
Birds have fascinating mating systems, but not all strategies lead to long-term success. Researchers found that polygamy, where birds form weak or temporary bonds, often collapses. Why do some species struggle with multiple mates while others thrive in lifelong pairs? Let’s examine the science behind bird relationships and what we can learn from them.
Why Mating Systems Matter in Bird Evolution

Birds don’t just pick mates randomly—how they form bonds impacts their survival. Some species evolve elaborate displays, while others defend territories for mates. But not all strategies last. Scientists analyzed over 6,600 bird species and found that specific mating systems persist while others vanish. Understanding these patterns helps explain how birds and other animals evolve.
Understanding Resource-Defense Polygamy

In resource-defense polygamy, one bird—usually the male—controls valuable territory to attract multiple mates. While this may seem like a winning strategy, it’s surprisingly unstable. The effort to defend land, compete with rivals, and provide limited parental care often leads to failure, forcing many polygamous species to revert to monogamy over time.
Why Polygamy Leads to Instability in Birds

Polygamous birds struggle to survive because their mating system isn’t built to last. Researchers found that species practicing resource-defense polygamy go extinct at higher rates. Why? These birds fail at parental care, and their unstable relationships make survival difficult. Over generations, their system collapses, forcing species to adopt monogamy for better reproductive success.
The Frequent Collapse of Polygamous Bird Species
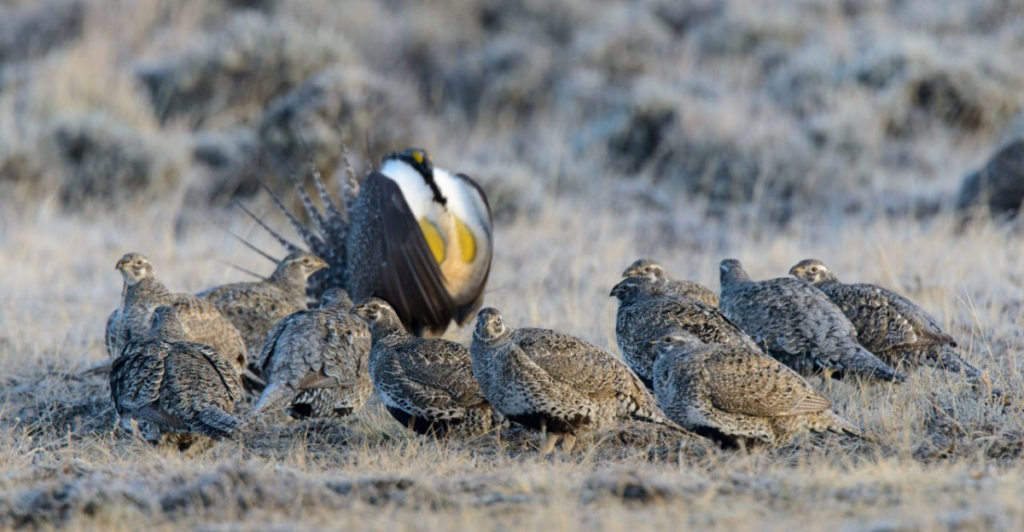

