
California was rocked by a double earthquake just hours apart last week, raising concerns about the potential for more significant seismic events to come. The state’s geology is complex and contains many active fault lines, making it susceptible to earthquakes. In this article, we will discuss the recent seismic activity, its effects on ecosystems, and its broader implications for California’s environment and residents.
Background on California Earthquakes
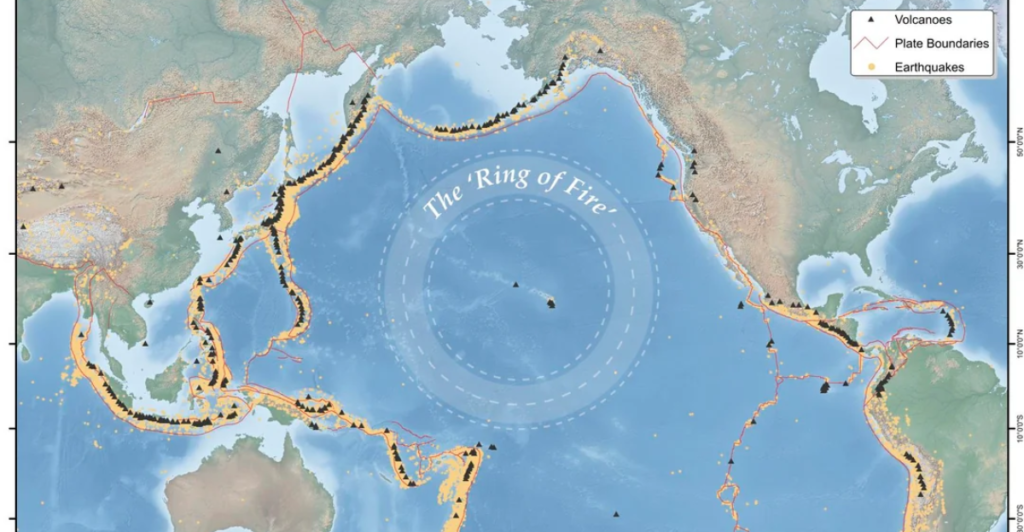
California’s position on the Pacific Ring of Fire places it in an earthquake-prone region of the world. The state is crisscrossed with major fault lines — including the San Andreas Fault and the Hayward Fault — both of which are capable of producing significant earthquakes. Recent activity has intensified fears that a major quake, often referred to as the “Big One,” could be imminent.
Recent Earthquake Activity

