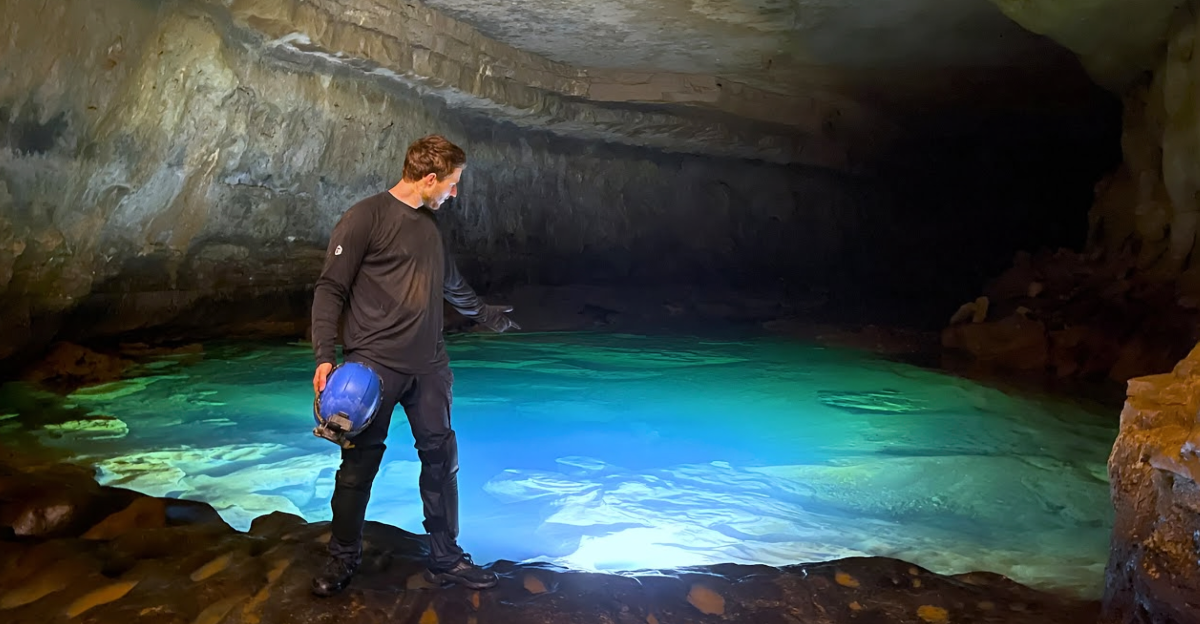

Geologists have discovered a deep blue hole that lays inside a 500ft cave. With this discovery we are one step closer to understand the karst formations with all its complexity of the coastal limestone regions. They named it Taam Ja’Blue Hole (TJBH) and it can be found in Chetimal Bay, Mexico.
This is the deepest blue hole in the world as it goes as deep as 420 meters. Basically a blue hole is vertical sinkholes under water. They are commonly formed by the dissolution of limestone and result in cave systems which could extend even further. By finding the Taam Ja’Blue Hole the existing geological frameworks are being challenged.
Historical Context
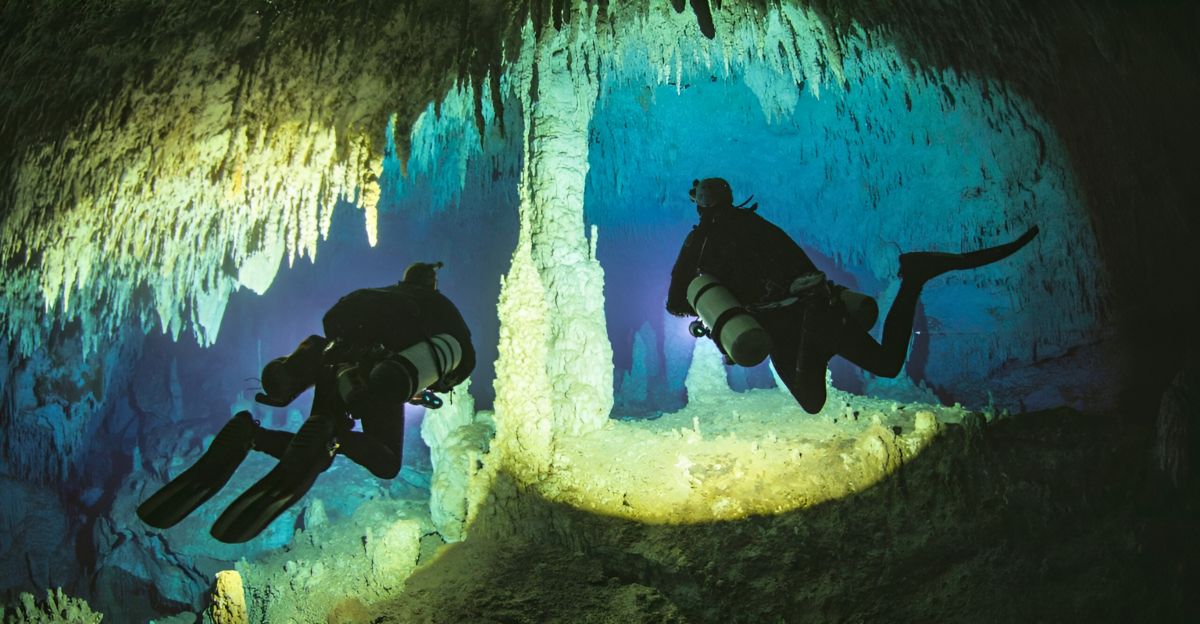

