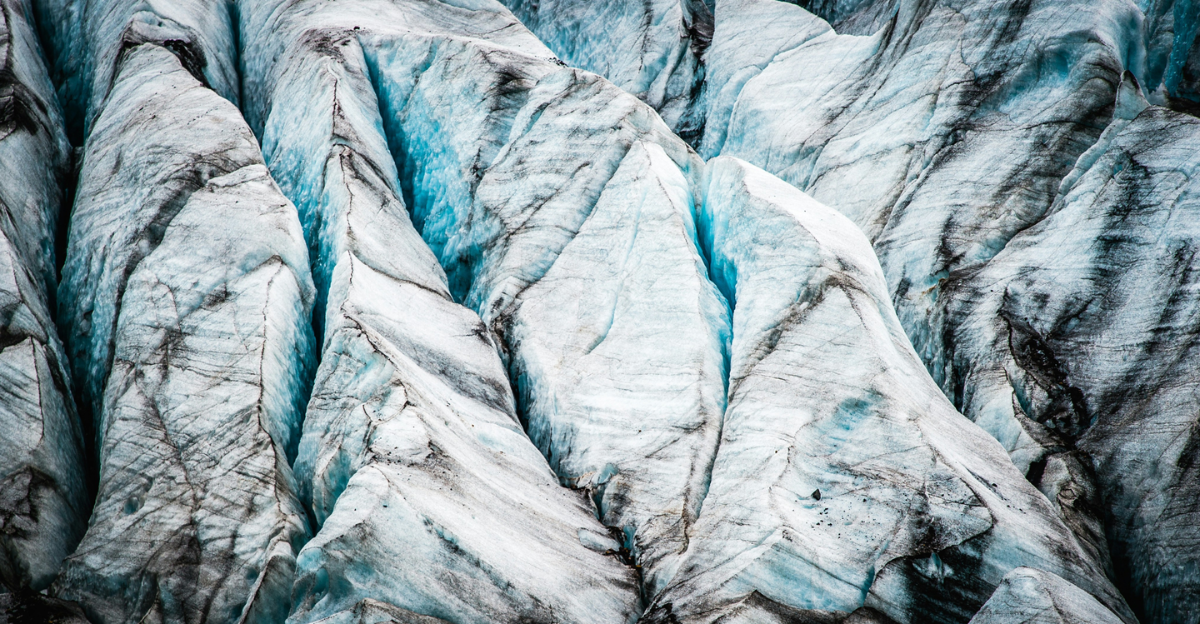

A new study is challenging everything we thought we knew about how life evolved on Earth. Scientists have found a surprising connection between ancient glaciers, uranium, and the conditions that allowed complex organisms to thrive. This discovery suggests that glaciers—once thought to be barren wastelands—may have been essential for life’s biggest evolutionary leap.
The Groundbreaking Study

A recent study from the University of Portsmouth, Curtin University, and St. Francis Xavier University has uncovered a shocking connection between glaciers, uranium, and the evolution of complex life. By analyzing ancient minerals, researchers found that massive ice sheets during the Neoproterozoic era scraped deep into Earth’s crust, releasing uranium into the oceans.
How the Study Was Conducted
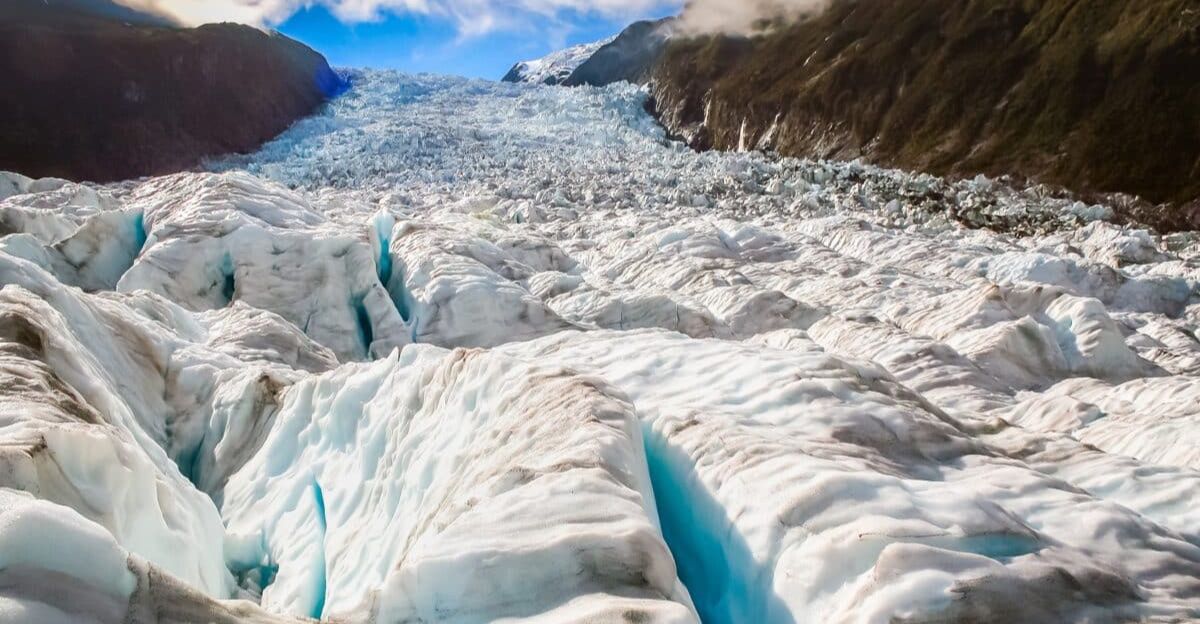

