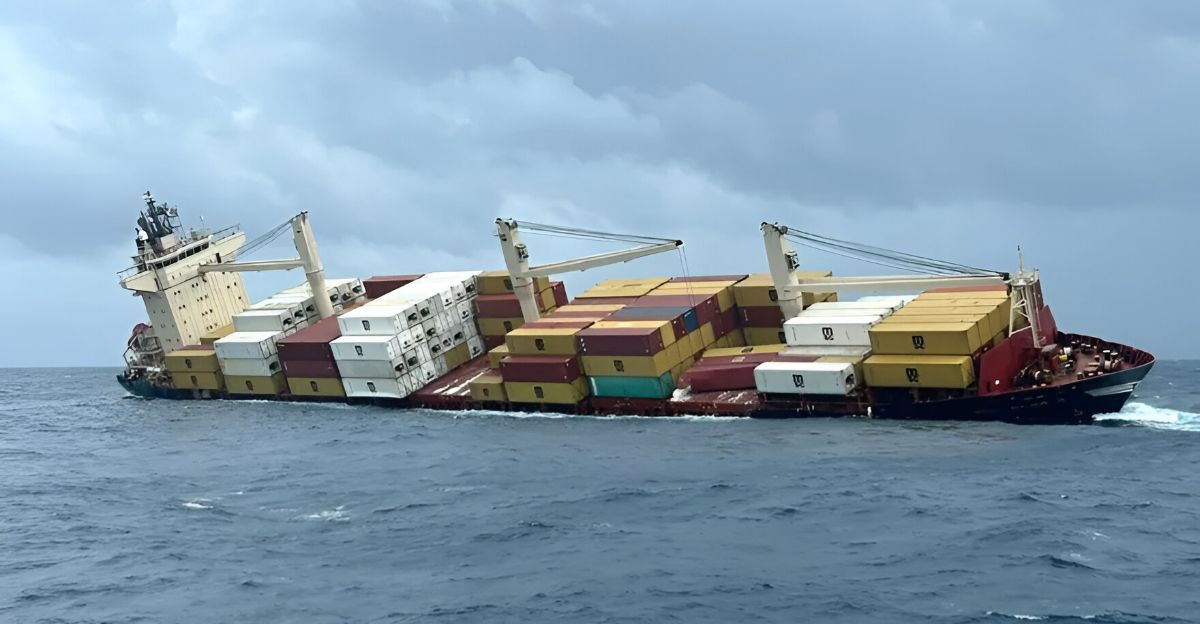

On May 25, 2025, the Liberian-flagged container ship MSC Elsa 3 sank about 38 nautical miles southwest of Kochi, India, after developing a severe starboard list due to flooding. The 184-meter vessel carried 640 containers, including 13 with hazardous cargo and 12 containing calcium carbide, plus over 450 metric tonnes of marine fuel (diesel and furnace oil).
The Indian Coast Guard and Navy safely rescued all 24 crew members. The sinking released numerous containers into the Arabian Sea, some washing ashore in Kerala, raising immediate concerns about toxic spills and threats to marine life and coastal ecosystems.
