
Antarctica’s ice sheets have been experiencing accelerated melting in recent decades, contributing significantly to global sea-level rise. This phenomenon affects coastal communities and profoundly affects ocean circulation and worldwide climate. Understanding the mechanisms behind Antarctic ice loss is crucial for predicting future climate scenarios and developing effective mitigation strategies.
The West Antarctic Ice Sheet’s Vulnerability

The West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS) is particularly susceptible to melting due to its position below sea level and exposure to warming ocean currents. Recent studies indicate that ice loss from the WAIS adds approximately 1,100 to 1,500 billion tons of freshwater to the Southern Ocean annually, influencing ocean salinity and density.
Freshwater Input and Ocean Stratification

The influx of freshwater from melting Antarctic ice leads to ocean freshening, reducing salinity levels. This freshening enhances stratification, stabilizing ocean layers and hindering the mixing of surface and deep waters. Such changes can disrupt nutrient cycles and impact marine ecosystems.
Impact on Southern Ocean Circulation

Increased stratification affects the Southern Ocean’s overturning circulation, a critical component of global ocean currents. The upper cell of this circulation has strengthened by 50–60% since the 1970s, while the larger lower cell has weakened by 10–20%. These shifts alter heat and carbon absorption, influencing global climate systems.
Antarctic Circumpolar Current Weakening

The Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC), which merges waters from the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans, has shown signs of weakening. Projections suggest that 2050 the ACC could lose 20% of its strength, affecting ocean circulation and climate patterns.
Potential Collapse of Deep Ocean Currents

There is concern that continued ice melt and freshwater input could lead to the collapse of deep ocean currents. Such a collapse would have long-term effects on global climate, including changes in precipitation patterns and marine ecosystems.
Methane Emissions from Melting Ice

Researchers have discovered methane plumes from “fire ice” beneath Antarctica’s seabed. These emissions, previously noted only in the Arctic and Black Sea, are not included in current climate models and need further examination to determine their atmospheric impact.
Record Low Antarctic Sea Ice Extent

Antarctic sea ice is nearing a record winter low for the second consecutive year, continuing a sharp decline in Southern Ocean ice coverage. On September 7, 2024, sea ice coverage was even less than the previous year’s record low, with the current coverage at 17 million square kilometers. In contrast, the long-term average is 18.4 million square kilometers.
Iceberg A23a Grounding Near South Georgia

The world’s largest iceberg, A23a, weighing nearly one trillion tons, has run aground near South Georgia island. While it may pose operational challenges for commercial fisheries, scientists are keen to observe how the iceberg will affect the ecosystem.
Implications for Global Sea Levels

The melting of Antarctic ice contributes to rising sea levels, posing threats to coastal communities worldwide. Understanding ice loss dynamics and ocean circulation is crucial for predicting future sea-level rise and implementing adaptive measures.
Feedback Loops and Climate Change

The interactions between ice melt, ocean circulation, and climate create feedback loops that can amplify global warming. For instance, reduced sea ice leads to less sunlight reflection, increasing ocean warming and further ice melt.
Ecological Consequences

Ocean circulation and temperature changes affect marine ecosystems, including nutrient distribution and habitat conditions. Species adapted to specific environments may face challenges, leading to shifts in biodiversity.
Future Outlook
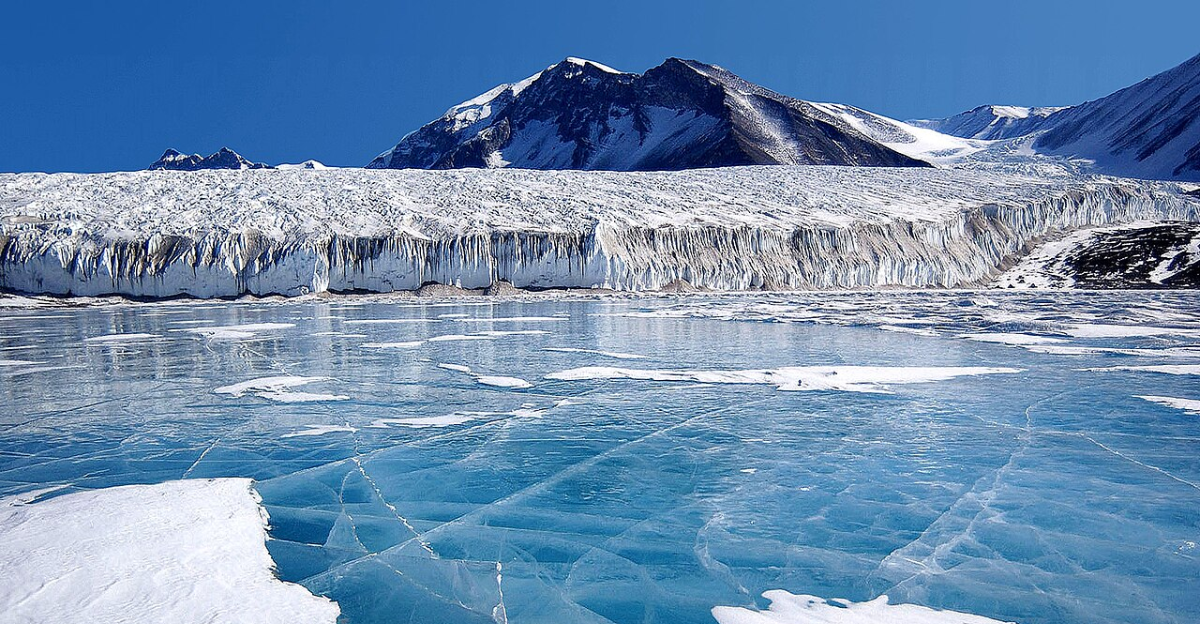

Antarctic ice loss is intricately linked to ocean dynamics and global climate. Ongoing research is essential to monitor these changes and inform policy decisions to mitigate climate impacts. Collaborative efforts are crucial to address the challenges of a changing Antarctic environment.
Explore more of our trending stories and hit Follow to keep them coming to your feed!
Don’t miss out on more stories like this! Hit the Follow button at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest news. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!







