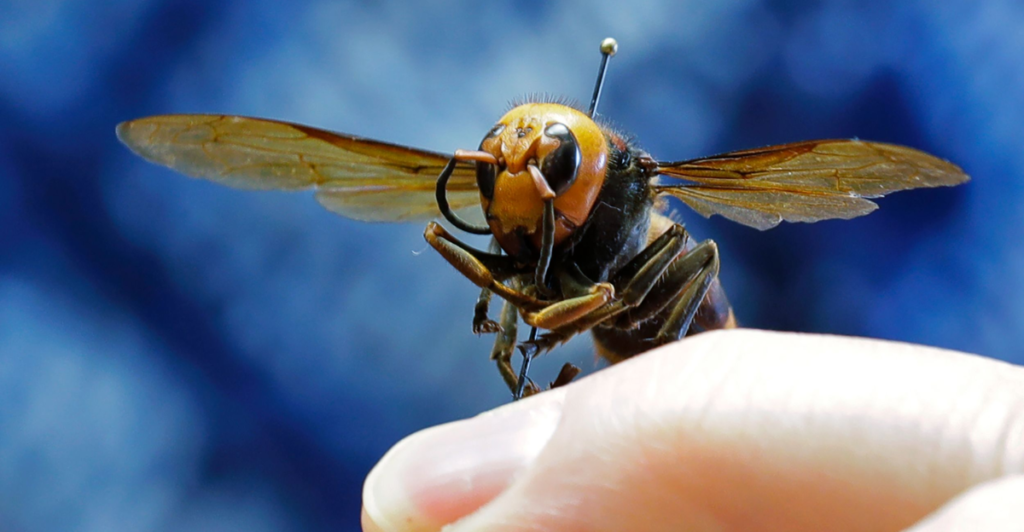

The Asian giant hornet (“Vespa mandarinia”), commonly dubbed the “Murder Hornet,” is the world’s largest hornet species. Growing up to 2 inches long, these hornets are notorious for their powerful stingers and ability to destroy honeybee colonies within hours. First detected in the U.S. in 2019, their presence alarmed scientists due to potential threats to local ecosystems and agriculture. However, recent developments have marked significant progress in managing their spread.
How They Entered the U.S.

Asian giant hornets were first spotted in Washington State in late 2019. Experts suspect they arrived through international shipping or cargo, a common pathway for invasive species. Their appearance triggered immediate concern, as these hornets could establish populations and disrupt ecosystems. Authorities quickly mobilized to identify and contain the threat before it could escalate, leading to extensive monitoring and eradication efforts across affected areas.
The Threat to Honeybees
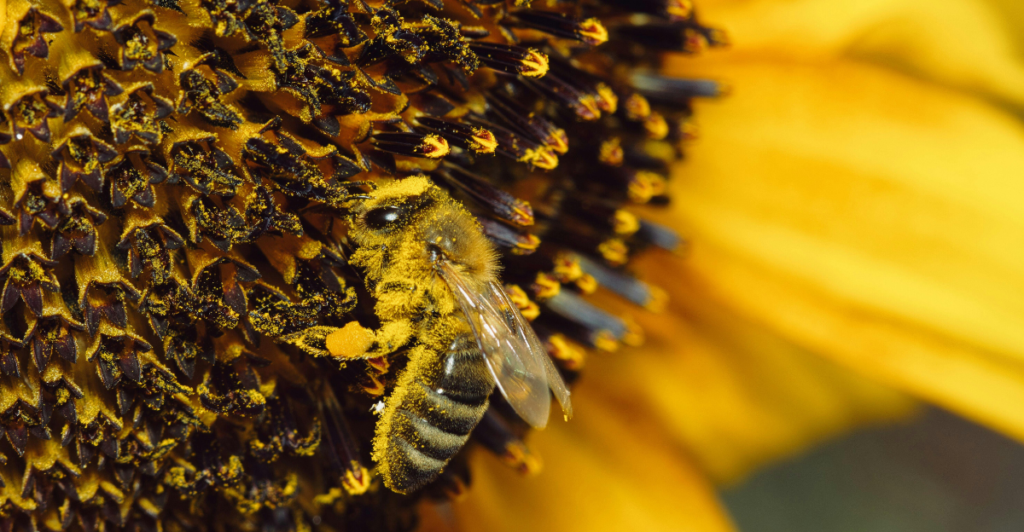

