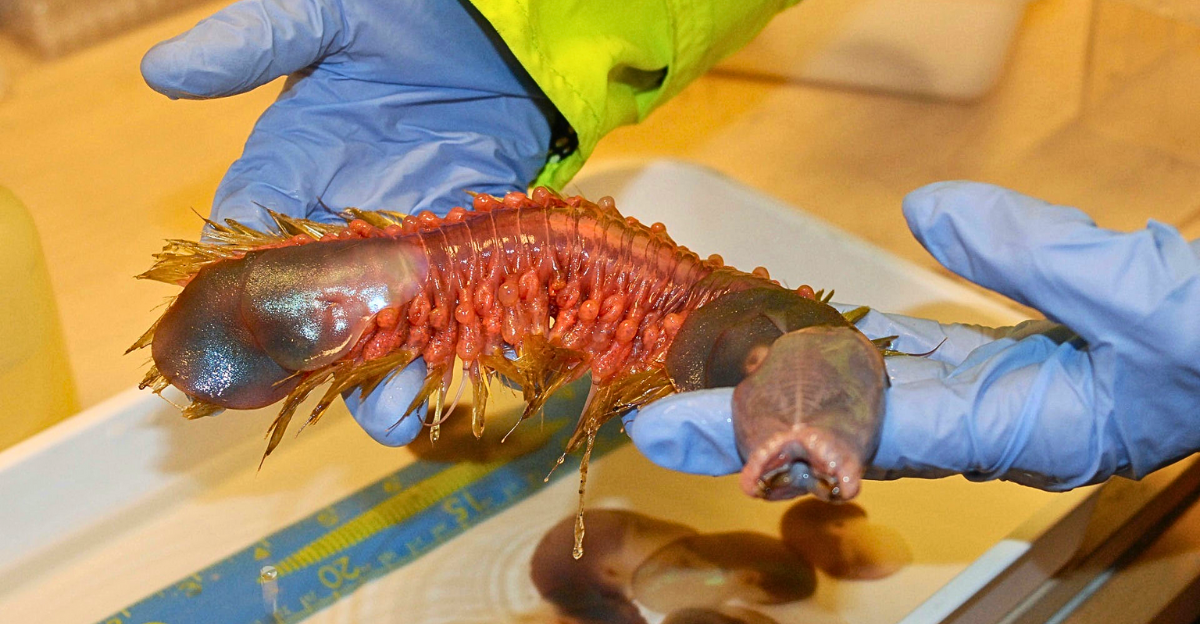

In the frigid depths of Antarctica’s Southern Ocean, over 500 meters beneath the surface, resides a creature that has both fascinated and perplexed scientists: the Antarctic scale worm, Eulagisca gigantea. This enigmatic annelid, measuring up to 20 centimeters in length, boasts a striking appearance characterized by golden elytra and formidable jaws. Despite its formidable presence, much about this deep-sea dweller remains shrouded in mystery, particularly its dietary habits.
A Worms World

The Southern Oceans’ extreme environment presents significant challenges to researchers aiming to study its inhabitants. The scarcity of direct observations has left many aspects of E. gigantea’s ecology, including its feeding behavior, largely speculative. Unraveling these mysteries is crucial, as understanding the role of such organisms can provide deeper insights into the complex food webs of deep-sea ecosystems.
