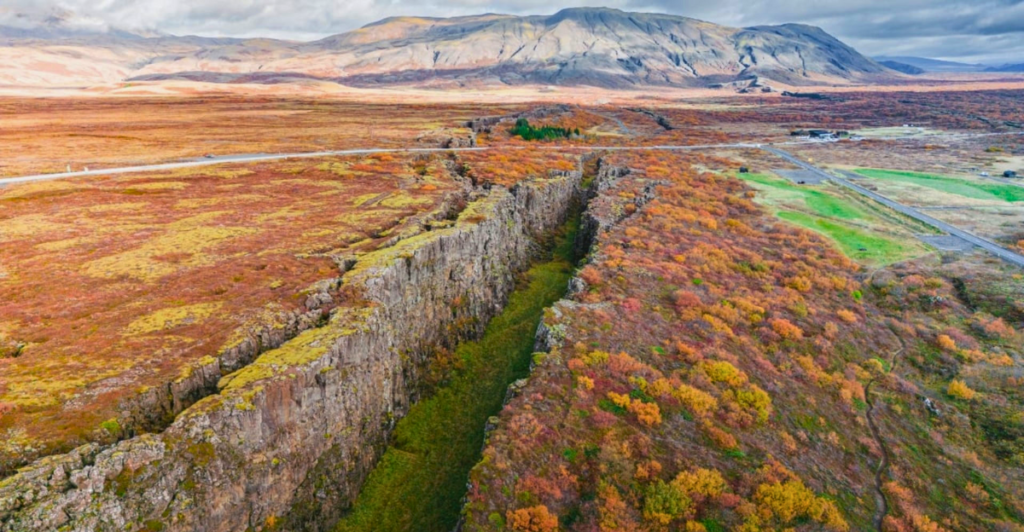

The Earth’s crust, the outermost solid shell of our planet, is not as static as we might perceive. Beneath our feet, a dynamic world of shifting plates and immense geological forces is constantly at play. Recent research from the University of Göttingen has brought to light new evidence suggesting that certain areas of the Earth’s crust are experiencing collapse, leading to significant structural shifts in the surrounding habitats. This phenomenon, while natural, has profound implications for ecosystems and human infrastructure alike.
The University of Göttingen’s Groundbreaking Research
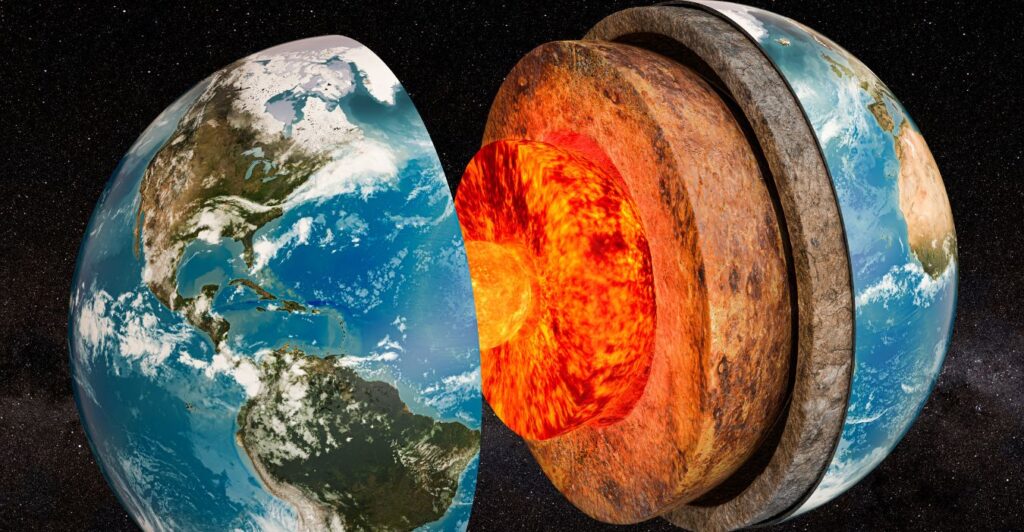