One of the primary concerns surrounding murder hornets is their impact on honeybees. These hornets are highly aggressive predators, capable of decimating entire hives within hours. Honeybees, essential pollinators for crops, are already facing challenges like habitat loss and pesticides. The presence of murder hornets added another layer of danger, prompting scientists to act swiftly to protect these vital pollinators and maintain ecological balance.
Tracking the Invasion
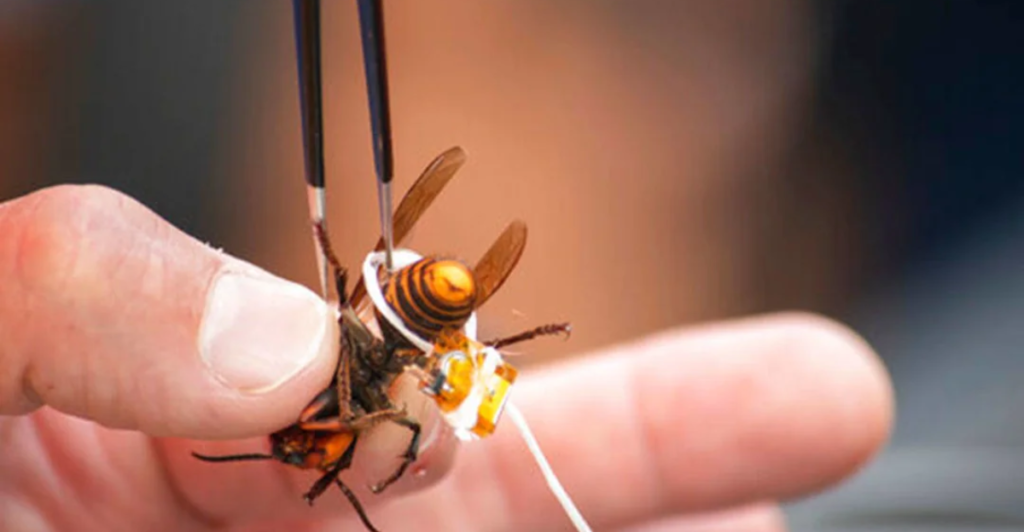

To combat the spread of murder hornets, scientists employed innovative tracking methods. Using radio trackers attached to captured hornets, researchers followed them back to their nests. This strategy allowed teams to locate and destroy nests efficiently, preventing the hornets from spreading further. These efforts were crucial in minimizing the hornets’ impact on local ecosystems and agricultural industries.
Nest Eradication Success
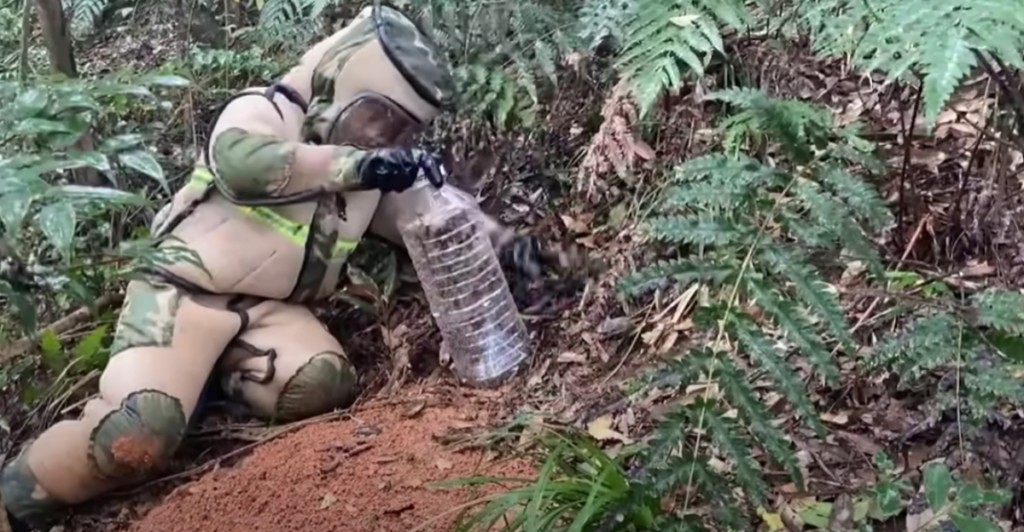