In recent weeks, California has experienced a surge in earthquake activity. These include several small to moderate quakes in the Los Angeles area and the Bay Area. A magnitude 4.3 earthquake occurred near Aal, and a few smaller quakes were detected near Hayward.
Los Angeles Earthquakes
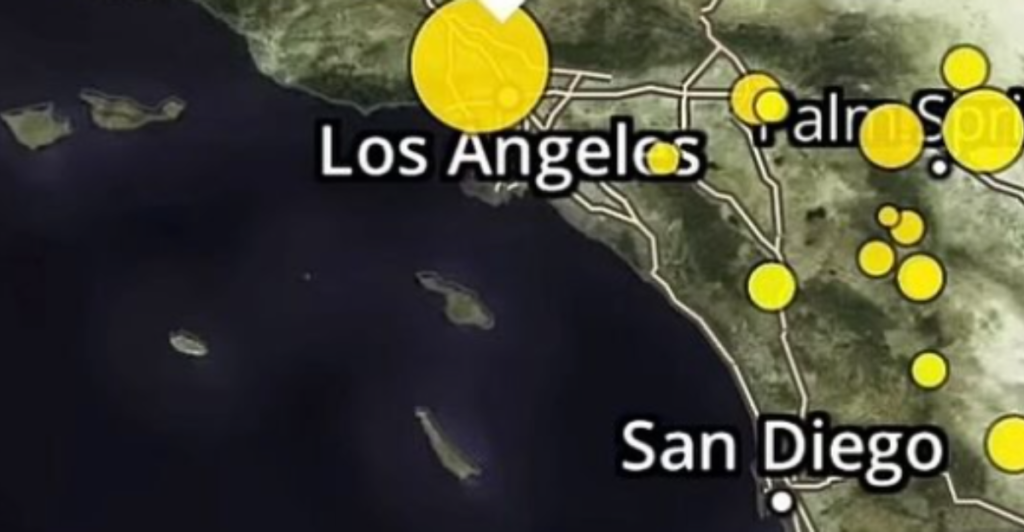
Over six dozen earthquakes have occurred in and around Los Angeles since March 2025, a notable increase in seismic activity. Two notable clusters of earthquakes have been identified near North Hollywood and Malibu, following mainshocks of magnitudes 3.8 and 4.1, respectively.
Malibu Earthquake
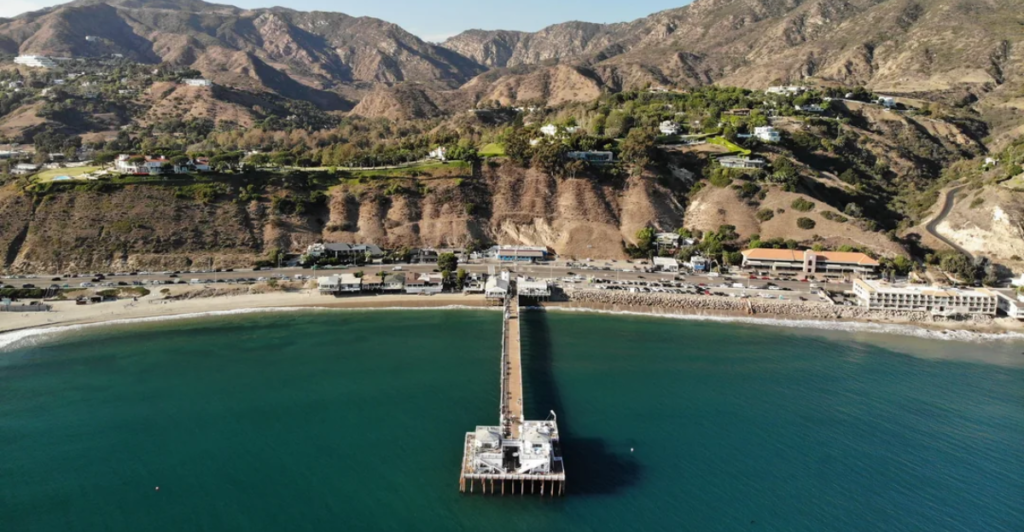

On March 9, 2025, a magnitude 4.1 earthquake centered north of Malibu caused light shakes in Southern California. Several aftershocks followed the quake, including a magnitude 2.5 event a minute later and another with a magnitude of 3 and a magnitude of 2.8.
Impact on Ecosystems

Earthquakes can significantly impact local ecosystems. They can alter landscapes, disrupt habitats, and affect wildlife populations. In California, where biodiversity is abundant, such disruptions can be especially troubling for sensitive ecosystems found in coastal areas and mountainous regions.
Environmental Concerns

