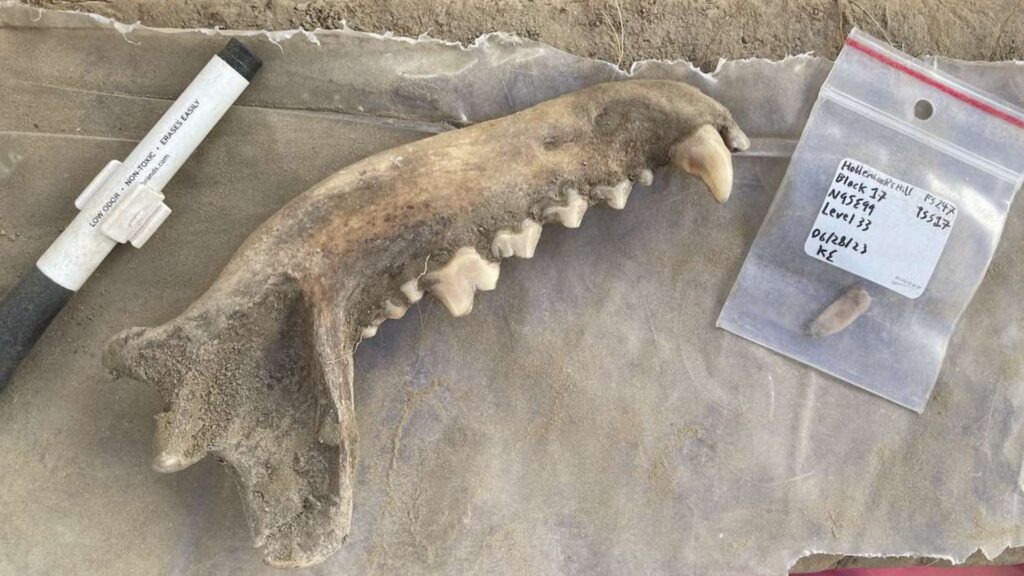

In a groundbreaking revelation, recent archaeological findings have uncovered that the deep bond between humans and dogs in the Americas dates back at least 12,000 years. This discovery sheds light on the longstanding companionship that predates written history, suggesting dogs have been “man’s best friend” far longer than previously understood.
Early Companionship in the Americas
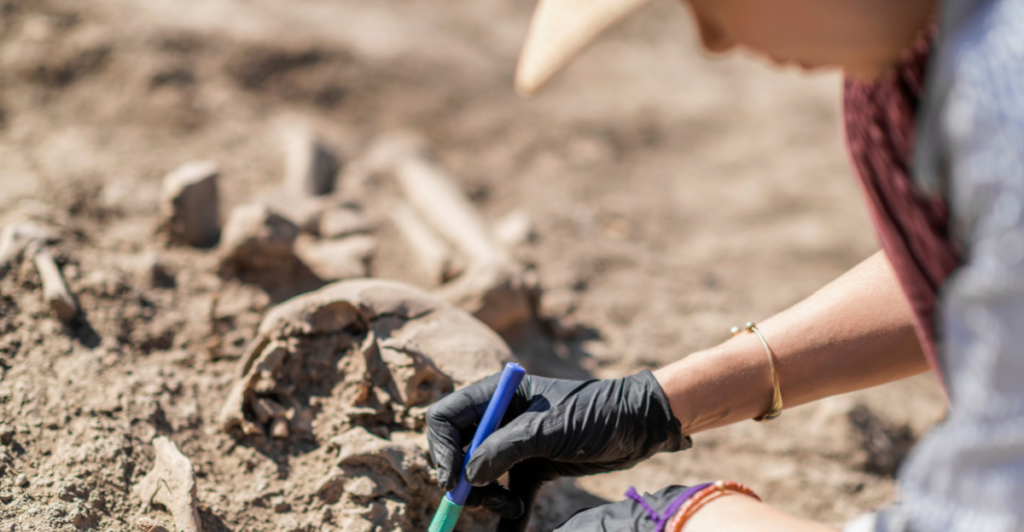

