
Alive worm species, particularly jumping worms and hammerhead flatworms, are posing an increasing ecological threat to Texas as they spread quickly throughout the state. Originating in Asia and New Guinea, these worms have established populations in both urban and rural locations, such as the Texas coast, Houston, Dallas, and Austin. These invasive worms damage ecosystems by outcompeting or preying on native earthworms, which lowers soil quality and stunts plant growth, in contrast to native earthworms, which improve soil health.
The spread of these worms is a major environmental problem that has repercussions on natural habitats, gardening, and agriculture. These worms endanger the delicate balance of Texas’s varied ecosystems, which include piney woods, arid plains, and coastal wetlands, in addition to the immediate ecological harm they cause.
Historical Background: Invasive Worm Arrival and Spread
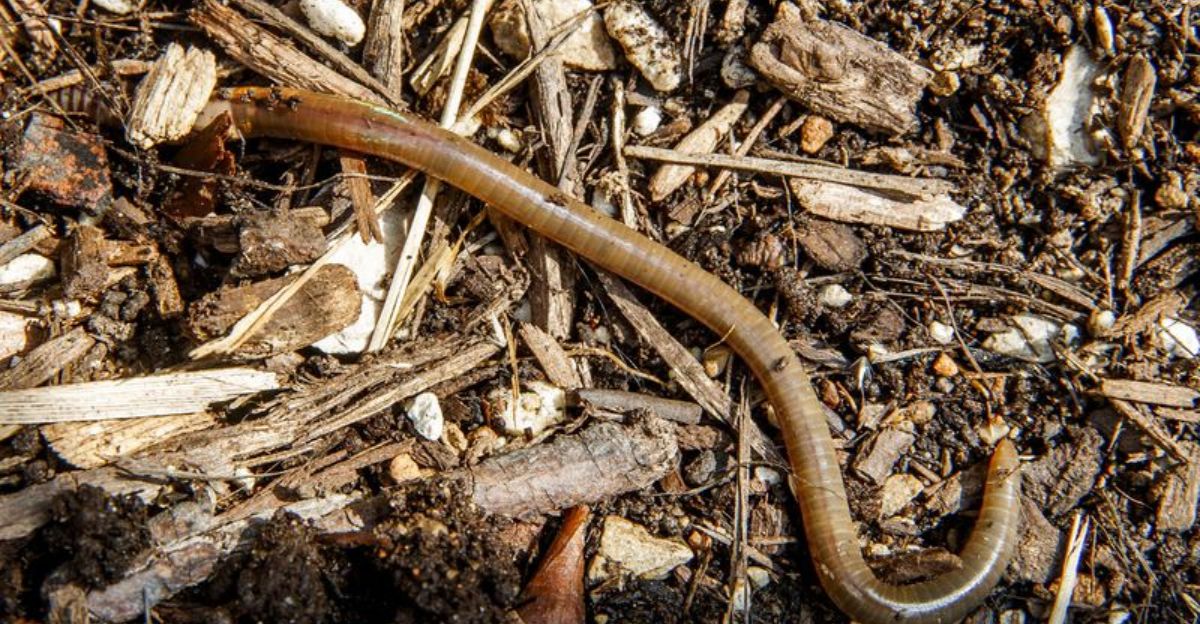

