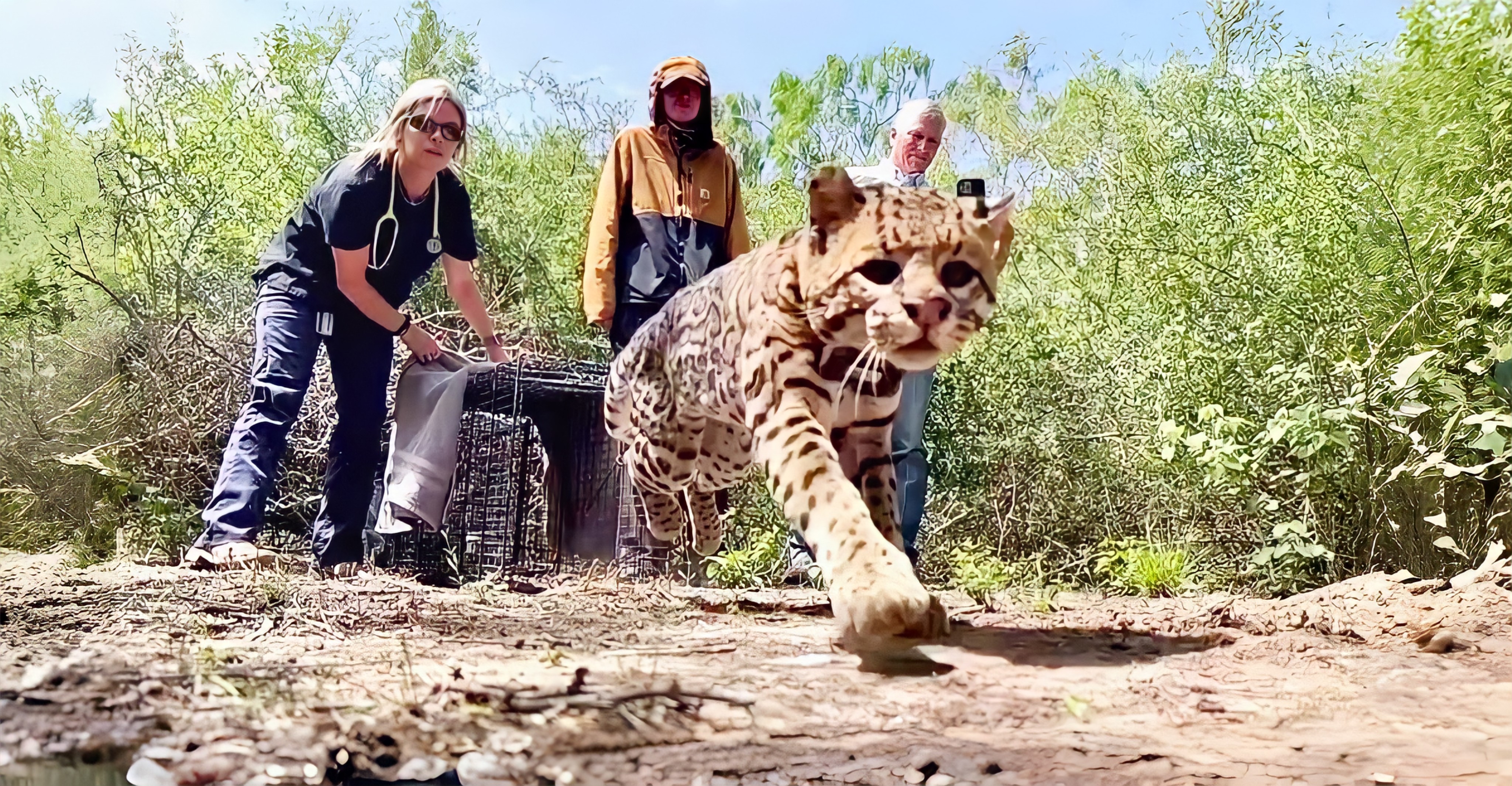

With fewer than 100 ocelots remaining in the U.S., these majestic, beautifully striped wild cats are on the brink of extinction in South Texas. As such, specialists and conservationists are racing against time to learn more about the species and strategize methods for rejuvenating their rapidly fading numbers before it is too late.