Researchers at the University of Göttingen have been at the forefront of investigating these crustal collapses. Their work involves advanced geological surveying, seismic monitoring, and sophisticated modeling techniques to understand the mechanisms driving these events and predict their potential impacts.
Understanding Crustal Collapse
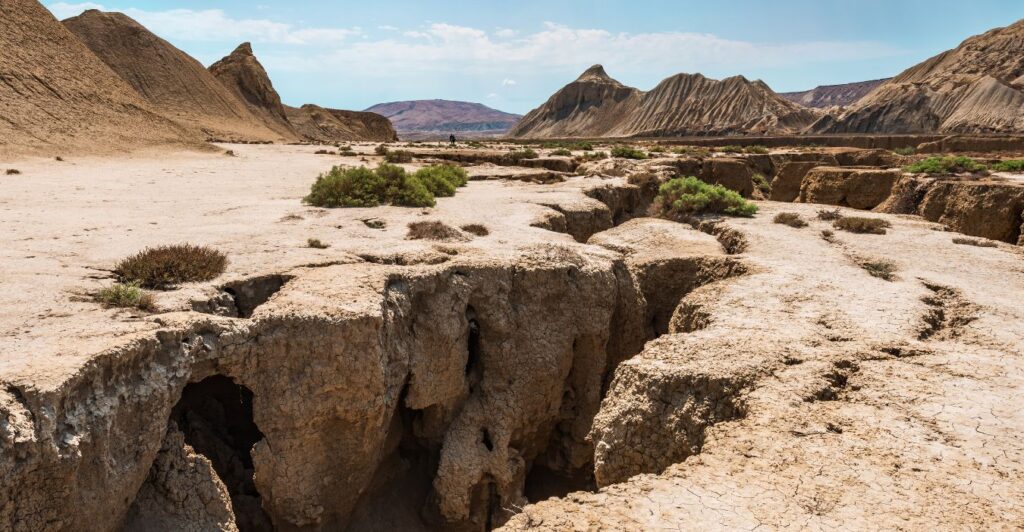

