
Freshwater is turning saltier, and it’s not because someone dropped a giant salt shaker into the river. Human activities like road de-icing, agriculture, and industrial processes are introducing excessive salts into freshwater systems. This phenomenon, known as freshwater salinization, is altering the delicate balance of our aquatic ecosystems.
The increasing salinity isn’t just a minor inconvenience. It’s a growing concern that threatens biodiversity, drinking water quality, and infrastructure. Salts like sodium, chloride, and magnesium are accumulating in rivers and lakes, leading to a cascade of environmental issues.
Understanding the sources and impacts of this salinization is crucial. It’s time to take a closer look at how our actions are making freshwater ecosystems uncomfortably salty.
The Culprits Behind the Salt
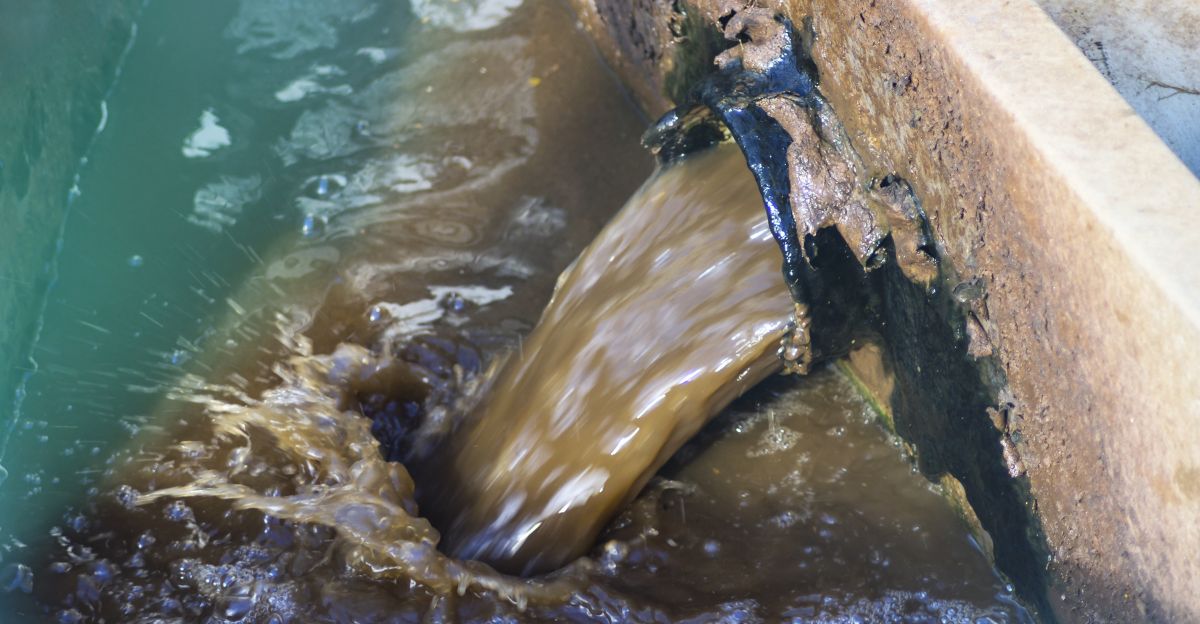

