
Enacted in 1973, the Endangered Species Act (ESA) serves as a cornerstone of wildlife conservation in the United States. Its primary goal is to prevent the extinction of imperiled plant and animal species by providing mechanisms for their protection and recovery. Over the decades, the ESA has been instrumental in safeguarding numerous species, ensuring that nearly 99% of those listed have survived.
The Act’s comprehensive approach includes listing species as endangered or threatened, designating critical habitats, and developing recovery plans to restore and protect these species.
The Role of the “God Squad” in ESA Decisions

The Endangered Species Committee, colloquially known as the “God squad,” possesses the authority to permit federal actions that may jeopardize the existence of endangered species. This committee can grant exemptions to the ESA’s stringent protections, even if such actions could lead to a species extinction. Historically, the “God squad” has been convened sparingly, reflecting the gravity of its decisions. However, recent administrative directives have called for more frequent meetings, raising concerns about potential impacts on species conservation.
Proposed Changes to ESA Protections

In August 2019, significant modifications to the ESA were proposed, aiming to streamline processes and reduce regulatory burdens. These changes included altering how species are listed and delisted, revising critical habitat designations, and considering economic impacts in decision-making. While industry groups and some lawmakers supported these revisions, critics expressed concerns that they could weaken protections for vulnerable species, especially during a global biodiversity crisis where many species face heightened extinction risks.
Impact on the Red Wolf Population
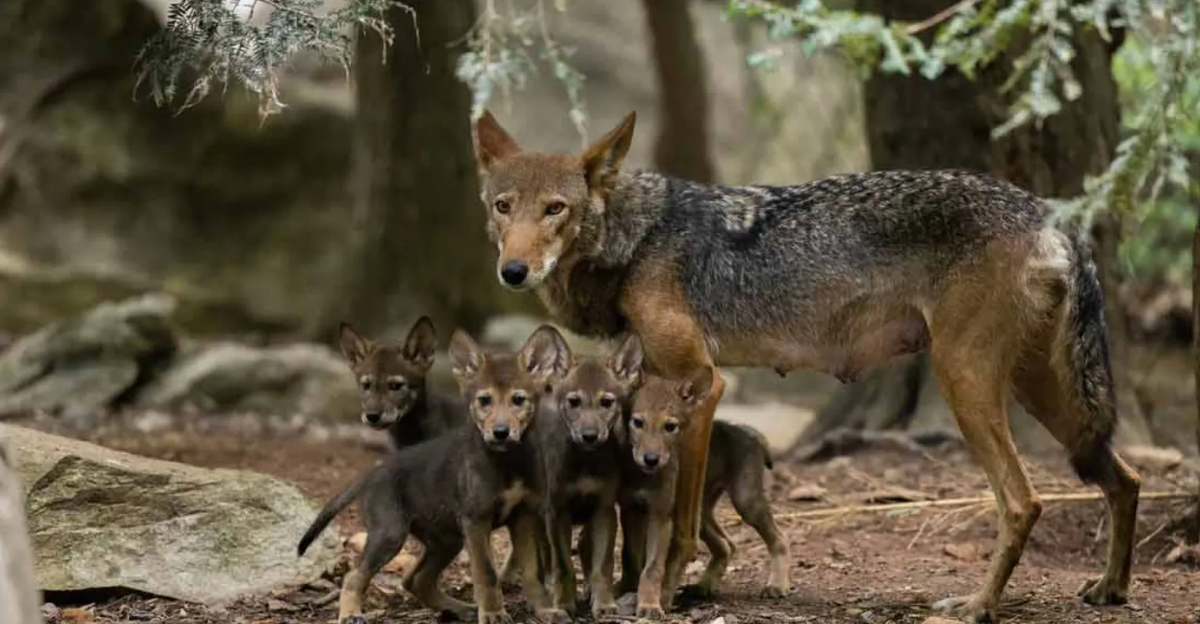

