
Globally, the fishing industry generates substantial waste, with estimates indicating that 20% and 80% of processed fish are discarded as by-products. These by-products, including heads, viscera, and bones, are rich in proteins, amino acids, and essential nutrients. Traditionally, such waste has been underutilized, often ending up in landfills or the ocean, contributing to environmental degradation.
However, recent studies highlight the potential of repurposing fish waste into poultry feed supplements. For instance, fermented pangasius fish waste has demonstrated enhanced digestibility and nutrient retention when used in poultry diets.
By integrating these by-products into poultry feed, the industry can reduce waste, lower feed costs, and promote sustainable practices. This approach addresses environmental concerns and offers economic benefits, making it a viable solution for fisheries and poultry sectors.
Nutritional Value of Fish By-Products
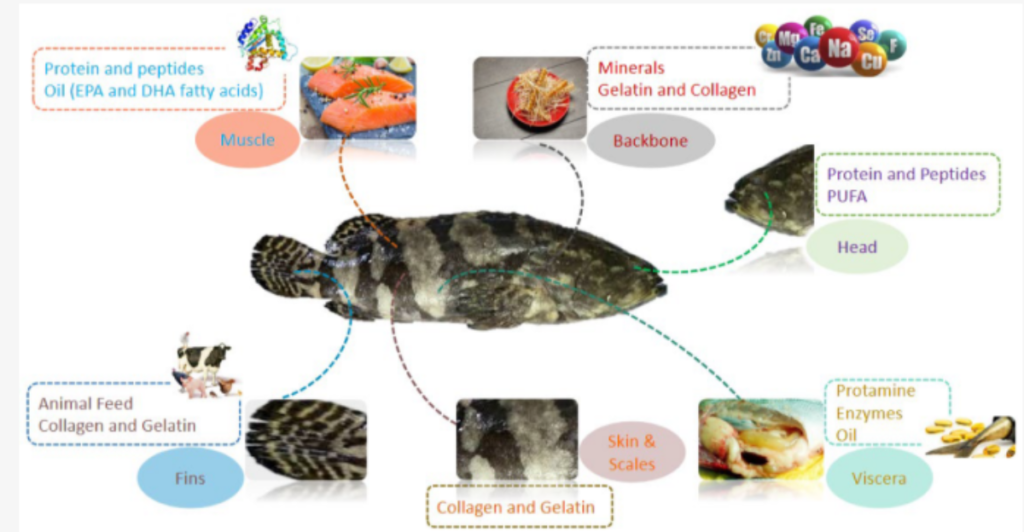
Fish by-products are not merely waste but a treasure trove of nutrients essential for poultry health. Components like fish heads, bones, and viscera are rich in high-quality proteins, omega-3 fatty acids, and minerals. When processed appropriately, these by-products can serve as excellent supplements in poultry diets, enhancing growth rates and feed efficiency.
Moreover, fermented fish waste has improved amino acid profiles, making it more digestible for poultry. Incorporating these nutrients into poultry feed can lead to healthier flocks and potentially reduce the reliance on conventional feed ingredients, which are often more expensive and less sustainable.
Environmental Implications of Fish Waste
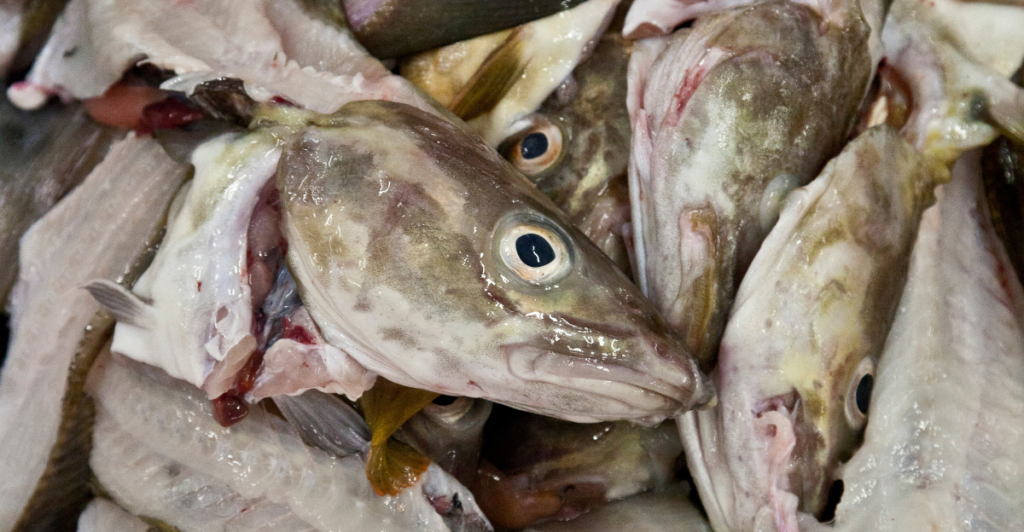

