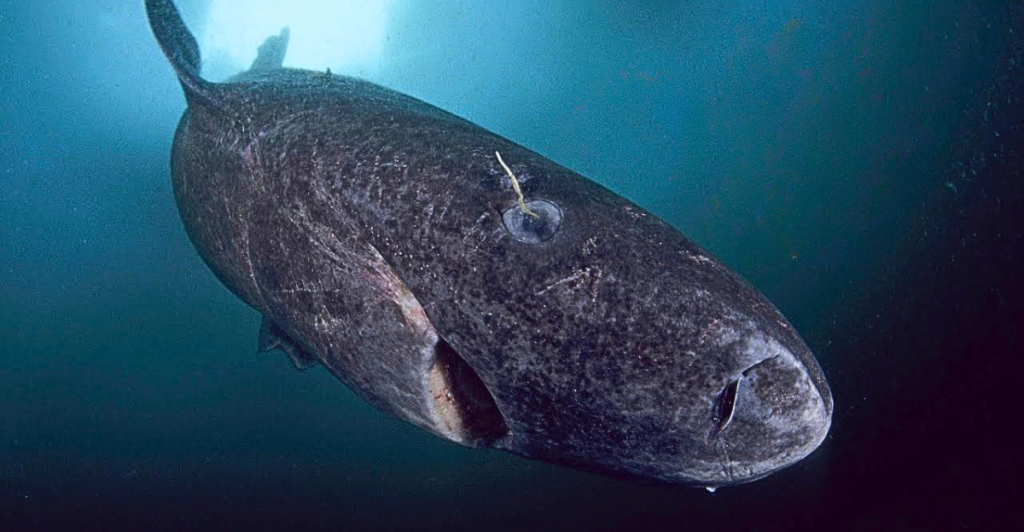

In the icy depths of the North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans resides a creature of remarkable endurance: the Greenland shark (Somniosus microcephalus). Renowned for their extraordinary lifespans, these elusive sharks can live for several centuries, with some individuals estimated to reach up to 500 years of age.
This unparalleled longevity has captivated scientists, prompting investigations into the biological mechanisms that enable such extended lifespans.
The Greenland Sharks
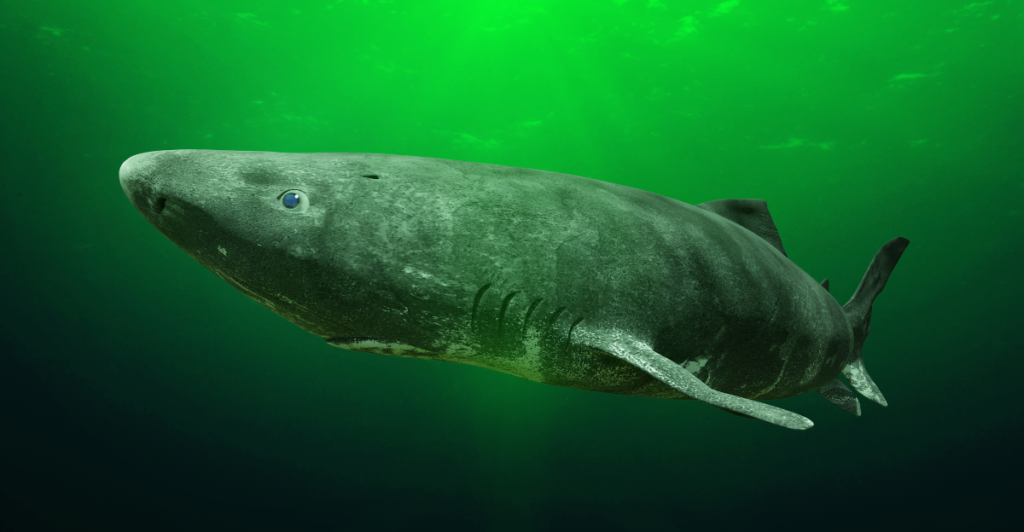