The horticultural trade was the primary source of invasive worms like jumping worms and hammerhead flatworms entering the United States. Since the early 1900s, these worms have been hitchhiking in potted plants. Since the 1980s, the hammerhead worm has been found in Texas, where it thrives in the hot, muggy weather. Initially discovered in the Northeast of the United States in the 1910s, jumping worms have since spread throughout the entire state of Texas, where they were found as early as 2004.
In the past, soil and plant materials have been the primary vectors for the introduction of invasive species, which frequently follow trends in international trade and human migration. These worms are unintentionally transported by the Texas horticultural sector, which imports enormous amounts of plants from all over the world. The expansion of the livable range for tropical and subtropical species, such as hammerhead worms, may also be a result of climate change.
Behavior and Biology: The Reasons These Worms Are So Perilous
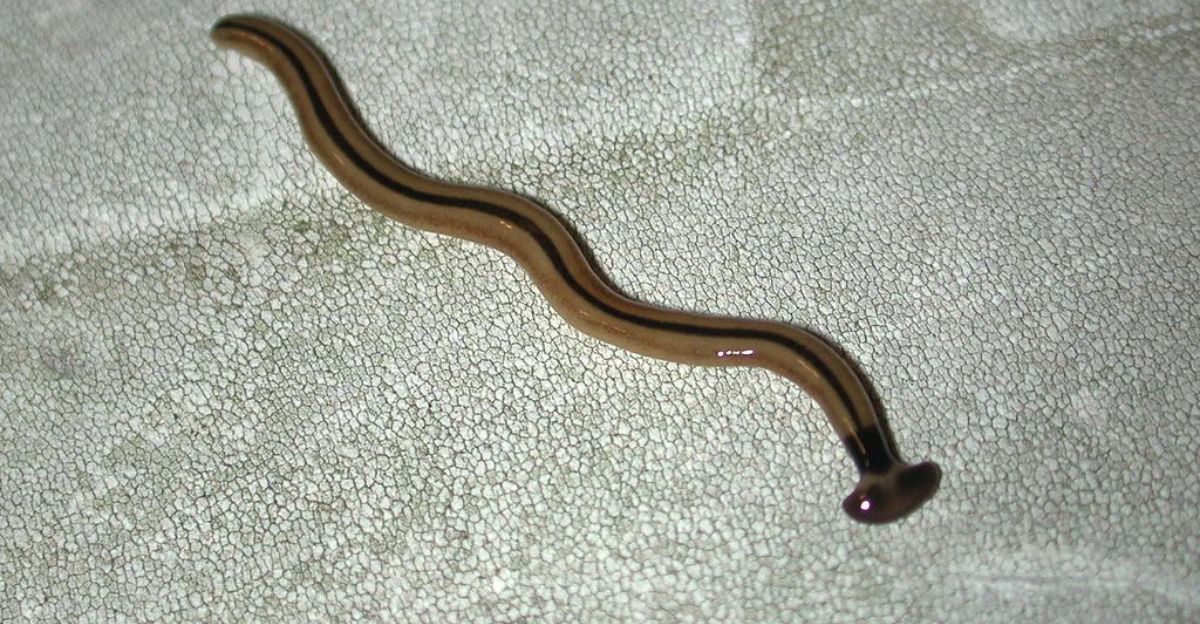