Discarding fish by-products poses significant environmental challenges. When improperly managed, these wastes can pollute water, attract pests, and emit unpleasant odors. In some regions, the accumulation of fish waste has been linked to the degradation of marine ecosystems. By redirecting these by-products into poultry feed, industries can mitigate environmental hazards.
This practice not only reduces the ecological footprint of fisheries but also promotes a circular economy, where waste is transformed into valuable resources. Such sustainable approaches are crucial in addressing the growing concerns over environmental conservation and resource management.
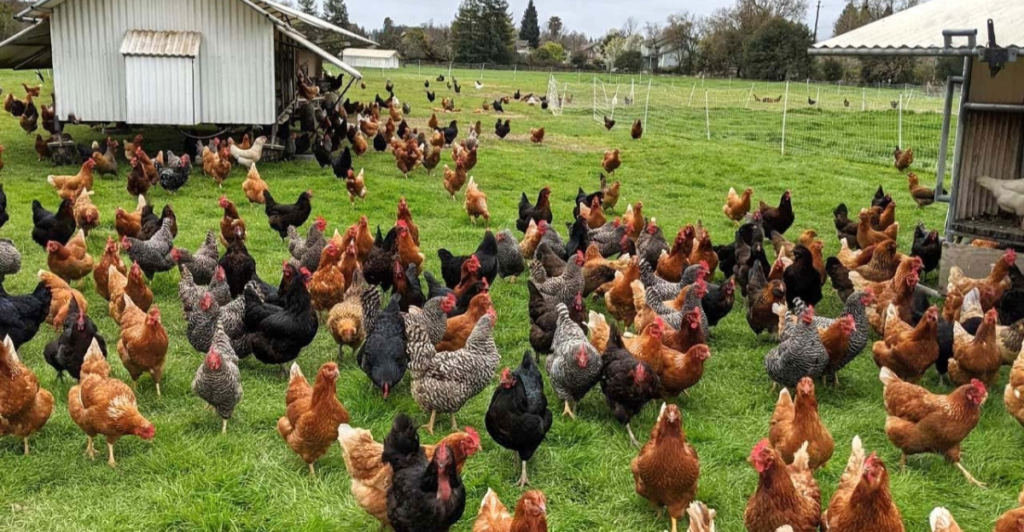
Economic Benefits for Poultry Farmers

Integrating fish by-products into poultry feed can offer substantial economic advantages. Traditional feed ingredients, such as soybean meal and corn, are subject to price volatility and supply chain disruptions. Fish waste, a readily available and often underutilized resource, presents a cost-effective alternative.
Studies have shown that poultry diets supplemented with fish by-products can maintain, if not improve, growth performance while reducing feed costs. This approach can enhance profitability and sustainability for small-scale poultry farmers, especially in developing regions. Moreover, utilizing local fish waste reduces dependency on imported feed ingredients, fostering self-reliance and economic resilience.
Challenges in Processing Fish Waste

While the benefits are evident, processing fish waste into poultry feed is challenging. Ensuring the safety and quality of the feed requires stringent processing methods to eliminate pathogens and toxins. Techniques like fermentation and rendering stabilize the by-products and enhance their nutritional value.
However, these processes can be resource-intensive and require significant infrastructure and technology investment. Additionally, regulatory frameworks governing the use of animal by-products in feed vary across regions, necessitating compliance with local and international standards. Addressing these challenges is crucial for successfully integrating fish waste into poultry nutrition.
Innovations in Fish Waste Utilization
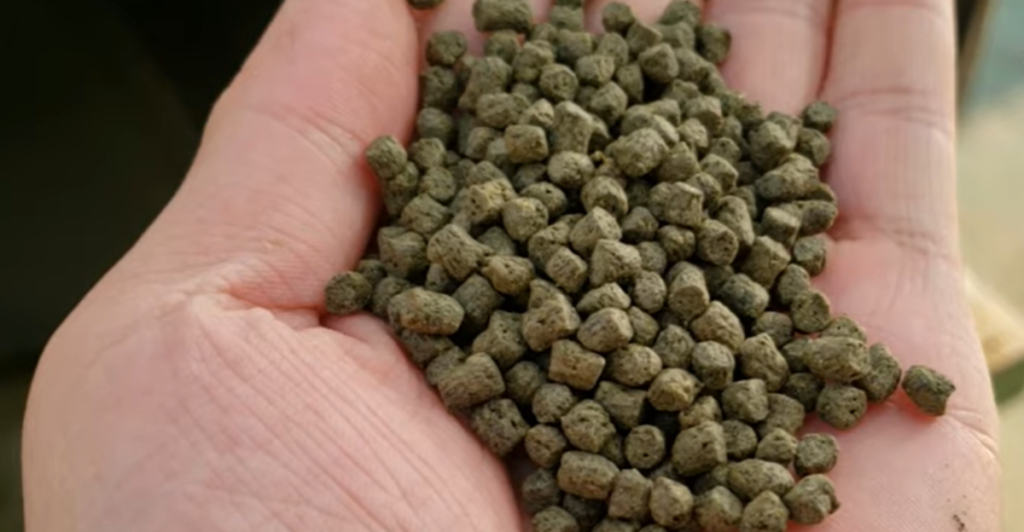