Crustal collapse occurs when portions of the Earth’s crust lose structural integrity and subside or sink. This can be triggered by a variety of factors, including the removal of underlying support, tectonic stresses, or the dissolution of subsurface materials.
Tectonic Activity and its Role
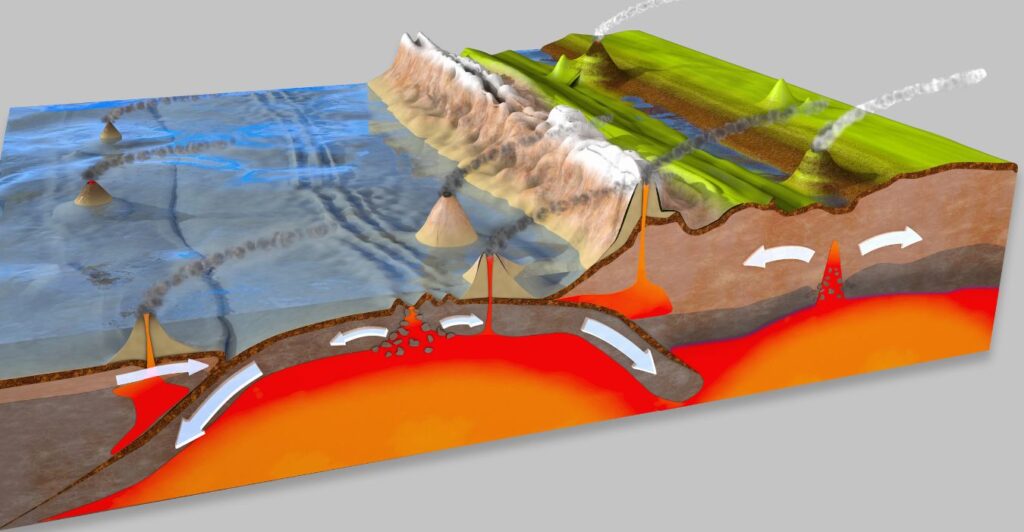
Tectonic forces, the same forces responsible for earthquakes and mountain building, can also contribute to crustal instability. When tectonic plates shift and collide, they can create zones of weakness in the crust, making them more susceptible to collapse.
The Dissolution Factor
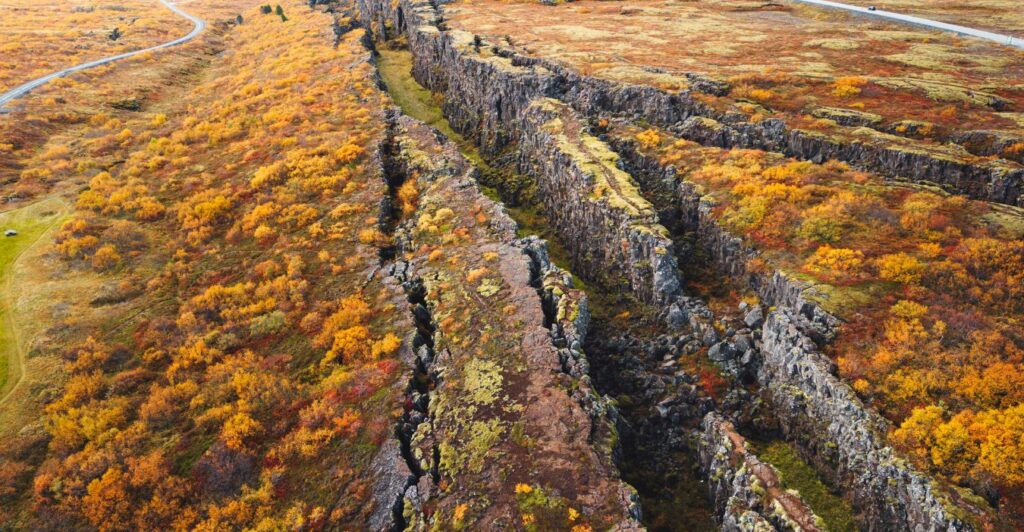

In regions with soluble rocks like limestone or gypsum, groundwater can dissolve these materials over time, creating underground cavities. If these cavities become too large, the overlying crust can collapse into them.
Impact on Habitats

The structural shifts resulting from crustal collapse can dramatically alter surrounding habitats. Changes in elevation, drainage patterns, and soil composition can all have cascading effects on plant and animal life.
Forest Ecosystems Under Threat

Forests are particularly vulnerable to crustal collapse. Subsidence can lead to the uprooting of trees, changes in water availability, and increased soil erosion, potentially leading to forest dieback.
Aquatic Habitats in Peril

Aquatic ecosystems, such as rivers, lakes, and wetlands, can also be severely affected. Crustal collapse can alter streamflow patterns, bury aquatic habitats, and introduce pollutants into the water.
The Domino Effect on Wildlife

The changes in habitats can have a domino effect on wildlife populations. As habitats shrink or become degraded, animals may struggle to find food, shelter, and breeding grounds, leading to population declines or even local extinctions.
Implications for Human Infrastructure
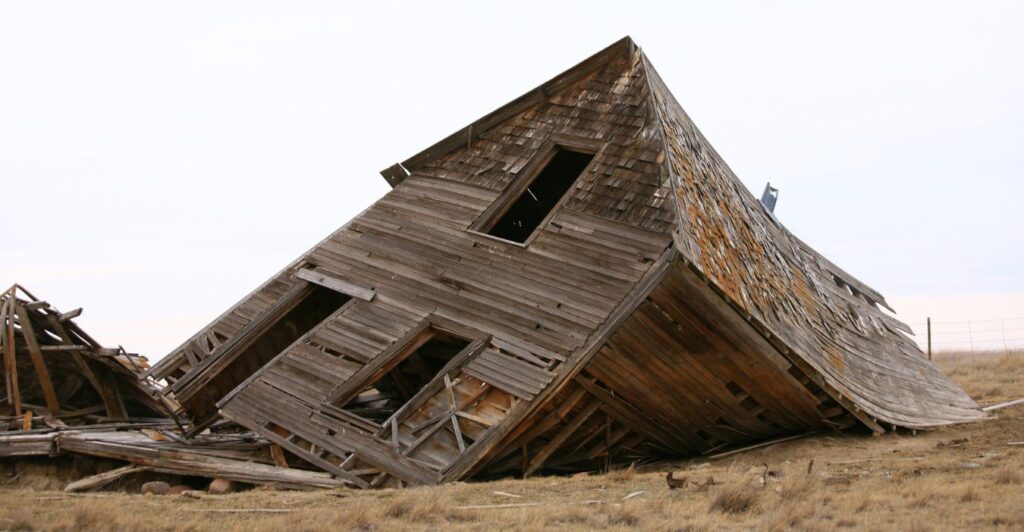