The research, conducted by a team of international archaeologists, involved the excavation of ancient burial sites in North and South America. They discovered the remains of domesticated dogs alongside human skeletons, indicating a close relationship between the species. These findings suggest that dogs were not only companions but also played integral roles in early human societies.
The Role of Dogs in Ancient Societies
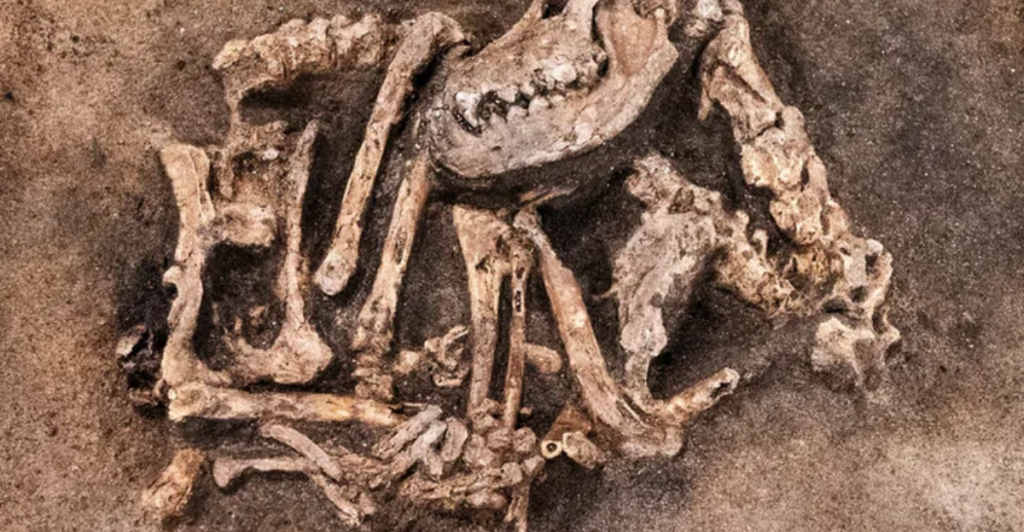

