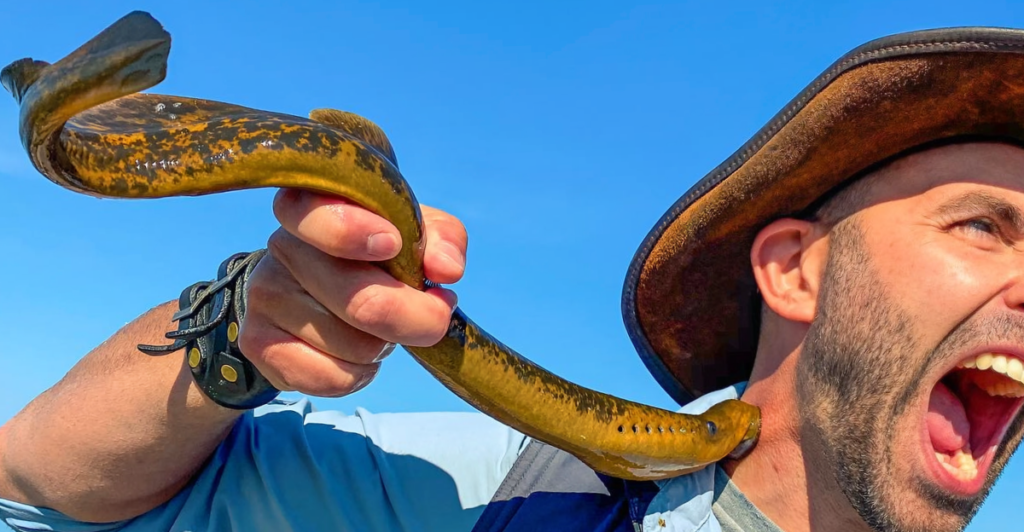

Sea lampreys are a non-endemic species of fish that has invaded the Great Lakes through 19th-century shipping canals. These “vampire” fish destroy native fish populations by preying on local fish and latching onto them, drinking their blood and bodily fluids.
One adult sea lamprey kills between 20 and 40 pounds of fish every year. Eradication efforts have been in effect for the last 75 years, catching the population, using lampricides, and installing barriers.
These conservation efforts have reduced the lamprey population considerably, with their population thought to be only 10% of what it was historically. Despite continued success, there is still a way to go and eradication efforts must be continued to keep up with their ever-breeding population.
Budget Cuts
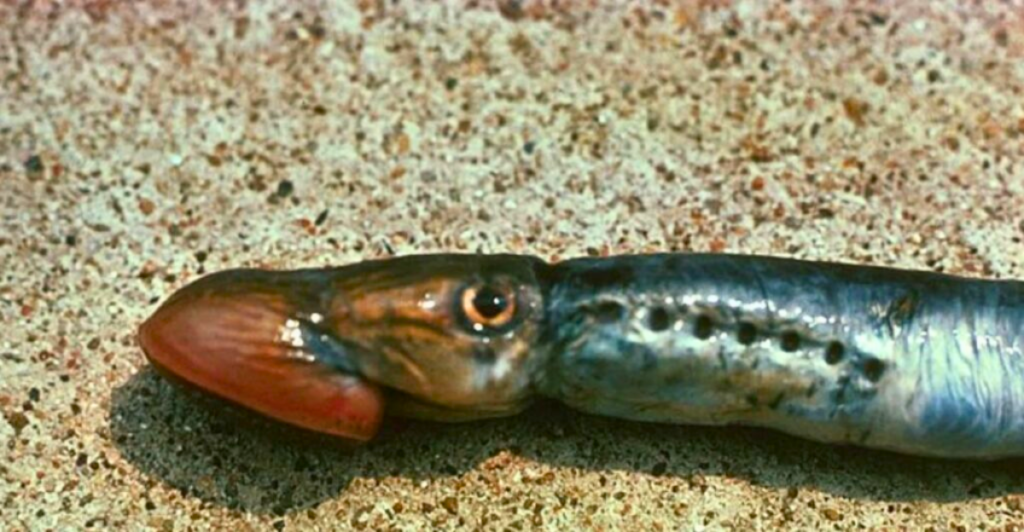

Recent DOGE (Department of Government Efficiency) driven budget cuts have had effects on many different governmental organizations including the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
These budget cuts have put a strain on the organization and threaten to reduce staff for field operations, delaying eradication and risking biological habitats. The maintenance required to keep sea lamprey populations in check is an undertaking, with over one hundred streams requiring annual chemical treatment with 480 infested tributaries.
A reduction in personnel could leave habitats open to the repopulation of this invasive species. A resurgence in the next few years could have implications for the Great Lakes ecosystems, which house many endangered species and play a vital role in their recovery efforts.
Historical Precedent