The Elusive Ocelot
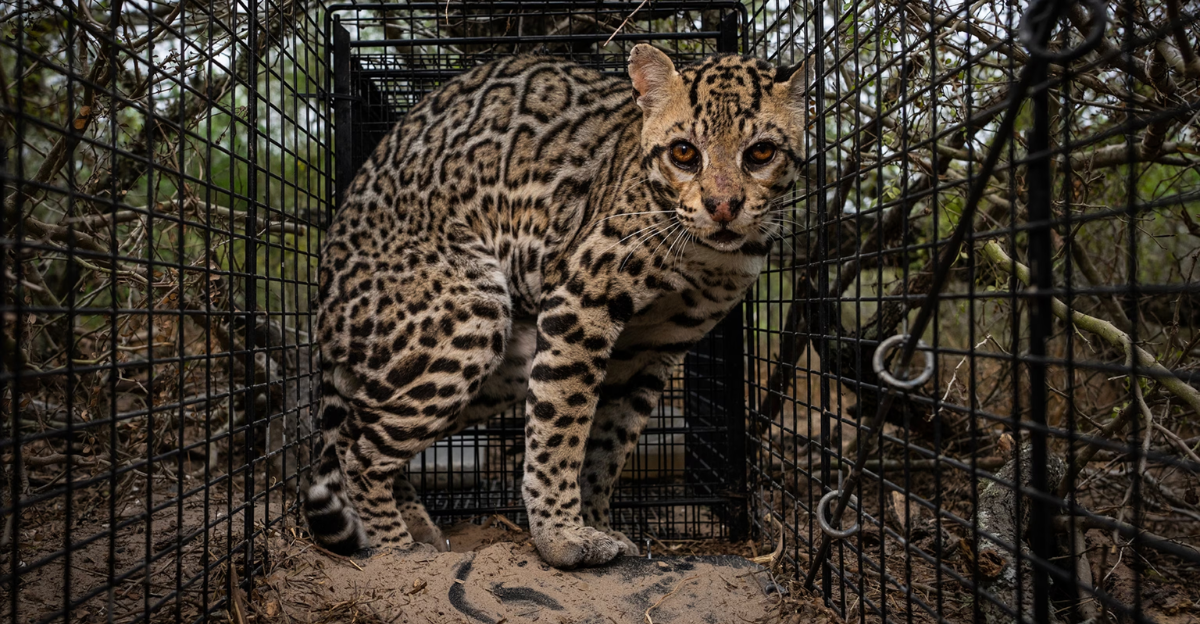

Ocelot (Leopardus pardalis) is a medium-sized wild cat of the Americas renowned for its dashing spotted fur and nocturnal habits. As a species that can climb, leap, and swim, it is often found near water sources with dense vegetation and plenty of food sources, such as armadillos and opossums. Historically, these cats have spread widely across the southwestern United States, but in the last century, their numbers have reduced considerably.
Decline in Numbers
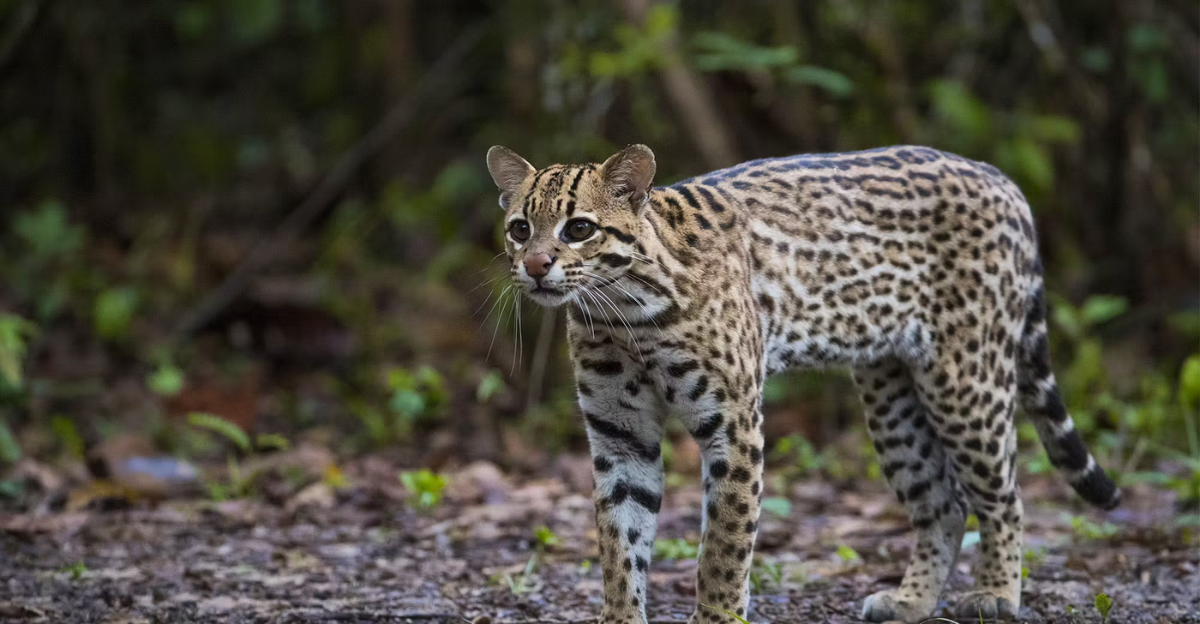

Historically, ocelots roamed across the southwestern United States, but their numbers began to decline significantly in the 1960s due to the fur trade and habitat destruction. Now, less than 100 ocelots are left in the United States as of 2025, with two tiny breeding populations in South Texas. Their decreasing numbers are also a result of habitat loss, being hunted for their fur, and human encroachment.
