communities.
Challenges in Implementing Regenerative Practices

Despite the benefits, adopting regenerative ranching practices can be challenging due to high initial costs, lack of technical knowledge, and limited access to markets for sustainably produced goods. Overcoming these obstacles requires education, financial support, and policy incentives to encourage widespread adoption among ranchers.
The Future of Regenerative Ranching

As awareness of environmental issues grows, regenerative ranching is gaining attention from farmers, consumers, and policymakers. Innovations in sustainable agriculture and emerging markets for carbon credits and sustainably produced products create new opportunities for ranchers to adopt regenerative practices and contribute to climate change mitigation.
The Synergy Between Enhanced Plant CO₂ Absorption and Regenerative Ranching
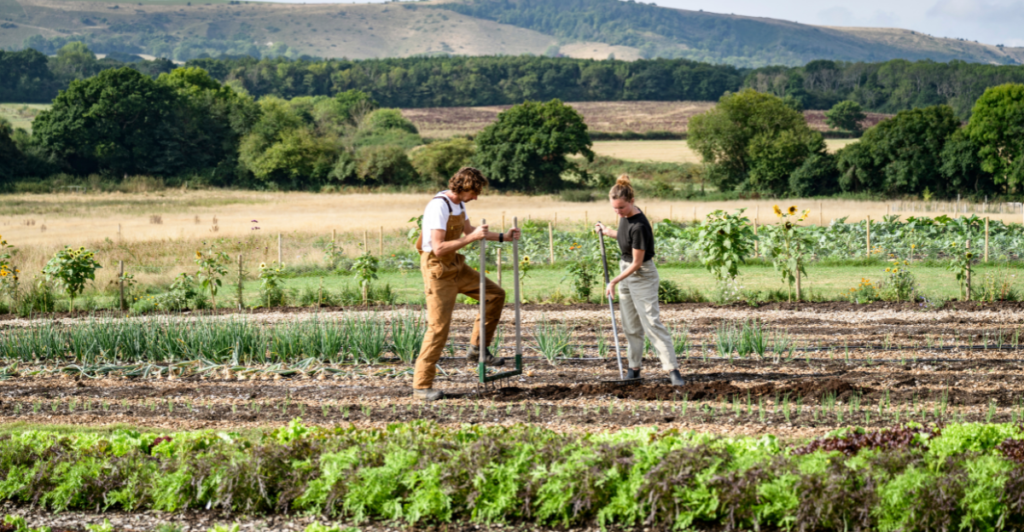

The discovery of increased plant CO₂ absorption aligns with the goals of regenerative ranching, as both highlight the potential of natural systems to mitigate climate change. By restoring soil health and promoting plant diversity, regenerative practices enhance ecosystems’ capacity to sequester carbon, complementing the natural CO₂ uptake by plants.
Embracing Nature-Based Solutions

Understanding the enhanced role of plants in absorbing CO₂ and implementing regenerative ranching practices offer promising pathways to address climate change. By working with natural systems, we can develop sustainable agricultural practices that benefit the environment, support food security, and build resilience against climate impacts.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them appearing in your feed
California Is Breaking Apart: A Fault Line Is Forming Faster Than Anyone Predicted
Philanthropist Promises To Cover $771.23M Annually After US Exit From Climate Accords
The War on Cows Is Over—And Green Extremists Have Lost
After 800 Years of Silence, This American Volcano Shows Signs of Activity
References:
Reference 1
Reference 2
Reference 3
This article first appeared here
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