Recent studies have shed light on the Greenland shark’s unique physiological traits, offering potential insights into human aging and longevity. Researchers are particularly interested in understanding how these sharks maintain metabolic stability and cardiovascular health over centuries. By unraveling these mysteries, scientists hope to uncover strategies that could one day contribute to extending human lifespan and improving health in our later years.
The Remarkable Lifespan of Greenland Sharks
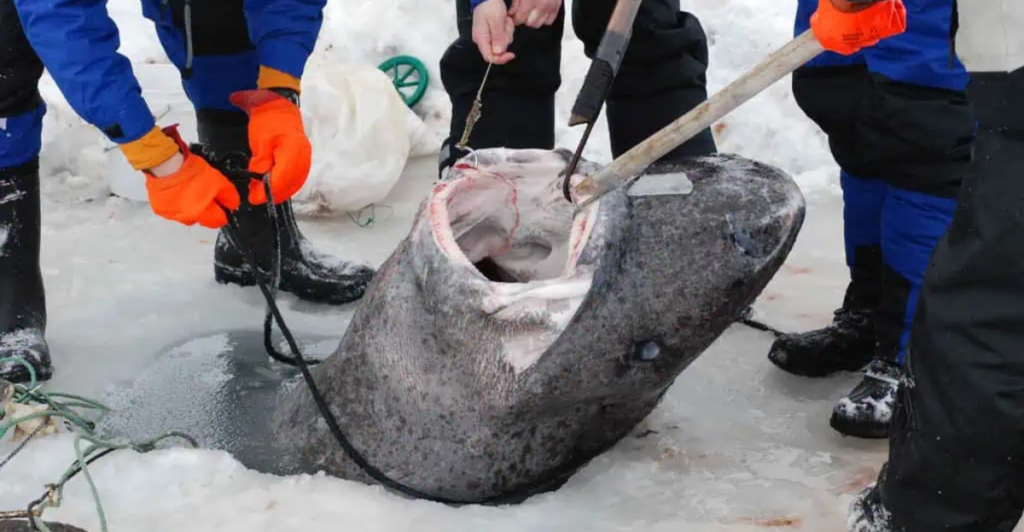

Greenland sharks hold the record as the longest-living vertebrates on Earth. Radiocarbon dating of eye lens tissues has revealed that these sharks can live for at least 250 years, with some estimates suggesting lifespans exceeding 400 years.
This exceptional longevity is attributed to their slow growth rate, low metabolic rate, and the frigid temperatures of their deep-sea habitat.
Why Do They Live So Long
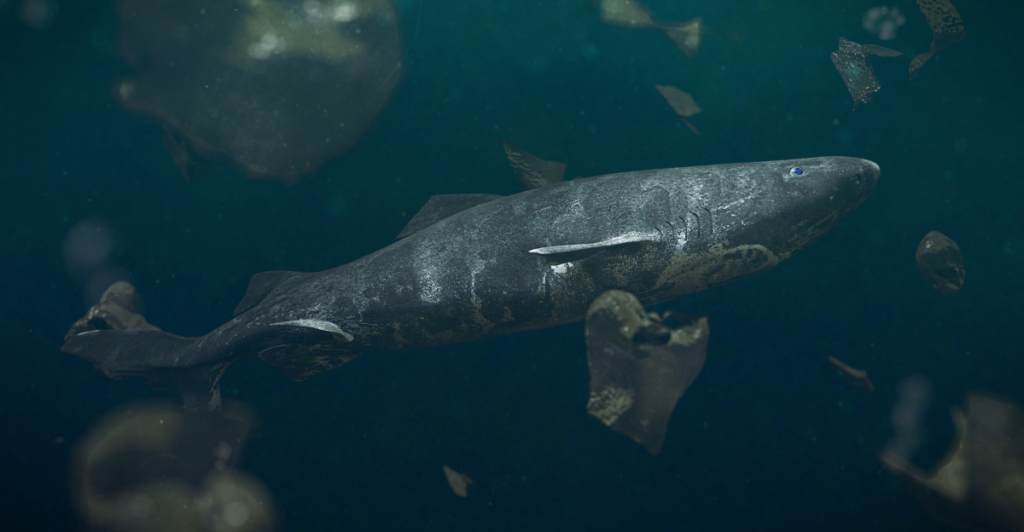

