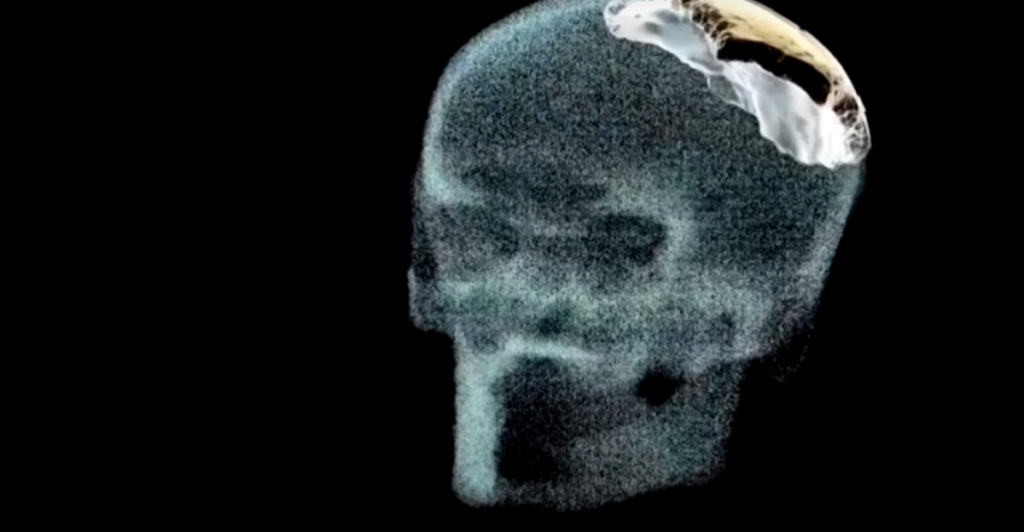
A stunning discovery in China is shaking up what we thought we knew about human evolution. Scientists have uncovered a hominid skull, nicknamed “Dragon Head,” near Hualongdong that doesn’t fit neatly into any known species. With a mix of ancient and modern traits, this fossil challenges the long-held “Out of Africa” theory. Could our evolutionary story be more complex than we ever imagined? Let’s dive into it.
Unique Features of the Fossil
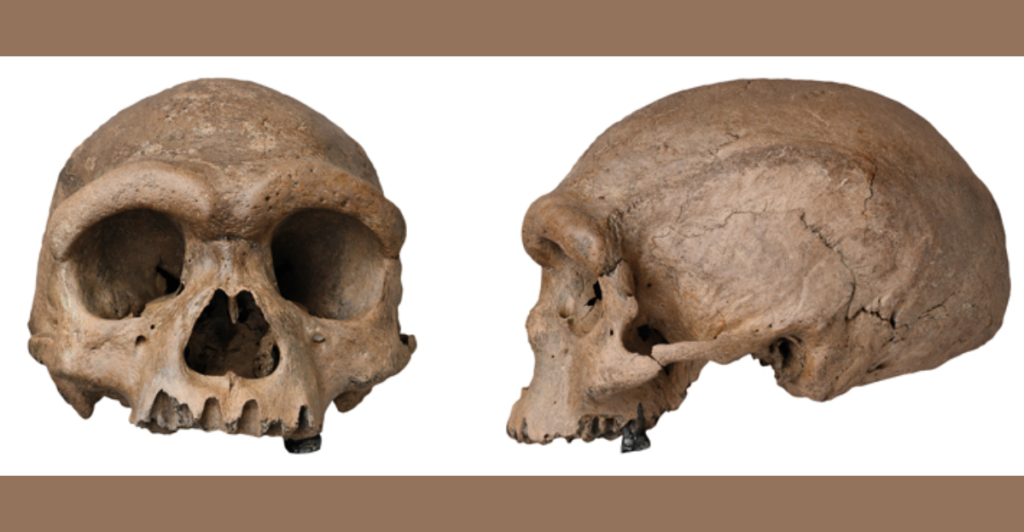

The newly discovered skull from Hualongdong presents a puzzling mix of traits—its large cranial capacity, sturdy jawline, and pronounced brow ridge set it apart from both modern humans and Neanderthals. This unique combination has left researchers debating whether it belongs to a separate lineage or represents a hybrid species. Its unusual structure challenges long-standing ideas about human evolution, hinting at a more diverse array of early Asian hominids than previously thought.
The Discovery Site