Recent advancements have led to innovative methods of converting fish waste into valuable feed ingredients. Companies like SuperGround have developed technologies to transform fish scraps into protein-rich powders suitable for animal feed. These innovations enhance the efficiency of fish waste utilization and ensure the safety and quality of the resulting feed products.
Moreover, research into microbial fermentation processes has shown promise in improving fish by-products’ digestibility and nutrient profile. Such technological advancements are pivotal in overcoming the challenges associated with fish waste processing and promoting its adoption in the poultry industry.
Regulatory Considerations and Standards

Incorporating fish by-products into poultry feed is subject to various regulatory standards to ensure food safety and animal health. Regulations often dictate the permissible levels of contaminants, processing methods, and labeling requirements. Compliance with these standards is essential to gain consumer trust and to facilitate market access.
Organizations like the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) provide guidelines on the safe use of animal by-products in feed. Adhering to these regulations ensures poultry products’ safety and promotes sustainable practices within the industry.
Global Perspectives and Adoption

The utilization of fish by-products in poultry feed is gaining traction worldwide. Integrating fish waste into feed has shown promising results in countries like Indonesia and India, where fisheries and poultry farming are prominent. These practices enhance the respective industries’ sustainability and contribute to waste reduction and economic development.
Furthermore, international collaborations and knowledge-sharing platforms facilitate the adoption of such practices across different regions. By learning from global experiences, countries can effectively tailor strategies to utilize fish waste in their poultry sectors.
Future Prospects and Research Directions
Integrating fish by-products into poultry feed presents a significant opportunity for advancing sustainable agriculture. Ongoing research explores optimal processing methods, including enzymatic hydrolysis and microbial fermentation, to enhance nutrient bioavailability and shelf life (ScienceDirect). Emerging studies also examine how fish waste-based feeds affect poultry immunity, egg quality, and gut microbiota.
Furthermore, academic and industry partnerships are fostering innovation in scalable waste-to-feed systems. As feed demand increases with global poultry consumption, leveraging fish waste could be critical in meeting nutritional needs without expanding agricultural land. With proper policy support, technical training, and investment in local infrastructure, especially in developing nations, the widespread adoption of this practice can improve food security, reduce waste, and increase profitability for farmers.
The next frontier involves integrating AI and biotechnology to tailor feed blends based on fish species, poultry type, and local environmental conditions for maximum efficiency.
Building a Circular Economy in Agriculture
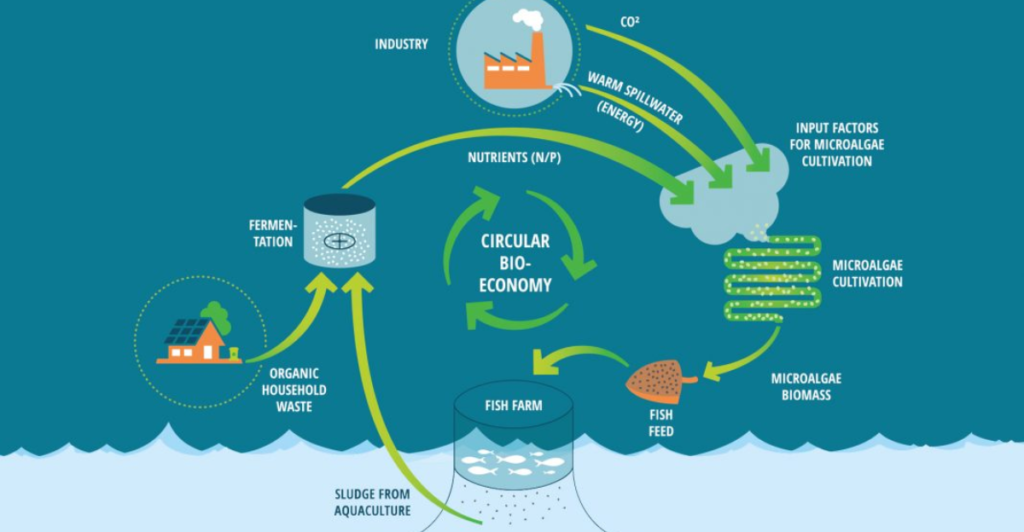
The use of fish waste in poultry feed is a prime example of circular economy principles in action. Instead of disposing of by-products, industries can close the loop by repurposing them into valuable resources, minimizing waste, and maximizing efficiency. According to the FAO, food systems must transition toward circular models to meet sustainability targets and feed a growing population.
This approach can reduce greenhouse gas emissions, lower production costs, and lessen the environmental footprint of both fisheries and poultry sectors. Moreover, encouraging collaboration across fisheries, agriculture, feed manufacturing, and waste management industries can drive innovation and policy reform.
Education and awareness programs for farmers and processors are also crucial in building capacity for sustainable practices. Ultimately, embracing the circular economy is not just a solution to waste. It’s a blueprint for a resilient and future-ready global food system where no resource is squandered.
Explore more of our trending stories and hit Follow to keep them coming to your feed!

Don’t miss out on more stories like this! Hit the Follow button at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest news. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!







