In a groundbreaking discovery that defies the boundaries of biology and evolution, scientists have observed the unprecedented merging of two distinct lifeforms into one. This phenomenon, which experts believe hasn’t occurred in over a billion years, could reshape our understanding of life on Earth and beyond.
A Rare Convergence
The event was first reported in a laboratory at the Genome Research Institute in Cambridge, where microbiologists had been studying extremophiles—organisms that thrive in harsh conditions. Among the specimens were Archaea Methanica and Bacterium Solventis, two ancient microbes. Historically, these lifeforms have coexisted in proximity but have never been known to physically integrate into one entity.
Lead researcher Dr. Elena Marks explained, “This wasn’t just symbiosis, where two organisms cooperate for mutual benefit. This was full integration at a cellular and genetic level—essentially, they fused to become a new species.”
The Moment of Fusion
The phenomenon occurred under controlled conditions meant to simulate early Earth environments. Researchers exposed the microbes to high pressures, elevated temperatures, and nutrient-rich surroundings. Over the course of several weeks, the team noticed unusual behavior: the microbes began moving toward each other in coordinated patterns, eventually joining and exchanging genetic material.
“This was like watching history unfold in real-time,” said Dr. Marks. “The fusion process was unlike anything we’ve ever seen in modern biology. Their membranes dissolved, and their genetic material combined seamlessly.”
The Birth of a New Species
The resulting organism, temporarily dubbed Archaebacterium Unum, displays unique traits not seen in its predecessors. It can produce energy in multiple ways, including photosynthesis, methane production, and sulfur-based respiration. Early tests suggest it is exceptionally resilient, capable of thriving in extreme conditions that neither parent organism could survive alone.
“This organism is a hybrid of the past and the future,” said Dr. James O’Leary, a molecular biologist who collaborated on the project. “It represents a potential blueprint for how life could adapt on other planets or under catastrophic conditions on Earth.”
Echoes of Evolutionary History
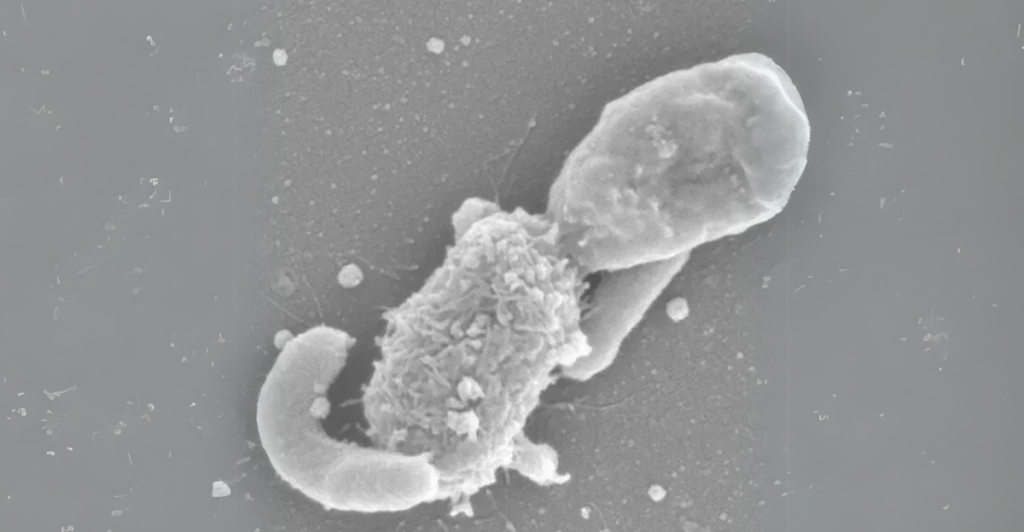
The last known event of such integration dates back over a billion years during the early stages of eukaryotic evolution. This was when simple cells likely absorbed other lifeforms, leading to the development of complex cells with nuclei. The mitochondria, known as the powerhouse of the cell, is thought to be a relic of this ancient merger.
“What we’ve witnessed is a modern echo of a process that shaped all multicellular life,” said evolutionary biologist Dr. Clara Yuan. “This discovery reinforces the idea that life is inherently innovative and adaptable.”
Implications for Medicine and Biotechnology
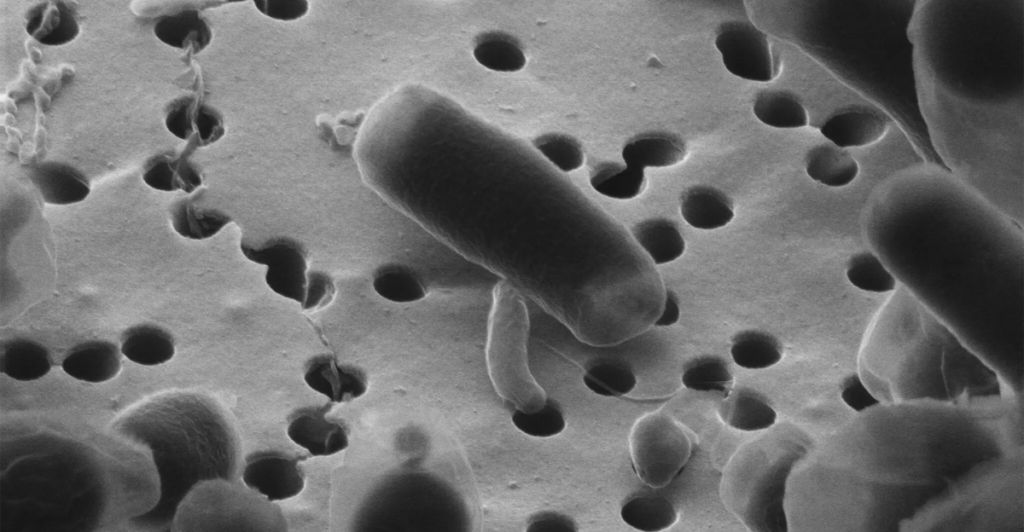
Beyond its evolutionary significance, Archaebacterium Unum could have revolutionary applications. Its resilience and multifunctional energy production could lead to breakthroughs in medicine, bioengineering, and sustainable energy.
“Imagine a single organism that could clean pollution, generate renewable energy, and survive in space,” said Dr. Marks. “The possibilities are endless.”
Biopharmaceutical companies are already expressing interest in studying the organism’s unique metabolic pathways, hoping to unlock new treatments for diseases that thrive in extreme environments.
Ethical and Ecological Concerns