Since their discovery, over 30 murder hornet nests have been successfully eradicated in Washington State alone. Equipped with specialized suits and tools, teams worked diligently to remove these nests, often located underground or in tree cavities. Each removal marked a victory in the fight to prevent establishing a permanent population in the U.S., safeguarding both the environment and agriculture.
Public Involvement in the Fight
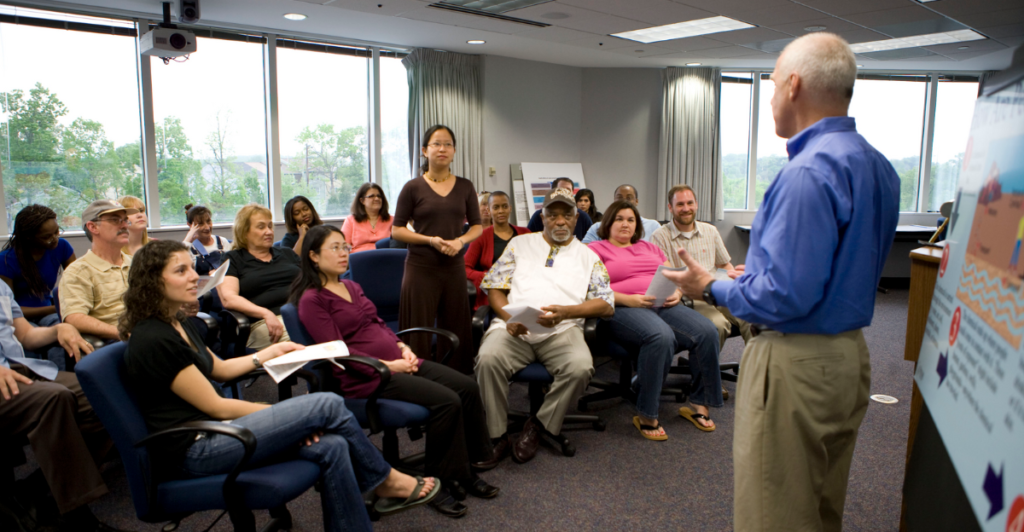

Public awareness played a vital role in combating the murder hornet threat. Officials encouraged residents to report sightings and provided educational resources to distinguish murder hornets from native species. Community participation significantly enhanced monitoring efforts, enabling scientists to act swiftly when new nests or hornets were identified. This collaboration underscored the importance of collective action in addressing invasive species.
The Role of Scientists
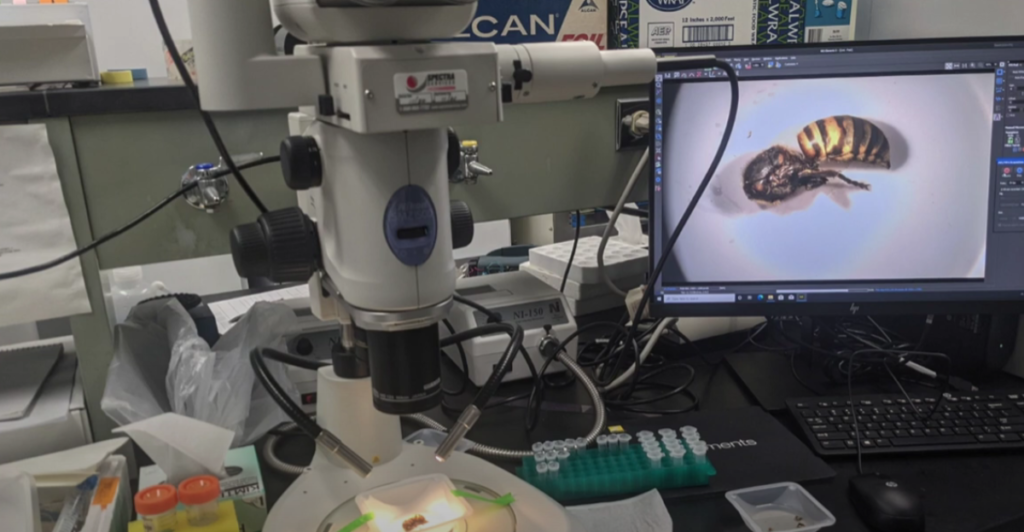
Entomologists and conservationists were at the forefront of the battle against murder hornets. Their expertise in insect behavior and ecology guided effective eradication strategies. These professionals also researched to understand the hornets’ lifecycle and potential environmental impacts. Their relentless efforts ensured a coordinated, science-based approach to addressing this invasive species.
Challenges Faced Along the Way
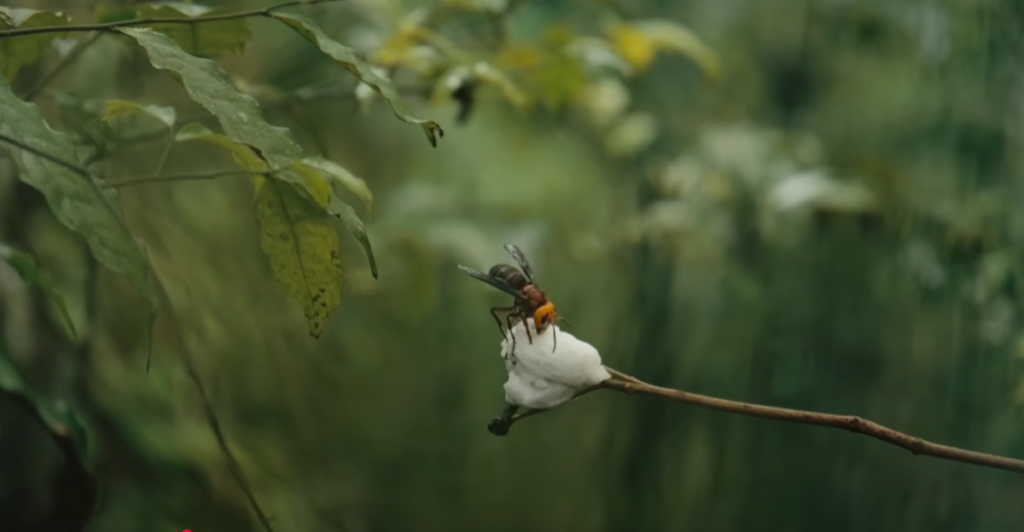