The person that first discovered the TJBH in 2003 was actually a lucky local diver from Chetumal Bay. To the diver it looked like a simple underwater cavern. He described it to be a vertical shaft but did not know the extent of the discovery he had made. Back then even scientists could not fully understand the extend of the discovery either, due to technological limitations.
Only when more sophisticated technology for underwater sensing such as CTD profilers became a reality, could more accurate measurement of the cave system be taken. While the bottom of the hole still elludes scientists, advanced sonar technology aided in exploration as deep as 900ft and up to 1 600 ft by cable in 2023.
Geological Significance
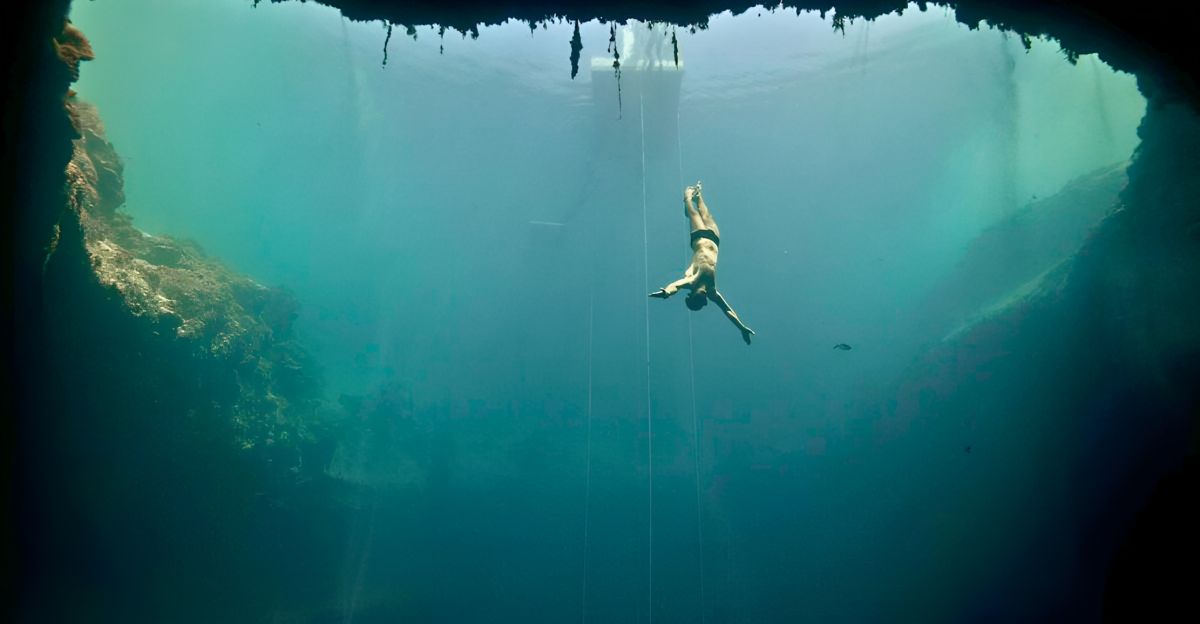