Hidden within a cave system in southeastern China, this fossil was found alongside stone tools and charred animal bones—evidence that its owner likely used fire and primitive hunting methods. Radiometric dating places the skull at around 300,000 years old, aligning with the emergence of Homo sapiens in Africa. The timing raises intriguing questions: Could early humans have evolved along multiple paths rather than following a single trajectory out of Africa?
Rethinking the Out of Africa Theory
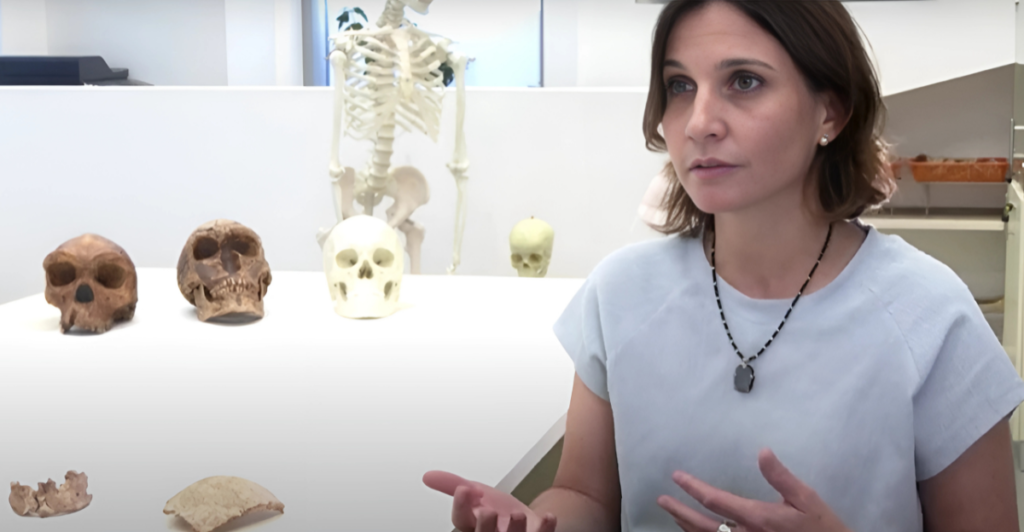

For years, the prevailing theory suggested that modern humans originated solely in Africa before migrating outward. But this discovery hints at a different possibility—could Asia have been home to its own evolutionary experiments? Some researchers believe this hominid may have coexisted with, or even interbred with early Homo sapiens. If true, it would add another layer to the complex story of human ancestry, pointing to a more intertwined and global evolutionary history.
Links to Other Ancient Asian Hominids
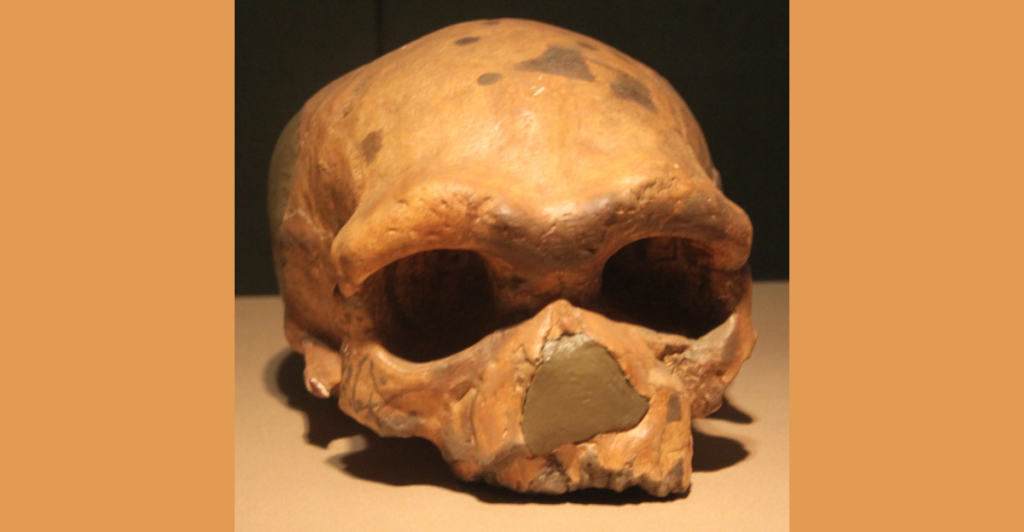

This fossil isn’t an isolated case—it joins a growing list of Asian hominids, including the Denisovans and the Dali Man, that share distinctive cranial traits and signs of advanced tool use. These connections suggest that Asia wasn’t just a migration route but a crucial region for human evolution itself. The evidence challenges the notion that Africa was the only birthplace of early humans, painting a richer and more complex picture of our past.
Genetic Clues and Ancestral Links
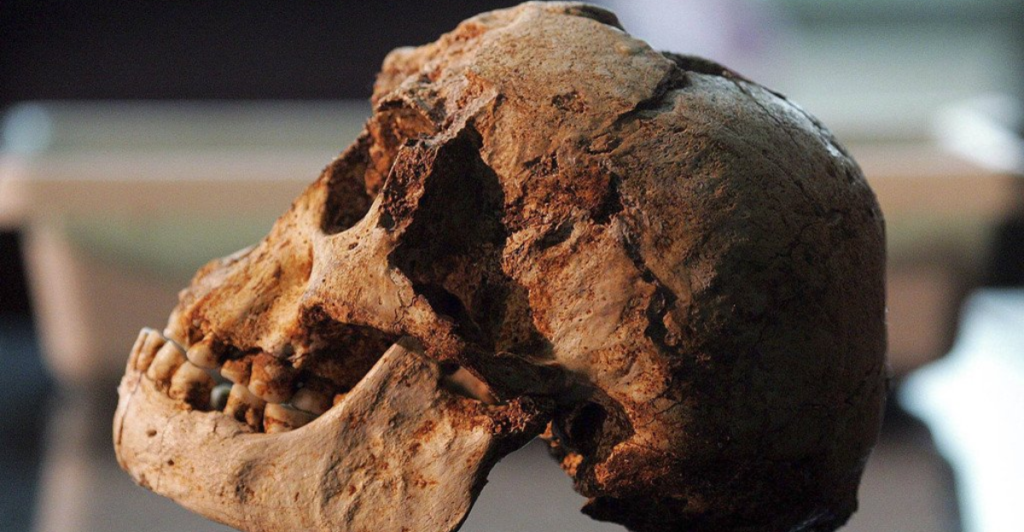