The Loss of Habitat
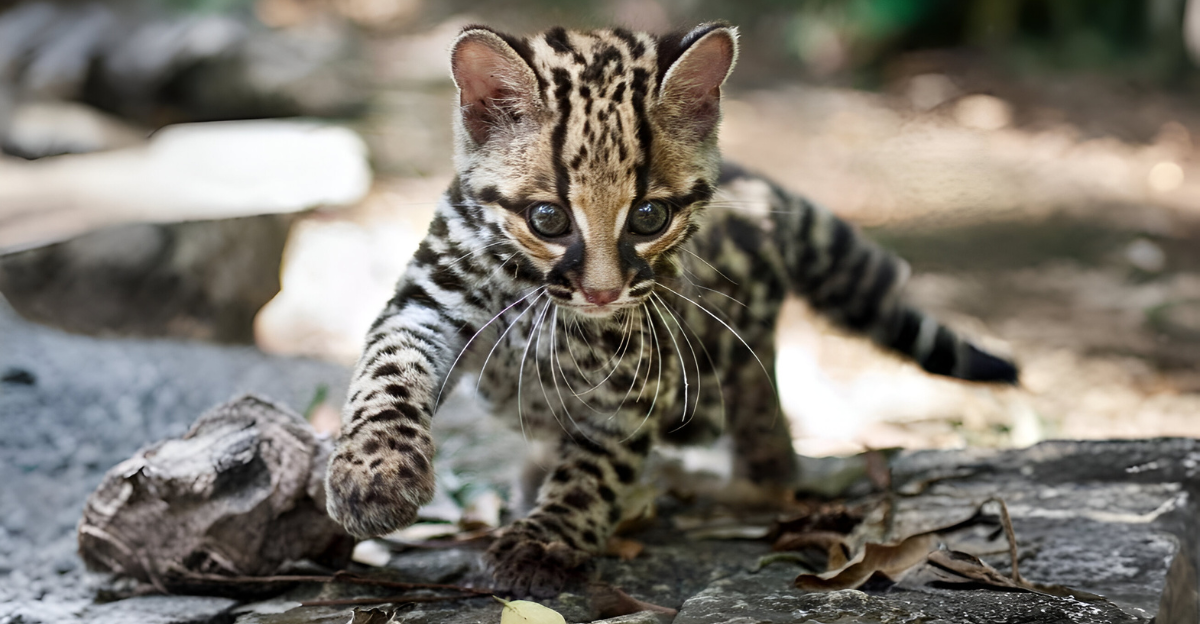

Today, urbanization and farming have led to a decrease in ocelot habitats as their ideal dense thorn scrub environments are cleared, reducing their living habitats and fragmenting populations. In the past, hunting ocelots for their beautiful fur was popular, leading to a significant decline in their numbers. Although hunting has declined, its past impact affects the current population.
Road Mortality
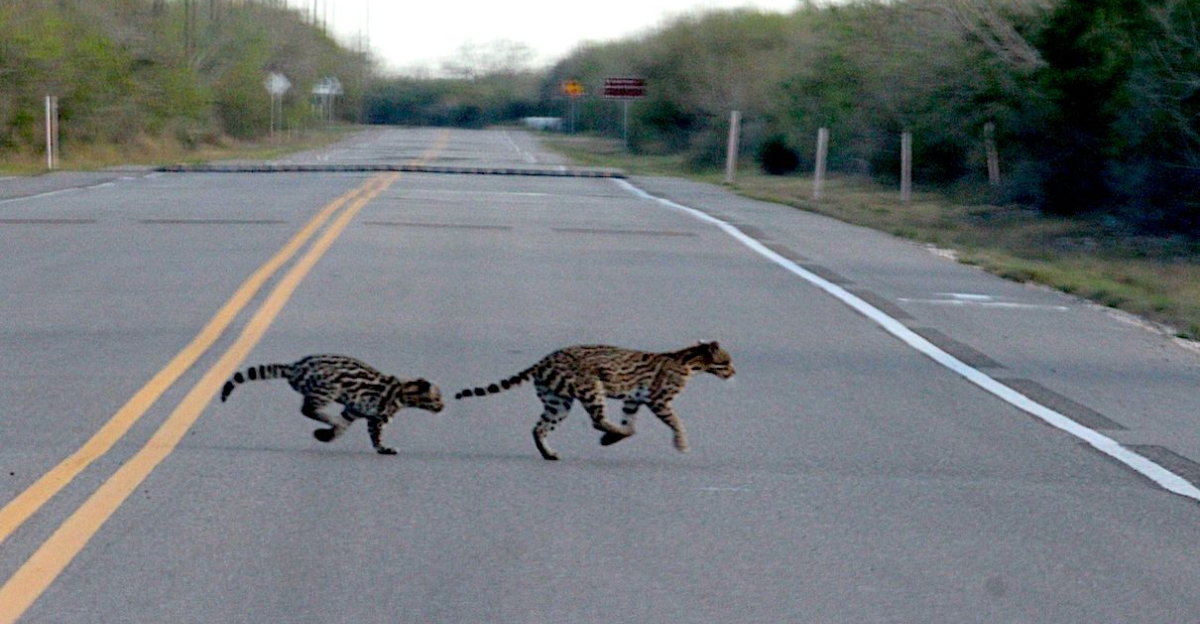

Another contributing factor to the decrease in the population of Ocelot is automobile accidents. Road mortality accounts for 40% of ocelot deaths in Texas, transforming highways into unnatural selection filters. To survive, the cats avoid roads, shrinking their hunting ranges and accelerating genetic isolation. Modern infrastructure now functions as a man-made evolutionary pressure, rewriting species’ trajectories in real-time.