Scientists analyzed zircon mineral grains from ancient rock formations. These tiny crystals recorded evidence of intense glacial erosion and mineral release during Earth’s “Snowball Earth” period. Chemical testing confirmed that uranium levels in ocean sediments spiked after glacial melts.
What Scientists Concluded

The study’s key finding? When glaciers scraped deep into Earth’s crust, they released a surge of minerals—including uranium—into the oceans. This uranium influx played a critical role in ocean chemistry, boosting oxygen levels and creating an environment where complex life could thrive. This discovery suggests that glaciers weren’t just reshaping landscapes—they were creating the conditions that allowed life to flourish.
Zircon: Time Capsules of Earth’s Past
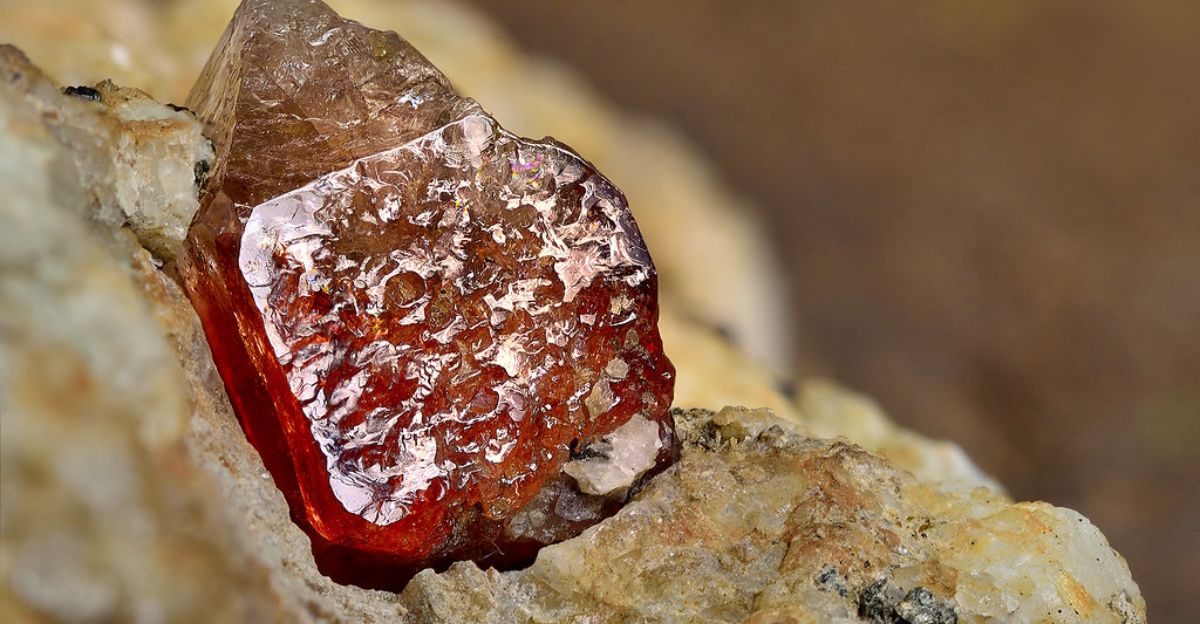

