
Leptospirosis is a bacterial disease that can be passed from dogs to humans through urine. Infected dogs may show no symptoms, but their urine can harbor the bacteria. Humans who come into contact with contaminated water or soil can develop flu-like symptoms, and in severe cases, it can lead to liver or kidney failure.
Cat Scratch Fever
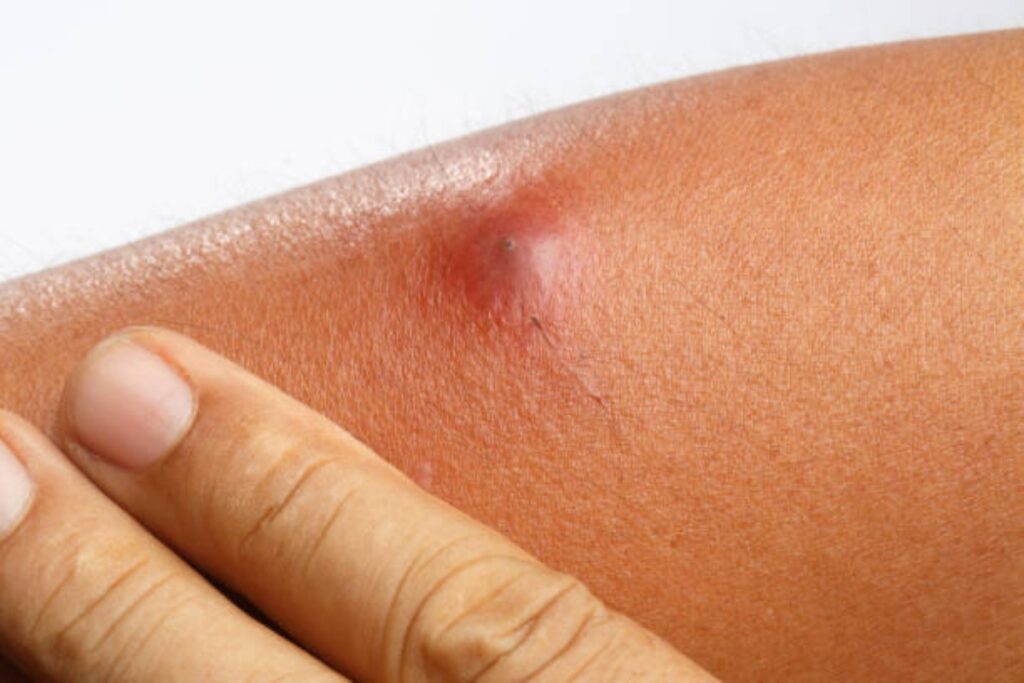
Despite its playful name, cat scratch fever is a serious bacterial infection caused by Bartonella henselae. Cats, particularly kittens, can transmit this disease through scratches or bites. Symptoms in humans include swollen lymph nodes, fever, and fatigue, often surfacing a few weeks after the initial scratch.
Ringworm
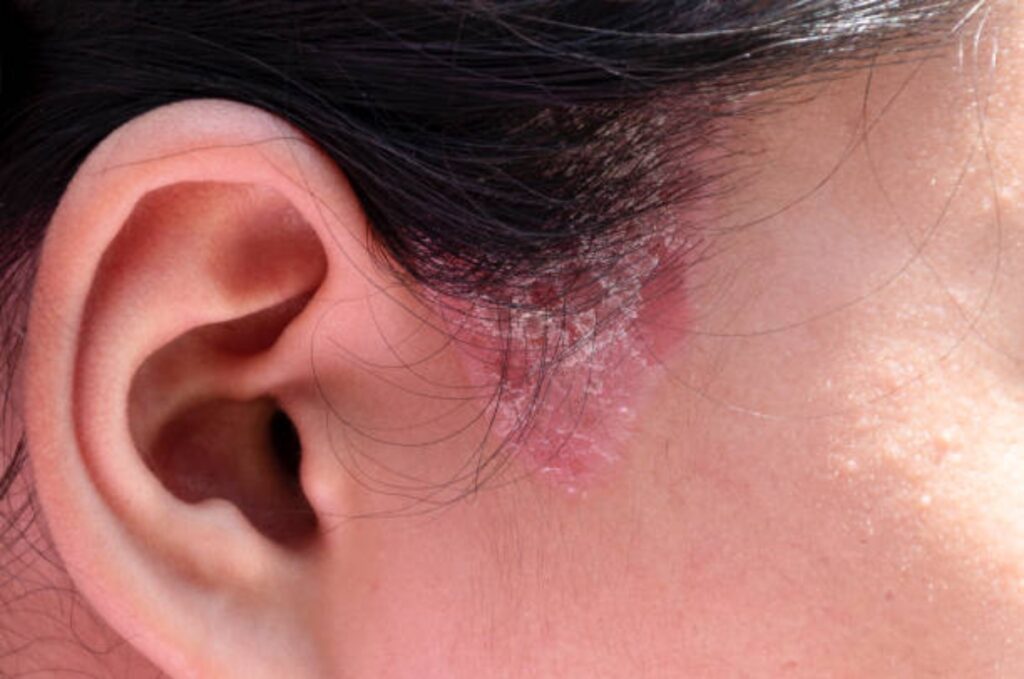
Ringworm isn’t a worm but a fungal infection that can affect the skin, hair, or nails. Dogs, cats, and even rabbits can carry this fungus and transmit it to humans through direct contact. The infection causes red, circular rashes that are itchy and scaly, making it easily identifiable.
Toxoplasmosis