Unlike many other species, Greenland sharks exhibit minimal decline in muscle metabolic rate as they age. Studies have shown that their enzyme activity remains consistent throughout their lives, a phenomenon that contrasts with the metabolic slowdown observed in aging humans and other animals.
This metabolic stability may play a crucial role in their extended lifespans, providing a model for understanding aging processes.
Metabolic Stability and Aging
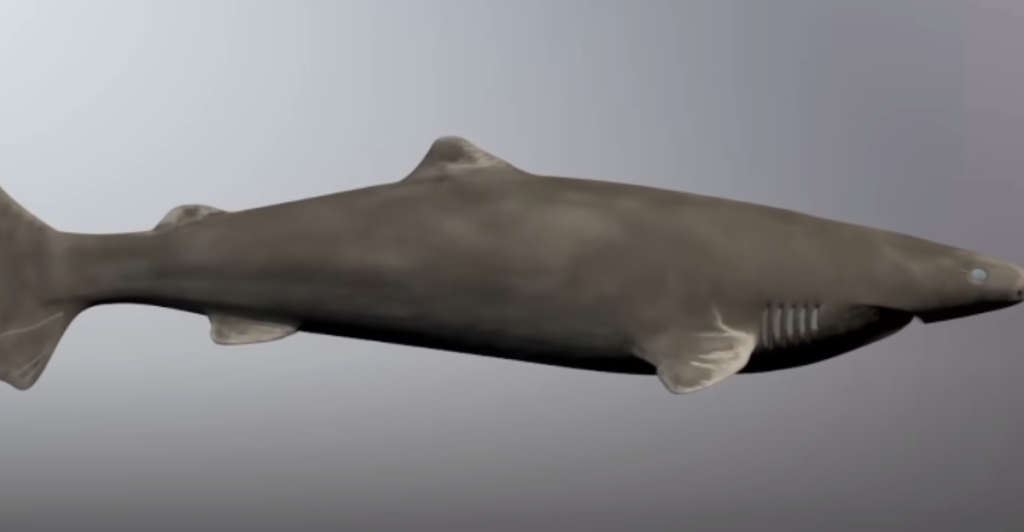

The consistent metabolic activity observed in Greenland sharks suggests a unique adaptation to their cold, deep-sea environment. Their slow metabolic rate, influenced by the low temperatures of their habitat, reduces the accumulation of cellular damage over time. This metabolic steadiness may contribute to their longevity by minimizing the wear and tear that typically accompanies aging in other species.
Slow Sharks
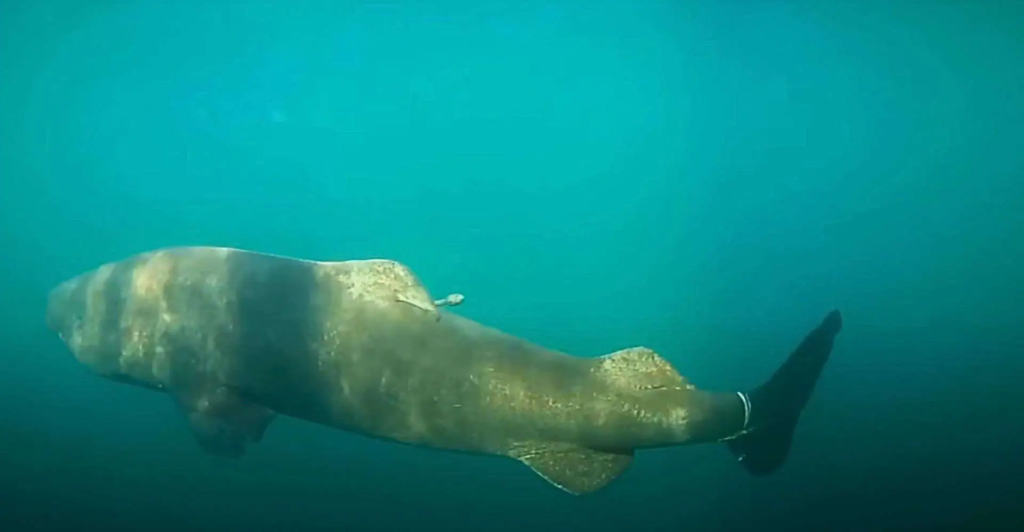