Unlike monogamous birds that form strong bonds, polygamous birds often experience high mortality rates. Without reliable partners to share parenting duties, chicks face greater risks. Over time, species that rely on polygamy tend to disappear or evolve into monogamous breeders—showing that teamwork, even in nature, leads to better survival.
Lekking vs. Polygamy—Which Strategy Wins?
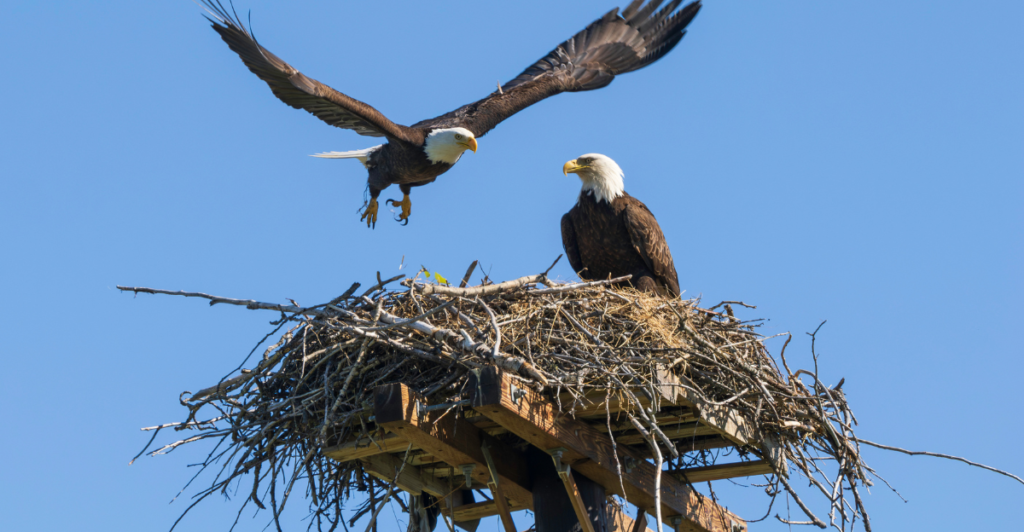

Some polygamous birds use “lekking,” where males gather to display for females without forming bonds. Unlike resource-defense polygamy, lekking is surprisingly stable. Why? Females still have complete control over mate selection, and males focus on impressing, not defending, territories. This system works because it removes the stress of parenting and territorial battles.
Why Monogamy Is the Most Reliable Mating System
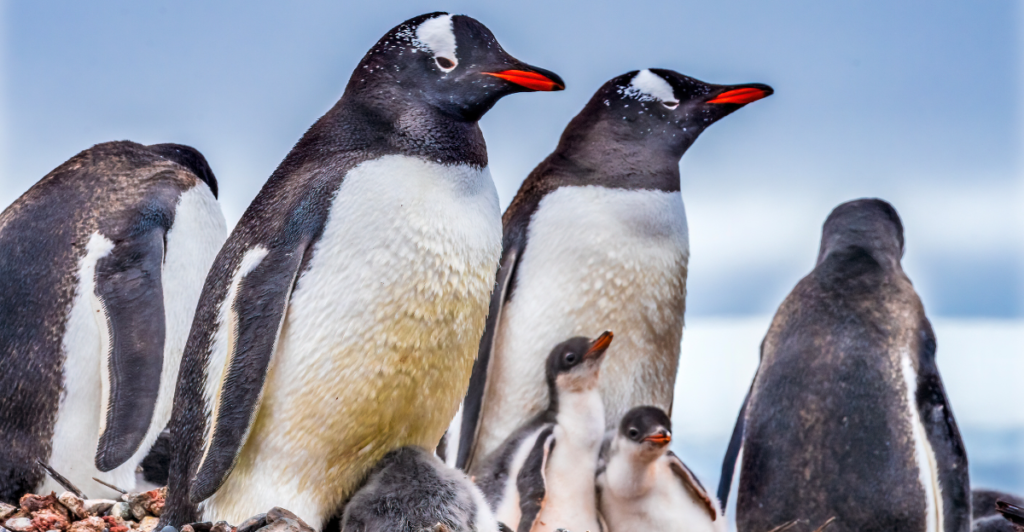

Most birds—about 90%—are monogamous, and for good reason. Research shows that monogamous pairs raise healthier chicks, distribute parenting duties, and adapt better to environmental changes. While polygamy may seem advantageous, long-term survival favors birds that commit to one mate, ensuring better reproductive success and species stability.
The Role of Parenting in Species Survival