So, who’s to blame for this salty situation? A significant contributor is the use of road salts during winter. While they keep roads safe, they also wash into nearby waterways. Agricultural runoff, laden with fertilizers and irrigation salts, adds to the problem.
Industrial activities, including mining and wastewater discharge, further exacerbate salinity levels. Even water softeners in households contribute by releasing salts into sewage systems, which eventually find their way into rivers and streams.
These combined sources are turning freshwater bodies into brackish environments, unsuitable for many native species. Addressing these contributors is essential to mitigate the salinization crisis.
Ecosystems Feeling the Pinch
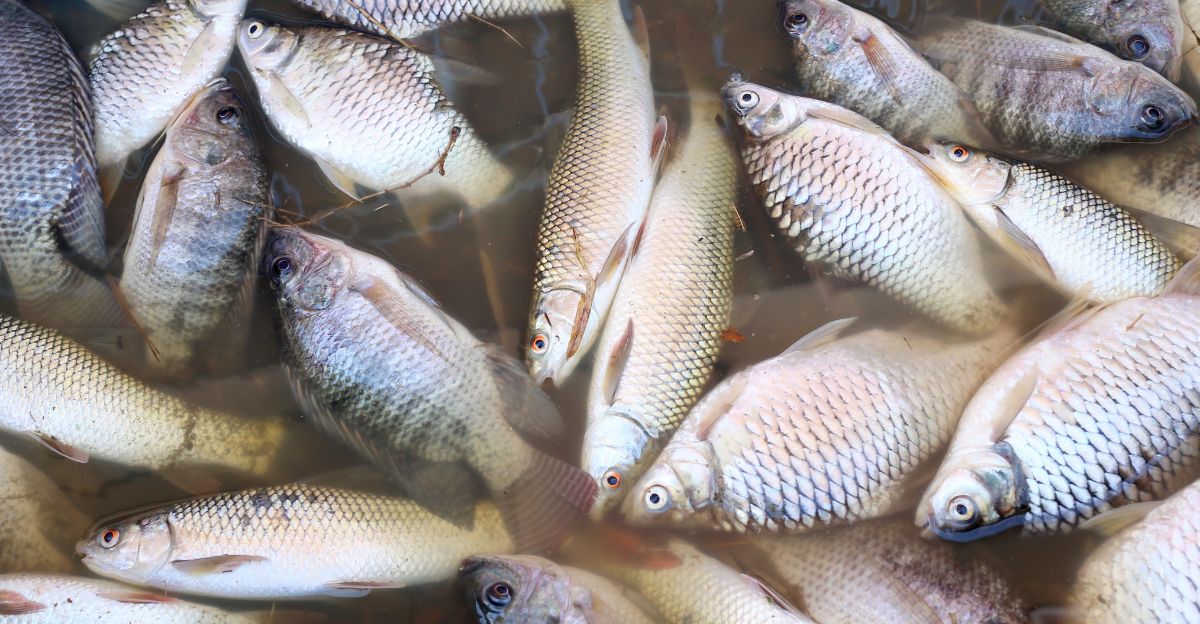

