
The Axial Seamount, an underwater volcano located off the coast of Oregon, has garnered attention from scientists due to signs indicating a potential eruption in 2025. This volcano, situated 300 miles from the shore and one mile beneath the Pacific Ocean, is the most active underwater volcano in the Pacific Northwest. Recent observations reveal significant swelling and seismic activity, prompting researchers to predict an imminent eruption. This article explores the current state of Axial Seamount, its monitoring efforts, and the implications of its potential eruption.
Location and Characteristics
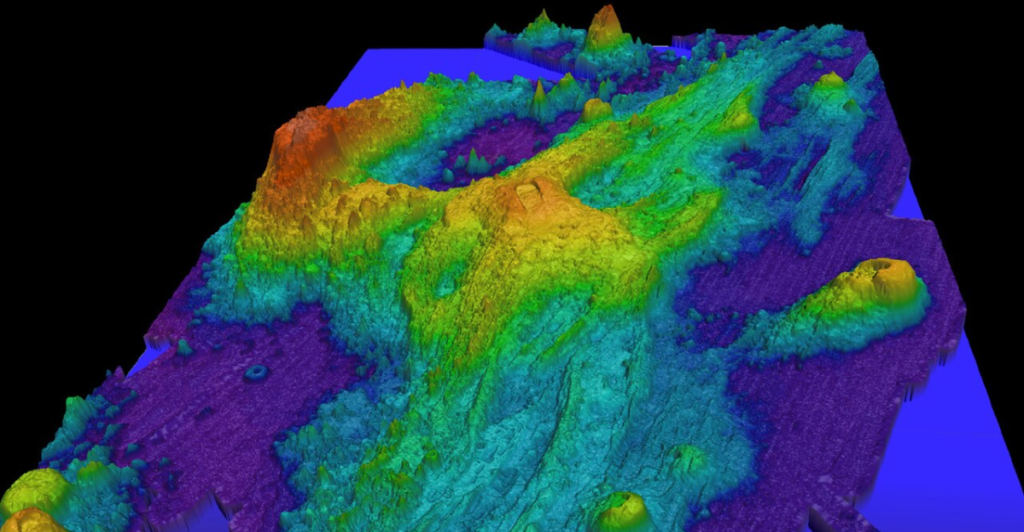
The Axial Seamount is positioned nearly 300 miles west of Cannon Beach, Oregon, making it one of the most remote yet closely monitored underwater volcanoes. It is classified as a shield volcano, which typically results in lava flows rather than explosive eruptions. This unique structure allows for extensive study without posing a direct threat to human populations on land.
Recent Activity
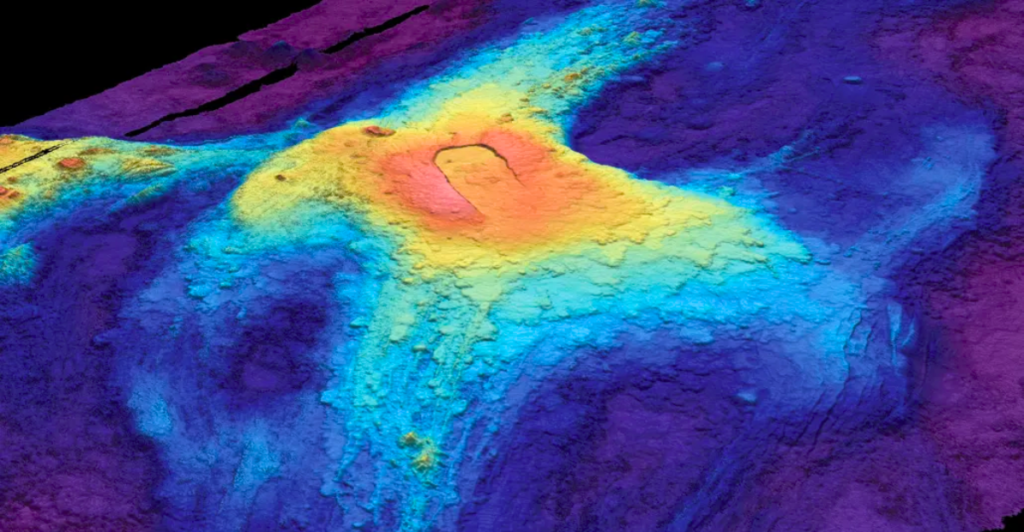
In late 2023 and early 2024, scientists noted a significant increase in the swelling of Axial’s surface. The volcano has been inflating at a rate of approximately 10 inches per year, with seismic activity recording hundreds of small earthquakes daily. This pattern mirrors the behavior observed before previous eruptions in 1998, 2011, and 2015.
Monitoring Efforts
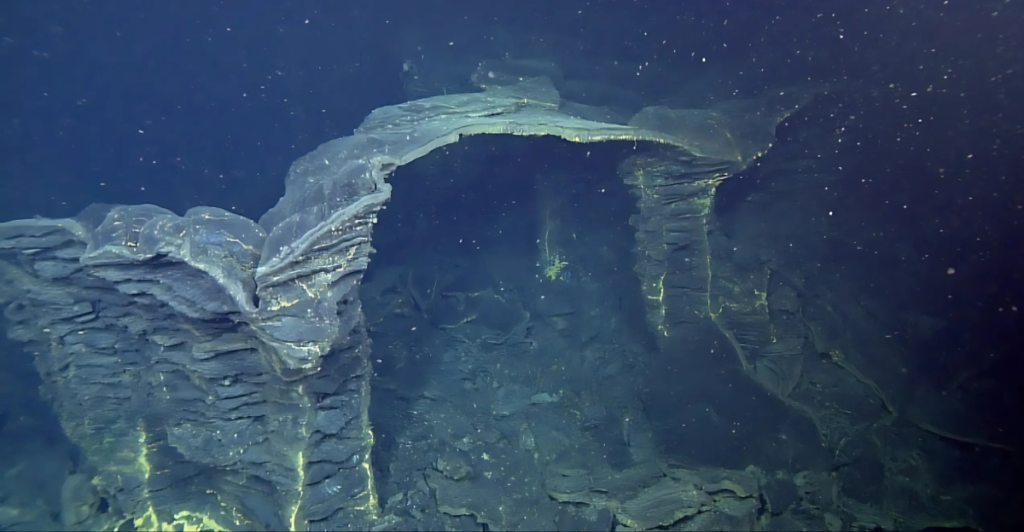

