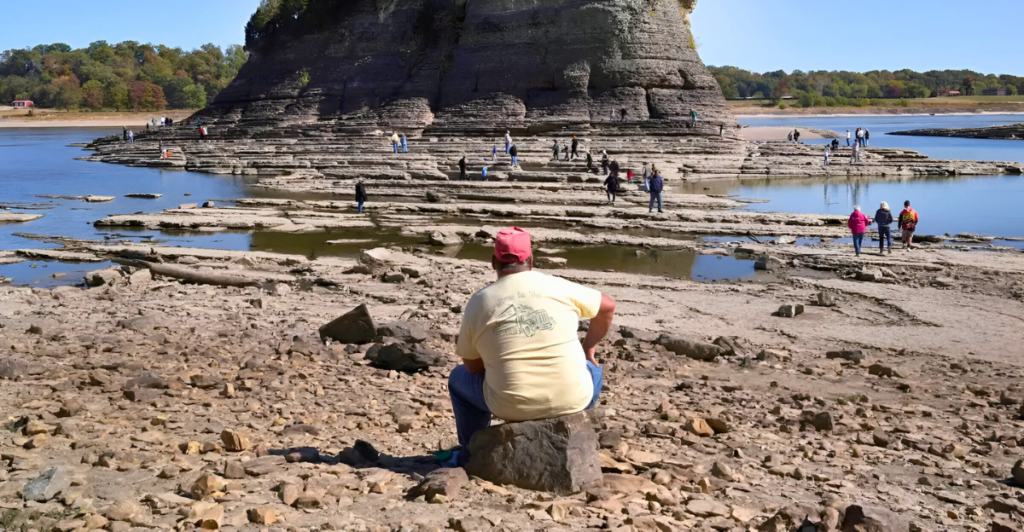

The Mississippi River, stretching over 2,300 miles, is a vital artery for the United States, supporting agriculture, industry, and transportation. It drains 41% of the contiguous U.S., encompassing one-third of its population. Beyond its economic significance, the river sustains diverse ecosystems and provides approximately 20 million people with drinking water. However, recent reports indicate alarming trends that could jeopardize this critical resource. Projections suggest that, without intervention, the Mississippi River could experience severe reductions in water levels by 2050, posing unprecedented challenges to both human and ecological systems.
Current Observations: A River in Decline
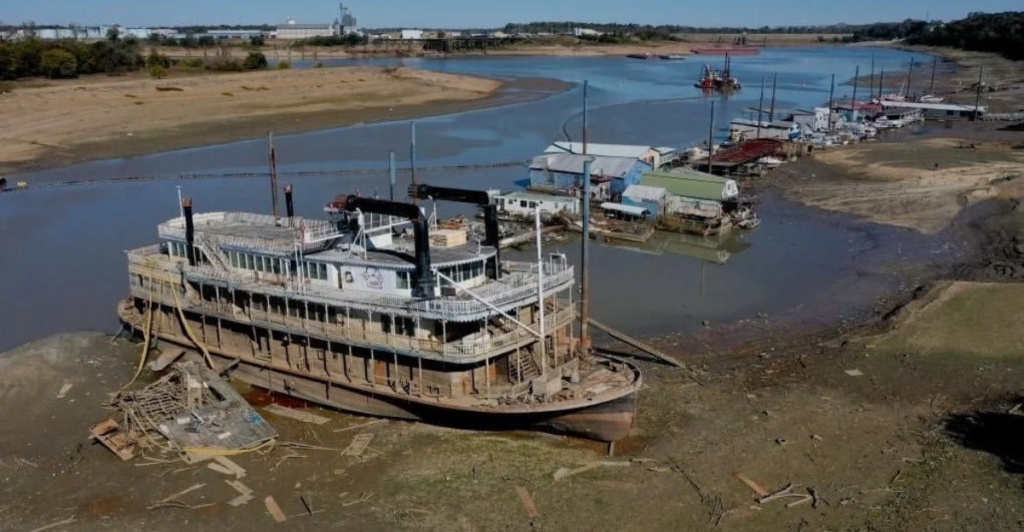