Understanding the mechanisms behind this metabolic stability could have significant implications for human health. If researchers can identify the factors that allow Greenland sharks to maintain consistent metabolic rates, it may lead to interventions that promote metabolic health and longevity in humans. Such discoveries could pave the way for therapies aimed at reducing age-related metabolic decline.
Cardiovascular Health and Longevity
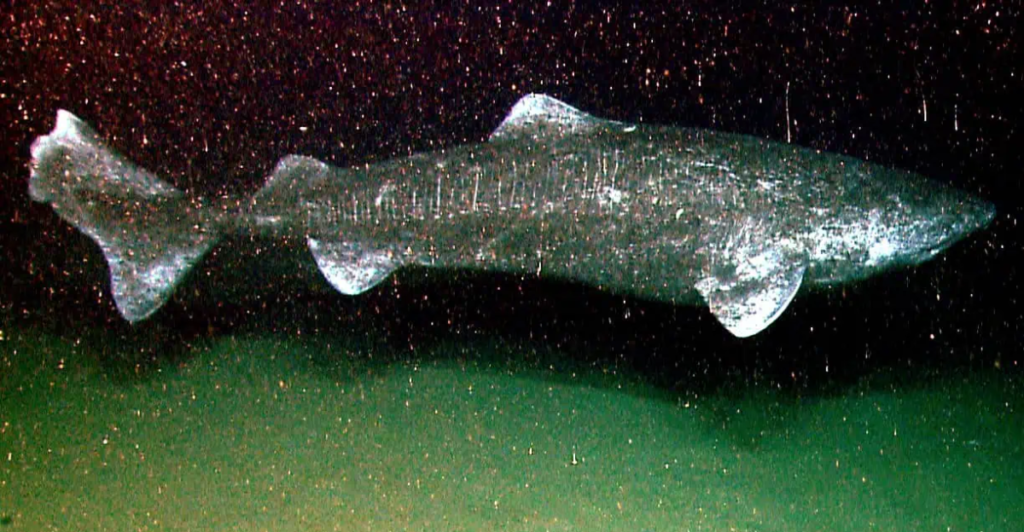
Another area of interest is the cardiovascular health of Greenland sharks. Despite their advanced age, these sharks do not exhibit the arterial stiffness commonly associated with aging in humans. Their heart cells and coronary arteries maintain flexibility and function even in old age, suggesting protective mechanisms that preserve cardiovascular health.
Investigating these protective mechanisms could offer valuable insights into preventing cardiovascular diseases in humans. By studying how Greenland sharks maintain arterial flexibility, scientists may identify novel approaches to combat age-related cardiovascular issues, potentially extending human lifespan and improving quality of life in older adults.
Genetic Insights into Longevity
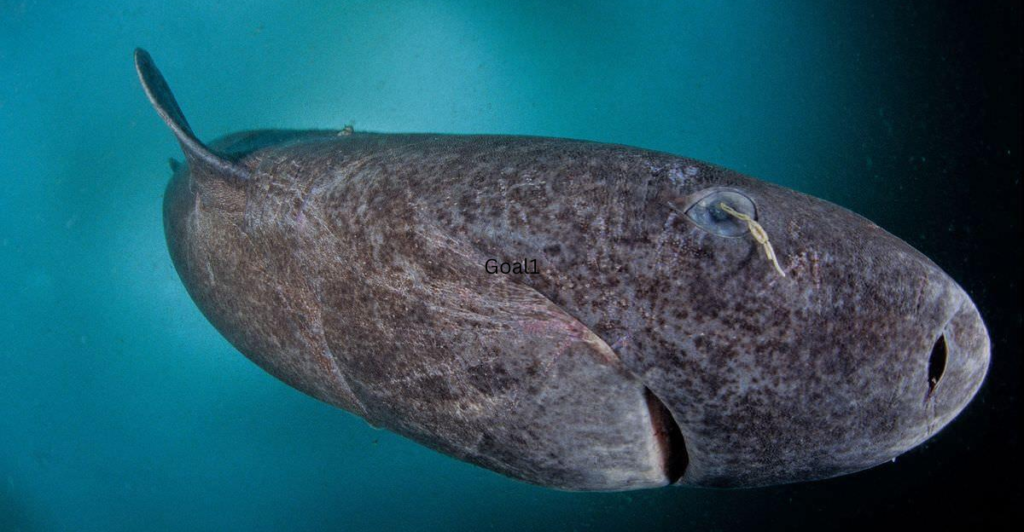

The genetic makeup of Greenland sharks is another focal point for researchers. Sequencing their genome has revealed unique genetic adaptations that may contribute to their longevity. Identifying genes associated with DNA repair, protein stability, and resistance to oxidative stress could provide clues about the biological processes that enable such extended lifespans.
In The Genes
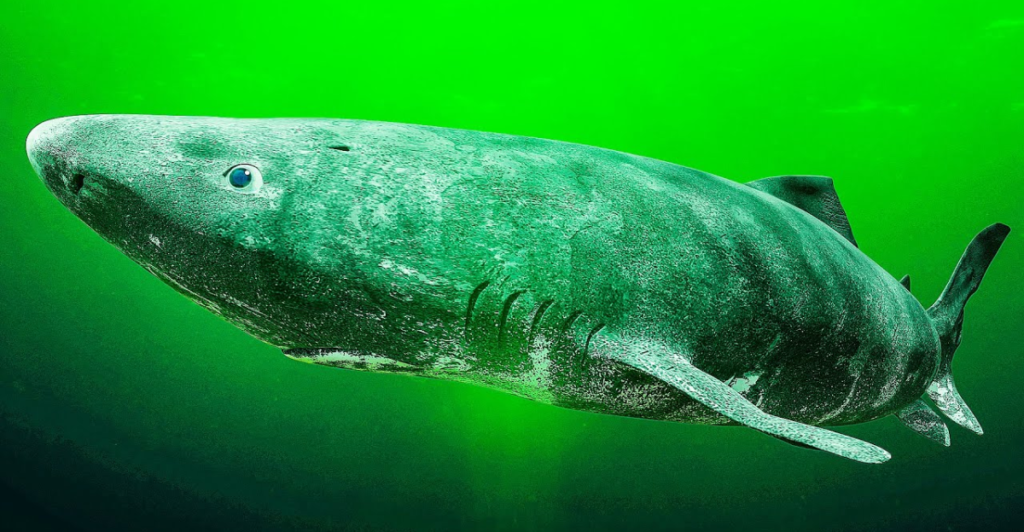