The Axial Seamount is equipped with sophisticated monitoring systems that have made it the most observed submarine volcano globally. The New Millennium Observatory (NeMO) utilizes a network of sensors to capture real-time data on seismic activities and surface changes. This continuous monitoring allows researchers to track changes closely and understand the dynamics leading up to an eruption.
The Significance of Inflation

Inflation of the volcano’s surface is a critical indicator of potential eruptions. Researchers have found that when magma accumulates underground, it causes the surface to swell, leading to increased pressure in the surrounding areas. The recent inflation has reached about 95% of the level recorded before the last eruption in 2015, raising alarms about an impending eruption.
Research Presentation
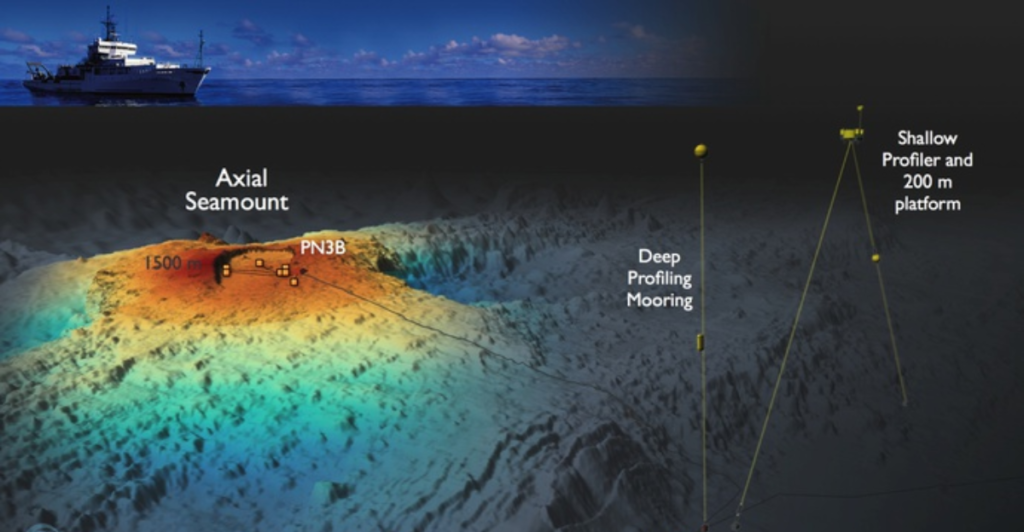
At a recent American Geophysical Union conference, scientists presented their findings regarding Axial Seamount’s inflation and seismic activity. The data collected over years has provided valuable insights into volcanic behavior and eruption forecasting techniques. Researchers emphasized that while predictions are becoming more reliable, they remain cautious about declaring an imminent eruption.
Implications for Eruption Forecasting
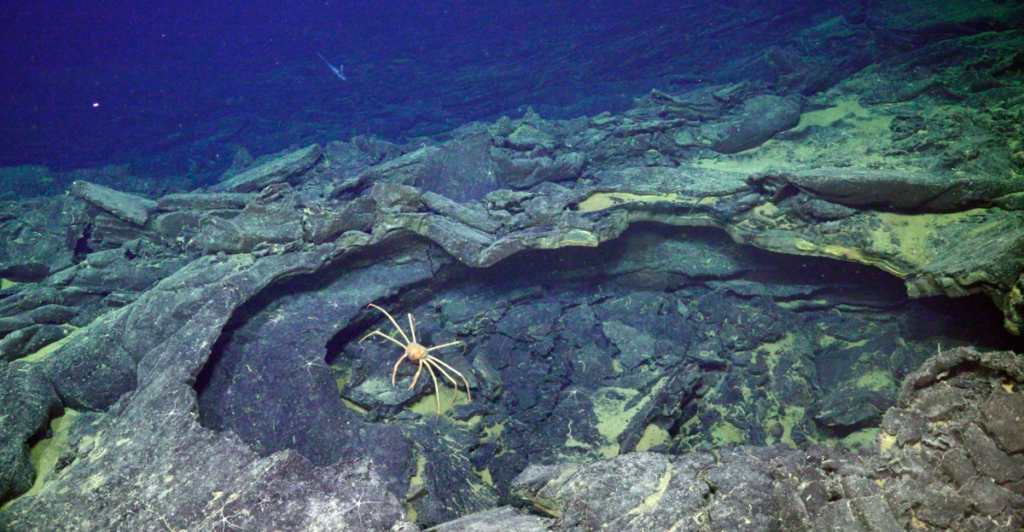