The Scale of Container Ship Losses and Environmental Impact
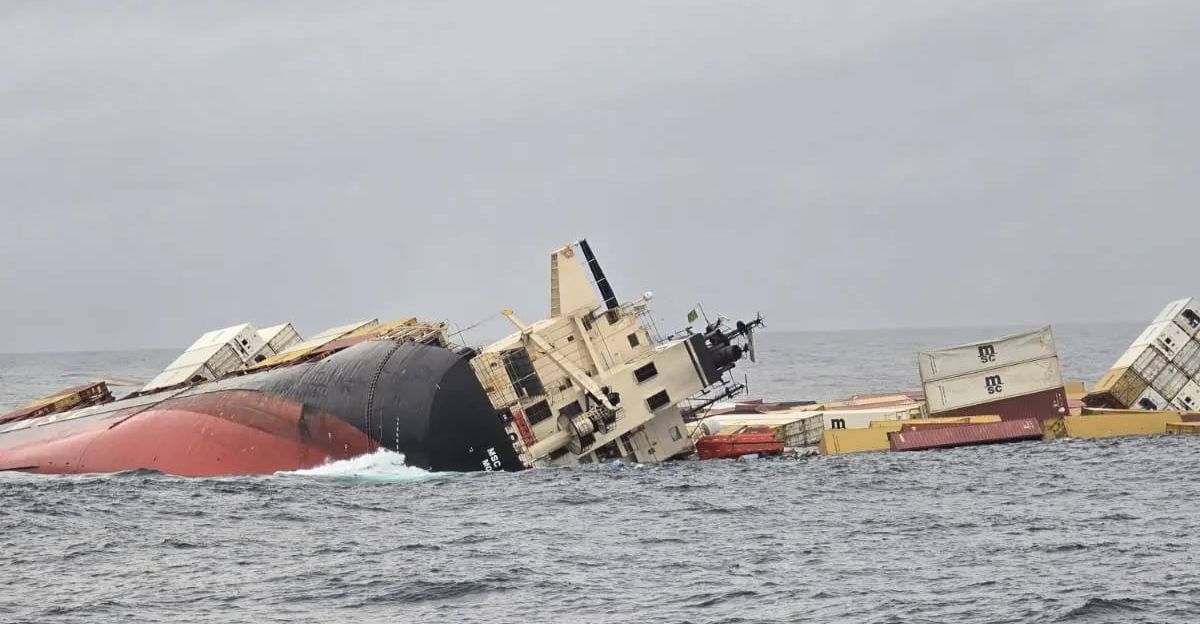

Globally, over 20,000 shipping containers have been lost at sea in the past 15 years, posing a persistent environmental hazard. Lost containers release plastics, chemicals, and hazardous materials that pollute oceans and coastlines. These pollutants degrade marine habitats, threaten biodiversity, and accumulate in deep-sea ecosystems.
The MSC Elsa 3 incident adds to this growing problem, with more than 100 containers reported lost in the Arabian Sea, some drifting toward sensitive coastal areas in Kerala.
Hazardous Cargo and Toxic Spills – Specific Risks to Marine Life
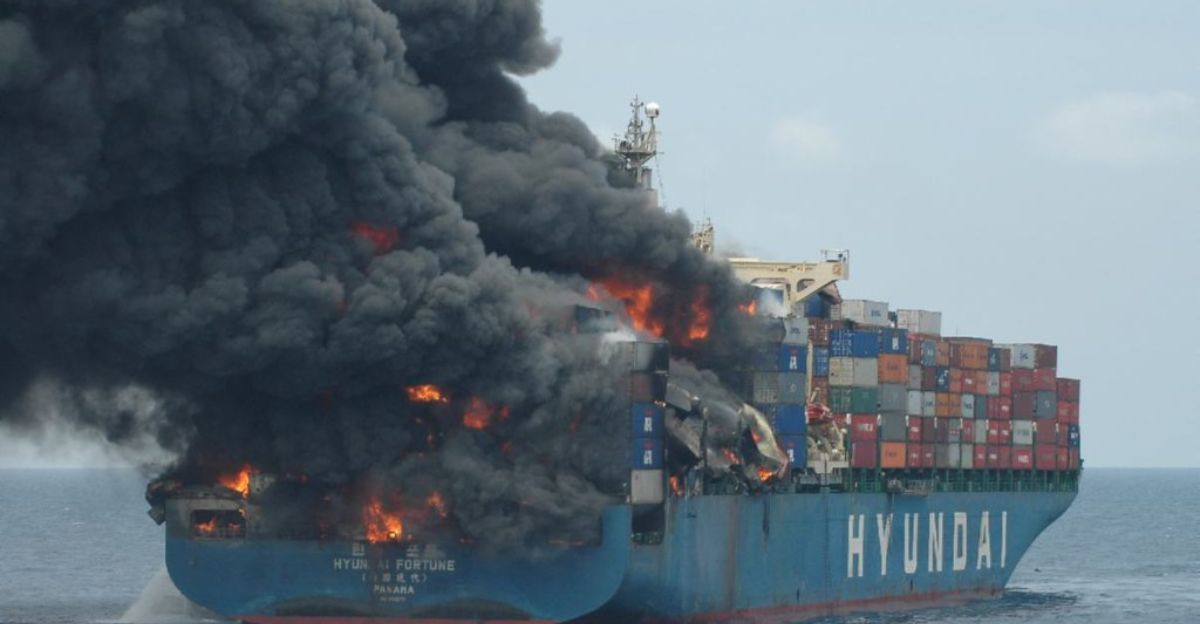