How do scientists study events from hundreds of millions of years ago? The answer lies in zircon crystals—tiny but incredibly durable mineral grains. Researchers analyzed zircons from the Dalradian Supergroup, a geological formation across Scotland and Ireland. These crystals, formed deep within Earth’s crust, contain uranium that decays at a predictable rate, allowing scientists to determine their exact age. By studying zircons from glacial and non-glacial periods, researchers traced how ice sheets eroded ancient rocks, providing crucial evidence of glaciers’ impact on ocean chemistry.
Uranium: The Unlikely Catalyst for Life

Uranium might not seem like an obvious ingredient for life, but its chemical properties made it a game-changer. When released into the ocean, uranium contributed to oxygen production and nutrient cycling. It also created energy-rich chemical gradients that primitive life forms could exploit. The timing is striking—just as uranium levels spiked, complex multicellular life began to appear.
How Did It Happen: The Snowball Earth Connection
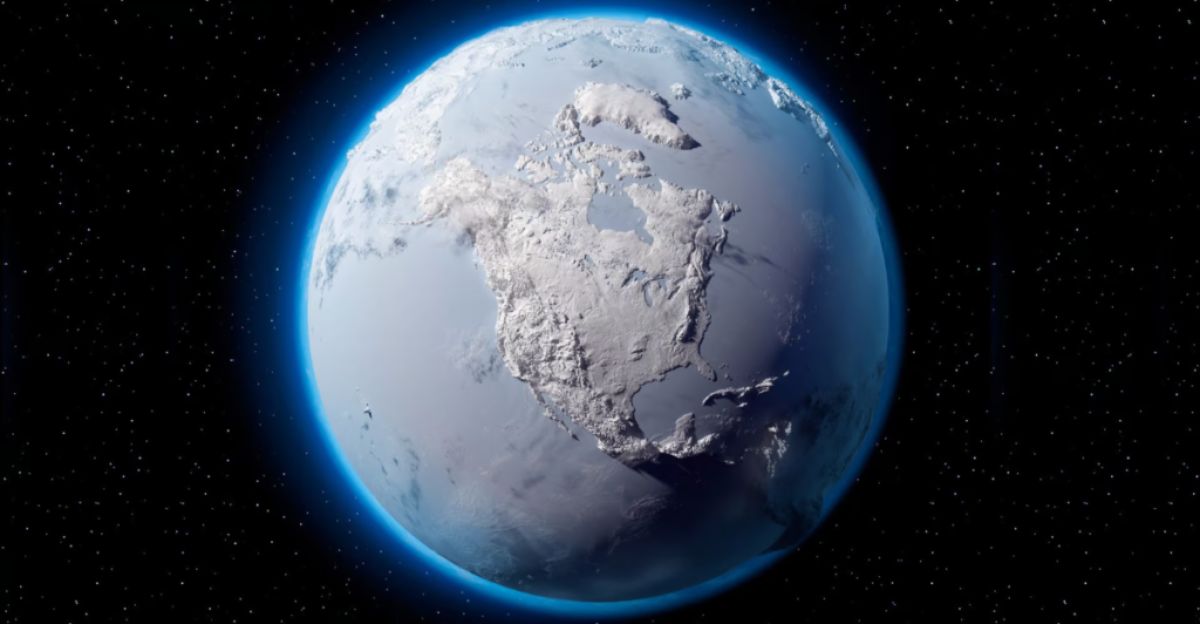