Aquatic life isn’t taking this salt influx lightly. Many freshwater species are sensitive to changes in salinity. Elevated salt levels can disrupt osmoregulation in fish and amphibians, leading to stress or death.
Macroinvertebrates, crucial for nutrient cycling and as a food source, are also affected. Their decline can ripple through the food web, impacting birds and larger predators. Additionally, increased salinity can favor invasive species that outcompete native ones.
The result? A shift in ecosystem dynamics, reduced biodiversity, and compromised ecosystem services. Salinization is not just a chemical change; it’s an ecological upheaval.
Drinking Water at Risk
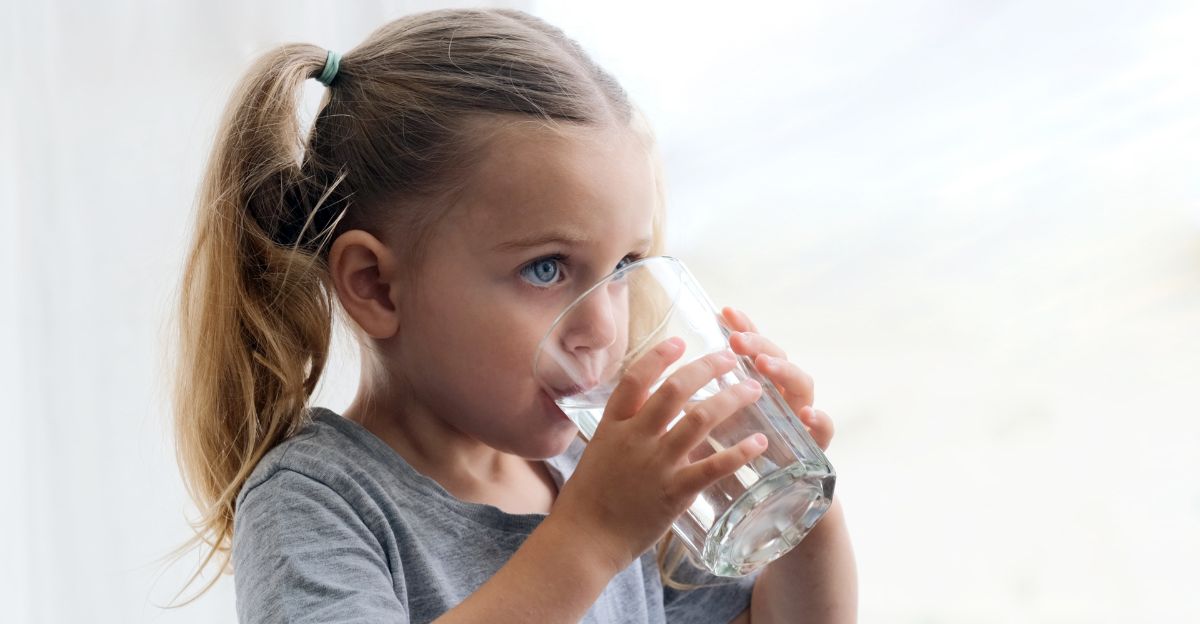

It’s not just wildlife that’s affected. Human health is on the line too. Many communities rely on surface water for drinking. As salinity rises, water treatment becomes more challenging and costly.
High salt concentrations can corrode pipes, leading to infrastructure damage and potential contamination, as seen in events like the Flint water crisis. Moreover, consuming high-salinity water can pose health risks, particularly for individuals with hypertension.
Ensuring safe drinking water requires addressing the root causes of salinization and investing in infrastructure resilient to these changes.
Infrastructure Feeling the Strain
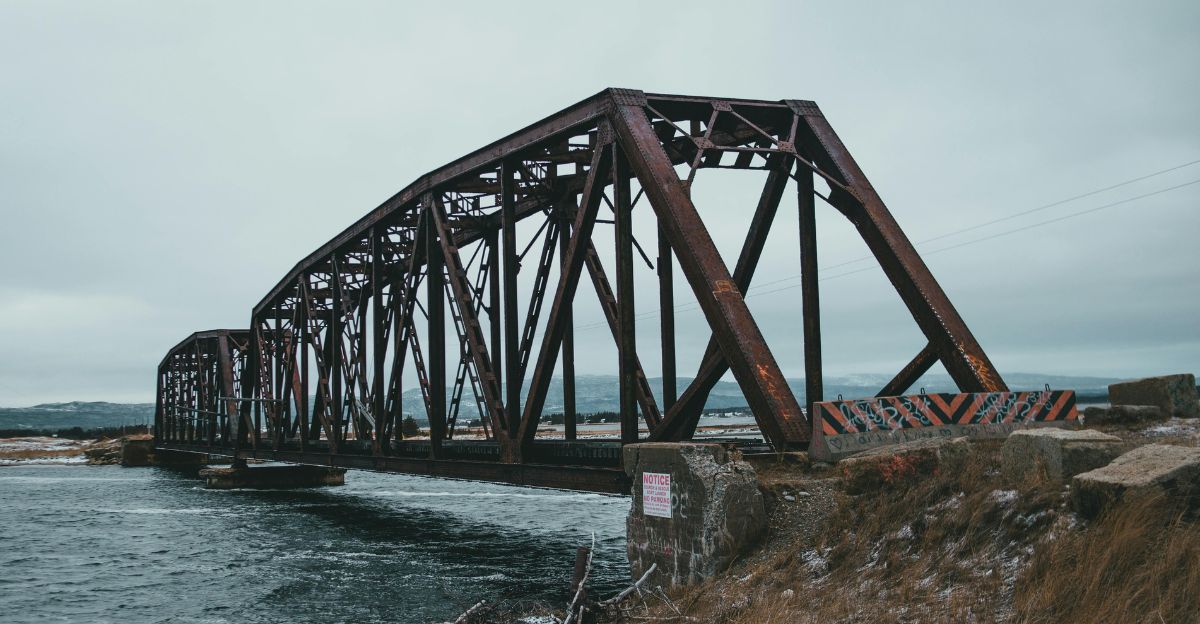