A Closer Look at Eulagisca gigantea

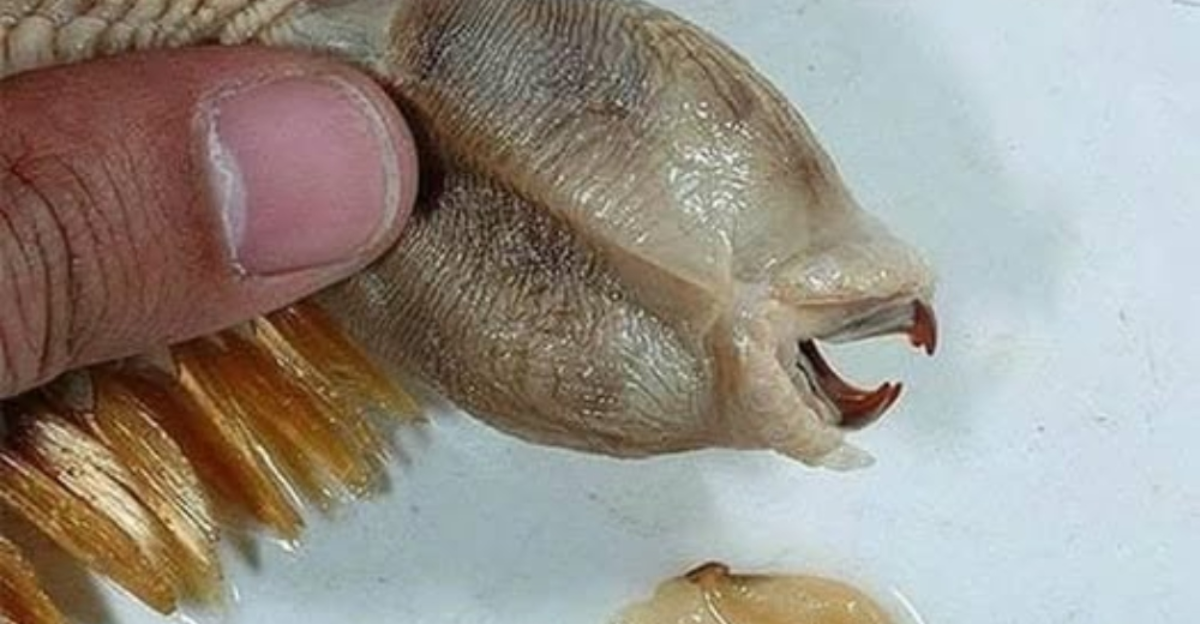
Belonging to the family Polynoidae, Eulagisca gigantea is distinguished by its overlapping scales, known as elytra, which lend it a distinctive armored appearance. These scales not only serve as protection but also contribute to its unique aesthetic, shimmering with a golden hue. The worm’s retractable proboscis is equipped with sharp jaws, an adaptation that suggests a predatory lifestyle.
First described in 1939 by Monro, E. gigantea has since intrigued marine biologists due to its unique morphology and the challenges associated with studying it in its natural habitat. Its presence in the inhospitable depths of the Southern Ocean underscores its remarkable adaptations to extreme cold and high-pressure environments.
Habitat and Distribution

Eulagisca gigantea is endemic to the Southern Ocean, predominantly found at depths exceeding 500 meters. The harsh conditions of this environment, characterized by near-freezing temperatures and complete darkness, have necessitated unique adaptations in its inhabitants. The worm’s distribution appears to be closely linked to the cold, stable conditions of these deep-sea habitats.
The Southern Ocean’s benthic zones, where E. gigantea resides, are known for their rich biodiversity. However, the inaccessibility of these depths means that much of this biodiversity remains undocumented. Studies utilizing remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) and deep-sea submersibles have begun to shed light on these communities, but comprehensive data on species like E. gigantea are still lacking.
The Enigma of Its Diet
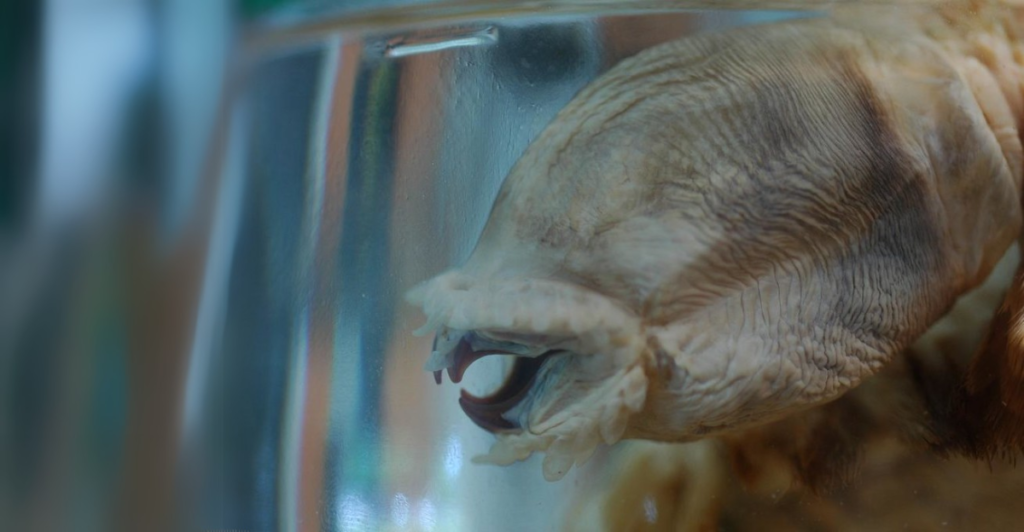

One of the most puzzling aspects of Eulagisca gigantea is its feeding behavior. Despite its well-developed jaws, direct observations of its diet are absent. It is hypothesized that the worm preys on other benthic organisms or scavenges organic debris. The structure of its proboscis and jaws supports the idea of a carnivorous diet, possibly involving the capture of smaller invertebrates.