Around 717–580 million years ago, Earth experienced extreme ice ages known as “Snowball Earth” events. During this time, glaciers covered vast areas of the planet, grinding away at ancient supercontinents. These weren’t ordinary ice ages—scientists believe the entire planet may have frozen over.
The Great Melt and the Flood of Life
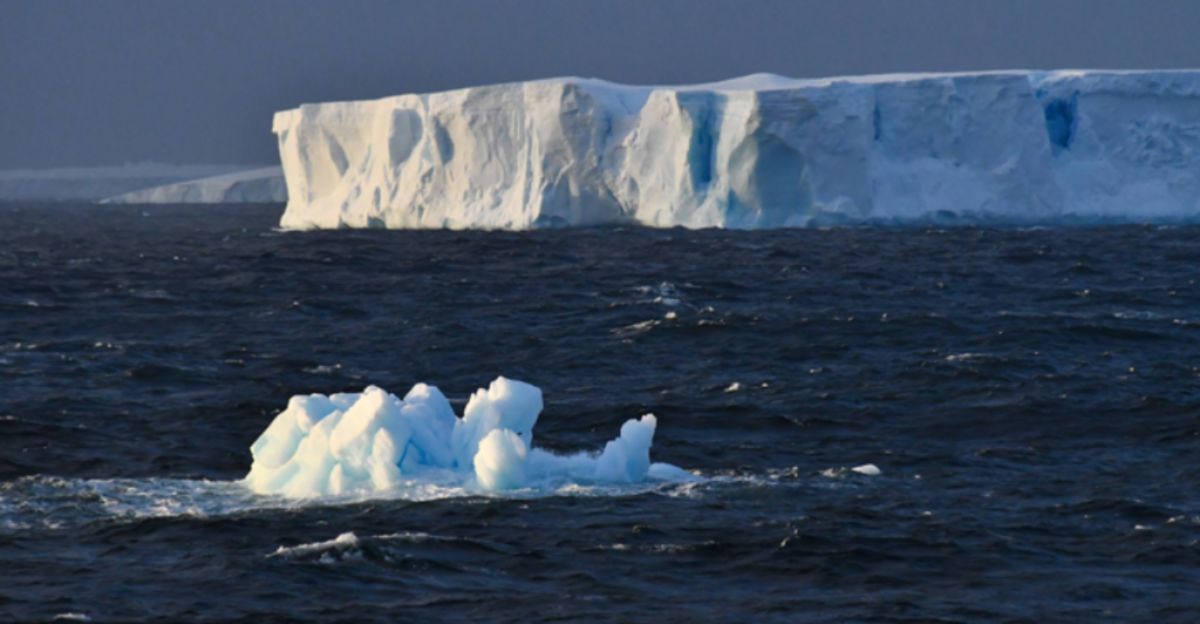

When Snowball Earth began to thaw, massive floods were released into the oceans, carrying newly exposed minerals. This influx of nutrients created a perfect storm for evolution—fertilizing marine environments and supporting the rapid expansion of early life. As ocean chemistry changed, oxygen levels rose, allowing more complex, multicellular organisms to thrive. In essence, the great melt wasn’t just an end—it was a beginning of life we know today.
Fueling Evolution: How Life Took Off
The Neoproterozoic era saw a dramatic biological shift. Before this period, life was mostly microscopic. But after the glaciers melted and uranium was introduced into the oceans, new forms of life occurred. The first large, multicellular organisms—like the mysterious Ediacaran biota—began to spread. This wasn’t a coincidence. The chemical conditions created by glaciers and uranium provided the spark needed for life to become more complex, setting the stage for future evolutionary explosions.
The Bigger Picture: Earth’s Ever-Changing Climate

Earth’s climate has always been in flux, and life has adapted alongside it. This study reinforces the idea that extreme climate events—though catastrophic in the short term—can drive long-term evolutionary success. The same forces that shaped life millions of years ago still operate today. Understanding how past ice ages influenced biology gives us a roadmap for predicting how modern climate shifts might impact ecosystems and biodiversity.
What This Means for Today’s Climate Crisis
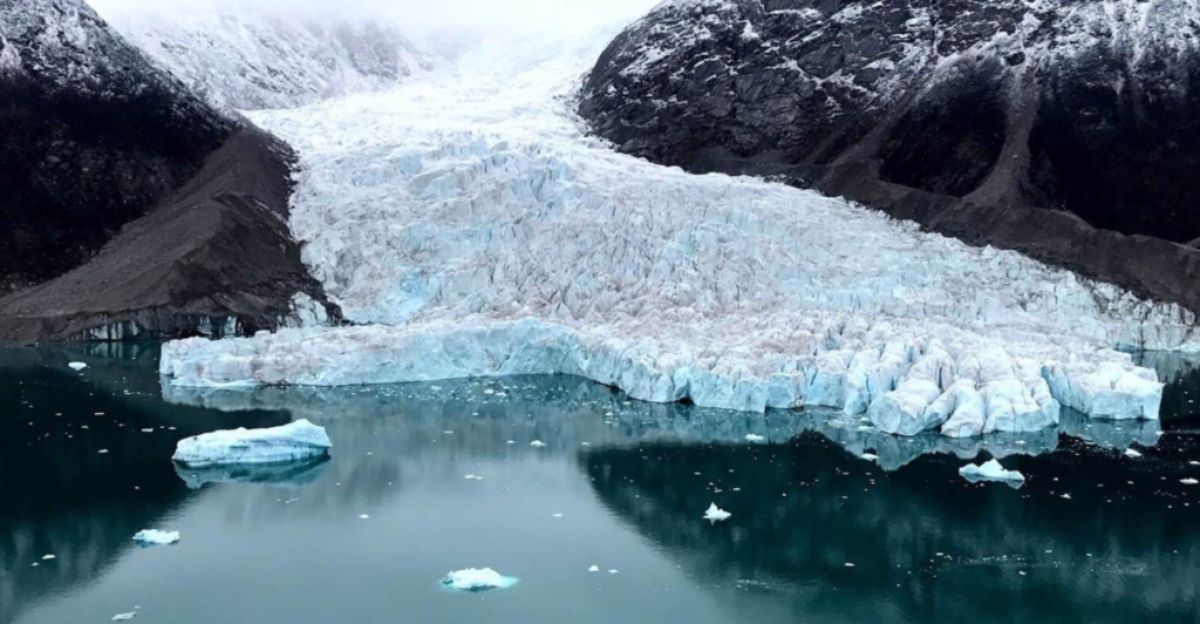

