
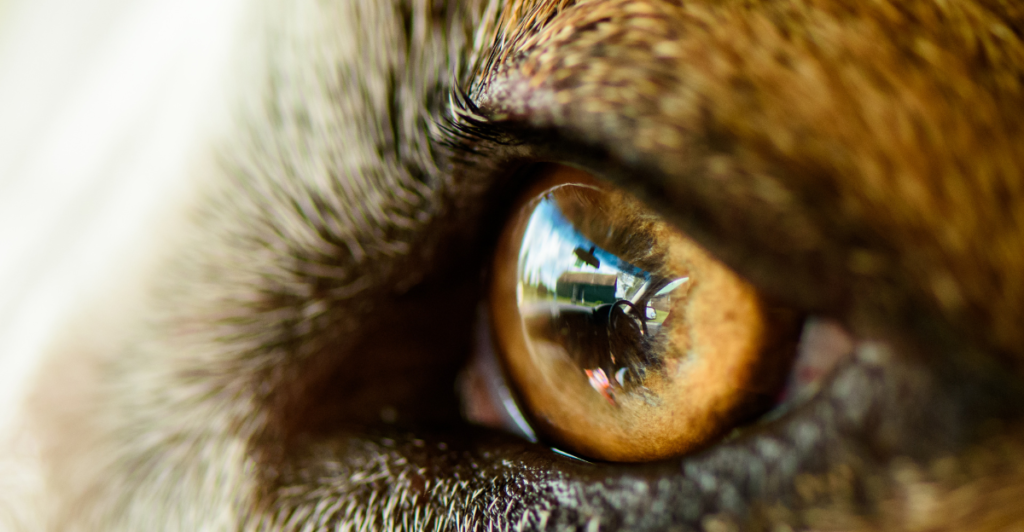
Dogs don’t see the world in black and white, but their color vision is limited compared to humans. They can only perceive shades of blue and yellow, as they lack red and green cones in their eyes. This makes their vision similar to a human with red-green color blindness. While they might not see the vibrant reds of a toy, they excel in distinguishing other details, such as movement and brightness levels.
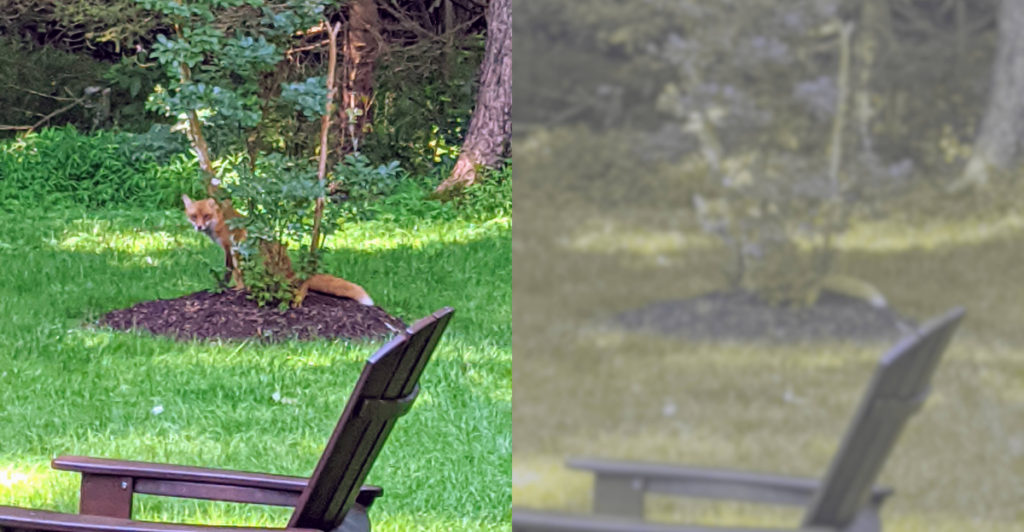
Superior Night Vision