A Zombie Population
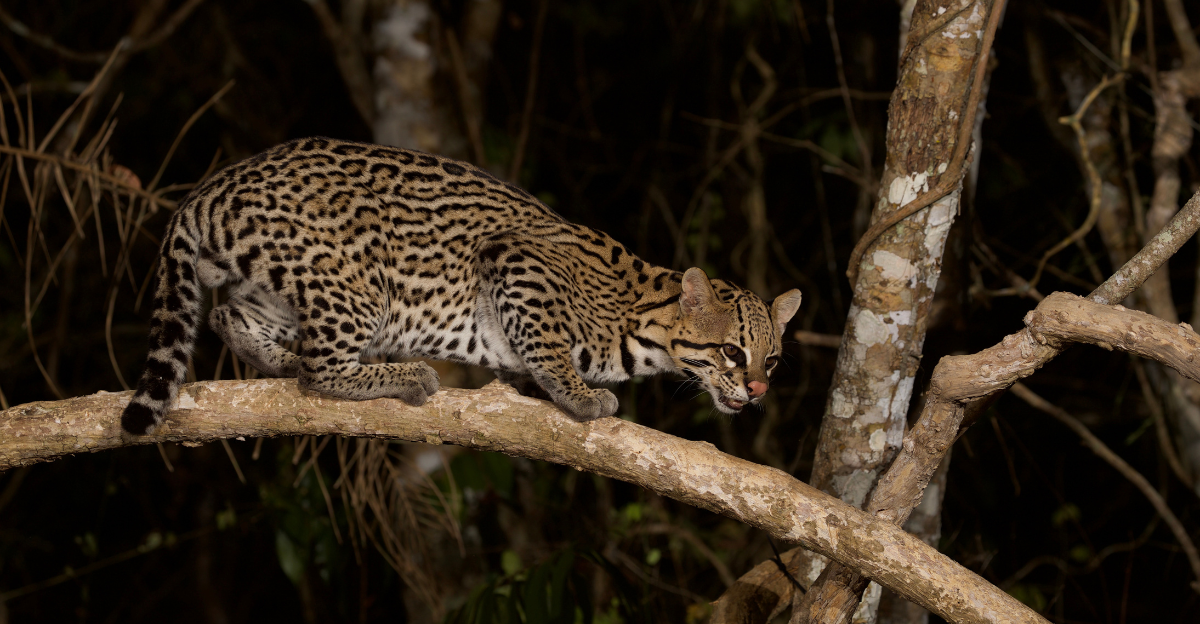

Furthermore, the ocelot is facing an evolutionary crisis in which its young are increasingly born with reduced fitness and survival skills. This makes it hard for young ocelots to survive in their changing environments and makes the species biologically alive but evolutionarily stagnant—a phenomenon known as a “zombie population.”