The Axial Seamount serves as an ideal natural laboratory for studying volcanic activity due to its regular eruptions and extensive monitoring capabilities. Bill Chadwick, a leading volcanologist at Oregon State University, noted that this research could enhance forecasting techniques for other volcanoes worldwide.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence
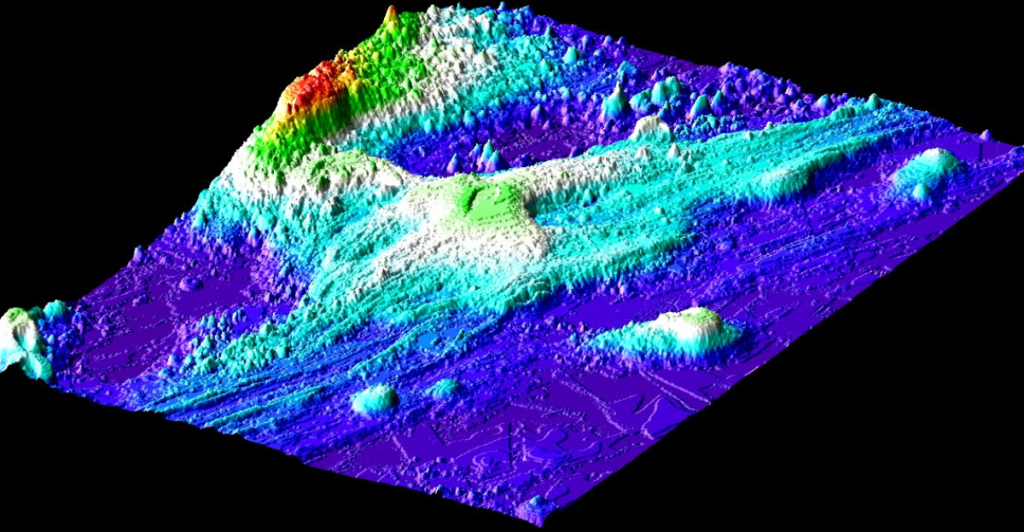
Recent advancements in artificial intelligence are being utilized to analyze earthquake patterns associated with previous eruptions at Axial Seamount. By identifying specific precursory signals from past events, researchers aim to improve their predictive models for future eruptions. This innovative approach could revolutionize how scientists forecast volcanic activity.
Challenges in Volcanic Forecasting
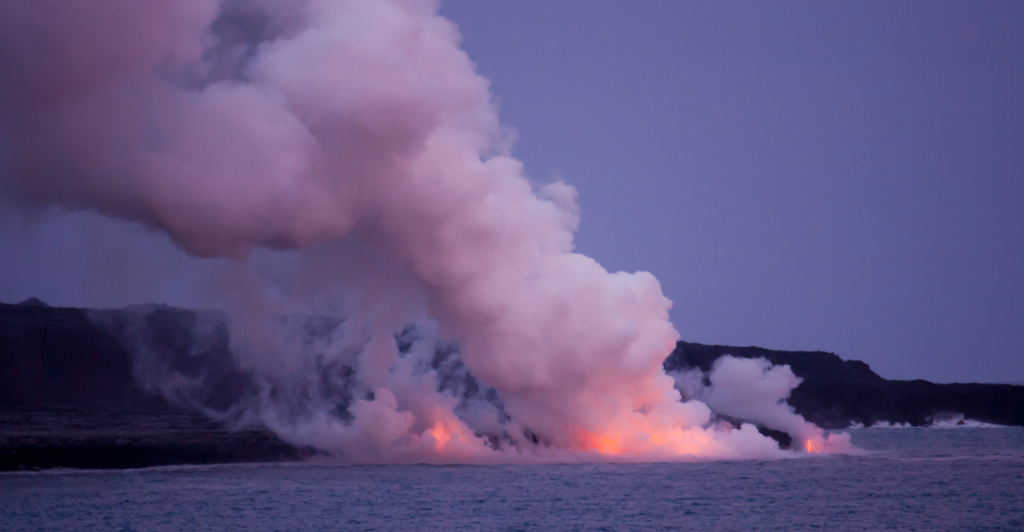