Budget cuts in the past have shown that the lamprey population will increase accordingly. In 2011, budget cuts led to a sharp increase in their numbers, showing a direct correlation.
The past can show us the risks of underfunded conservation efforts in the face of dangerous invasive species that negatively impact local endangered populations. If staffing is reduced, the areas where lampreys breed the most may not be properly treated, meaning their population would only grow.
This would undermine 75 years of conservation efforts working hard to reduce to population by 90%. Even temporary lapses in conservation efforts can have lasting impacts on endangered populations, emphasizing the need for consistent funding to keep the ecosystem balanced.
Staffing Cuts
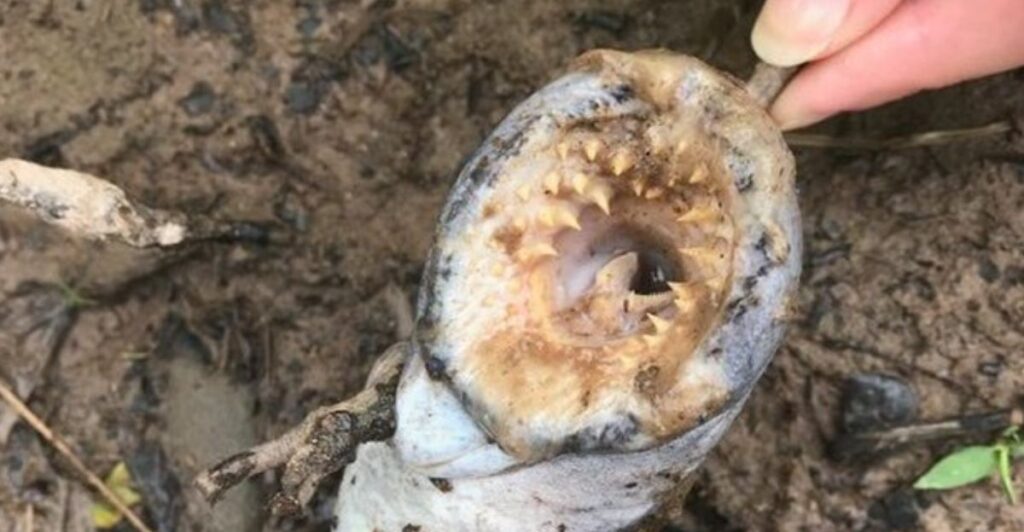
The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service needs seasonal workers to go out into the field and apply lampricides to more than 100 streams and monitor the lamprey population, ensuring they are being controlled.
These positions are crucial to combating the lamprey population, and if the future of their staff members is in question, so could the future of many endemic fish species that are preyed on by lampreys.
Critical work could be compromised, leading to significant harm to fish populations that have only just recovered from being threatened, like the lake trout. Once lampreys reach Lake Superior, they are hard to catch and monitor. This is why the lampricides are so important in preventing them from reaching the lakes.
Economic Consequences

Although budget cuts may be a way of saving money, this strategy could backfire entirely. In the short term, it will save money, but it could lead to much higher costs in the long run.
As previous lapses in funding prove, the lamprey population will increase, which will result in losses for fishing industries and tourism. Many states’ economies rely on income from these industries, and just one year of sea lamprey being left unchecked could cost Michigan and Wisconsin $2.8 billion in lost revenue.
A proactive approach is needed, and funding needs to be prioritized to ensure that these invasive species cannot do both ecological and economic damage. This would have far-reaching impacts that would affect more than just local communities; it would have a regional impact as well.
Threat To Native Species
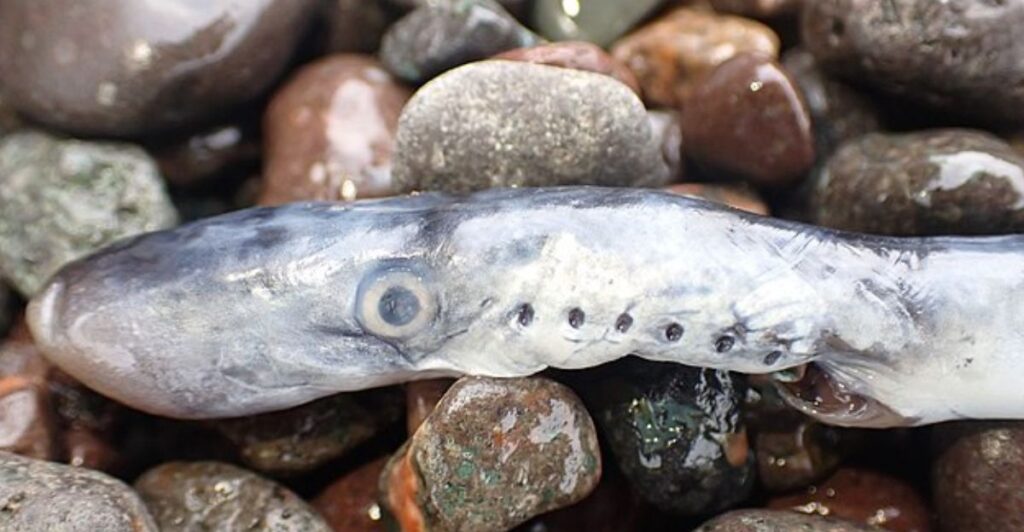