Comparative studies with related polynoid species suggest a range of feeding strategies, from active predation to scavenging. Without direct evidence, however, the exact nature of E. gigantea’s diet remains speculative. Further research, potentially involving in situ observations or gut content analyses, is necessary to confirm these hypotheses.
Adaptations to the Deep Sea

Surviving in the extreme conditions of the deep Southern Ocean requires remarkable adaptations. Eulagisca gigantea‘s elytra provide protection against predators and the harsh environment, while its muscular proboscis allows it to capture prey effectively. Additionally, its metabolic processes are likely adapted to function efficiently at low temperatures and high pressures.
The worm’s sensory adaptations are also of interest. In the absence of light, tactile and chemical senses become paramount. It is plausible that E. gigantea has developed heightened sensitivity to environmental cues, aiding in the detection of prey and mates in the dark depths.
Reproductive Mysteries
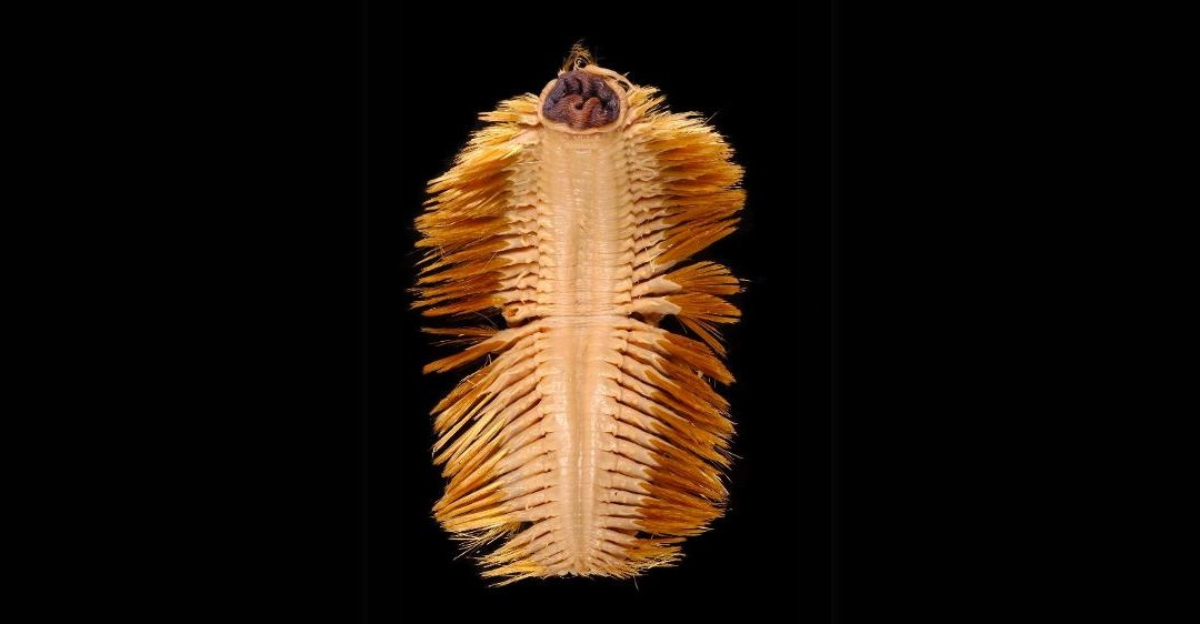

Little is known about the reproductive strategies of Eulagisca gigantea. Inferences from related species suggest that it may have separate sexes, with external fertilization being a common mode of reproduction among polychaetes. The development of larvae and their dispersal mechanisms in such a stable yet vast environment remain areas ripe for research.