Despite advancements in monitoring technology and data analysis, predicting volcanic eruptions remains fraught with challenges. Eruptions can be unpredictable; there is always a risk that a volcano may behave differently than expected based on historical patterns. Scientists must remain vigilant and adaptable in their forecasting methods.
Nature of Potential Eruptions
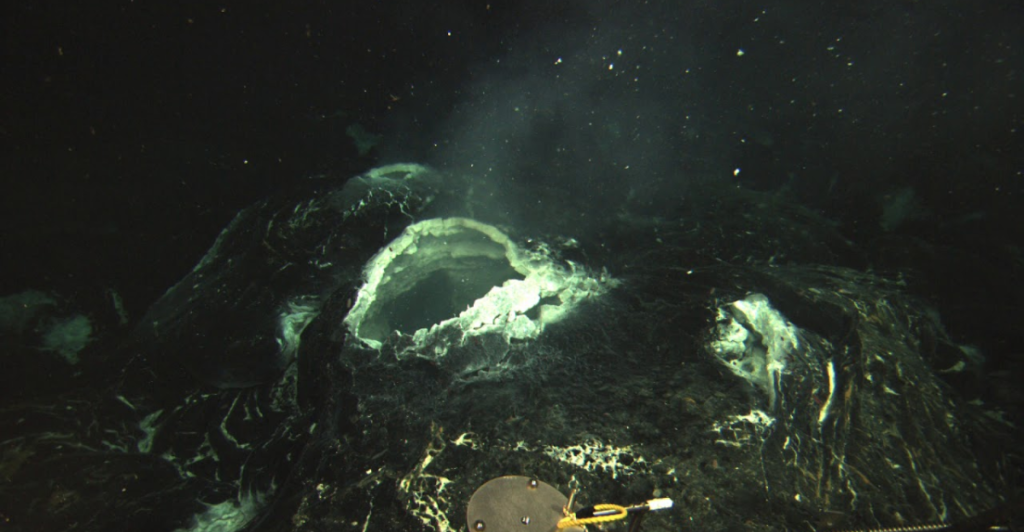

When Axial Seamount does erupt, it is expected to do so quietly rather than explosively. As a shield volcano, it will likely release lava flows rather than ash clouds or violent explosions. This characteristic allows for safer observation and study during eruptive events.
Learning from Eruptions

Researching volcanic eruptions provides invaluable knowledge about geological processes and environmental impacts. Understanding how magma behaves before an eruption can inform not only scientific inquiry but also public safety measures in areas near active volcanoes.
An Ongoing Study

The ongoing study of Axial Seamount highlights the importance of monitoring underwater volcanoes and developing reliable forecasting techniques. As scientists continue to gather data and refine their models, they hope to unlock new insights into volcanic behavior that can be applied globally. The potential eruption of Axial Seamount serves as both a warning and an opportunity for scientific advancement in understanding these powerful natural phenomena.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them appearing in your feed
California Is Splitting Apart: A Fault Line Is Forming Faster Than Anyone Predicted
Deepest Hole On Earth Permanently Sealed After 2 Billion Year Old Discovery
“There Will Be Eruptions”: Concerns Mount as Yellowstone Supervolcano Activity Increases
Dormant for 800 Years, This American Volcano Is Waking Up
References:
An Undersea Volcano Near Oregon May Erupt in 2025, Scientists Predict. It Could Help Improve Eruption Forecasts
Undersea volcano off Oregon coast could erupt this year, geologists predict
Underwater volcano off the US coast could erupt at any moment
Pacific Northwest’s busiest volcano predicted to erupt by end of 2025
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