The red wolf, one of the world’s rarest mammals, has seen its wild population dwindle to fewer than 20 individuals. Conservation efforts, such as building wildlife crossings in North Carolina, were initiated to protect these wolves from threats like vehicle collisions. However, funding for these projects faced challenges, with crucial federal grants being halted, jeopardizing the completion of vital infrastructure to safeguard the remaining red wolf population.
The Dunes Sagebrush Lizard Controversy
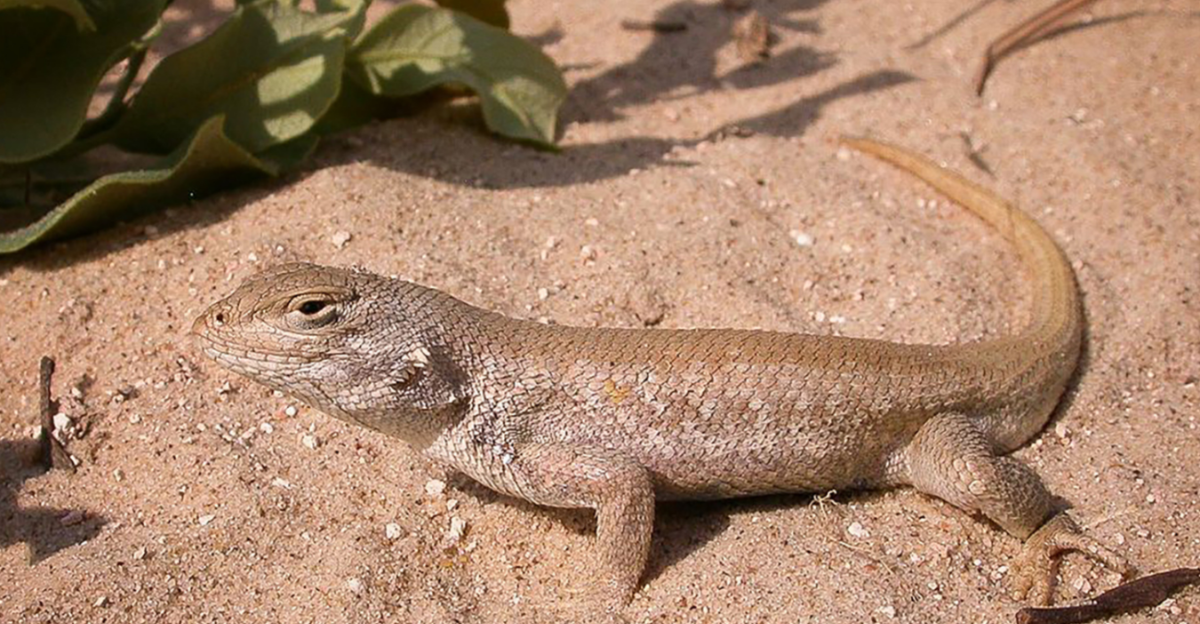

The dunes sagebrush lizard, native to parts of Texas and New Mexico, has been at the center of legal battles concerning its endangered status. The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service listed the lizard as endangered, prompting lawsuits from state officials and industry groups who argued that the listing overlooked existing conservation efforts and lacked comprehensive data. Environmental organizations, however, have intervened, advocating for the species’ protection under the ESA, highlighting the ongoing tension between development interests and wildlife conservation.
Proposed Owl Management Strategies
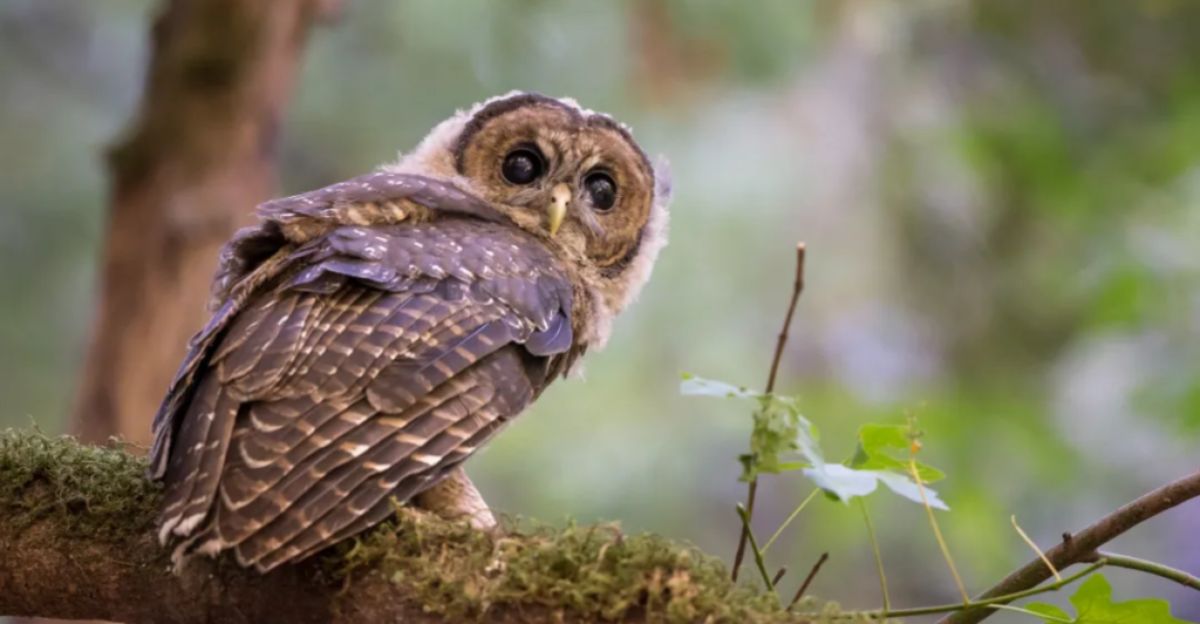