As we face a rapidly changing climate, this study is a stark reminder of how environmental shifts reshape life on Earth. The same mechanisms that drove evolution in the past—glacial erosion, ocean chemistry changes, and mineral redistribution—are still at play. But today’s changes are happening at an unprecedented pace. Studying ancient climate-driven transformations could help us understand and mitigate the long-term impacts of human-driven climate change.
Uranium’s Modern Role in Energy and Sustainability
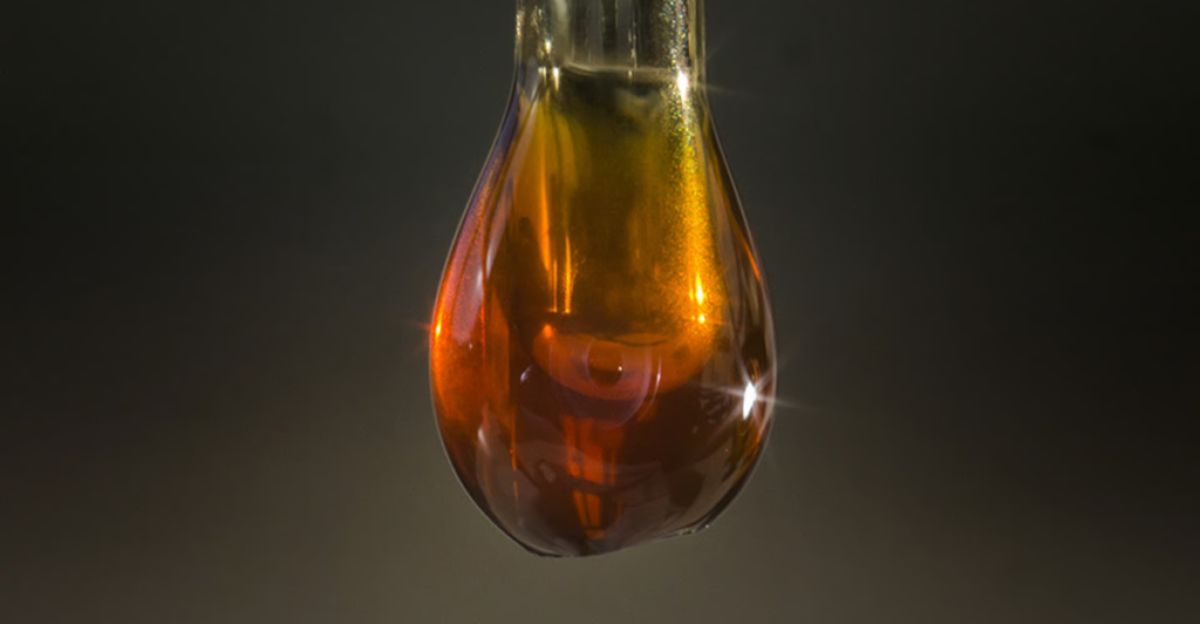

The story of uranium isn’t just ancient history. Today, uranium plays a key role in nuclear energy—a major low-carbon power source. Interestingly, scientists have discovered that uranium in seawater is continuously replenished, making it a potentially renewable resource. Just as uranium once fueled biological evolution, it may now play a part in fueling a more sustainable future. This unexpected connection between ancient geology and modern technology highlights how deeply Earth’s past and future are intertwined.
Final Thoughts: The Hidden Forces Behind Life on Earth

The discovery that glaciers and uranium helped shape life’s evolution challenges everything we thought we knew. What seemed like a frozen wasteland was actually a cradle for complex life. This study is a powerful reminder that Earth’s history is written in rock, ice, and water. And just as the past shaped life’s trajectory, the changes happening today will define the future of life on our planet. The question is—how will we respond?
Explore more of our trending stories and hit Follow to keep them coming to your feed!
Don’t miss out on more stories like this! Hit the Follow button at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest news. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!