Hazardous cargo like calcium carbide, diesel, furnace oil, and fertilizers carried by container ships are highly toxic to marine organisms. Spills can damage mangroves, coral reefs, and sediments, as seen in past oil spills such as the Wakashio disaster.
Chemical contaminants bioaccumulate, entering the food chain and threatening fish, seabirds, and mammals. The MSC Elsa 3’s cargo leakage risks similar toxic impacts on marine biodiversity and fisheries along the Kerala coast.
Disruption of Marine Ecosystems and Biodiversity
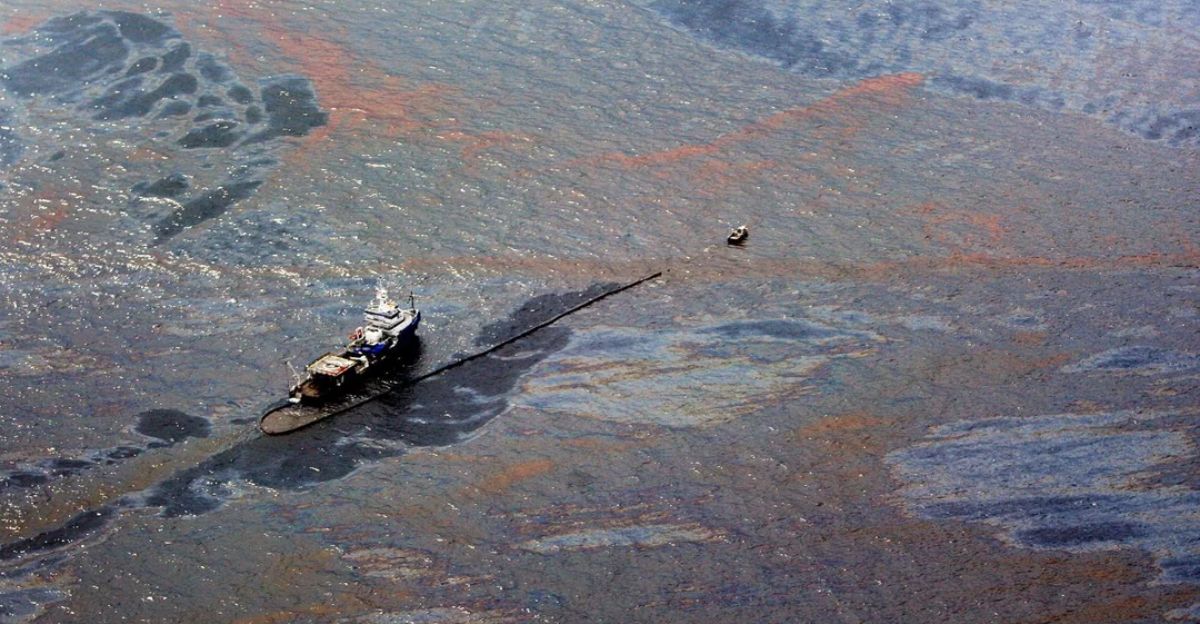