Evidence from these burial sites highlights the multifaceted roles dogs played in ancient human life. From assisting in hunting to providing protection and companionship, dogs were deeply embedded in the daily lives of their human counterparts. Their presence in burial sites suggests that they were highly valued, even in death.
The Journey of Domestication
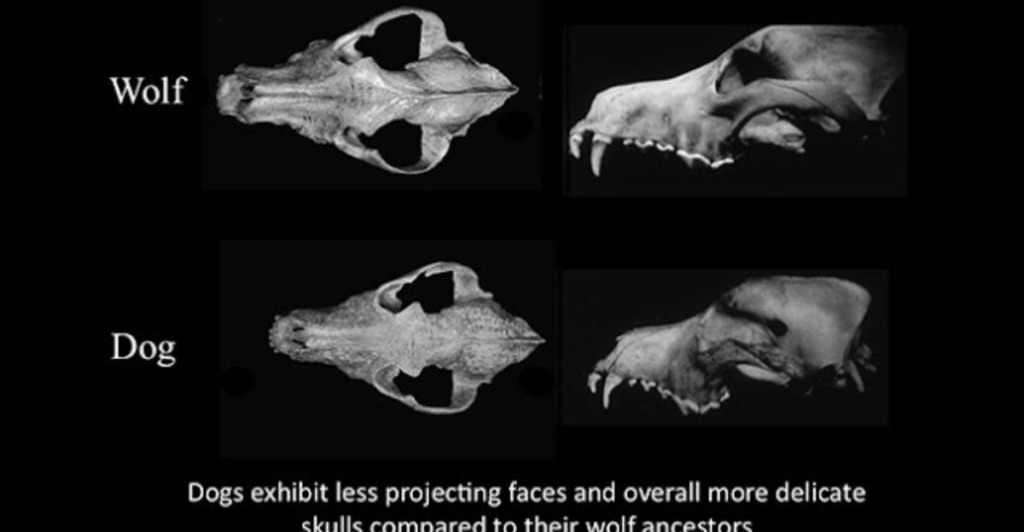
The domestication of dogs is believed to have originated from wolves, with the process beginning thousands of years earlier in Eurasia. However, the spread of domesticated dogs to the Americas demonstrates the adaptability and resilience of this species. The transition from wild wolves to domesticated dogs likely involved a mutual relationship that benefited both species.
Genetic Evidence and Migration Patterns
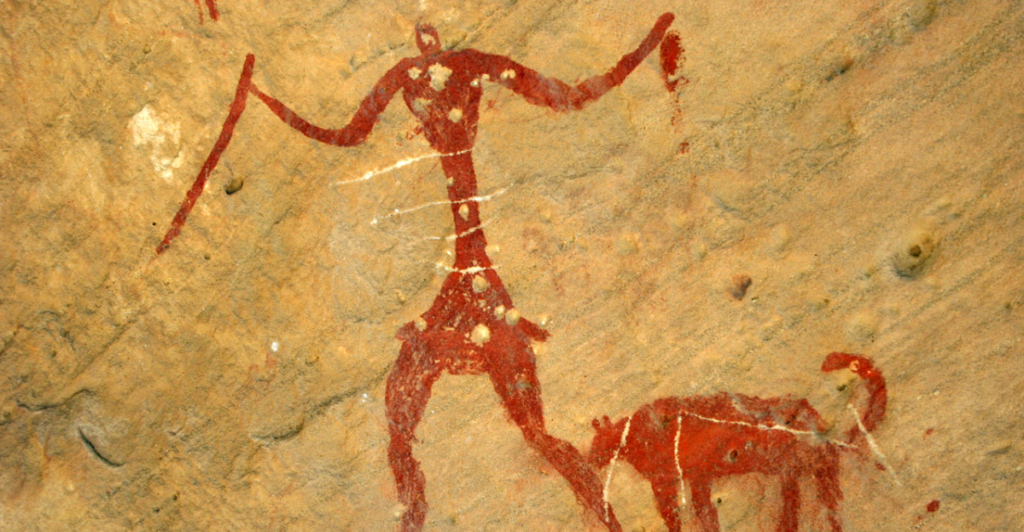

Genetic studies on the remains of these ancient dogs provide insights into the migration patterns of early human settlers in the Americas. The DNA of these dogs reveals a shared lineage with dogs found in other parts of the world, suggesting that as humans migrated, they brought their canine companions with them. This intercontinental journey underscores the enduring partnership between humans and dogs.
Cultural Significance and Symbolism

Dogs held significant cultural and symbolic value in many ancient societies. In some cultures, they were seen as spiritual guides or protectors in the afterlife. The placement of dog remains in burial sites, often with grave goods, indicates their revered status. This cultural importance is reflected in various indigenous myths and legends that celebrate the bond between humans and dogs.
Dogs as Early Working Partners
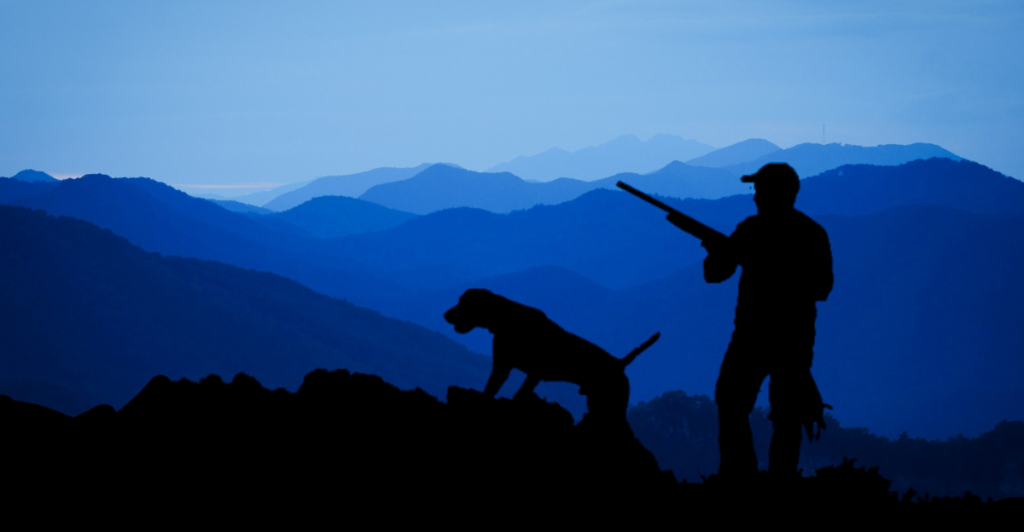

