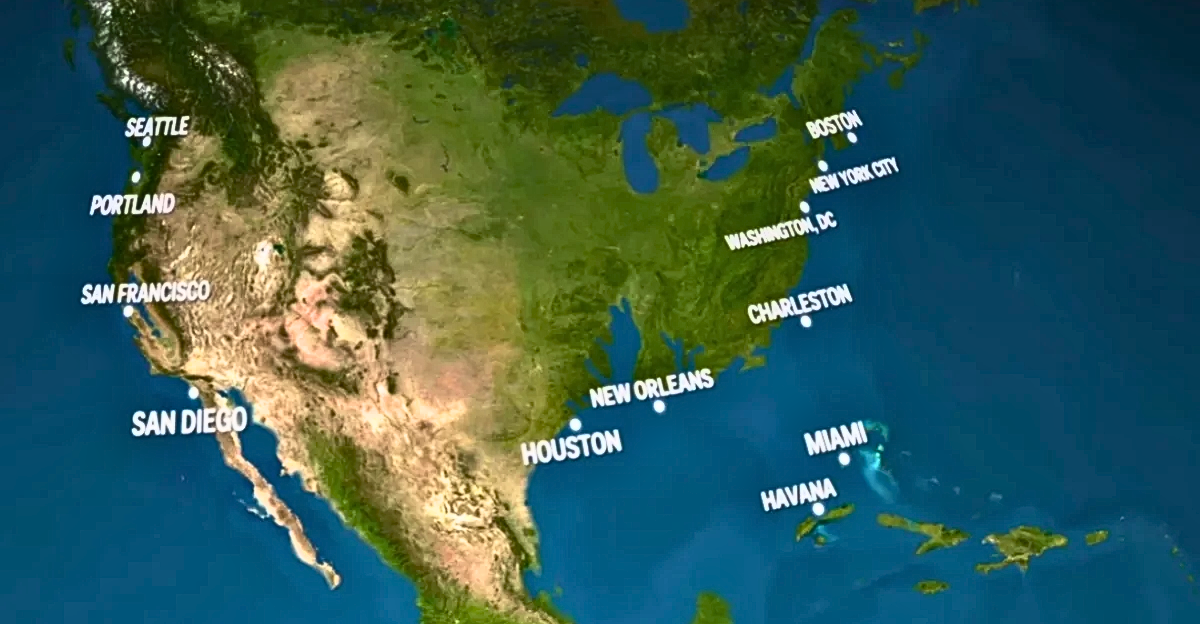
The rapid melting of ice in polar regions is dramatically reshaping coastlines worldwide, a transformation with profound implications for both human populations and delicate ecosystems. The scale of this change is immense, with forecasts suggesting that thousands of miles of coastline could be redrawn by the end of the year due to melting ice.
This phenomenon is driven by rising global temperatures, accelerating the melting of glaciers and ice sheets, and increasing sea levels. The urgency to understand and address these changes cannot be overstated, as they directly impact coastal communities, economies, and natural habitats. The accelerating rate of ice melt requires immediate attention and concerted action to mitigate its far-reaching consequences.
The Science Behind Ice Melt and Sea Level Rise

Melting polar ice contributes to sea level rise, with land ice melt having a greater impact on coastlines than sea ice melt. When land ice, such as glaciers and ice sheets, melts, the water flows into the ocean, increasing its volume and causing sea levels to rise. On the other hand, sea ice already floats in the ocean, so it doesn’t significantly change sea levels when it melts.
Recent data confirm ongoing ice loss in the Arctic and Antarctic, exacerbating the threat to coastal regions. The distinction between these two types of ice melt is crucial for understanding the specific drivers of sea level rise and predicting future impacts on coastal communities worldwide.
Spotlight on Antarctica’s Melting Ice Sheets
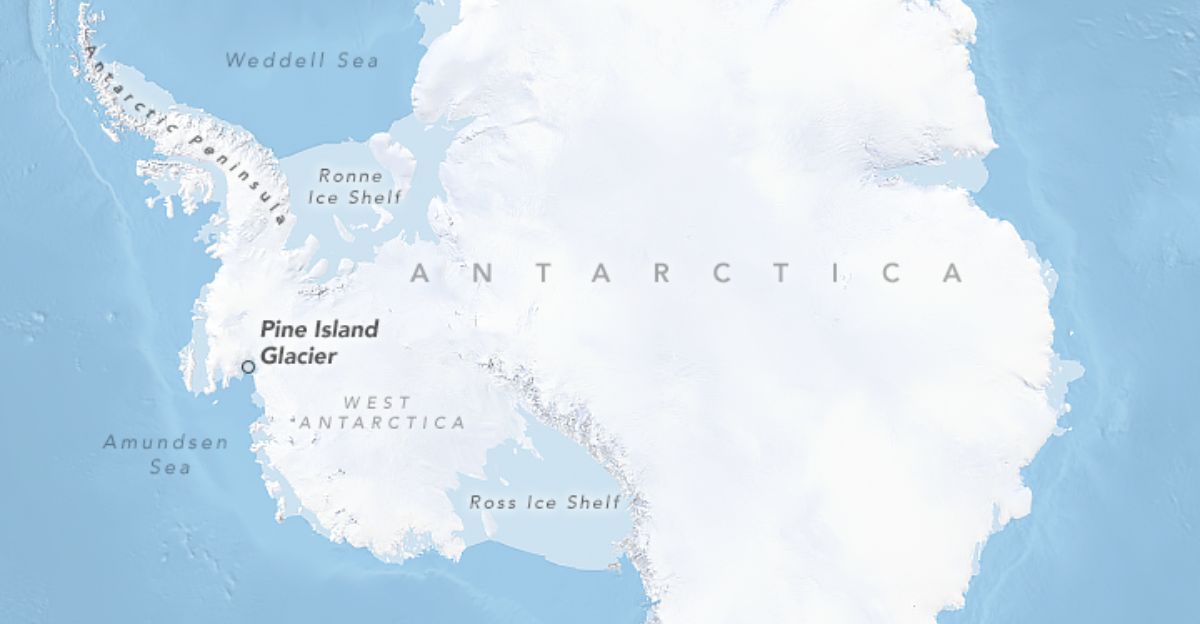
Antarctica’s Thwaites and Pine Island glaciers are critical “weak underbellies” of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet. Relatively warm ocean currents are weakening the base of the Thwaites Glacier, contributing to significant ice retreat. These glaciers are losing ice faster than in the past 5,000 years and may contribute over three meters to sea level rise.
Their potential collapse could lead to rising sea levels, threatening coastal cities globally. The synchronous retreat of both glaciers suggests that external oceanographic and atmospheric drivers, modulated by climate variability, are causing the retreat.
Arctic Sea Ice Decline and Its Global Implications