Understanding the reproductive biology of deep-sea organisms is crucial for assessing their population dynamics and resilience to environmental changes. For E. gigantea, this knowledge could inform conservation efforts, particularly in the face of increasing human activities in the Southern Ocean.
Ecological Role
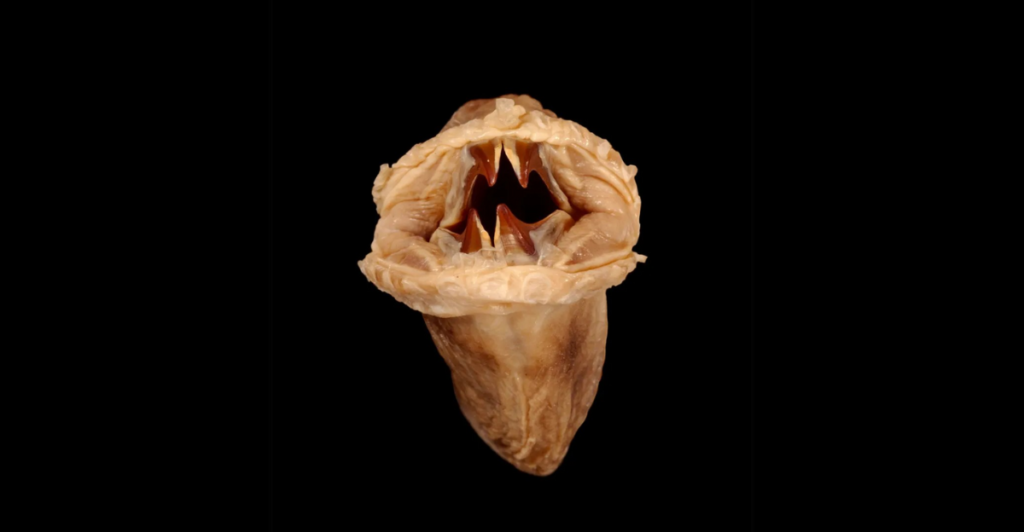
As a member of the benthic community, Eulagisca gigantea likely plays a significant role in the deep-sea ecosystem. If it is indeed a predator, it may help regulate the populations of other invertebrates, contributing to the ecological balance. Alternatively, if it functions as a scavenger, it would be integral in the breakdown and recycling of organic material.
The ecological roles of deep-sea organisms are often interconnected, with many species relying on the activities of others for survival. Determining the specific niche of E. gigantea will enhance our understanding of these complex relationships and the overall functioning of deep-sea ecosystems.