The findings also highlight the practical roles dogs played as working partners. Archaeological evidence points to their involvement in hunting and gathering, where they would have helped track and retrieve game. This partnership would have been crucial for survival, especially in harsh environments where resources were scarce.
A Symbol of Loyalty and Protection
Throughout history, dogs have symbolized loyalty and protection. The ancient remains discovered in the Americas provide a testament to this enduring trait. The companionship and protection offered by dogs were likely vital in early human settlements, fostering a bond that has endured for millennia.
Dogs in Burial Practices
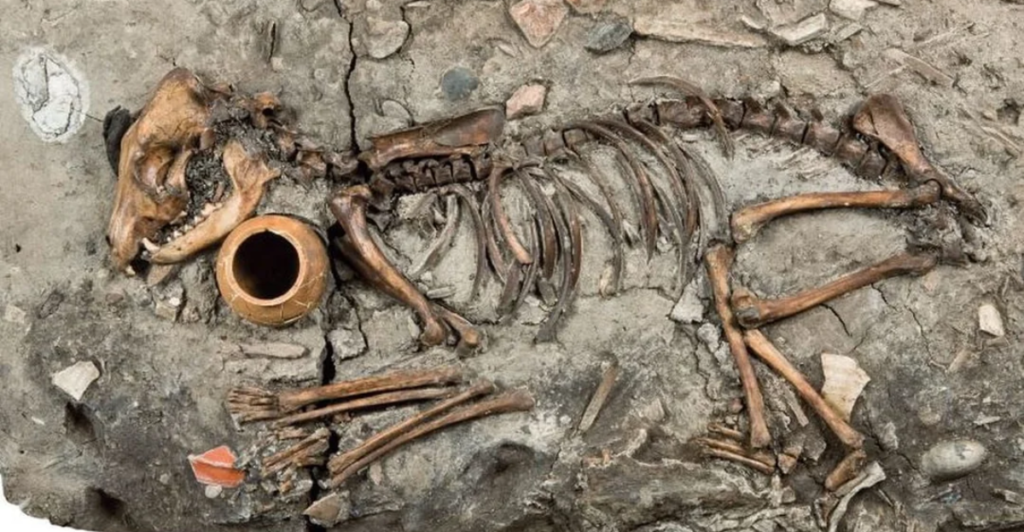

The inclusion of dogs in human burial practices is particularly telling. In some cases, dogs were buried with their owners, suggesting a belief in their companionship extending into the afterlife. This practice highlights the deep emotional connection and respect humans had for their canine companions.
Impact on Modern Understanding of Human-Animal Relationships

These ancient findings challenge and expand our understanding of human-animal relationships. They demonstrate that the bond between humans and dogs is not a recent development but rather a fundamental aspect of human history. This relationship has evolved over thousands of years, shaping the way humans and dogs interact today.
Technological Advancements in Archaeology
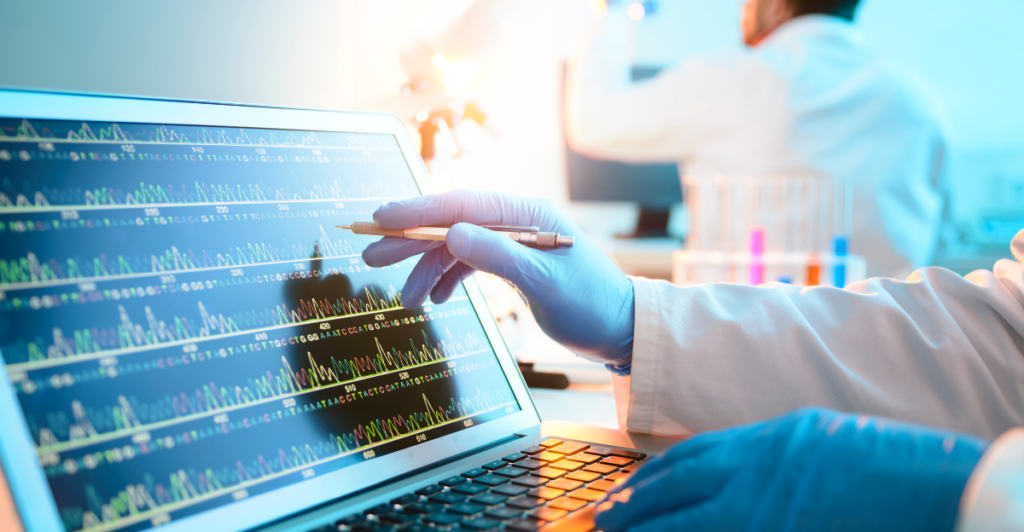