Arctic sea ice’s extent, area, and volume have dramatically declined in recent decades. This decline influences global climate patterns and sea levels. As Arctic ice melts, the Earth’s albedo is reduced, causing the planet to absorb more solar radiation and further accelerate warming.
Addressing misconceptions and climate skeptic arguments with scientific evidence is crucial to understanding the global implications of Arctic melt. The rapid loss of Arctic sea ice indicates climate change and its far-reaching effects on the planet.
Extreme Case Studies and Surprising Trends

Record low sea ice years and short-term “recovery” periods can mislead public perception about the long-term trends of ice melt. It is essential to consider long-term data rather than short-term fluctuations when assessing the overall impact of climate change on sea ice.
Citizen science and community monitoring efforts are crucial in real-time tracking and analyzing sea ice changes. These efforts provide valuable data and insights into the complex dynamics of sea ice and its impact on the environment.
Geoengineering Proposals to Protect Glaciers

Innovative but controversial geoengineering ideas have been proposed, such as the “bubble curtain” to slow glacier melting in Antarctica. A key debate exists between geoengineering advocates and climate scientists, with the latter emphasizing the need for emission reductions. Economic and ethical considerations surround these large-scale intervention projects.
Geoengineering proposals spark discussions about their feasibility, potential side effects, and whether they distract from addressing the root causes of climate change.
Historical Context – Early Warnings and Scientific Predictions

Warnings from the 1970s and 1980s highlighted the vulnerability of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet. These early scientific insights have evolved into present-day urgency as the impacts of climate change become more pronounced. The historical context of these warnings underscores the importance of heeding scientific advice and taking proactive measures to address climate change.
Understanding the progression of scientific knowledge on ice melt helps to contextualize the current state of urgency and the need for immediate action.
Intersections with Other Fields and Industries

Shifting shorelines impact coastal infrastructure, real estate, and insurance industries. Fisheries, shipping routes, and indigenous communities dependent on stable ice conditions also face implications. Technology and data analytics play a role in forecasting and adaptation strategies.
The far-reaching consequences of melting ice extend beyond environmental concerns, affecting various sectors and communities worldwide. Addressing these intersections requires interdisciplinary collaboration and comprehensive adaptation strategies.
Contrarian Views and the Importance of Scientific Consensus

Climate skepticism and denialism tactics often target ice melt data, necessitating clear and honest communication to counter misinformation. Promoting informed policy decisions requires addressing contrarian views and reinforcing the importance of scientific consensus.
Overcoming misinformation and promoting accurate information is essential for fostering public understanding and support for climate action. Highlighting the consensus among climate scientists helps to dispel doubts and promote evidence-based decision-making.
Preparing for a Redrawn World

Global cooperation in mitigation and adaptation is urgently needed. Combining emission reductions with innovative solutions and robust scientific monitoring is essential. Policymakers, scientists, and the public must engage with the evolving reality of our coastlines.
Preparing for a redrawn world requires collective action, informed decision-making, and a commitment to addressing the challenges of melting ice. Embracing a collaborative approach is crucial for navigating the uncertainties and ensuring a sustainable future for coastal communities and ecosystems.
Explore more of our trending stories and hit Follow to keep them coming to your feed!
Don’t miss out on more stories like this! Hit the Follow button at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest news. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!