Scientists are now analyzing the fossil’s DNA to determine whether it shares ancestry with modern humans or other archaic hominids. Early results hint at distinct genetic markers, suggesting it could be a missing link in the evolutionary chain. If this species interbred with Homo sapiens or Denisovans, it would reshape our understanding of human ancestry, revealing a more profound genetic interconnection between ancient populations.
Impact on Anthropology

This finding has sparked heated debate among experts. Some view it as groundbreaking evidence of a more intricate human evolution, while others urge caution until more fossils and genetic data are analyzed. Regardless, it has prompted renewed interest in Asia’s role in our origins, encouraging researchers to revisit archaeological sites and expand their understanding of early hominid migration and adaptation.
Global Reactions and Scientific Collaboration
The fossil is celebrated in China as a significant piece of the nation’s prehistoric legacy. Globally, it has drawn a mix of excitement and skepticism, with scientists calling for further research to verify its place in human history. This discovery highlights the need for international collaboration in unraveling the mysteries of our past—because the story of human evolution is far from complete.
The Power of Technology in Unlocking the Past

Modern technology has been instrumental in studying this remarkable fossil. Using 3D imaging, scientists reconstructed the skull in detail, revealing features unlike any known species. Advanced dating techniques confirmed its age, while artificial intelligence is being used to compare it with fossils worldwide. These tools are helping researchers uncover its place in the human evolutionary tree like never before.
Rethinking Human Migration
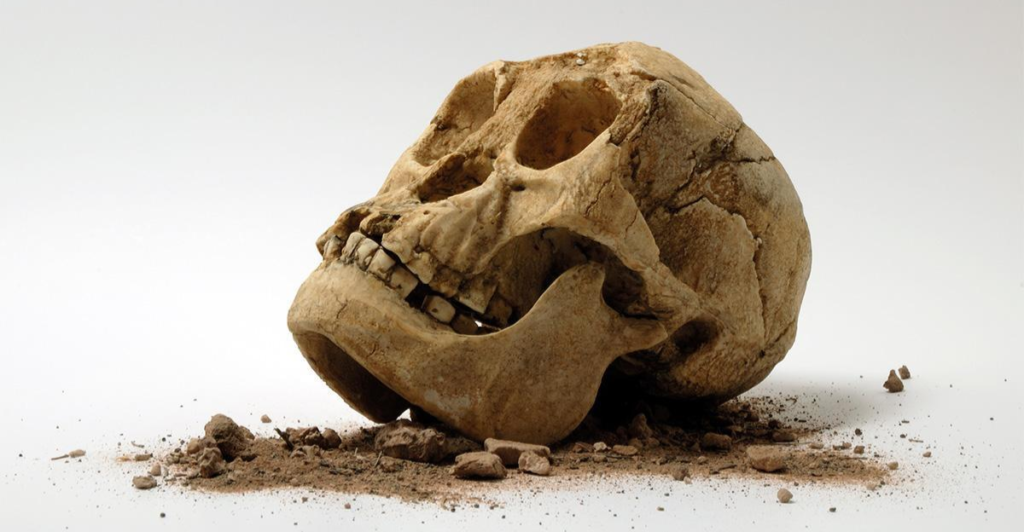

This discovery challenges the traditional view that Asia was merely a passageway for migrating hominids—it may have been a thriving center of human evolution. Evidence suggests that multiple species lived, traveled, and interbred in the region, painting a more complex picture of how early humans spread across the globe. The Dragon Head fossil adds yet another piece to this evolving puzzle.
A Cultural and Scientific Milestone

This fossil is more than just a scientific breakthrough in China—it’s a source of national pride. Museums and educational programs are showcasing the discovery, sparking curiosity and excitement about the region’s ancient past. As more people engage with the findings, the Dragon Head is becoming a symbol of China’s role in shaping our understanding of human history.
What’s Next for Research?
This discovery has set the stage for further exploration. Scientists are now searching for similar fossils in nearby caves, hoping to uncover more clues about this enigmatic species. With experts from anthropology, genetics, and technology working together, future discoveries could deepen our understanding of early hominids and their place in human evolution.
A New Perspective on Our Origins

The Dragon Head fossil proves that human evolution is far more intricate than we once believed. Each new discovery reshapes our understanding of our origins and how different hominid groups interacted. As research continues, this fossil may become one of the most significant finds in unraveling the mysteries of our ancient past.