The environmental impact of earthquakes is not limited to habitat destruction. Seismic events can also cause soil liquefaction, landslides, and changes in groundwater flow that might trigger longer-term ecological changes.
Economic Implications
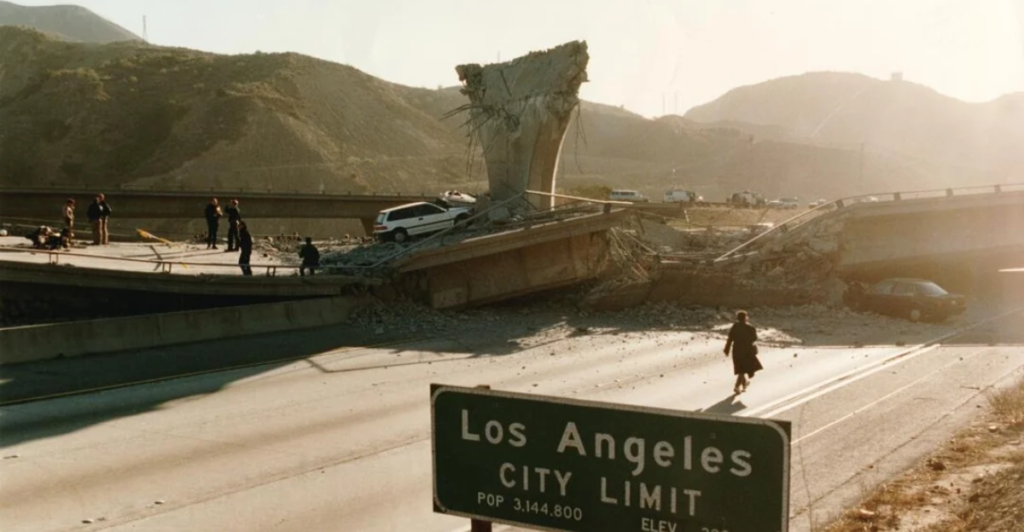

Earthquakes have significant economic implications beyond environmental impacts as well. Damage to infrastructure, disruptions to businesses, and expenses for recovery efforts can burden local and state economies.
The Public Reaction and Response to Preparedness
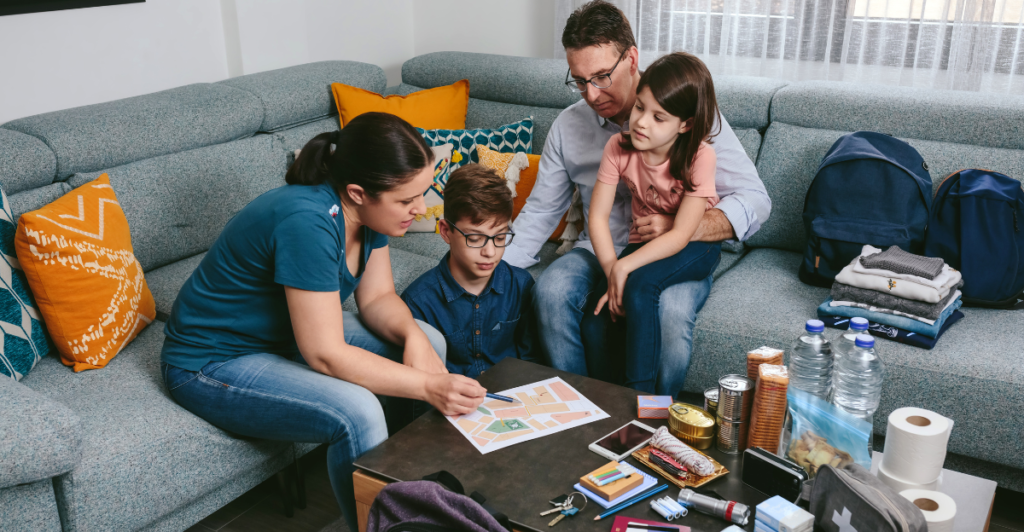