Spilled oil and chemicals physically smother habitats and chemically alter water quality, disrupting sensitive ecosystems. Marine mammals and fish suffer from toxic exposure and habitat loss, while shipwreck debris increases noise pollution and collision risks.
Additionally, invasive species can spread via ballast water or hull fouling from sunken vessels, further threatening native biodiversity. The MSC Elsa 3 sinking exemplifies these multifaceted ecological threats.
Economic and Social Consequences for Coastal Communities

Coastal communities in Kerala rely heavily on fisheries and marine resources. The sinking disrupts fishing activities, especially during breeding seasons like the monsoon, causing economic hardship.
Cleanup costs and damaged cargo add financial strain. Socially, communities face health risks from contaminated seafood and polluted beaches. The MSC Elsa 3 incident highlights the vulnerability of artisanal fishers and coastal livelihoods to maritime disasters.
Historical Context – Lessons from Past Container Ship Disasters
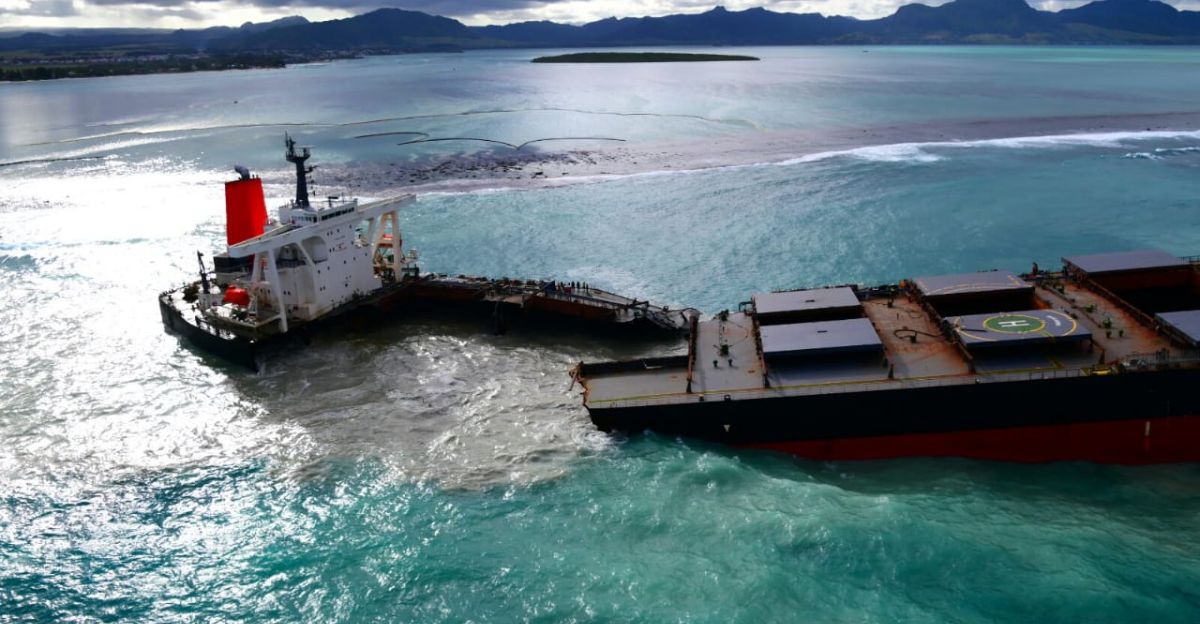