The Great Lake systems are crucial ecosystems that house many native fish populations, including many that have come back from near extinction due to the lamprey eradication efforts.
Species like the bloater and lake sturgeon are already vulnerable species due to habitat loss and other factors. If lampreys are allowed to get to the lake unchecked, their species could decline into dangerous territory, and have them potentially face extinction.
The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service have been protecting these species through decades of conservation efforts, but with budget cuts threatening staff positions, these decades of recovery could be undermined. It remains up in the air whether or not the USFWS will have the necessary capacity to keep the lamprey population controlled, but if historical records are anything to go off of, it could be disastrous.
Impact On Innovation
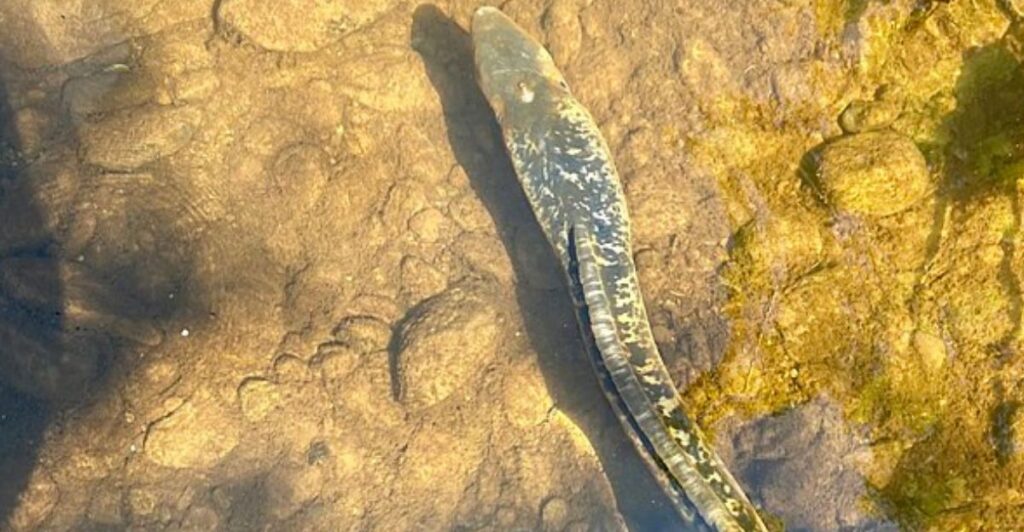

The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service have faculty dedicated to researching species populations and developing new and innovative methods of conservation with their findings. With these key personnel’s jobs in jeopardy, innovative methods like genetic biocontrol and pheromone traps may be affected.
Breakthroughs that were only months away could be delayed to be years out of reach with reduced faculty doing important research. The future could see a reduction on the need for chemical solutions and provide more sustainable solutions if the USFWS received full funding from the government.
The United States could be left behind as other countries are researching similar solutions in innovative conservation strategies. In a rapidly changing world, developing new methods and technologies to combat conservation challenges is important to preserving the habitats and species that call these environments home.
Public Perception
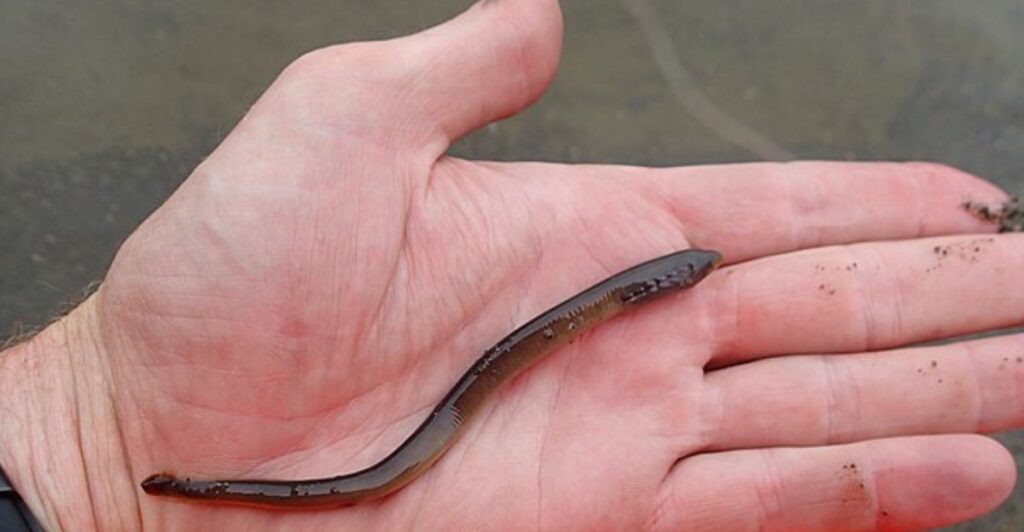