Public awareness and preparedness are critical in light of the increased seismic activity. Residents have been warned to prepare emergency plans, including evacuation routes and emergency supplies. Regular drills and education programs also keep communities alert and ready for when disasters strike.
Scientific Analysis
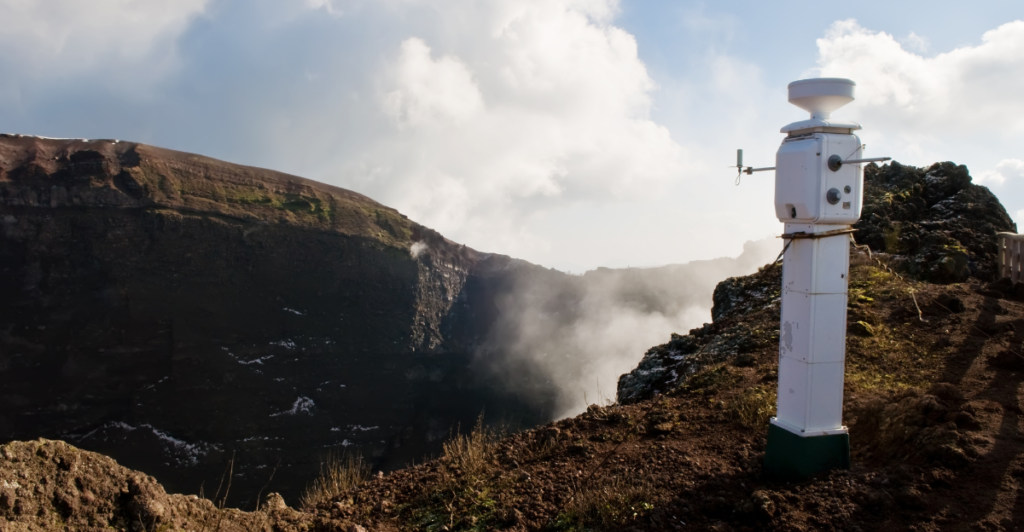

Scientists continue to monitor seismic activity closely, using advanced technologies to predict and understand earthquake patterns. Although accurately predicting the time of earthquakes is quite challenging, the ongoing research assists in upgrading preparedness and responses to these geological phenomena.
Historical Context
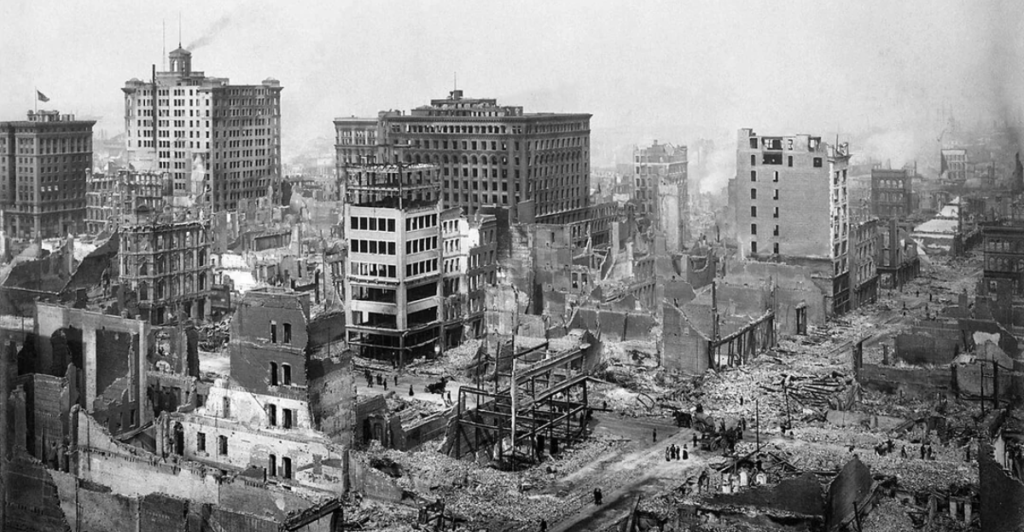

California has a history of major earthquakes, such as the 1906 San Francisco earthquake and the 1994 Northridge earthquake. These events remind us of the state’s susceptibility to large-scale seismic events and further emphasize the need for continued preparedness initiatives.
Future Risks

The threat of a major earthquake like the “Big One” still looms over California. Scientists predict that such an event could reach a magnitude of 7.8 or higher, causing widespread devastation across Southern California.
The Need for Ongoing Preparedness

In conclusion, California’s recent earthquakes remind us of the state’s seismic vulnerabilities. Although these recent quakes have had limited immediate impacts, they emphasize the need for ongoing preparedness and scientific study to mitigate the potential effects of these quakes going forward. As California moves forward, addressing both environmental and economic concerns will be essential in managing the risks associated with its earthquake-prone landscape.







