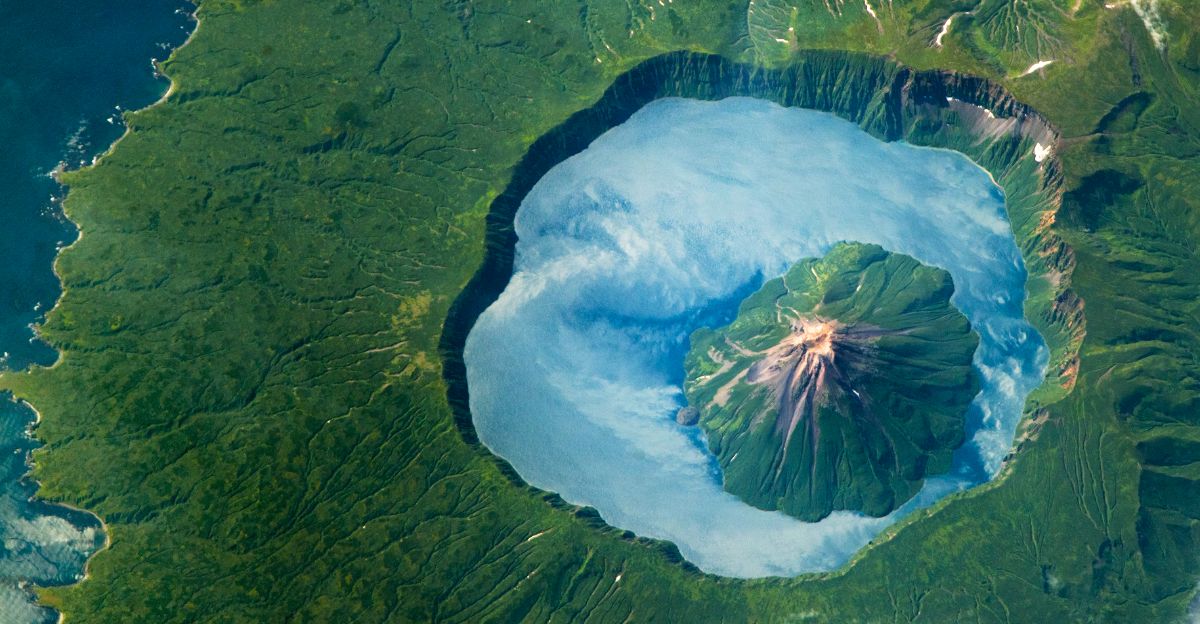

Recent research by NASA in collaboration with the Smithsonian Institution has uncovered a groundbreaking natural indicator for volcanic eruptions: the greening of tree leaves near active volcanoes. This phenomenon occurs as trees absorb volcanic carbon dioxide (CO₂) released by rising magma underground, causing increased photosynthesis and leaf greenness detectable from space.
Using satellite imagery, scientists can now monitor these subtle vegetation changes as early warning signs of volcanic unrest. This innovative approach enhances early warning systems, crucial for protecting millions living near active volcanoes worldwide.
The Science Behind Tree Signals
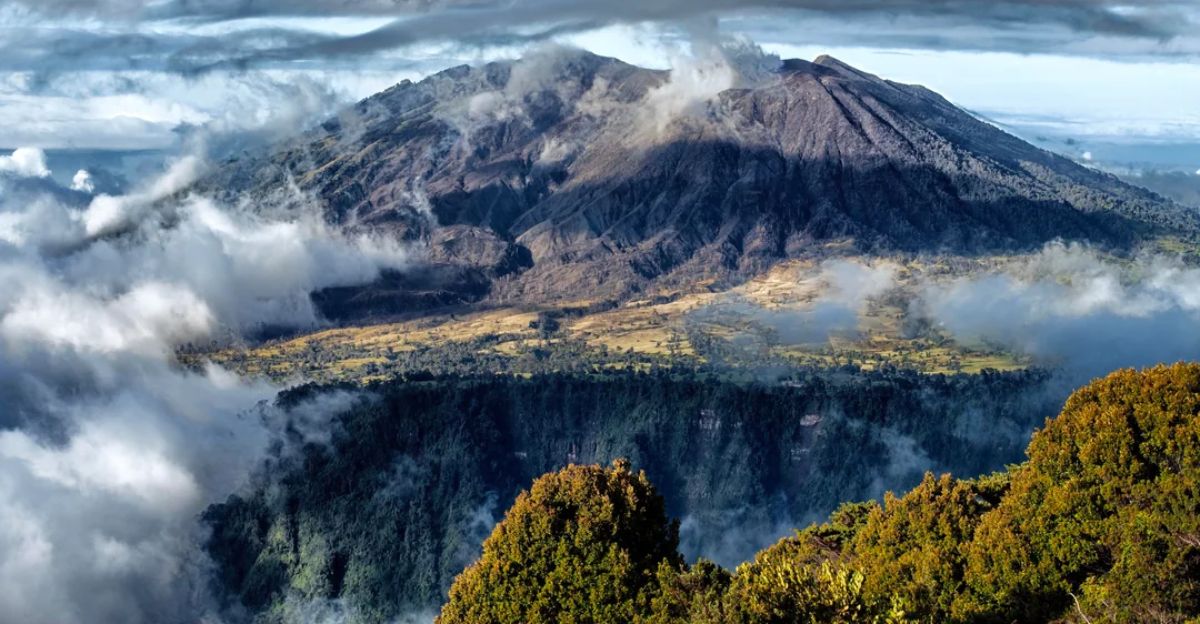

