
An individual was found in Yunnan, China, and found to be more than 7,000 years old. The remains of the woman are now called Xingyi_EN and were found at the bottom of an old burial site.
Through the use of carbon dating, scientists found her age, which was consistent with burial practices of the time, being buried to nothing else. The woman was most likely a hunter-gatherer when she was alive, which means there are implications for the ancient wildlife of the region.
A Ghost Lineage

The DNA of Xingyi_EN is among the first physical proofs of a “ghost lineage,” which was only found through traces of DNA in living humans.
For years, scientists had no reliable physical evidenc,e such as bones or artifact,s to prove this lineage existed, but that all changes now with the study of Xingyi_EN.
Special DNA
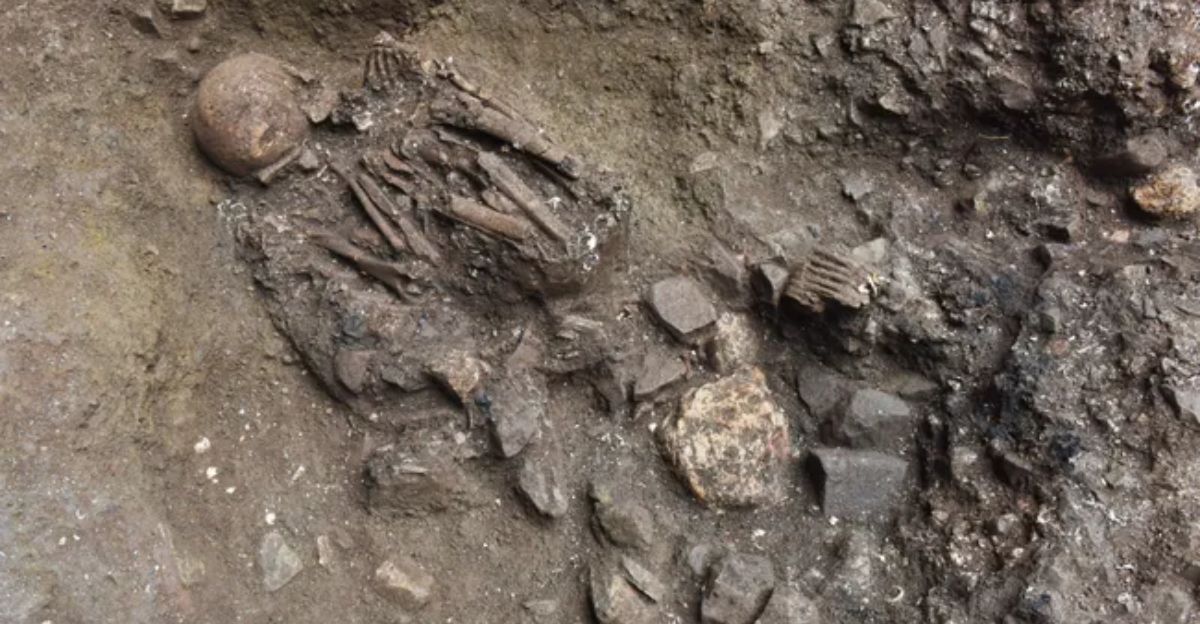

Xingyi_EN’s DNA was special once researchers examined it. Typically, scientists expect to find similar DNA in people found in certain regions, but Xingyi_EN ‘s DNA wasn’t the same as that of ancient and modern South or East Asian people.
Looking closer at her genes, it was discovered that her DNA was part of a different human group that varied from other humans and split off 40,000 years ago.
An Ancient Lineage

Xingyi_En’s lineage seems to be part of a bigger picture, and her group of people could have lived in the Yunnan area for thousands of years in complete isolation.
Her DNA showcases that there was no mixing of other human DNA, which meant it was a pure bloodline that suddenly disappeared. Humans are social animals, and even in ancient times, different groups would have interacted and interbred, but not this lineage.
Ties To Modern Lineages

Clues to Xingyi_En’s lineage have been present for many years, with scientists first finding it in modern-day Tibetan people. While 80% of Tibetans have a lineage from northern Chinese populations who moved into the region thousands of years ago, the last 20% was unique in that it couldn’t be found anywhere else.
The first time this “ghost” DNA has been found is in Xingyi_EN, providing a clearer picture of the ancient world.
A Separate Branch Of Human History