Beyond the ecological impacts, crustal collapse poses significant risks to human infrastructure. Buildings, roads, pipelines, and other structures can be damaged or destroyed by subsidence, leading to economic losses and potential safety hazards.
Case Studies: Examples of Crustal Collapse
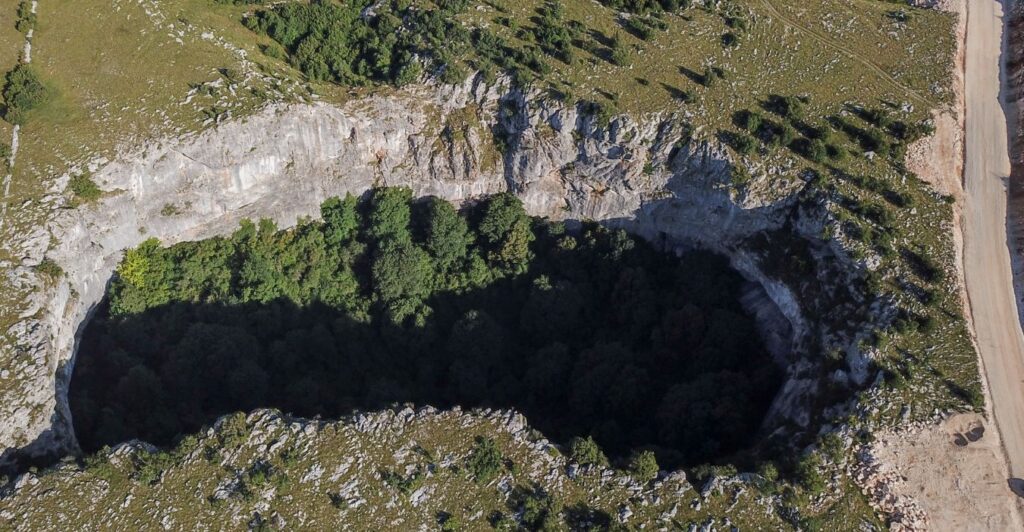