Previous container ship accidents, like the Med Taipei and Wakashio spills, demonstrate long-term environmental damage and costly cleanups. Monitoring these events has improved our understanding of spill dynamics and response strategies.
However, gaps remain in preparedness and containment. The MSC Elsa 3 sinking underscores the need to apply lessons from past disasters to better manage future incidents and reduce ecological harm.
Intersection with Geopolitical and Security Issues
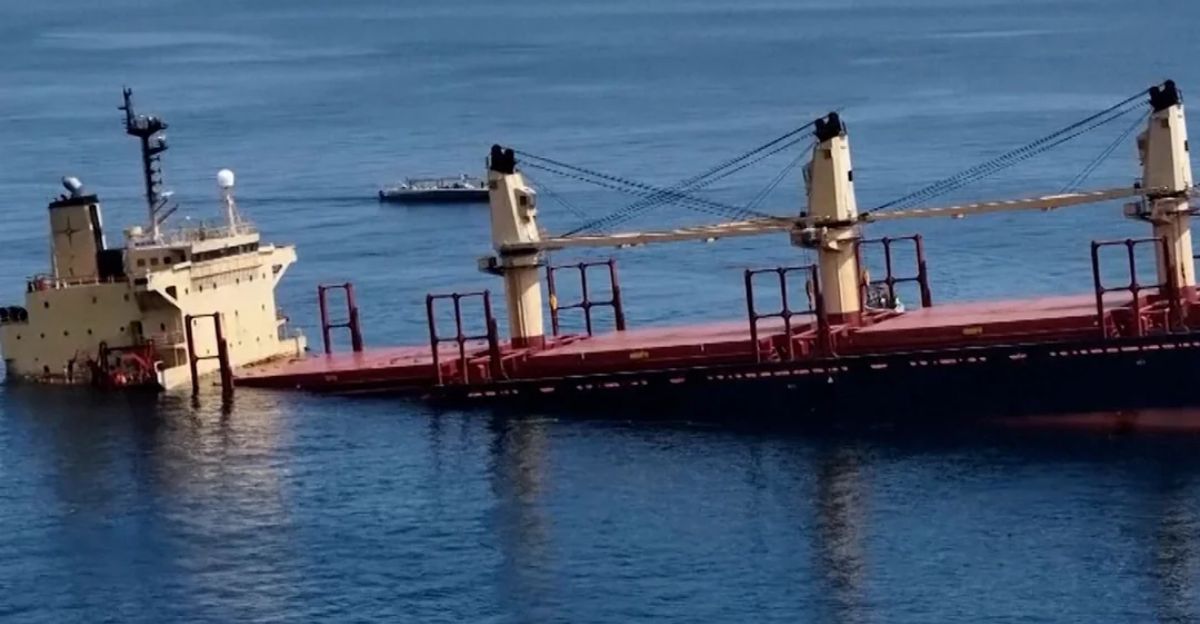

Maritime incidents like the sinking of the Rubymar in the Red Sea show how geopolitical conflicts exacerbate environmental risks by complicating rescue and cleanup efforts.
The MSC Elsa 3 sinking in a busy trade corridor highlights vulnerabilities in global shipping routes. These challenges call for enhanced international cooperation to secure marine trade lanes and mitigate environmental threats from accidents linked to geopolitical tensions.
Regulatory Gaps and the Need for Stronger Shipping Controls

Current regulations inadequately address container packaging, weight limits, and stacking safety, contributing to container losses. Emergency response protocols and crew training also require strengthening.
The MSC Elsa 3’s history of deficiencies and prior incidents reveals systemic weaknesses. International maritime organizations must enforce stricter standards and transparency to prevent similar disasters and protect marine environments.
Innovative Solutions and Industry Responses

Advances in container tracking technologies and loss prevention systems promise to reduce at-sea container losses. Sustainable shipping practices, including marine spatial planning and collaboration among shipping companies, governments, and conservation groups, aim to minimize environmental impacts.
Encouraging sustainable consumption patterns can also reduce shipping demand. The MSC Elsa 3 incident may catalyze the adoption of such innovations to safeguard oceans.
Protecting Marine Life and Future Outlook

The MSC Elsa 3 sinking illustrates the severe environmental and socio-economic stakes of container ship disasters carrying hazardous cargo. Coordinated global action is urgent to improve risk mitigation, emergency response, and regulatory frameworks.
Ongoing research and monitoring of sunken containers are essential to understanding and managing long-term impacts. Balancing global trade with marine ecosystem preservation remains a critical challenge for the future.
Explore more of our trending stories and hit Follow to keep them coming to your feed!
Don’t miss out on more stories like this! Hit the Follow button at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest news. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!