The reduction in staff for crucial environmental workers could skew public perception and erode their trust in the government. There has already been widespread outcry over many park rangers losing their jobs due to budget cuts.
This distrust could seep into environmental issues, making it far more difficult to address them effectively. Public support is an important tool in maintaining funding for conservation efforts.
Many conservation programs rely on donations to keep their efforts sustained. Transparency in lamprey control is important to keep the trust of the public.
Prioritizing Conservation

The reduction in budget has led to the prioritization of more visible conservation that can keep public moral high rather than less visible, and less glamorous conservation, like lamprey control.
Despite much lamprey control being an unseen effort in conservation, its reduction would have impacts that would be noticeable. Lampries cause a lot of harm to the habitat that they invade, and this will have a visible effect on fish populations, so much so that the public will notice.
Resources should be allocated based on the potential consequences of their negligence. Feral horse management receives more funding, while lampreys kill 100 million pounds of fish every year. A balanced approach is needed to address ecological and economic risk factors.
Impacts On Conservation Inaction
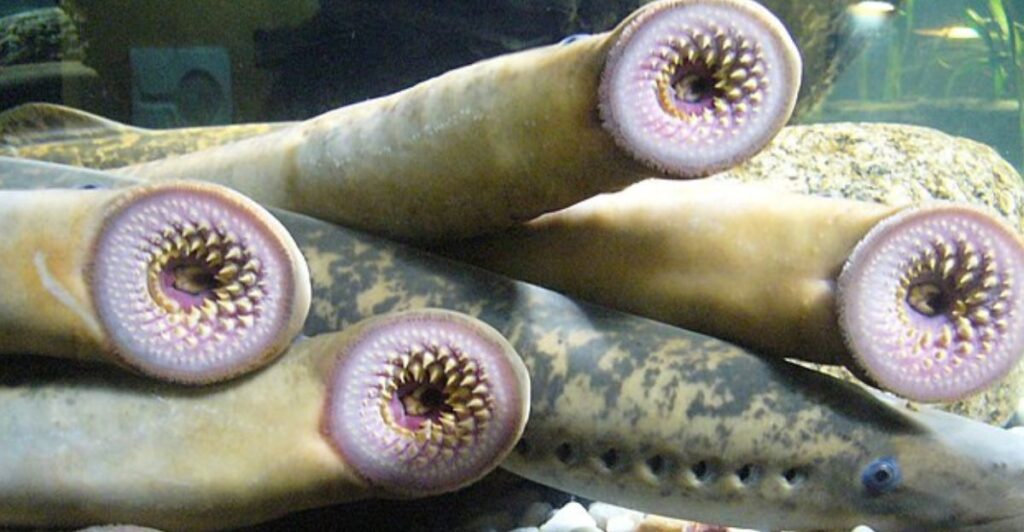

Conservation inaction on the lamprey population could have the following effects: much higher conservation costs in the future, ecological destruction as lampreys kill endemic and endangered fish, and an economic impact as fishing and tourism industries are negatively affected.
While budget cuts may seem like a good short-term solution to save money, they will most probably have long-term consequences that will cost more. For example, higher funding for emergency treatments would have to be implemented if the lamprey population gets out of hand, adding more costs in the future.
Responsibility must be taken to protect countless wild species and not undermine the collaborative efforts of the past 75 years.
Explore more of our trending stories and hit Follow to keep them coming to your feed!

Don’t miss out on more stories like this! Hit the Follow button at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest news. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!