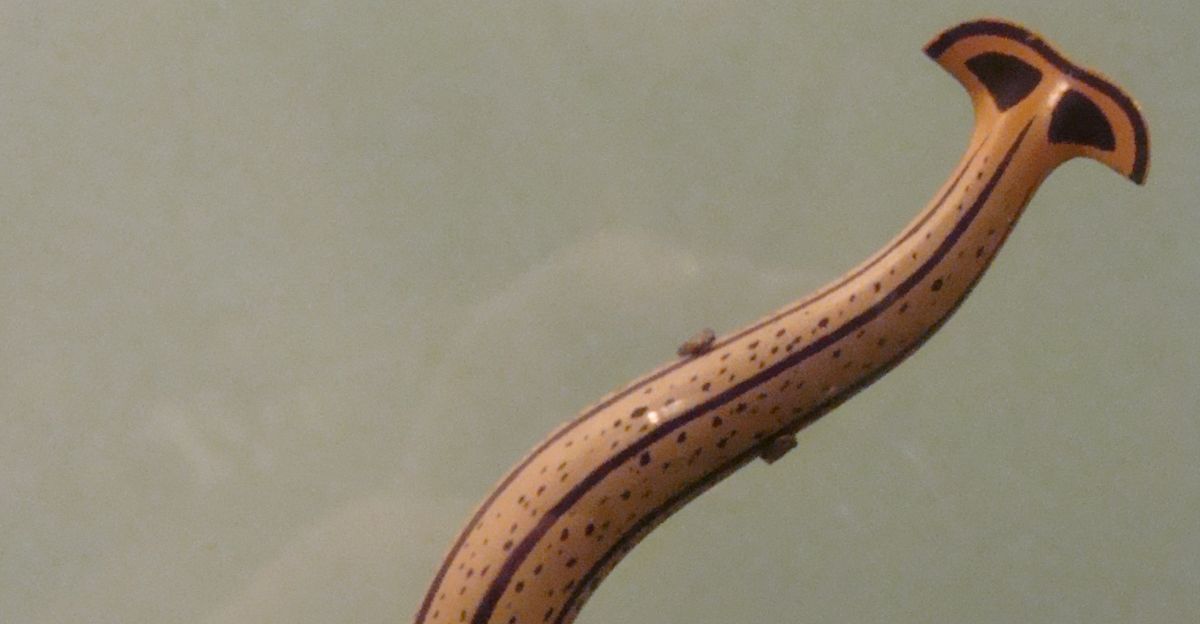
Hammerhead flatworms can reach a maximum length of 15 inches and are characterized by their broad, hammer-shaped heads. They are predators that use neurotoxins to subdue their prey, which are native earthworms. Because they reproduce by fragmentation, chopping off one worm can cause more issues because each fragment grows back into a new worm in a matter of days.
Although this toxin is not fatal, it raises concerns about accidental exposure because it can cause mild to moderate skin irritation. However, by eating leaf litter and organic matter so quickly that they leave behind a grainy, nutrient-poor soil that resembles coffee grounds, jumping worms drastically change the structure of the soil.
Slide 4: Ecological Impact: Native Species at Risk and Soil Health
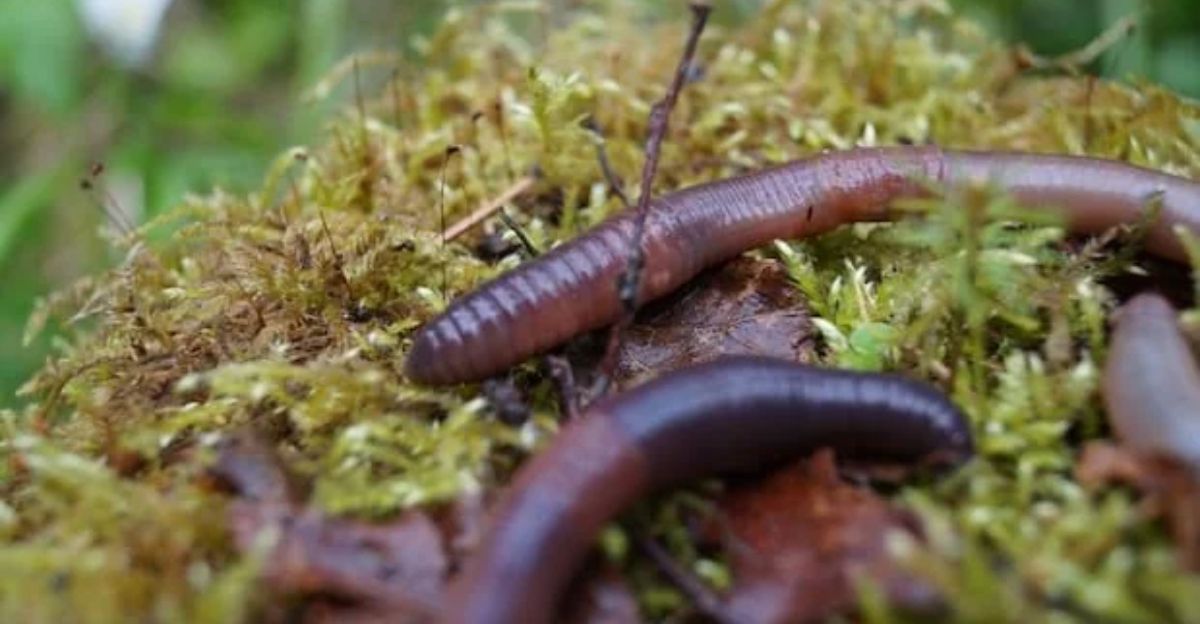

Because they improve water drainage, aerate the soil, and break down organic matter to increase soil fertility, native earthworms are essential to Texas ecosystems. These processes are hampered by invasive worms: jumping worms break down soil structure by consuming organic matter and leaf litter too quickly, while hammerhead worms decrease earthworm populations through predation. This can have a detrimental effect on forests, agricultural lands, and urban gardens because it results in lower soil quality, slower plant growth, and changed nutrient cycles.
Beyond soil chemistry, above-ground biodiversity—which includes larger animals, insects, and plants that depend on healthy soil ecosystems—is also impacted. Reduced earthworm activity, for instance, may make fewer nutrients available to native plants, which may have an impact on pollinators and herbivores. Reduced crop yields and greater susceptibility to pests and drought are the results of degraded soil in agricultural systems.
Human and Animal Health Concerns