Volcanic eruptions begin with magma rising beneath the surface, releasing gases like CO₂ underground before any eruption occurs. Trees near volcanoes absorb this volcanic CO₂ through their roots, which stimulates photosynthesis, resulting in greener and healthier leaves.
Detecting volcanic CO₂ directly from space is challenging due to its mixing with atmospheric gases, but trees act as natural sensors, amplifying this signal through their leaf color changes. This biological response provides a reliable proxy for volcanic activity.
Satellite Technology Monitoring Vegetation
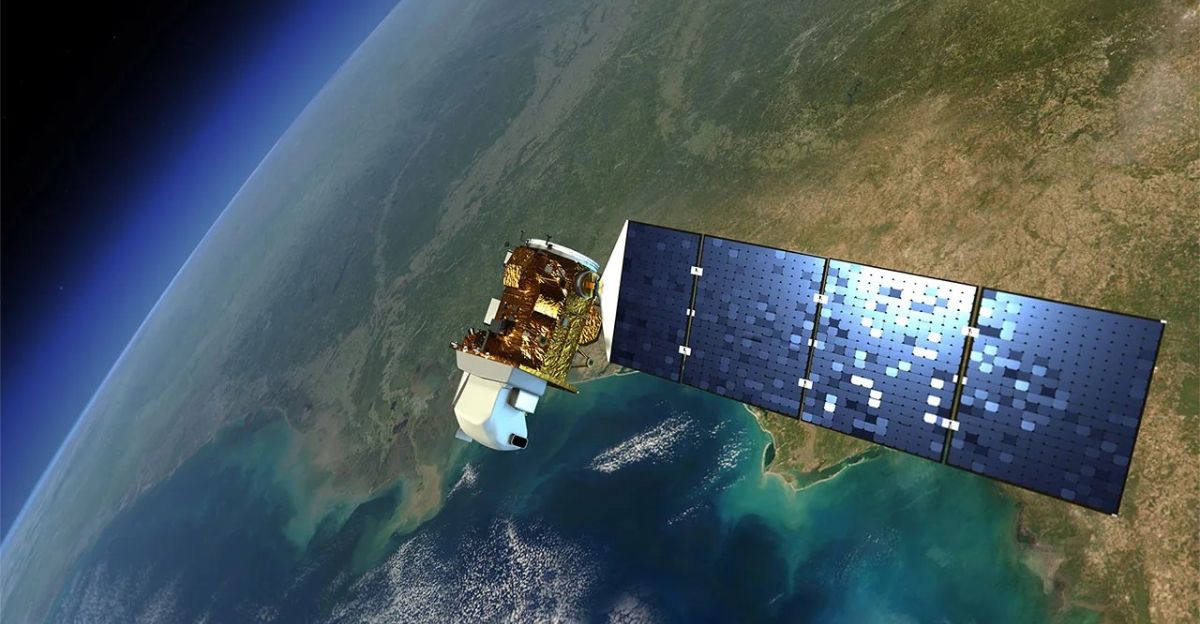