Challenges in Research
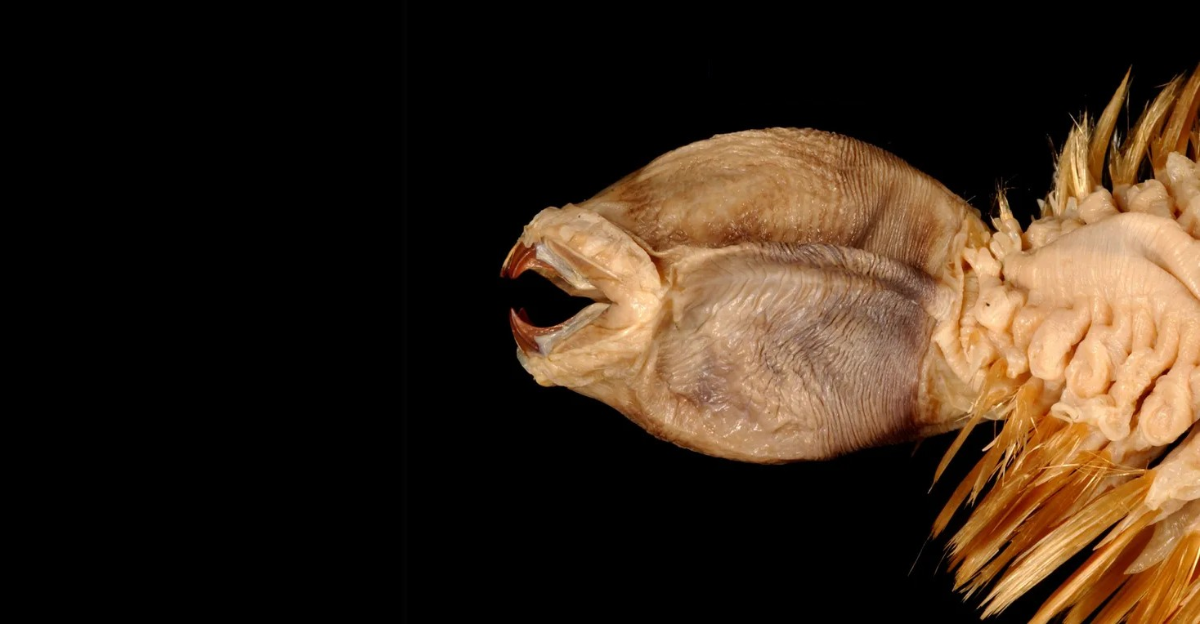
Studying Eulagisca gigantea presents numerous challenges. The depths at which it resides are difficult to access, requiring specialized equipment and technology. Additionally, the fragile nature of deep-sea organisms means that specimens are often damaged during collection, complicating morphological and genetic analyses.
An Expensive Expedition
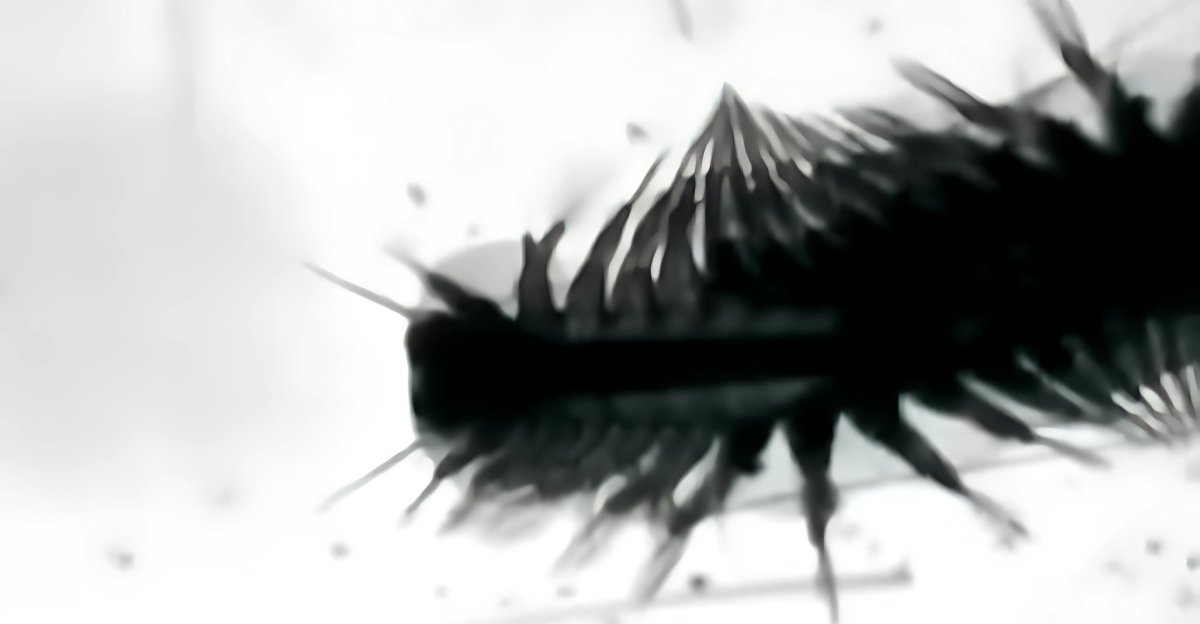

Advancements in deep-sea exploration technology, such as improved ROVs and autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), offer new opportunities to observe these creatures in their natural habitats. Non-invasive techniques, like environmental DNA (eDNA) sampling, may also provide insights without the need for physical specimens.