Conservation Efforts Begin
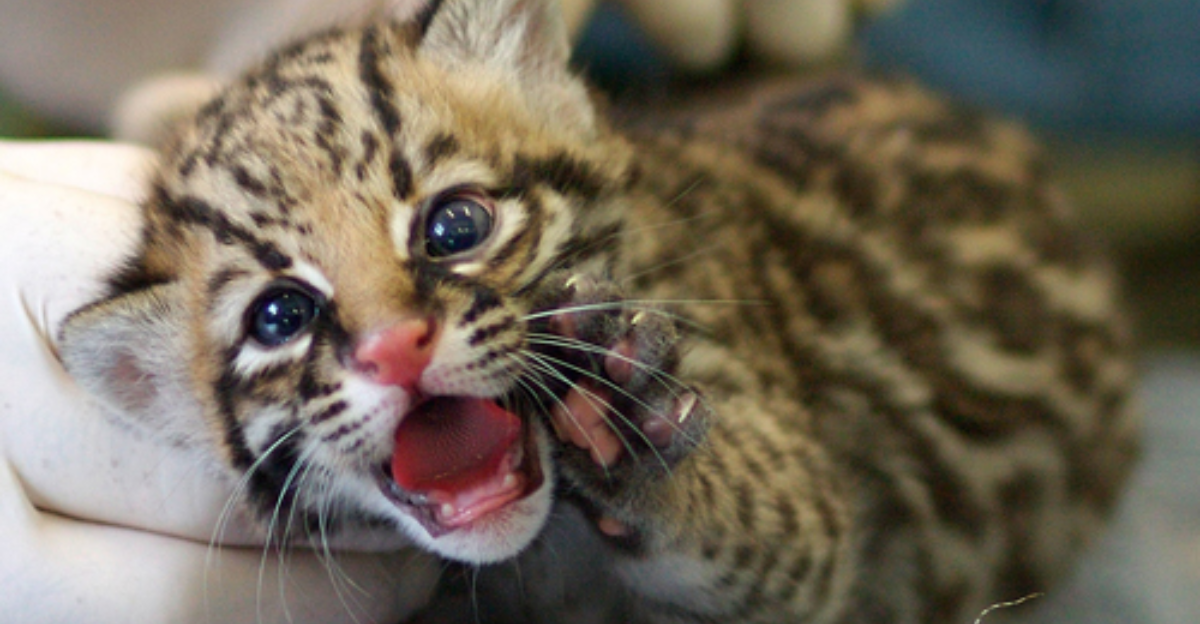

To save the species, conservationists embarked on efforts to protect and restore their populations. Organizations, such as the East Foundation, have been instrumental in these initiatives. For example, the East Foundation, based in San Antonio, has over 200,000 acres of South Texas ranchland on which the ocelot has its crucial habitat, where they aim to preserve the cats’ habitat and research other methods of ocelot conservation.
Challenges to Breeding
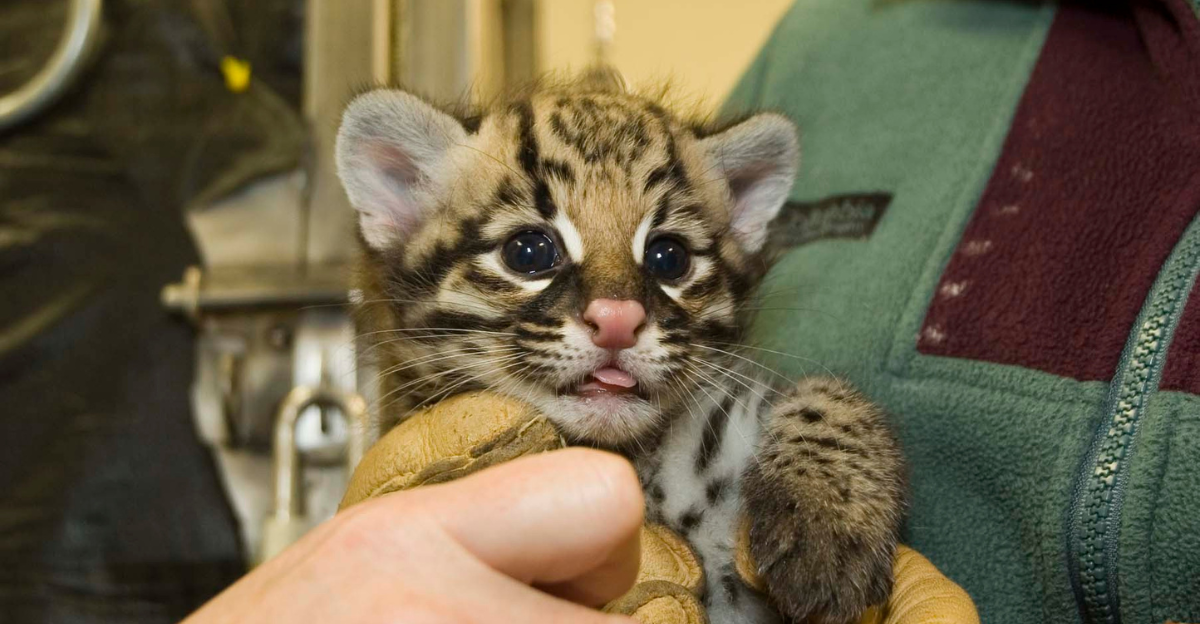

Since 2021, scientists have tried to breed ocelots using artificial insemination and in-vitro fertilization. Professionals, such as Bill Swanson from the Cincinnati Zoo, have traveled across the nation to aid in breeding projects that mirror de-extinction projects (such as those done to revive the woolly mammoth). However, the procedures have been impaired by low-quality sperm due to inbreeding and environmental stress.