Cat owners may be familiar with toxoplasmosis, a parasitic infection caused by Toxoplasma gondii. Cats can excrete the parasite in their feces, and humans may contract it by handling contaminated litter. While it usually causes mild flu-like symptoms, toxoplasmosis can be particularly dangerous for pregnant women and those with weakened immune systems.
Campylobacteriosis
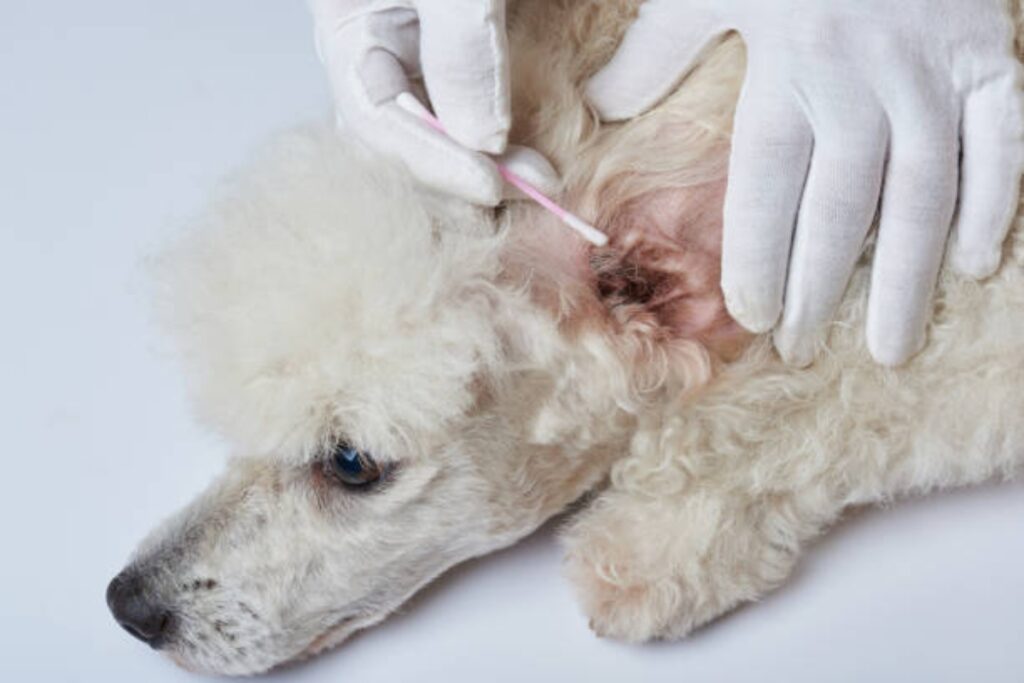
This bacterial infection is often linked to food poisoning, but it can also be transmitted by pets, especially young puppies and kittens. Campylobacter bacteria are present in the feces of infected animals and can be transmitted through direct contact. In humans, it can cause diarrhea, cramping, and fever.
Rabies

One of the most well-known zoonotic diseases, rabies, is a viral infection that affects the nervous system. Although it’s rare in domesticated pets due to widespread vaccination, wild animals like bats, raccoons, and foxes can still transmit it to pets, who may then pass it to humans through bites. Rabies is almost always fatal once symptoms appear, making prompt treatment crucial.
Psittacosis

Bird enthusiasts should be aware of psittacosis, also known as parrot fever. It’s caused by the bacterium Chlamydia psittaci, which can be transmitted from infected birds through their droppings or respiratory secretions. Humans may experience flu-like symptoms, including fever, chills, and a dry cough.
Salmonella Infection

Salmonella isn’t just a risk from undercooked chicken—it can also be transferred by pets like reptiles, amphibians, and even small rodents. These animals can carry the bacteria on their skin, making it easy to transfer to humans through handling. Infected individuals may experience severe stomach cramps, diarrhea, and vomiting.
Plague

While it might seem like an ancient problem, plague is still present in some areas and can be transmitted by fleas carried by pets like cats. The bacterium Yersinia pestis is responsible for this disease, which can cause severe flu-like symptoms and swollen lymph nodes. Quick medical intervention is key to preventing severe complications.
Hookworms

Hookworms are parasitic worms that can infect both pets and humans, usually through direct contact with contaminated soil. Dogs and cats can carry hookworm larvae in their feces, which can then enter the human body through bare skin. The larvae can cause a red, itchy rash known as “cutaneous larva migrans” as they burrow under the skin.
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