The Mississippi River has witnessed historically low water levels in recent years, disrupting navigation and commerce. In 2022, sections near Memphis, Tennessee, saw water levels drop so significantly that barge traffic was impeded, necessitating emergency dredging. Such occurrences underscore the river’s vulnerability to changing climatic conditions and highlight the immediate need for comprehensive water management strategies.
Climate Change: A Driving Force
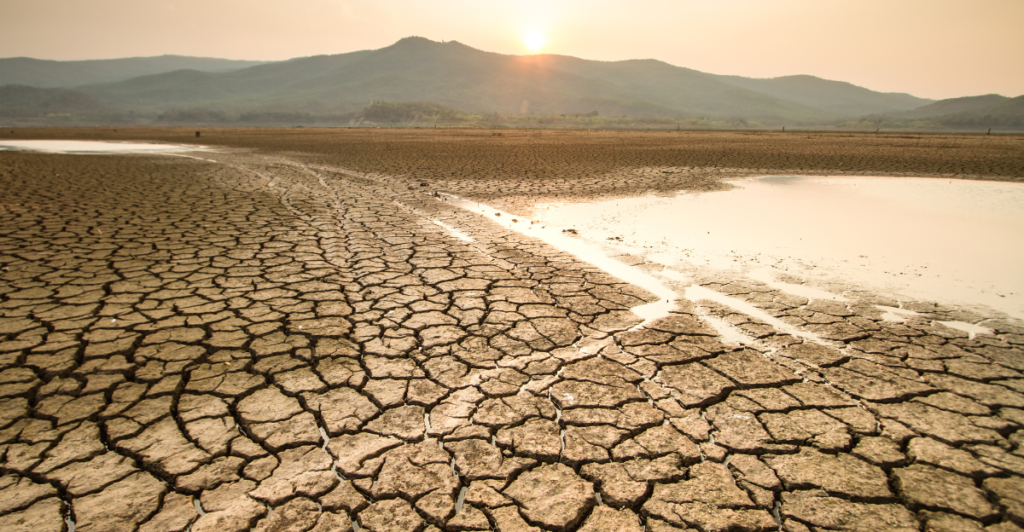

Climate change significantly contributes to the Mississippi River’s dwindling water levels. Increased temperatures lead to higher evaporation rates, while altered precipitation patterns result in prolonged droughts and, paradoxically, more severe flooding events. This variability strains the river’s capacity to maintain consistent flow levels, exacerbating the risk of low-water conditions.
Agricultural Impacts: Feeding the Nation at Risk
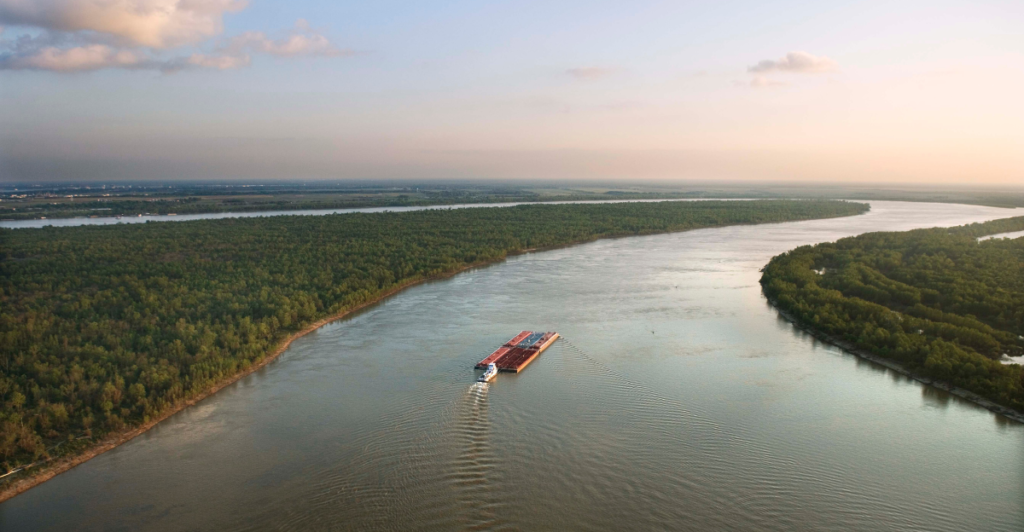