The TJBH demonstrates just how powerful geological forces can be in shaping landscapes. Slightly acidic groundwater leads to the dissolution of limestone, a process called karstification. It is through karsification that these vertical shafts eventually come to be.
Through a combination of karst dissolution as well as tectonic faulting complex cave frameworks are formed. Many such systems remained unexplored in the world. Furthermore, layers of stratified water within the blue hole also shows interesting hydrological dynamics. The deeper you go into the water the more there is an increase in salinity and reduced oxygen levels. Understanding the complexities that this hole holds could inform coastal aquifer behavior models.
Challenges in Exploration
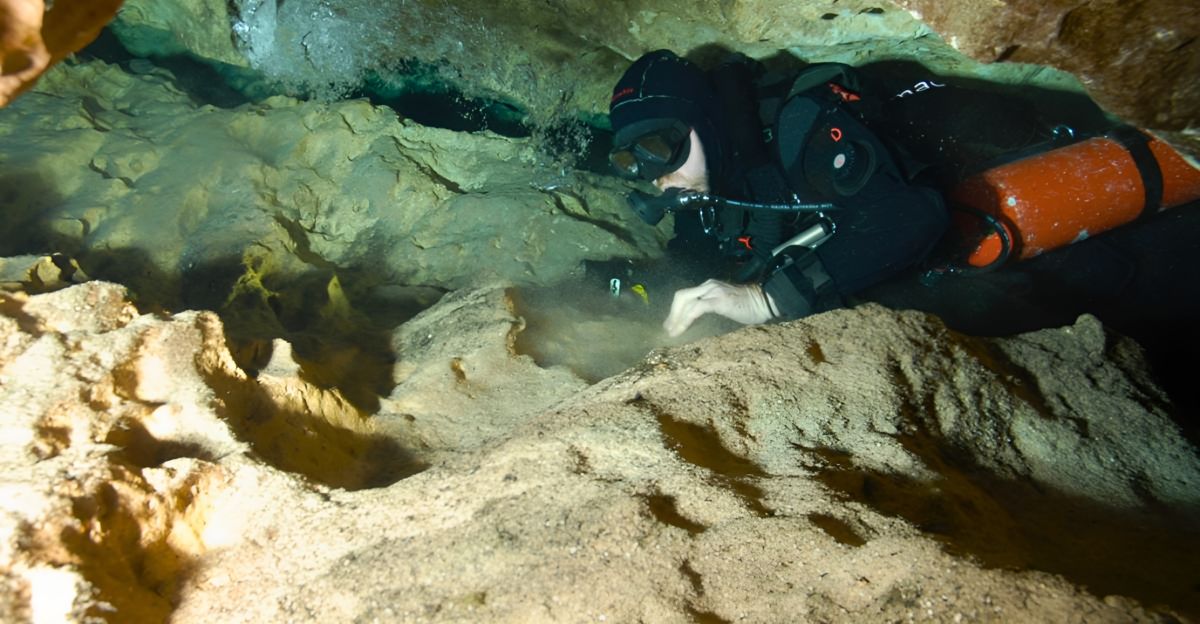

Scientists are challenging the limitations of underwater exploration while exploring the TJBH. Aside from those ambitions, human endurance is also tested as depths as deep as 1380 pose technical and physiological limitations. Deep divers need specialized equipment like closed-circuit rebreathers.
The hazardous conditions of the hole makes for an extreme environment. These conditions include very low oxygen levels, strong underwater currents as well as toxic hydrogen sulfide. Maneuvering in the narrow caves with low visibility also makes exploration even more challenging. The hope is that future technological innovation would aid in these challenges.
Biological and Ecological Implications
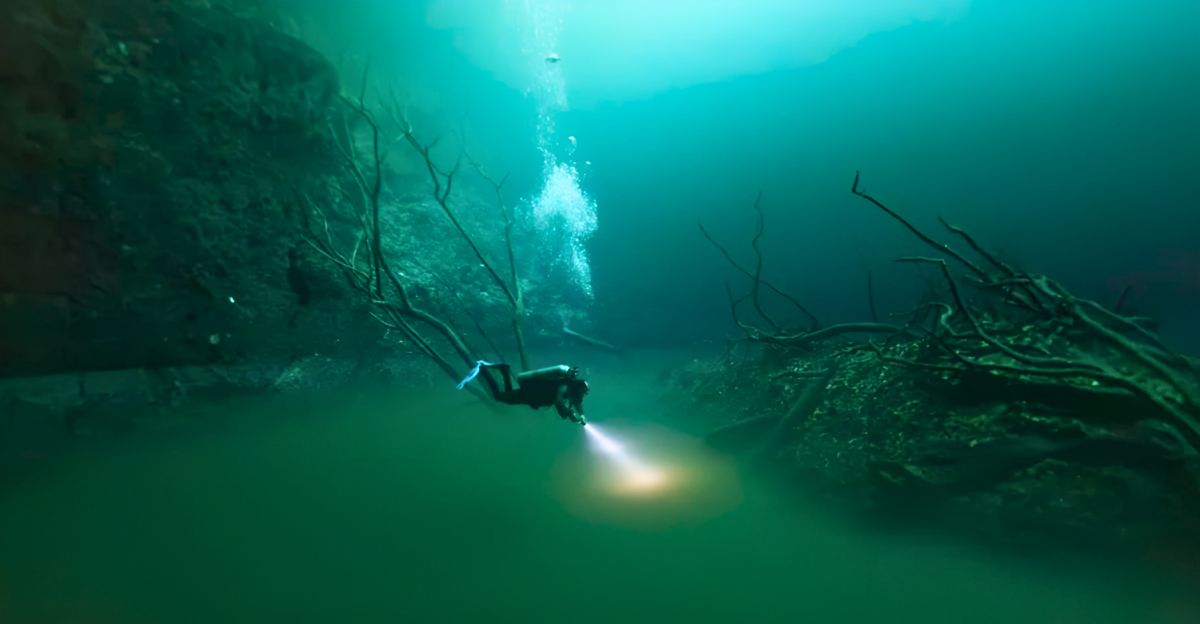