A Conservation Facility
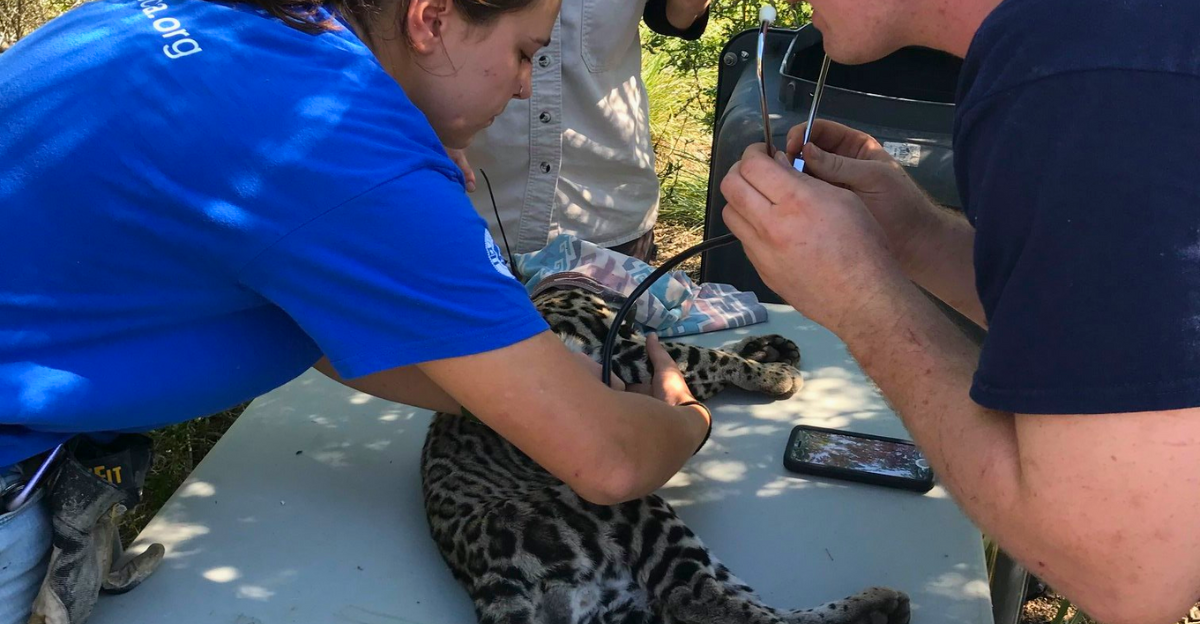

In October 2024, the Caesar Kleberg Wildlife Research Institute at Texas A&M University-Kingsville began work on a $20 million Ocelot Conservation Facility. The state-of-the-art facility will advance ocelot research and breeding efforts. However, while captive breeding programs aim to preserve the species, they risk creating conservation dependency, where wildlife populations cannot survive or thrive without human intervention.
Criteria for Release
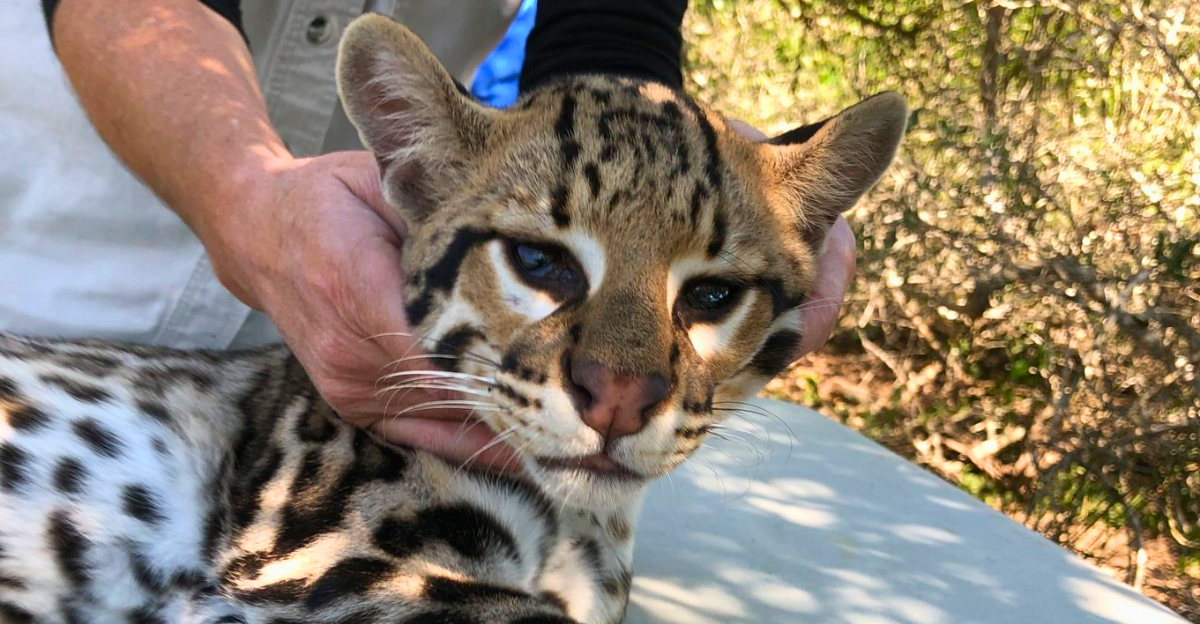

The new facility will provide room for young ocelots to learn hunting and other natural instincts, preparing them for release into the wild and assisting in population recovery. The success of this project relies on collaboration among various organizations and stakeholders, including the East Foundation, Cincinnati Zoo, and private landowners, who share a common vision.