While the discovery is a triumph for science, it raises ethical and ecological questions. Could the release of such a hybrid organism into natural ecosystems disrupt existing life? Some environmentalists warn that humanity’s history of unintended consequences should give researchers pause.
“We’re playing with forces we barely understand,” said activist Leah McConnell. “What happens if this organism escapes the lab and outcompetes natural microbes, causing an ecological imbalance?”
A Controlled Environment

Dr. Marks assured the public that rigorous safety protocols are in place. The new organism is being studied under strict containment, with no plans to release it outside laboratory conditions. However, debates about regulation and oversight are likely to intensify as research progresses.
“This discovery underscores the need for an international framework to govern synthetic biology,” said Dr. Yuan. “We’re entering uncharted territory.”
The Search for Other Fusions
As excitement grows, researchers worldwide are exploring whether similar integrations could be occurring in nature undetected. Extreme environments such as hydrothermal vents, frozen tundras, and acidic caves are being scrutinized for signs of microbial mergers.
“If this can happen in a lab, there’s a chance it’s happening in the wild,” said Dr. O’Leary. “We need to broaden our search to understand the full scope of this phenomenon.”
Philosophical Implications

The discovery also raises profound questions about the nature of identity and individuality in biology. If two organisms can become one, where do we draw the line between separate lifeforms?
“This challenges our very definition of what it means to be alive,” said bioethicist Dr. Maya Torres. “Are we looking at the creation of a singular consciousness or a collective entity? The implications are staggering.”
Public Fascination

The phenomenon has captured the public imagination, sparking debates on social media and inspiring speculative fiction about the future of life on Earth. Documentaries and podcasts are already in production, seeking to unpack the science and implications of the discovery.
“This is like something out of a science fiction novel,” said filmmaker Jordan Hart. “It’s thrilling and terrifying at the same time.”
A Turning Point for Humanity
As humanity stands on the precipice of this scientific breakthrough, one thing is clear: the merging of Archaea Methanica and Bacterium Solventis is a turning point in our understanding of life. It reminds us that the boundaries between species, and even between individuality and unity, are more fluid than we ever imagined.
“Our discovery is not just about microbes,” said Dr. Marks. “It’s about the potential of life itself to evolve, adapt, and create something entirely new. This is the beginning of a journey that will take us far beyond what we thought we knew.”
Watch This Space
The fusion of two lifeforms into one marks a new chapter in science and humanity’s quest to understand the mysteries of existence. What comes next remains to be seen, but the possibilities are as vast as life itself.
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