Explorations into the depths of these caves and deep blue holes open up a whole new word of different ecosystems to be uncovered. Blue holes are often associated with extreme environments such as limited oxygen, low light and very high concentrations of hydrogensolfide.
All these conditions come together to create habitats for microorganisms. These microorganisms have adapted to survive, demonstrating just how resilient and adaptable life can be.These organisms play an important role in biogeochemical cycles. Further research into these microorganisms and their ecosystems could hold valuable information for biotechnology, medicine, and other fields of study.
Technological Advances Enabling Discovery
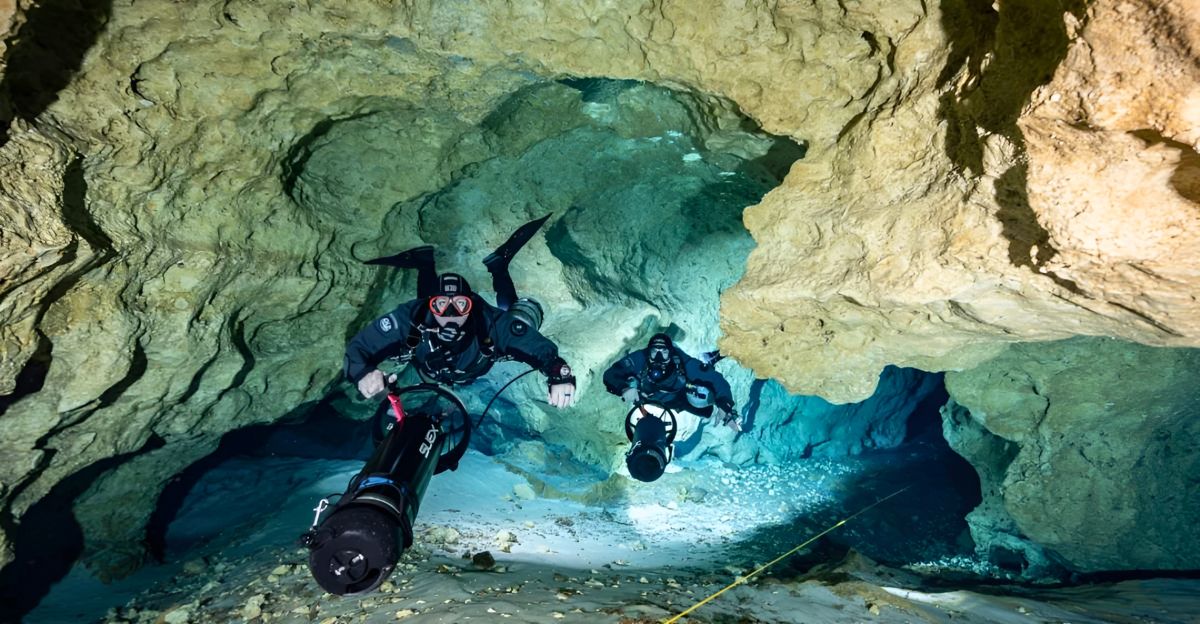

The rescent technological advances in underwater sensing and exploration have been vital in revealing the true scale and complexity of the TJBH. Unfortunately the traditional echo sounders are limited in their ability to be precise at such extreme depths. The innovations in diving technology have expanded our human capacity to explore these harsh environments.
Currently, we have closed-circuit rebreathers that recycle the exhaled gases that allow us to dive for even longer. This also reduces our compression time. This technology also reduces the amount of bubbles being produced, which is essential in protecting the fragile ecosystems at play.
Other Perspectives and Skepticism