The Mississippi River Basin is one of the world’s most productive agricultural regions, responsible for a significant portion of the nation’s grain exports. Reduced river levels hinder barge transportation, delaying shipments and increasing costs. Furthermore, diminished water availability affects irrigation, potentially leading to decreased crop yields and threatening food security.
Ecological Consequences: Disrupting Natural Habitats

Beyond human concerns, the river’s declining health severely threatens its rich biodiversity. Lower water levels can lead to habitat loss for numerous aquatic species, while increased temperatures may alter migration patterns and reproductive cycles. Also, prolonged droughts can exacerbate saltwater intrusion from the Gulf of Mexico, further destabilizing freshwater ecosystems.
Economic Ramifications: Commerce at a Standstill
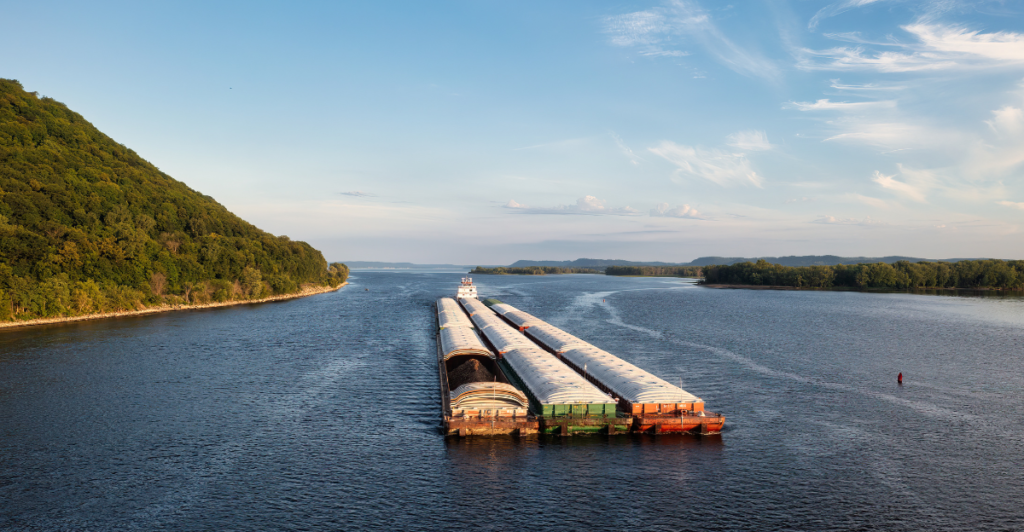

The Mississippi River is a crucial conduit for commerce, with barges transporting commodities such as coal, petroleum, and building materials. Low water levels disrupt this transportation network, leading to economic losses estimated in the billions. Industries reliant on the river face increased operational costs, which may be passed on to consumers, affecting the broader economy.
Water Quality Concerns: A Tenuous Balance
As water levels drop, the concentration of pollutants can increase, degrading water quality. This poses risks to public health, particularly for communities dependent on the river for drinking water. Moreover, lower flows reduce the river’s ability to dilute and transport waste, leading to the accumulation of contaminants.
Infrastructure Challenges: Adapting to a New Reality

Existing infrastructure, including levees, dams, and locks, was designed based on historical flow patterns. The emerging reality of fluctuating water levels necessitates reevaluation and adaptation of these structures to ensure they remain effective in managing flood and drought conditions.
Mitigation Strategies: Charting a Sustainable Course

Addressing the challenges facing the Mississippi River requires a multifaceted approach. Strategies include implementing sustainable water management practices, restoring wetlands to enhance natural water storage, and investing in climate-resilient infrastructure. Collaborative efforts among federal, state, and local agencies are essential to develop and implement effective solutions.
The Path Forward: Collective Responsibility

The projected decline of the Mississippi River by 2050 serves as a clarion call for immediate action. Stakeholders, including policymakers, industries, and communities, must unite to address the multifaceted challenges of climate change. Through proactive measures and sustained commitment, it is possible to preserve the Mississippi River for future generations, ensuring it continues to serve as a vital resource for the nation.
Explore more of our trending stories and hit Follow to keep them coming to your feed!

Don’t miss out on more stories like this! Hit the Follow button at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest news. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!