Arguments Against Conservation
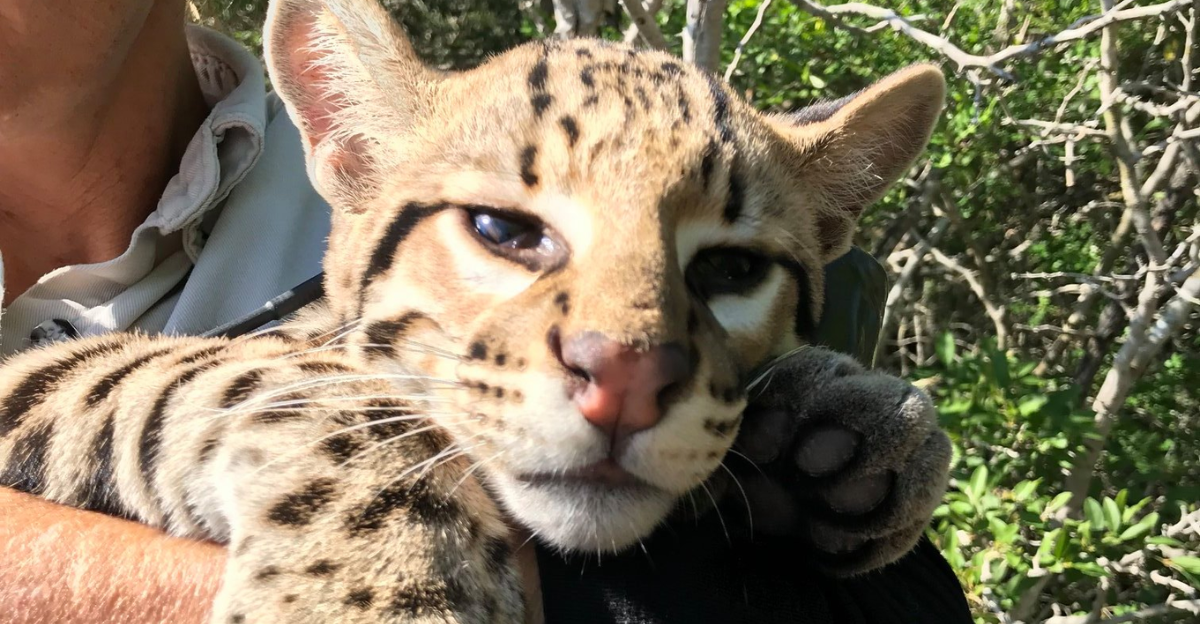

Some argue that focusing solely on ocelot conservation overlooks broader ecosystem issues. For example, many may believe that the $20 million spent on the Ocelot Conservation Facility might be better spent by trying to reduce greenhouse gas emissions nationwide. Other concerns question the effects of restoring the ocelot population on species that they prey on. However, there is at least one good reason to protect the ocelots – they help mitigate climate change.