When first discovered, the ghost lineage could have been thought of as Neanderthal or Denisovan, which were other groups of early humans that did interbreed with our ancestors.
However, looking at the lineage, it’s clear that it was pure and kept completely intact even thousands of years ago. The first finding of it in physical human remains gives scientists a better window into the most diverse region of China.
A Diverse Region

Yunnan is one of the most diverse regions on the planet, boasting many different ethnic origins and languages. From studying DNA from ancient people, it is believed that the region was a staging ground for many different human migrations.
The importance of the region in human evolution is only further proved by the new discovery of Xingyi_EN and her strange lineage.
An Ancient Hunter-Gatherer

Researchers have managed to study Xingyi_En’s remains and find out key insights into what ancient life would have been like for her and her people. She lived a hunter-gatherer lifestyle, meaning that she would have interacted with ancient wildlife that even altered the local populations of deer, wild pigs, birds, and fish. Her survival would have depended on understanding animal behavior and local seasonal changes.
This would contrast farming practices, which would explode in the region later on. She wasn’t buried with anything, highlighting the way of life her people would have lived without having an attachment to physical items.
More Questions Arise

While the discovery of Xingyi_EN’s remains has given us unprecedented insight into a little-known lineage, it has also opened doors to more questions.
Scientists want to know why she has been the only one to be found with DNA, and are looking to find more of her people. As time goes on, they hope to find more evidence and see just how far this DNA has spread in the region as it has, in part, shaped the DNA of modern-day humans.
Changing Previous Notions
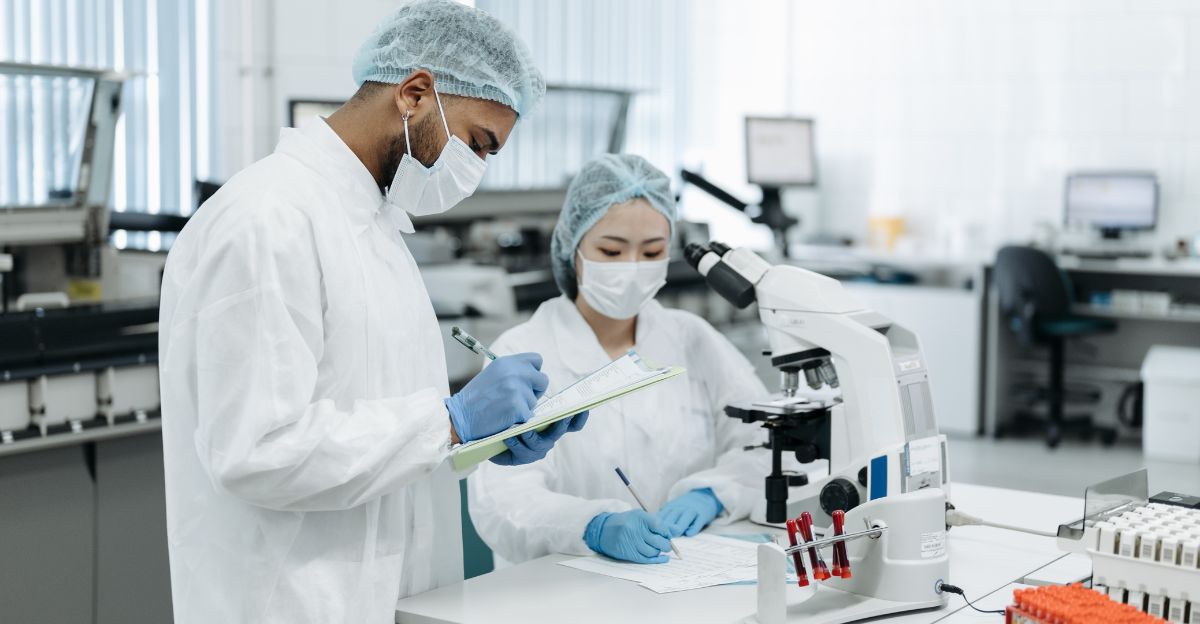

The “ghost” DNA found in the Yunnan region is changing previous notions about our ancient origins. This find alone proves that there are still undiscovered lineages that are waiting to be found.
New insights may be found as researchers continue to search for new remains and study found ones, possibly changing our perceptions of how human groups interacted with one another and survived through DNA to the modern era.
Explore more of our trending stories and hit Follow to keep them coming to your feed!
Don’t miss out on more stories like this! Hit the Follow button at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest news. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!