Dogs have excellent night vision thanks to a special reflective layer in their eyes called the tapetum lucidum. This layer enhances their ability to see in low-light conditions, allowing them to navigate the dark far better than humans. Combined with their ability to detect motion, this feature gives dogs an advantage as natural hunters or watchdogs during the night. This is one reason they’re often used for security purposes.
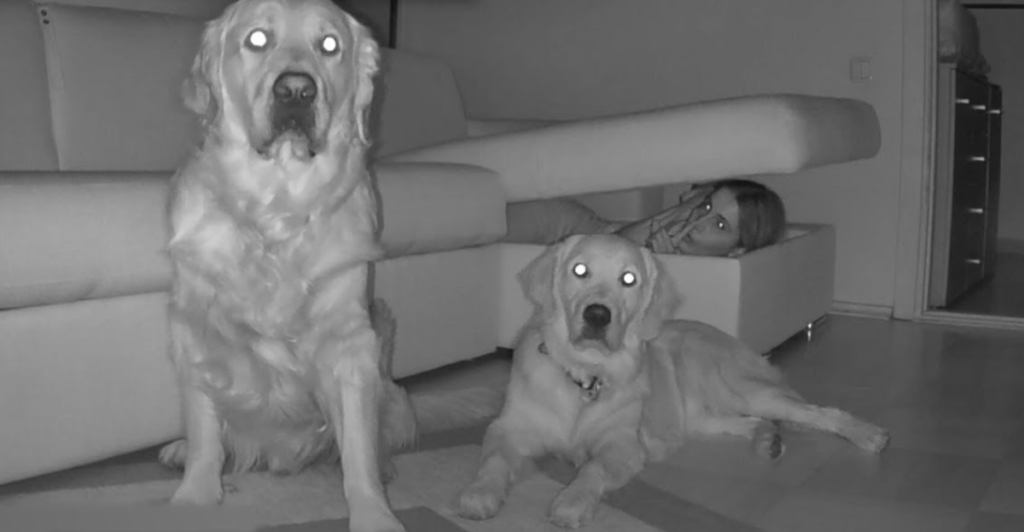
A Wider Field of Vision

Dogs have a wider field of vision than humans due to the placement of their eyes on the sides of their heads. While humans have a 180-degree field of vision, dogs enjoy a panoramic view of about 250 degrees, depending on the breed. However, this wide range comes with slightly less depth perception than humans, which can make judging distances more challenging for them.
Motion Detection Experts

One of the most impressive aspects of a dog’s vision is its ability to detect movement. Dogs are susceptible to motion, even at a distance. This trait has evolutionary roots, helping them quickly spot prey or potential dangers. While their static visual acuity isn’t as sharp as humans, their ability to pick up subtle movements makes them excellent hunters and companions for outdoor activities.
Dogs Are Nearsighted

While dogs excel at sensing movement, they’re generally nearsighted. Most dogs can only clearly see objects within 20 feet, compared to the human ability to see details up to 75 feet away. This explains why your dog might not recognize you from a distance until you call out or move closer. However, their other senses, such as smell and hearing, quickly compensate for this visual limitation.
Shades of Gray Are Vibrant to Dogs

While dogs may not see a full spectrum of colors, they are excellent at distinguishing between shades of gray. Their retinas contain more rods than cones, enhancing their ability to see in dim light and pick out fine details in black-and-white contrasts. This feature is beneficial for tracking in low-light conditions, making it a valuable skill for hunting and search-and-rescue dogs.
Puppies’ Vision Develops Over Time

Newborn puppies are born blind and only begin to open their eyes around 10 to 14 days after birth. Even then, their vision remains blurry for the first few weeks. It can take several months for a puppy’s eyes to mature and fully provide clear vision. This gradual development coincides with their growing ability to explore and interact with the world around them.
Dogs See Fewer Details Than Humans

Dogs have fewer cone cells in their retinas than humans, which limits their ability to see fine details. While humans rely heavily on their eyesight to interpret the world, dogs depend more on their keen senses of smell and hearing. This is why they may focus on sniffing and listening rather than relying solely on visual cues, especially in unfamiliar environments or situations.
Breed Affects Vision Range
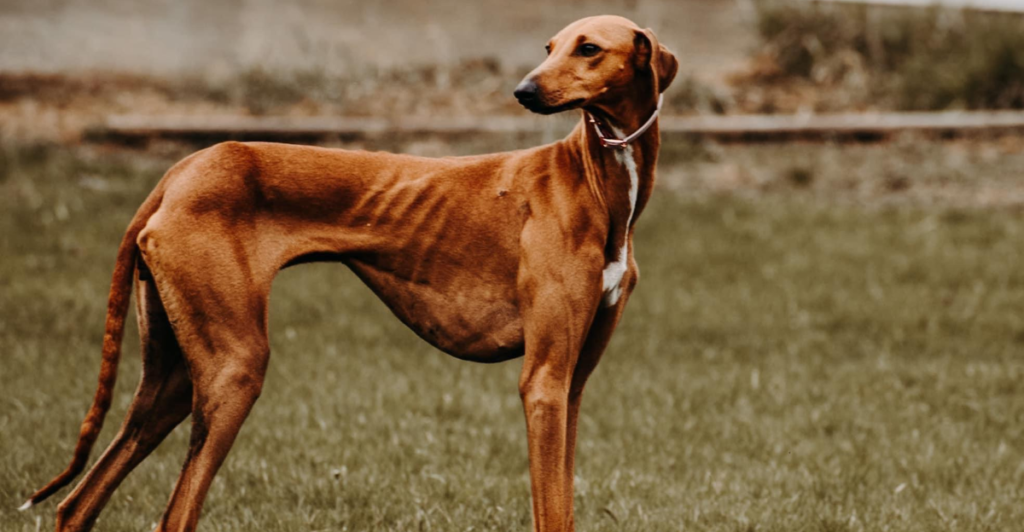