NASA employs advanced satellites such as Landsat 8, Orbiting Carbon Observatory 2, and ESA’s Sentinel-2 to sense vegetation health near volcanoes remotely. These satellites use the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), a metric quantifying leaf greenness, to detect subtle changes in tree health.
Complementary airborne instruments like the Smithsonian’s AVUELO project validate satellite data with ground measurements, ensuring accuracy. This integrated remote sensing approach enables continuous, large-scale monitoring of volcanic regions that are inaccessible by traditional methods.
Mount Etna and Rincon de La Vieja
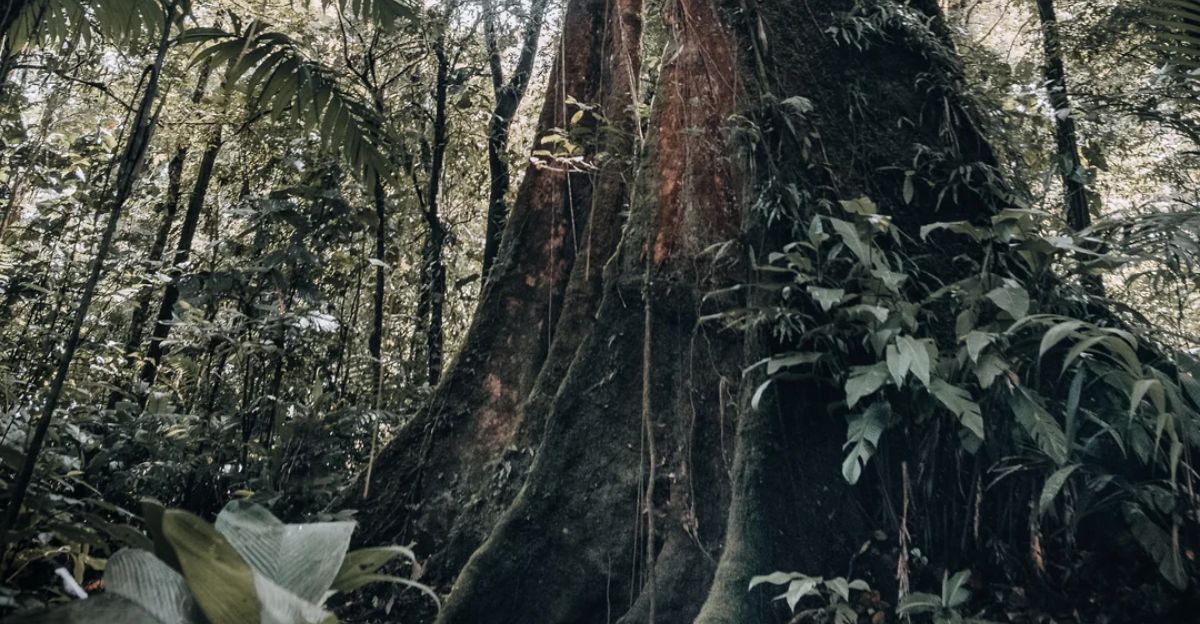

At Mount Etna in Italy, researchers observed a strong correlation between volcanic CO₂ emissions and increased tree greenness over two years, confirming the method’s reliability. Similarly, studies near Costa Rica’s Rincon de La Vieja volcano showed lush vegetation responding to volcanic activity, with greener leaves signaling elevated CO₂ levels.
These diverse environments validate the technique’s applicability across different tropical volcanic ecosystems, demonstrating its potential for global use.
Advantages Of Traditional Volcano Monitoring

Traditional volcano monitoring relies on seismic activity, ground deformation, and sulfur dioxide detection, which can be limited by terrain and sensor placement. Trees provide an earlier and more accessible signal, especially in remote or forested areas where ground-based instruments are sparse.
This biological indicator complements existing systems, potentially extending lead times for eruption warnings and improving overall forecasting accuracy.
Unexpected Intersections with Ecology and Remote Sensing

This research bridges volcanology, botany, and satellite environmental monitoring, revealing how geological processes influence ecosystems. Trees act as biological indicators, linking underground volcanic activity to surface ecological responses.
This interdisciplinary approach opens new avenues for using vegetation as proxies in predicting other natural hazards, expanding the role of environmental monitoring in disaster science.
Challenges and Limitations

Not all volcanoes have sufficient or responsive vegetation cover, limiting the method’s applicability. Variability in tree species’ sensitivity to CO₂ and environmental factors like drought can affect signal reliability.
Additionally, satellite resolution and atmospheric interference may obscure subtle vegetation changes. These challenges necessitate combining tree monitoring with traditional methods for robust eruption forecasting.
Historical Context and Evolution of Volcano Early Warning

Volcano monitoring has evolved from ground-based seismic and gas sensors to satellite observations. The new tree-based method represents a novel addition, providing earlier and more widespread detection capabilities.
Historical eruptions, such as the 2018 Mayon volcano event in the Philippines, highlight the importance of timely warnings, where integrated monitoring saved thousands of lives. This tree-signal approach continues this evolution toward more effective disaster preparedness.
Potential Impact and Future Directions

Integrating tree health monitoring into global volcano early warning networks could significantly enhance disaster preparedness, benefiting millions living near volcanoes.
Future research aims to expand this method to other volcanic regions and refine detection algorithms for greater precision. Continued investment in satellite and ecological monitoring technologies promises to improve eruption forecasting and risk reduction worldwide.
Trees as a Green Alarm System from Space

Trees provide a novel, reliable early warning signal for volcanic unrest by reflecting underground CO₂ emissions through leaf greenness detectable from space.
Combining satellite technology and ecological science, this interdisciplinary approach offers a promising tool to save lives and improve volcanic monitoring. Sustained support for such innovations is essential to enhance global safety and disaster resilience in volcanic regions.
Explore more of our trending stories and hit Follow to keep them coming to your feed!
Don’t miss out on more stories like this! Hit the Follow button at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest news. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!