Parental care is a game-changer in bird evolution. Parenting is often uneven in polygamous species, leading to lower survival rates. Monogamous pairs, however, share responsibilities, increasing the chances of raising strong, healthy offspring. The study highlights that good parenting—not just flashy mating rituals—is key to a species’ long-term success.
How Female Mate Choice Shapes Bird Evolution
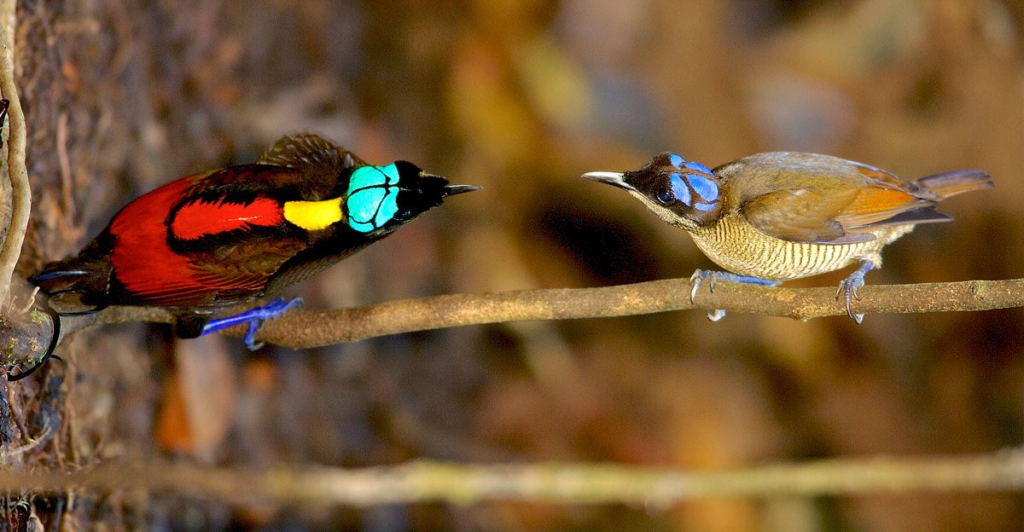

In the bird world, females have an influential role in shaping evolution. Their preferences determine which traits get passed down. Studies show that in lekking and monogamous species, female selection leads to more vigorous, more resilient offspring. In contrast, resource-defense polygamy often collapses because males prioritize territory over genetic quality.
The Link Between Mating Systems and Extinction

Mating behaviors aren’t just about romance—they affect survival. Species with unstable polygamous systems face higher extinction rates due to poor parental care and environmental pressures. In contrast, monogamous birds maintain more substantial populations, proving that reliable relationships are a winning strategy for long-term survival.
How Birds Adapt to Changing Mating Pressures

Birds don’t stick to one mating system forever. When polygamy fails, many species shift to monogamy for better survival. This adaptability helps them thrive, even when environmental conditions change. The study reveals that flexibility in mating behavior is crucial for avoiding extinction and ensuring long-term success.
Lessons for Humans from Bird Mating Behavior

Birds show us that relationships built on cooperation and commitment tend to last. While flashy displays might temporarily attract mates, species that invest in long-term bonds and shared responsibilities thrive. The same principle applies beyond the bird world—partnerships based on teamwork and care lead to better outcomes.
The Future of Bird Mating Strategies

As environments change, bird mating behaviors will change. Some species will continue with stable monogamy, while others may experiment with new strategies. Scientists will continue studying these patterns to understand how evolution shapes survival. One thing is clear—when it comes to birds, strong relationships are the key to thriving in the wild.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them appearing in your feed
Wolves Still Roam In These States in 2024—Is Yours On The List?
Scientists Are Bringing Back The Wooly Mammoth
California Is Breaking Apart: A Fault Line Is Forming Faster Than Anyone Predicted
Philanthropist Promises To Cover $771.23M Annually After US Exit From Climate Accords
References:
Reference 1
Reference 2
This article first appeared here
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