Conservation Considerations
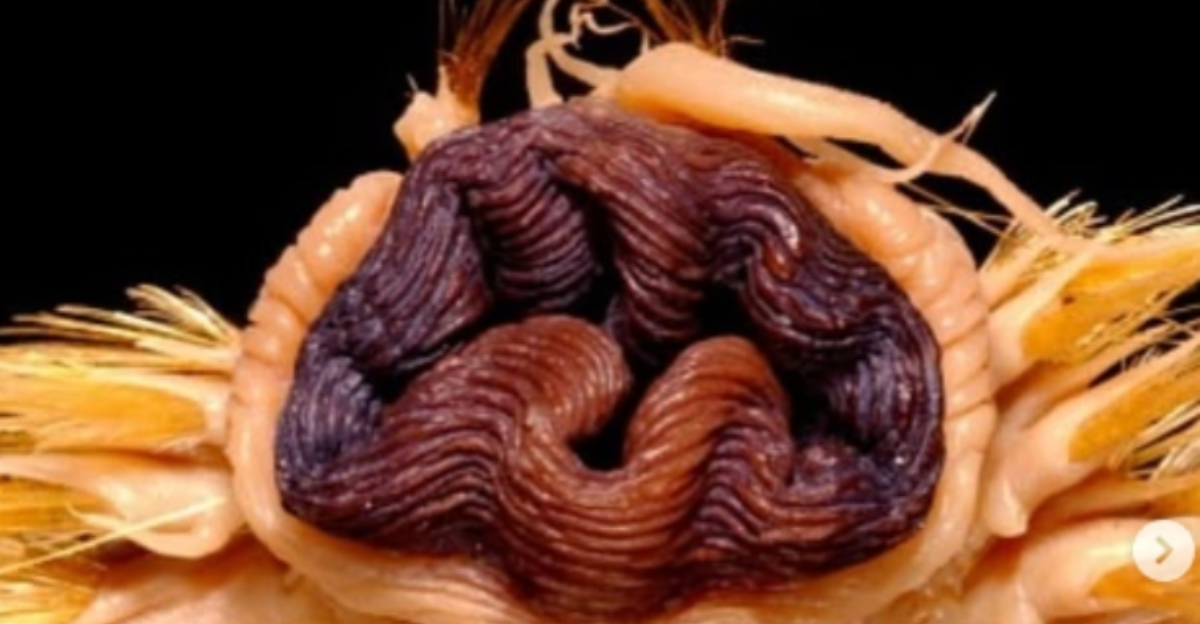
The Southern Ocean remains one of the least disturbed marine ecosystems, but climate change and human activities pose increasing threats. Warming ocean temperatures and shifts in ice coverage could impact the deep-sea habitat of Eulagisca gigantea, altering its food sources and ecosystem dynamics. Furthermore, potential future deep-sea mining and commercial fishing in Antarctic waters could disturb benthic communities, affecting species like E. gigantea.
Conservation efforts for deep-sea ecosystems require a proactive approach. International agreements, such as the Antarctic Treaty and the Convention for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR), aim to protect the region’s biodiversity. However, continued research and monitoring are essential to assess how environmental changes impact deep-sea species and to implement necessary protections.
Will We See The Worm

The Antarctic scale worm, Eulagisca gigantea, remains one of the deep ocean’s most enigmatic inhabitants. With its formidable jaws, armored appearance, and mysterious diet, it stands as a testament to the incredible adaptations of deep-sea life. Yet, much about this species remains unknown, emphasizing the need for further research and exploration.
More About The Worm

As technology advances, scientists may finally uncover the secrets of this elusive creature, shedding light on its role in the deep-sea ecosystem. Understanding E. gigantea not only expands our knowledge of marine biodiversity but also reinforces the importance of preserving the fragile and largely unexplored habitats of the Southern Ocean. In a time of rapid environmental change, protecting these mysterious species ensures that the deep sea remains a world of discovery for generations to come.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them appearing in your feed
Mutant Wolves of Chernobyl Show Incredible Resistance to Cancer – How Did They Adapt So Quickly?
Scientists Discover First Animal That Doesn’t Breathe—How Does It Survive?
Lake Shasta’s Remarkable Comeback From Drought Captured in Stunning Images
Advanced Sub Reports Anomalous Structure In Antarctica—Then Immediately ‘Disappears’
References:
Reference 1
Reference 2
This article first appeared here
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