A controversial plan proposed removing over 450,000 invasive barred owls to protect the endangered northern spotted owl in West Coast forests. This strategy, estimated to cost around $1.3 billion, faced bipartisan opposition from lawmakers who questioned its efficacy and financial prudence. Critics argued that such large-scale culling might not yield the desired conservation outcomes and could set a concerning precedent for wildlife management practices.
The Border Wall’s Environmental Implications
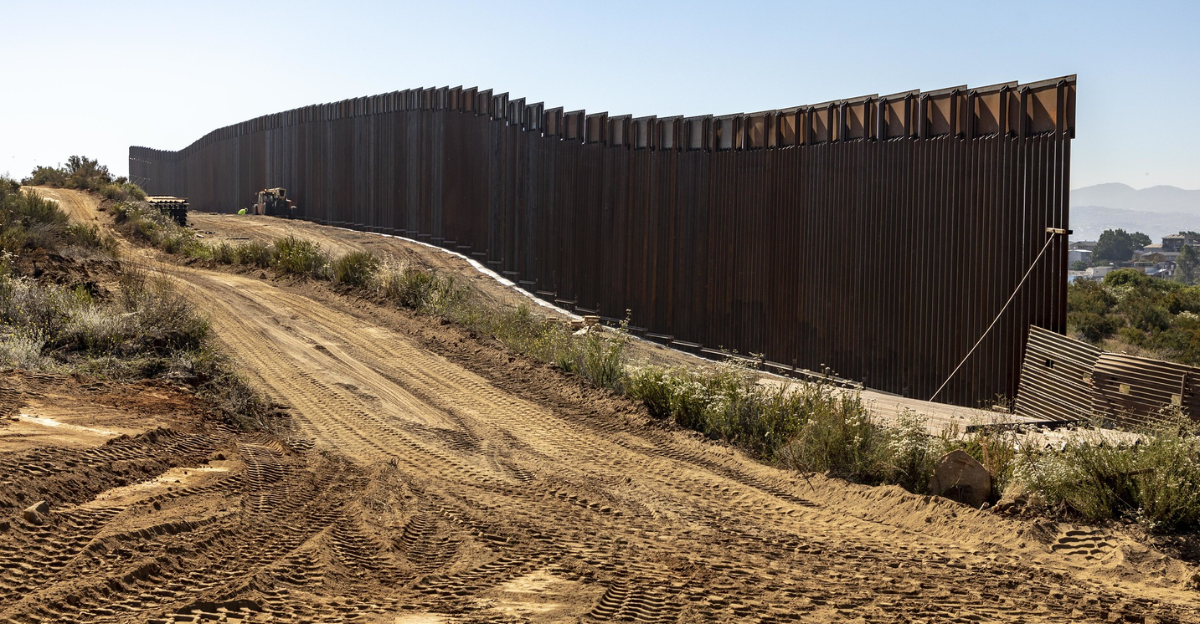

The construction of the U.S.-Mexico border wall has raised environmental concerns, particularly regarding its impact on wildlife habitats. The wall’s trajectory intersects with critical habitats, potentially disrupting migration patterns and fragmenting species like the jaguar, ocelot, and Sonoran pronghorn. Environmentalists warn that such barriers could hinder genetic diversity and increase the vulnerability of these species to extinction.
Funding Challenges for State Conservation Efforts