Although invasive worms, such as hammerhead flatworms, do not bite, their skin secretes a neurotoxin that can irritate human skin or cause rashes. It can also be dangerous if pets or wildlife consume it. Families with children and pets are concerned about the presence of these toxic worms in residential areas, particularly after heavy rains when the worms emerge to breathe.
Although there is little research, wildlife exposed to these toxins may also suffer population-level effects. Despite being generally low, the risk to human health emphasizes the necessity of clear communication between environmental and public health agencies. Campaigns for education that integrate sound identification, handling, and disposal practices with a more comprehensive ecological background can enable locals to take responsible action and stop the worms from spreading.
Control and Management Difficulties

Because of their resilience and reproductive strategies, invasive worms are difficult to control. Squeezing or cutting hammerhead worms can inadvertently increase their population because they reproduce asexually through fragmentation. Worms should be disposed of by freezing them for 48 hours to guarantee death or by sealing them in bags with vinegar or salt.
When used on soil fauna, conventional pest control techniques like pesticides are either environmentally hazardous or mainly ineffective. Furthermore, early detection is difficult due to these worms’ cryptic habits, which include living underground and mostly emerging at night or after rain. The problem is made worse by Texas’s lack of natural predators, which permits populations to increase unchecked.
Implications for Agriculture and Socioeconomics

The gardening and agricultural productivity sectors in Texas are at risk due to the invasive worms’ degradation of soil health. Inadequate soil quality raises expenses for both farmers and gardeners by decreasing crop yields and increasing the need for fertilizers and soil amendments. Damaged soil ecosystems can have an impact on community gardens and green spaces in urban areas, compromising local food security and quality of life.
Texas could suffer losses if soil fertility decreases because it is a central agricultural state that produces vegetables, corn, and cotton. In addition to increasing production costs, increased fertilizer use increases the risk of environmental pollution through runoff, which exacerbates problems with water quality.
Exceptional Views: Strategic and Psychological Aspects
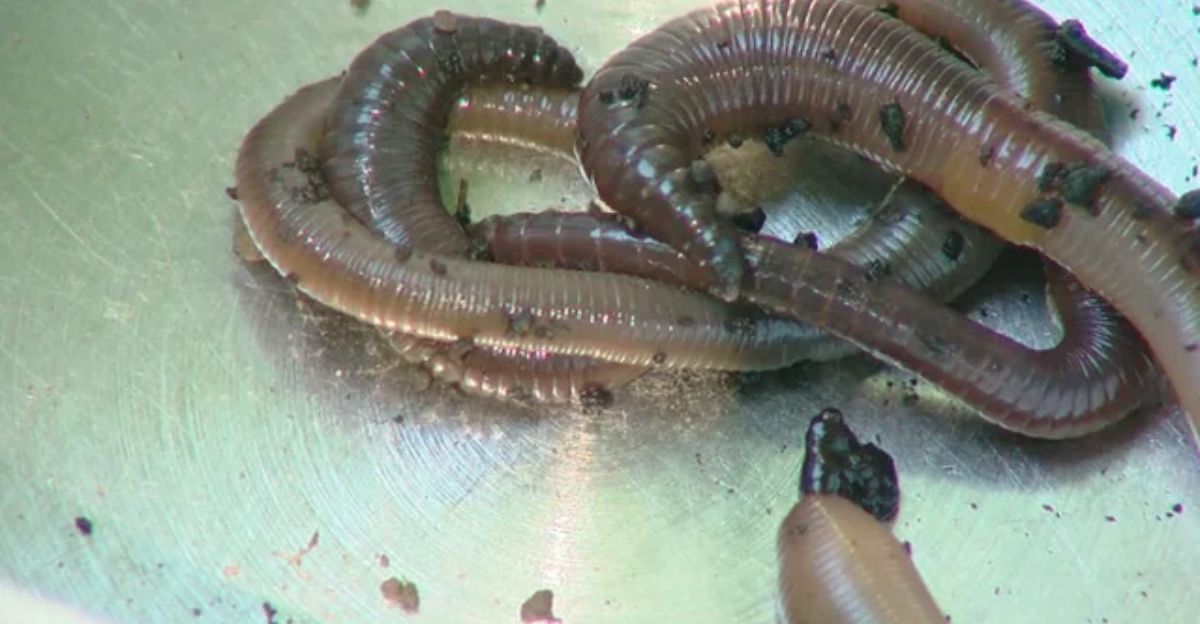