Crustal collapse can be observed in various regions worldwide. For instance, a notable example is the limestone mine collapse in Pennsylvania, where structural weaknesses led to significant subsidence. The Scandinavian Caledonides experienced orogenic collapse during ancient mountain-building processes, while the Basin and Range Province in North America show extensive faulting due to crustal extension. The Aegean Sea Plate has undergone changes due to slab rollback, and parts of the Tibetan Plateau exhibit lateral stretching despite ongoing compression. Additionally, southwestern China has seen rapid thickening followed by collapse during certain geological epochs. These diverse examples highlight how different geological processes lead to crustal instability across various environments globally.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
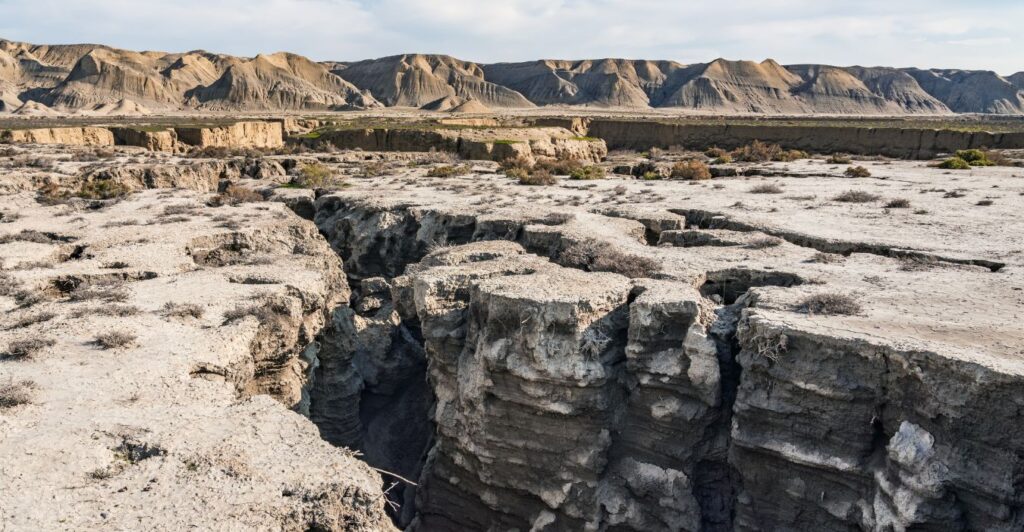

Addressing the challenges posed by crustal collapse requires a combination of mitigation and adaptation strategies. This includes geological monitoring, land-use planning, and engineering solutions to stabilize affected areas.
The Future: Monitoring and Prediction
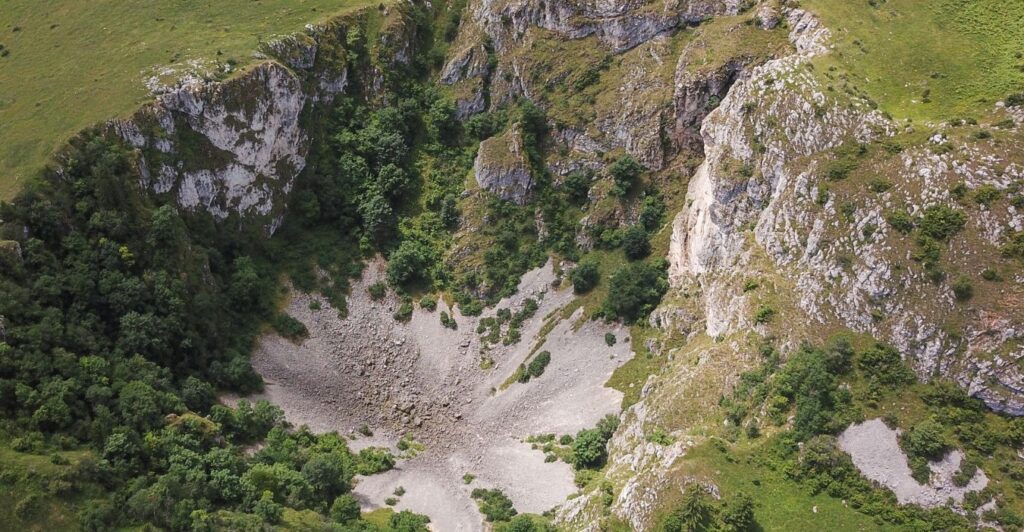

Continued research and monitoring are crucial for understanding the complex processes driving crustal collapse and predicting future events. By improving our ability to forecast these events, we can better protect both natural ecosystems and human communities.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them appearing in your feed
California Is Breaking Apart: A Fault Line Is Forming Faster Than Anyone Predicted
California Is Splitting Apart: A Fault Line Is Forming Faster Than Anyone Predicted
The War on Cows Is Over—And Green Extremists Have Lost
There Will Be Eruptions”: Concerns Mount as Yellowstone Supervolcano Activity Shifts
References:
Reference 1
Reference 2
Reference 3
This article first appeared here
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