The eradication efforts were not without challenges. Dense forests, limited resources, and the hornets’ elusive nature made tracking and nest removal difficult. Additionally, distinguishing murder hornets from similar-looking native insects required precision and expertise. Despite these obstacles, the dedication of scientists, government agencies, and the public led to a successful outcome.
Declaring the Threat Eliminated
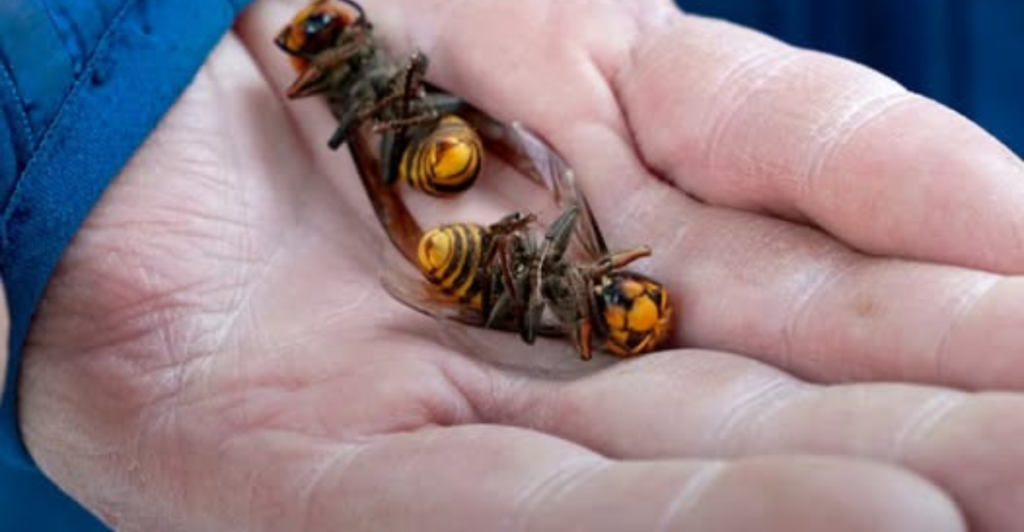

In a historic announcement, scientists declared the murder hornet threat eliminated from the U.S. This milestone reflects years of collaboration, research, and perseverance. While vigilance remains necessary to prevent future invasions, the declaration marks a significant victory for conservation efforts. It also highlights the effectiveness of proactive measures in addressing invasive species.
Lessons Learned

The fight against murder hornets provided valuable insights into managing invasive species. Early detection, public involvement, and scientific innovation proved crucial in containing the threat. These lessons can be applied to future challenges, ensuring that ecosystems and agriculture remain protected. The success story serves as a reminder of the importance of preparedness and collaboration.
The Importance of Biodiversity

The murder hornet’s arrival underscored the delicate balance of ecosystems. Protecting biodiversity is essential to maintaining healthy environments and supporting agriculture. Efforts to combat invasive species like murder hornets highlight the interconnectedness of species and the need for continued conservation initiatives. This experience reinforces the importance of safeguarding native wildlife and habitats.
What’s Next?

Although the immediate threat has been eliminated, scientists remain vigilant. Monitoring programs will continue to ensure no new invasions occur. Efforts to educate the public about invasive species and their impacts will persist. By staying proactive, researchers and communities can safeguard against future threats and protect local ecosystems.
Celebrating a Victory

The elimination of the murder hornet threat is a cause for celebration. This achievement reflects the power of teamwork, scientific expertise, and public engagement. It also serves as a hopeful example of how communities can come together to address environmental challenges. While the fight against invasive species is ongoing, this victory offers a moment to appreciate the progress made in protecting our planet.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them appearing in your feed
There Will Be Eruptions”: Concerns Mount as Yellowstone Supervolcano Activity Shifts
Climate Change Overestimated? New Data Shows Oceans Are Cooling The Planet Faster Than Predicted
520-Million-Year-Old Fossil Amazes Scientists With Preserved Brain and Guts
New York Declares War On Fossil Fuels With $75 Billion In New Climate Fines
This article first appeared here
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