Ocelots Help Mitigate Climate Change
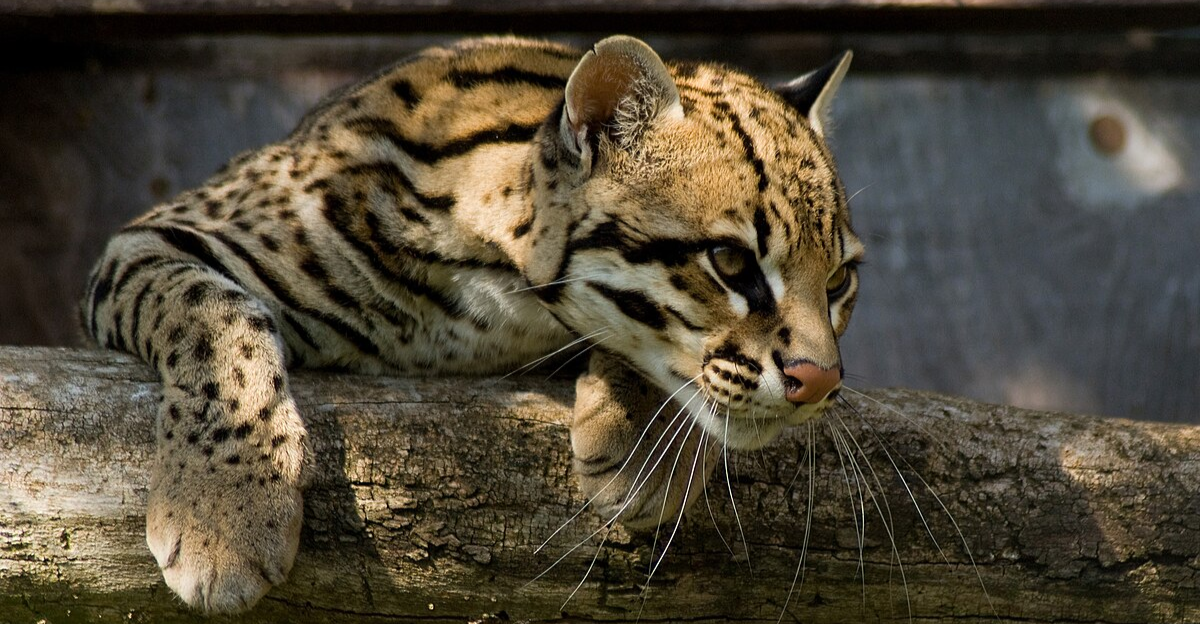

The species’ preferred habitat is known to act as a carbon sink (the process of absorbing carbon from the atmosphere, mitigating climate change), and flood barrier. Protecting ocelot corridors could sequester three times more carbon than adjacent grasslands – making their conservation a climate strategy disguised as species preservation. The Kingsville facility’s work is thus not just about protecting and preserving the cat species but about geoengineering through biodiversity.
A Promising Future
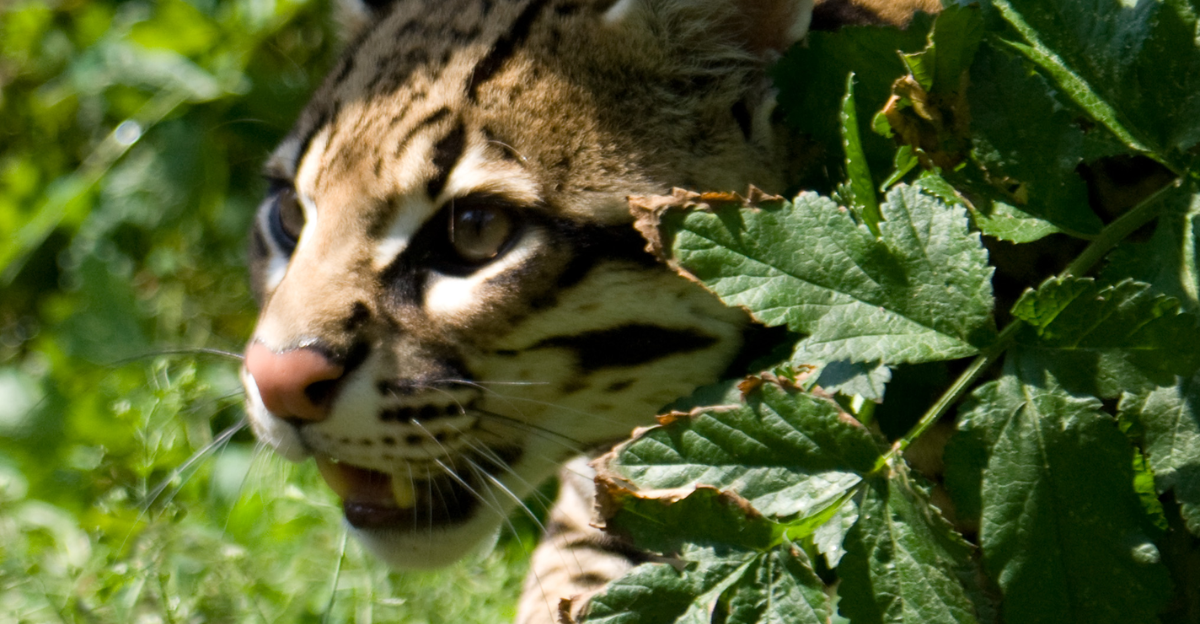

As the ocelot faces numerous challenges, including evolutionary stagnation, there is still hope for this species. Despite habitat losses, inbreeding, road mortality, and artificial breeding challenges, a collaborative effort between scientists and conservationists could make all the difference in ensuring a better future for the ocelot in America, where these beautiful cats flourish again in their native countries.
Explore more of our trending stories and hit Follow to keep them coming to your feed!
Don’t miss out on more stories like this! Hit the Follow button at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest news. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!