These genetic insights have the potential to inform human medicine. By understanding the genetic factors that promote longevity in Greenland sharks, scientists may develop gene-based therapies or interventions that enhance human healthspan, delaying the onset of age-related diseases and extending healthy living.
Conservation Concerns

Despite their resilience, Greenland sharks face conservation challenges. Their slow growth and late maturity make them vulnerable to overfishing and environmental changes. Climate change, in particular, poses a threat to their deep-sea habitat, potentially disrupting the delicate balance that supports their longevity.
Save Our Sharks
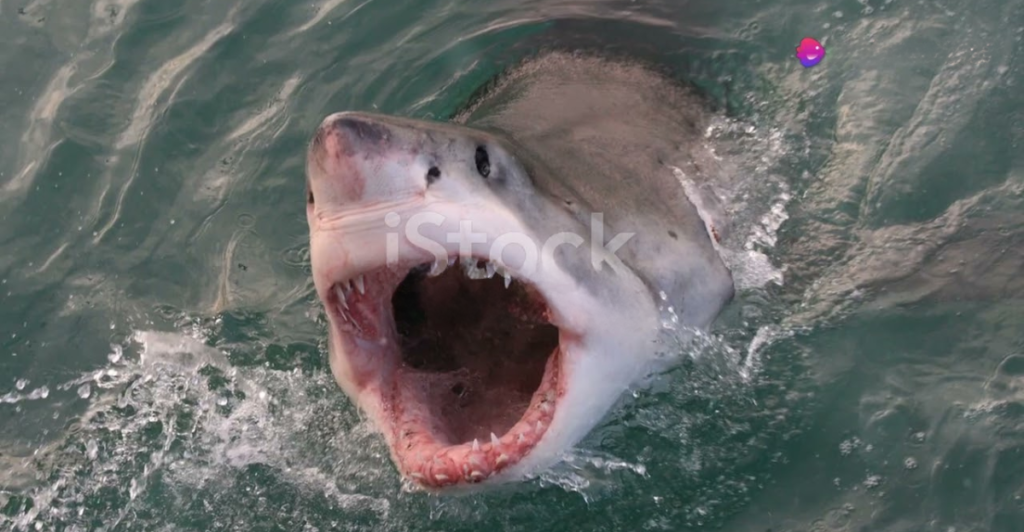

Protecting Greenland sharks is essential not only for preserving biodiversity but also for maintaining the opportunity to study their unique biology. Conservation efforts that safeguard their populations will ensure that researchers can continue to explore the secrets of their longevity, with the potential to unlock benefits for human health.
Implications for Human Longevity

The study of Greenland sharks offers a promising avenue for understanding the biological underpinnings of aging. Their exceptional lifespans and unique physiological traits provide a natural model for exploring how longevity can be achieved. Insights gained from these studies may inform the development of interventions that promote healthy aging in humans.
By translating the lessons learned from Greenland sharks into human medicine, there is potential to extend human lifespan and improve health outcomes in older adults. Research into their metabolic stability, cardiovascular health, and genetic adaptations could lead to breakthroughs that mitigate age-related decline and enhance quality of life.
Testing The Research

The Greenland shark’s extraordinary lifespan and resilience offer a window into the possibilities of extended longevity. Through continued research, scientists aim to uncover the biological mechanisms that enable these sharks to thrive for centuries. Such discoveries hold promise not only for understanding the natural world but also for applying these lessons to human health and aging.
As we delve deeper into the mysteries of the Greenland shark, we move closer to unlocking the secrets of longevity. The potential applications of this knowledge could revolutionize our approach to aging, paving the way for a future where extended healthspan and lifespan are within reach.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them appearing in your feed.
Meet the Massive Crocodiles That Make Their Homes 40 Feet Underground
The 10 Largest Sharks Ever Known to Roam the Seas
The 12 Most Aggressive Sharks and Where to Find Them
How Sharks Became Earth’s Ultimate Survivors
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