The discovery was made possible through advanced archaeological techniques, including radiocarbon dating and DNA analysis. These technologies have allowed researchers to accurately date the remains and trace the genetic lineage of the dogs, providing a clearer picture of their historical significance.
Future Research Directions
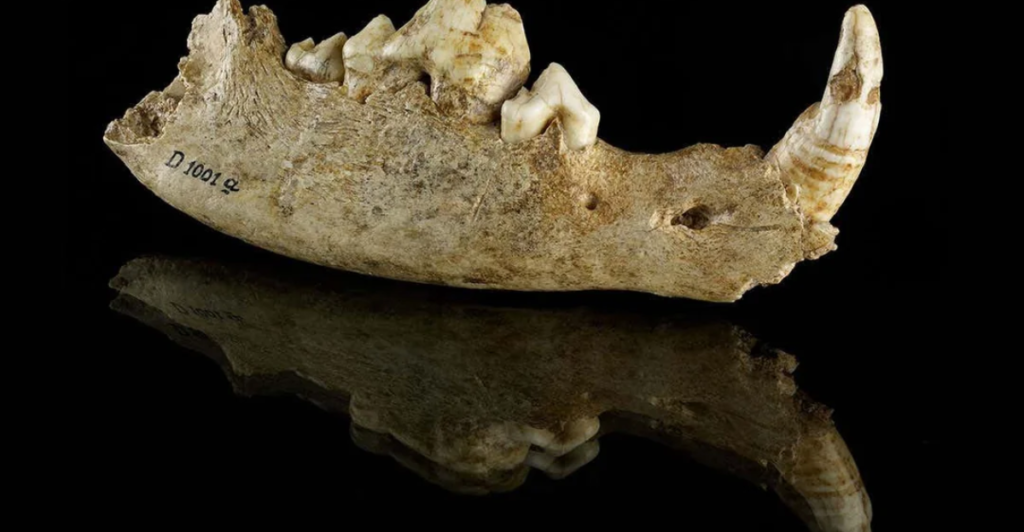

The findings open up new avenues for research into the domestication and migration of dogs. Future studies aim to explore the genetic diversity of ancient dogs and their role in various cultural contexts. This research will further illuminate the deep-rooted relationship between humans and dogs.
A Timeless Bond

The discovery of ancient domesticated dogs in the Americas underscores the timeless bond between humans and dogs. For at least 12,000 years, this relationship has been a cornerstone of human life, providing companionship, protection, and partnership. As research continues, the story of dogs as “man’s best friend” will undoubtedly reveal even more fascinating insights into our shared history.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them appearing in your feed.
11 Strongest Animals On Earth and Where to Find Them
12 Bold Animals That Have No Fear of Predators – Nature’s Underrated Fighters
Tips for Bringing an Outside Cat Inside Before the Winter Comes
Best 14 Dog Breeds to Terrify Intruders
References:
80 prehistoric tombs filled with bizarre animal skulls found in Wyoming
Fossil amphibians found in burrows where they waited for the next rainy season
Amphibian fossils found in burrows reveal ancient survival strategies
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