Salt doesn’t play nice with infrastructure. Elevated salinity accelerates the corrosion of bridges, roads, and pipelines. This not only shortens their lifespan but also increases maintenance costs.
Wastewater treatment plants face challenges too. High salt levels can disrupt microbial processes essential for treating sewage, leading to inefficiencies and potential environmental violations.
The economic implications are significant. Municipalities must allocate more funds for repairs and upgrades, diverting resources from other essential services.
Climate Change Complicates Matters

Climate change is adding fuel to the salinization fire. Rising sea levels lead to saltwater intrusion into coastal freshwater aquifers. Droughts reduce river flows, concentrating salts, while intense storms can flush large amounts of salts into waterways.
These climatic shifts amplify the existing salinization problem, making it more unpredictable and harder to manage. The interplay between climate change and salinity underscores the need for integrated environmental strategies.
Addressing salinization isn’t just about reducing salt inputs; it’s also about adapting to a changing climate that influences how salts move through our ecosystems.
Global Hotspots and Vulnerabilities
Salinization isn’t confined to one region. It’s a global issue with hotspots in North America, Europe, and Asia. In the U.S., the Northeast and Midwest experience significant salinity spikes due to road salt usage.
Coastal regions worldwide face challenges from saltwater intrusion, threatening agriculture and freshwater supplies. In countries like Bangladesh, salinity affects both drinking water and crop yields, posing food security risks.
Recognizing these vulnerable areas is crucial for targeted interventions. Global collaboration and knowledge sharing can help address the unique challenges each region faces.
Mitigation and Management Strategies

Combating freshwater salinization requires a multifaceted approach. Alternatives to traditional road salts, such as beet juice mixtures or sand, can reduce salt runoff. Implementing best management practices in agriculture, like buffer strips and controlled irrigation, minimizes salt leaching.
Upgrading infrastructure to resist corrosion and investing in advanced water treatment technologies can mitigate impacts. Public education campaigns can also play a role, encouraging responsible salt use and awareness of the issue.
Policy measures, including regulations on salt application and incentives for sustainable practices, are essential components of a comprehensive strategy.
The Road Ahead

Freshwater salinization is a pressing environmental challenge with far-reaching implications. Addressing it requires concerted efforts from individuals, communities, industries, and governments.
By understanding the sources and impacts, implementing effective mitigation strategies, and fostering global cooperation, we can protect our freshwater resources. It’s a complex issue, but with proactive measures, we can turn the tide on salinization.
Preserving the integrity of freshwater ecosystems is not just about environmental stewardship; it’s about ensuring a sustainable future for all life that depends on these vital resources.
A Salty Wake-Up Call

The steady salinization of our freshwater is a global wake-up call. It’s easy to overlook, but the consequences are creeping up on ecosystems, economies, and communities alike. Once the salt is in, it’s hard and expensive to get out.
Proactive change is still possible. From better salt management on roads to smarter farming practices and stricter regulations, we have the tools to push back. But it’ll take commitment across the board to see results.
The sooner we act, the better our chances of keeping freshwater fresh and protecting all the life that depends on it.
Explore more of our trending stories and hit Follow to keep them coming to your feed!
Don’t miss out on more stories like this! Hit the Follow button at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest news. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!