An exceptional case study of ecosystem resilience and human-nature conflict is provided by the invasive worm crisis. Psychologically, the instinctive response to “demonic” hammerhead worms is a reflection of ingrained anxieties about unmanageable natural hazards invading human areas. To strategically outmaneuver a rapidly reproducing adversary, this scenario necessitates a combination of citizen science, public education, and creative control techniques.
Psychologically speaking, hammerhead worms’ eerie appearance and poisonous nature arouse innate fears of contamination and invasion, which can spur public action but also spread false information and panic. By strategically using targeted messaging to capitalize on these emotional reactions, control measures compliance, and community engagement can be improved.
New Approaches and Future Research Paths
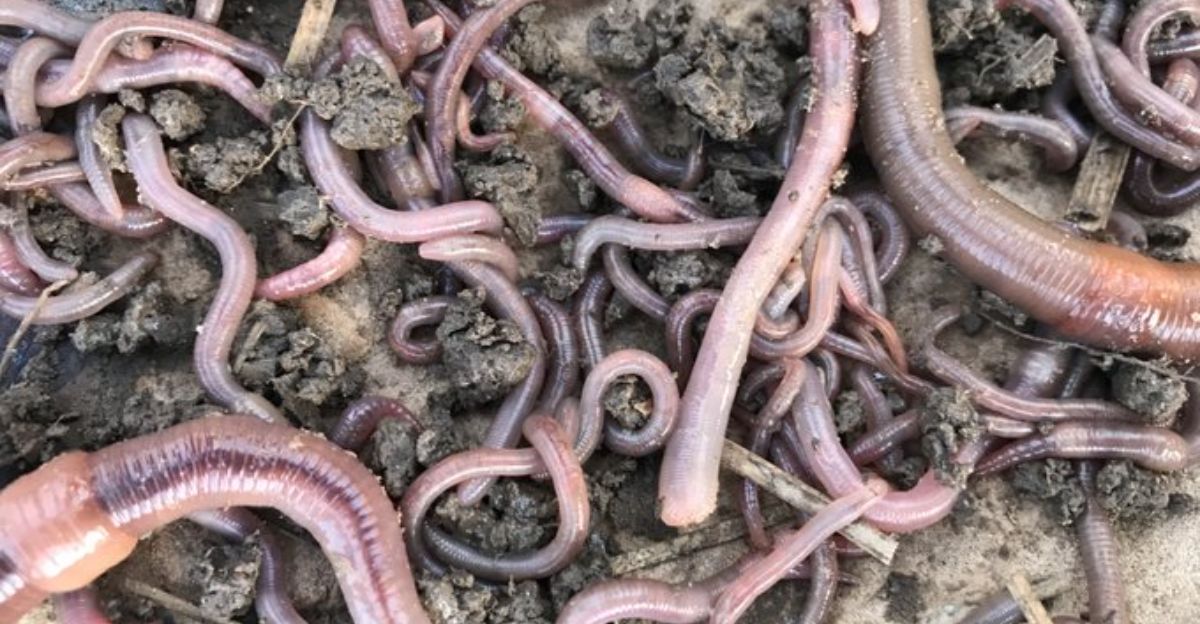

Worm populations are being tracked by research organizations such as the Texas Invasive Species Institute, which is also creating management plans that involve habitat modification, chemical controls, and public reporting. Mapping infestations and increasing awareness are essential tasks for citizen science. Although experimental strategies like soil treatments or targeted biological controls are being considered, they need to be carefully assessed to prevent unforeseen ecological effects.
Furthermore, studies on these worms’ microbiomes might uncover weaknesses that could be used for biocontrol. Universities, governmental organizations, and local communities must work together to share resources and expertise. Partnerships between the public and private sectors may also help create novel goods or approaches, like soil amendments that keep invasive worms away without endangering native species.
The Telos of the Texas Invasive Worm Challenge

In Texas, the proliferation of harmful invasive worms is more than just an ecological annoyance; it is a complicated, multidimensional problem with social, economic, and environmental facets. These worms represent the unexpected effects of globalization and the spread of species caused by humans. The fundamental mechanisms supporting Texas’s ecosystems and agriculture are in danger due to their effects on soil health.
This calls for moving past dispersed initiatives in the direction of a cohesive, scientifically based strategy that incorporates prevention, control, and restoration. Furthermore, in a time of rapidly changing environmental conditions, this challenge presents a crucial chance to reconsider how humans interact with nature, placing an emphasis on stewardship, caution, and resilience.
Explore more of our trending stories and hit Follow to keep them coming to your feed!
Don’t miss out on more stories like this! Hit the Follow button at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest news. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!