A dog’s breed plays a significant role in its vision capabilities. Like Greyhounds and Whippets, Sighthounds are known for their exceptional eyesight and ability to spot objects at great distances. On the other hand, brachycephalic breeds like Bulldogs and Pugs have a more limited field of vision due to their flat faces. Understanding a dog’s breed can provide insights into its visual strengths and challenges.
Dogs Use Eye Contact for Communication
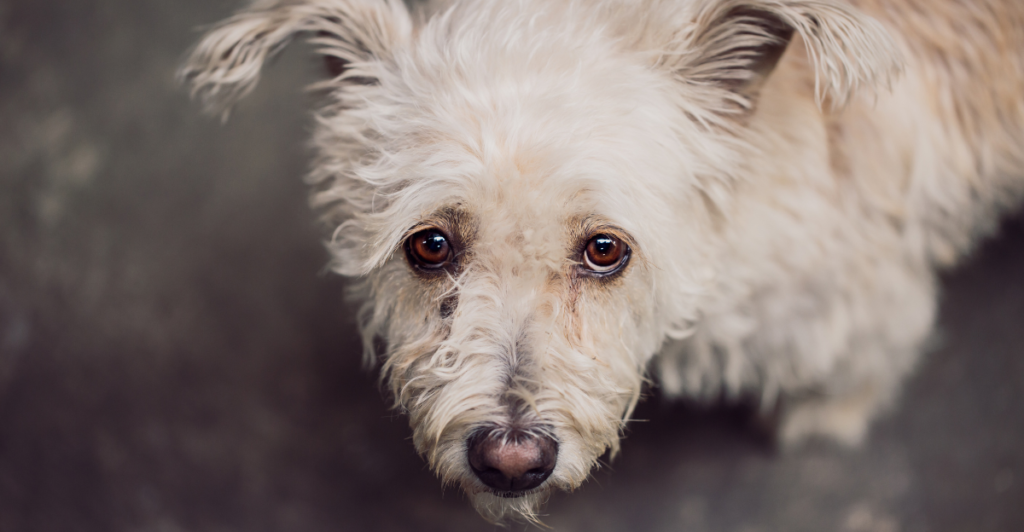

Dogs rely heavily on eye contact to communicate with humans and other animals. While their visual acuity isn’t as sharp as ours, they are incredibly adept at reading facial expressions and body language. Prolonged eye contact can signal trust and connection while avoiding it might indicate stress or submission. This ability strengthens the bond between dogs and their human companions, fostering a unique form of nonverbal communication.
Dogs Are Sensitive to Brightness
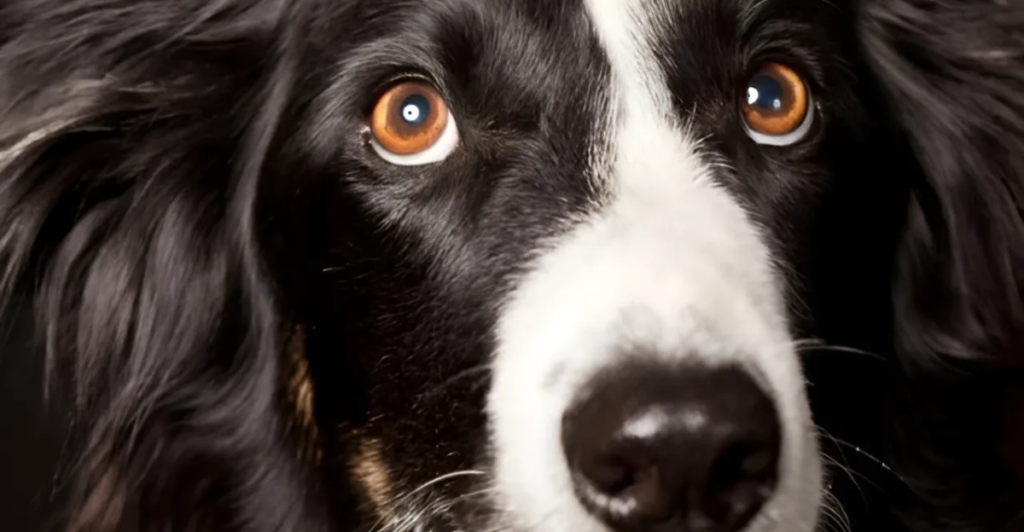