In the 2019 budget proposal, funding for state-led endangered species recovery initiatives was notably absent. The Cooperative Endangered Species Conservation Fund, which supports various conservation activities, faced potential cuts. This raised alarms among conservationists, who argued that reduced financial support could impede ongoing and future efforts to protect and recover threatened species at the state level.
The Yellowstone Grizzly Bear Delisting Debate
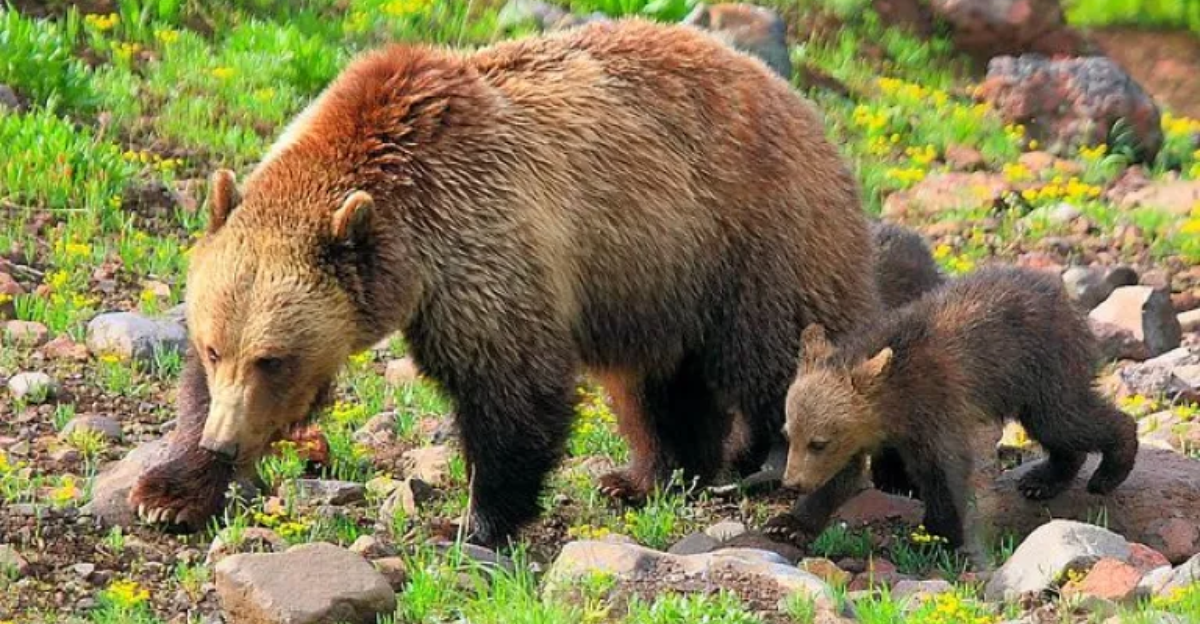

In June 2017, the administration announced the removal of Yellowstone grizzly bears from the endangered species list, citing population recovery. However, conservationists and tribal organizations contested this decision, pointing to genetic vulnerabilities and potential threats from hunting and habitat loss. Subsequent legal challenges led to the restoration of federal protections for grizzly bears, underscoring the complexities of delisting species under the ESA.
Migratory Bird Treaty Act Revisions

Proposed revisions to the Migratory Bird Treaty Act aimed to limit federal authority in prosecuting industries for unintentional bird deaths. Under the new proposal, only deliberate killings would be punishable, potentially reducing protections for migratory birds affected by industrial activities. This shift sparked debates about balancing economic interests and wildlife conservation, with concerns about increased bird mortality.
Gray Wolf Delisting and Its Ramifications

In October 2020, gray wolves were removed from the endangered species list, which conservationists argued was premature given the species’ limited recovery in certain regions. The delisting opened the door to state-managed hunting, raising fears about the potential decline of wolf populations. Legal challenges ensued, and in February 2022, a federal judge reinstated protections for gray wolves in 45 states, highlighting the contentious nature of species management decisions.
Policy Reversals and Their Impact on Conservation

Environmental policies, including those related to the ESA, have experienced shifts corresponding to changes in presidential administrations. Under the Trump administration, efforts were made to streamline protections and reduce regulatory constraints, aiming to balance economic growth with conservation. However, critics argued that these changes weakened safeguards for endangered species. The Biden administration has since signaled intentions to restore or strengthen certain protections, sparking an ongoing debate about how best to preserve biodiversity while accommodating development. The back-and-forth highlights the delicate balance between policy, science, and conservation.
The Future of the Endangered Species Act

The future of the ESA hinges on finding a middle ground between protecting wildlife and addressing economic interests. Experts emphasize the importance of science-based decision-making, transparent policymaking, and collaborative conservation efforts with states, tribes, and industry leaders. While the ESA has been remarkably successful in preventing extinctions, evolving threats like climate change and habitat loss pose new challenges. The Act’s resilience will depend on adaptive strategies that protect species without stalling economic progress, ensuring ecological and human interests are considered.
Explore more of our trending stories and hit Follow to keep them coming to your feed!
Don’t miss out on more stories like this! Hit the Follow button at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest news. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!