This discovery is groundbreaking but there are individuals in the scientific community that have shared their criticism. Caution has been advised by marine experts against over publicizing this discovery without more in-depth studies.
We are physically unable to reach the bottom of the whole, and this leaves too many unanswered questions about its true geological nature. Making exploration even more dangerous. Debates about the significance of these massive and deep blue holes have scientists contending about whether the extreme conditions, in fact, limit biodiversity rather than expand it. Overpricing these discoveries might lead to an influx in tourism, which would threaten the habitats of the organisms because of possible pollution.
Potential Cultural and Economic Impact

The initial scientific allure of this discovery holds economic and cultural potential for the Yucatan region as these holes can become a hotspot for eco-tourism. This holds advantages such as economic growth but also disadvantages, as mentioned before. The increase of visitors to the region could likely influence local economies for example by creating job opportunities in many different fields.
On the other hand, managing this influx in tourism along with possible degrading of the environment could be challenging. The discovery of the TJBH also could inform cultural narratives as stories about this deep, dark hole could be passed along through generations as one of the oceans many mysteries.
Broader Trends

The discovery of the TJBH is a broader symbol of scientific as well as environmental trends. It ispires more exploration of extreme environments to unlock the secrets that may liay beneath the surface. We now have even more access to natural archives such as these blue holes as they can preserve sediment layers.
These sediment layers hold record of our past climate fluctuations, sea level changes and other ecological dynamic shifts. This information could inform how we view issues such as climate change in the modern day. Although there is a trend for deeper and wider exploration we must not forget our responsibility to protect these new fragile ecosystems.
Future trajectory
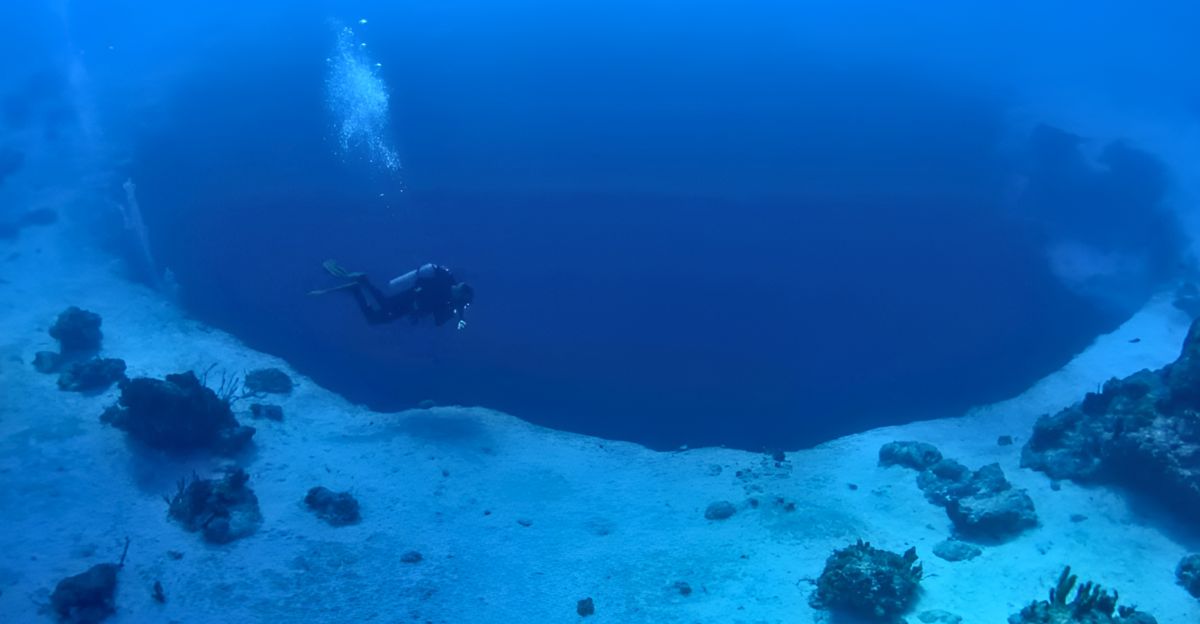

One thing is certain, that this discovery of the deepest blue hole inside massive 500ft cave represents the intersecting achievements of geological and marine sciences. Collaboration of these fields could lead to further exploration and further insight into earth’s mysteries.
Remember that we have not seen the bottom yet so much more is yet to be uncovered. The full extent of the TJBH are to be discovered. Hopefully future technological advances in these fields would make further exploration a reality. It goes to show that more investment is needed in the exploration under the waves just like there is in space exploration.
Explore more of our trending stories and hit Follow to keep them coming to your feed!
Don’t miss out on more stories like this! Hit the Follow button at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest news. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!