Although dogs have fewer color-detecting cone cells than humans, they are more sensitive to brightness and contrast. This sensitivity helps them navigate their environment and detect movement, even in challenging lighting conditions. It also explains why dogs may squint or avoid direct sunlight. They see the brightness more intensely than we do. Providing shaded areas during outdoor activities can help protect their eyes.
Visual Cues in Training
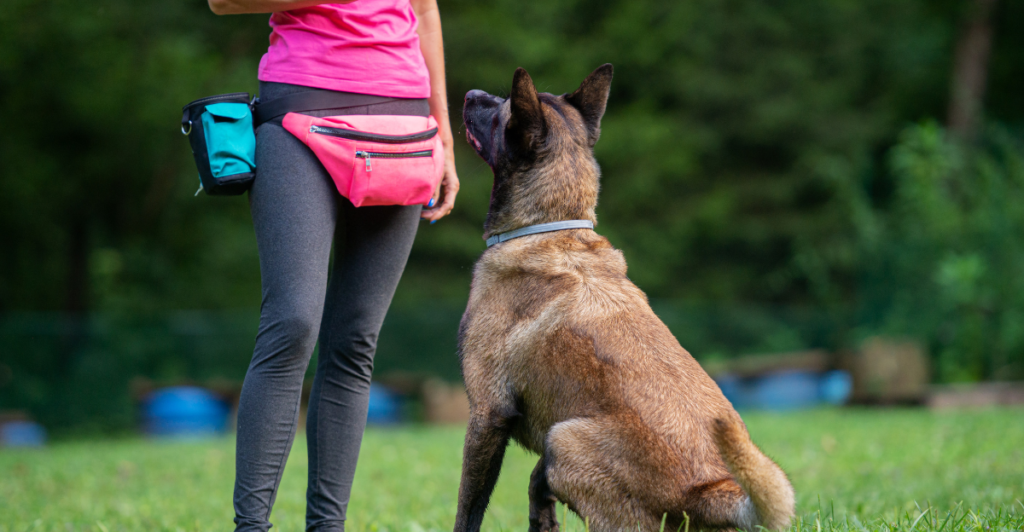

Dogs often respond better to visual cues than verbal commands during training. Their brains process and react to physical gestures faster than spoken words. Using consistent hand signals alongside verbal commands can improve communication and enhance training success. Pairing visual and verbal cues also helps dogs build stronger associations, making them more likely to follow commands reliably over time.
Their Vision Complements Other Senses
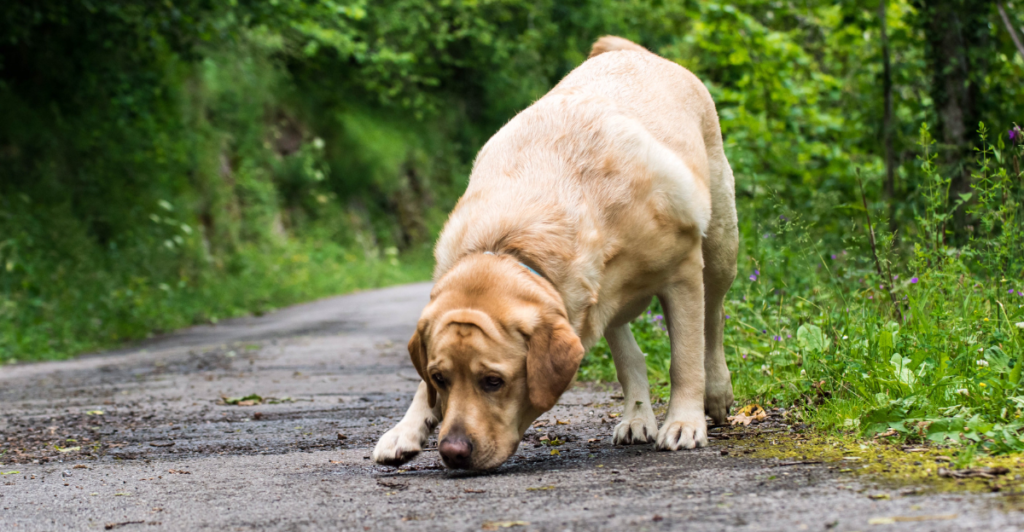

While dogs’ vision has limitations, it works in harmony with their incredible sense of smell and hearing. This combination of senses makes them exceptional at tracking, herding, and search-and-rescue tasks. Their vision may not compare to humans in color or detail, but it is perfectly adapted to their unique needs as loyal companions and skilled workers. Their sensory world is truly remarkable.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them appearing in your feed
California Is Splitting Apart: A Fault Line Is Forming Faster Than Anyone Predicted
10 Dog Breeds That Are Just Like Golden Retrievers
12 German Dog Breeds That Really Define Man’s Best Friend
12 Dog Breeds That Will Never Leave Their Humans’ Side
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







