
Antarctica is like the gift that keeps on giving, and this time, it has opened up a whole new world for researchers. Recent events have revealed a unique and thriving ecosystem beneath a collapsed ice shelf, offering an unprecedented glimpse into a previously hidden world. This discovery is fascinating and critical for understanding climate change’s impacts on these fragile environments.
The Ice Shelf Collapse
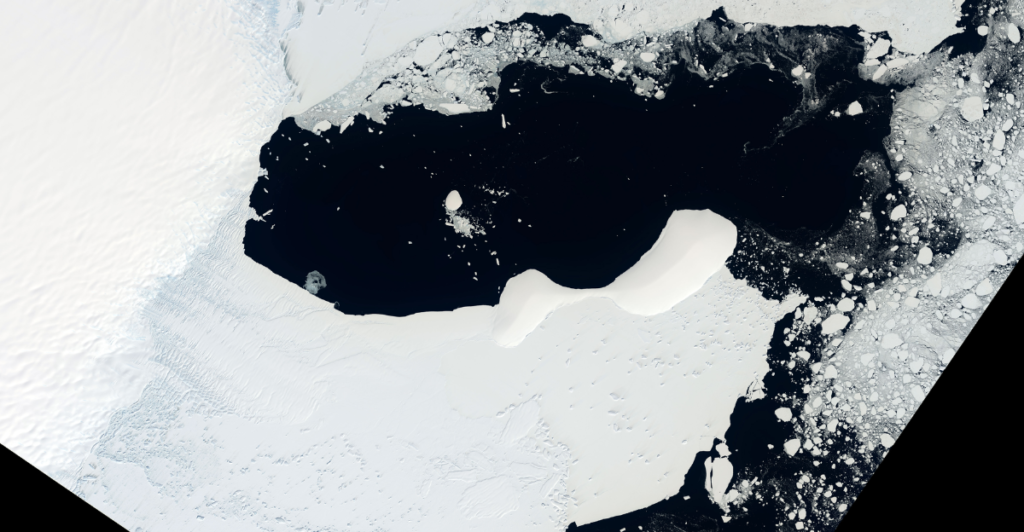

Ice shelves are extensions of glaciers that float on the ocean’s surface. They play a vital role in stabilizing the land-based ice and slowing the flow of glaciers into the sea. Recently, a significant Antarctic ice shelf collapsed due to rising temperatures, a direct consequence of global warming. This collapse exposed a vast area of the seabed, which had been covered for millennia.
This allowed nearby researchers to see a whole new ecosystem that they had never been exposed to before. Findings like these keep researchers on their toes, with ever-changing findings helping them better understand the world around them.
Unveiling a Hidden World
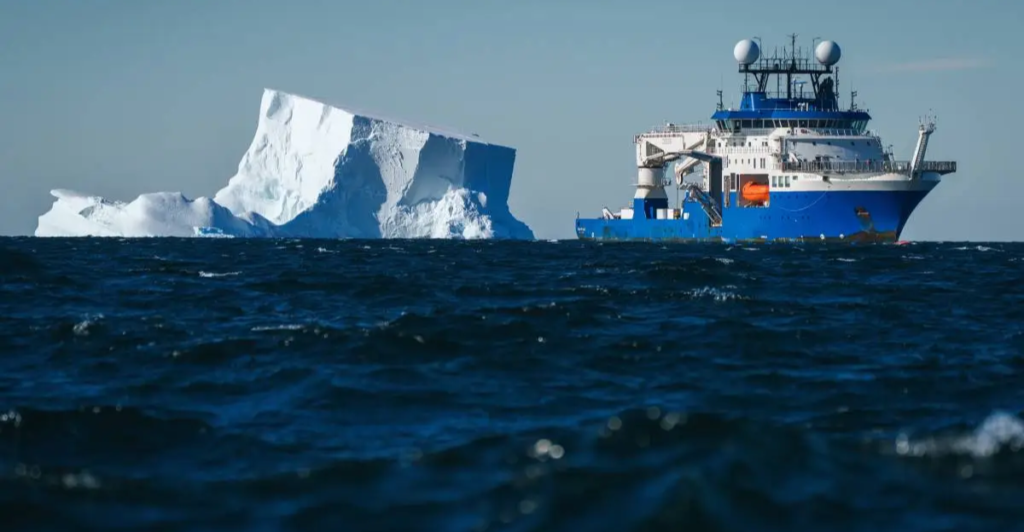
This iceberg, named A-84, broke off the George VI Ice Shelf, which is estimated to be around the same size as Chicago. With the ice shelf gone, researchers explored the newly exposed seafloor. Around 209 square miles (540 square kilometers) of exposed seafloor has never been explored. A team of researchers took to the Schmidt Ocean Institute’s R/V Falkor on the 25th of January to explore this area and see what it might have in store.
“We seized upon the moment, changed our expedition plan, and went for it so we could look at what was happening in the depths below,” said Co-chief scientist Patricia Esquete, a researcher at the Center for Environmental and Marine Studies (CESAM) and the Department of Biology (DBio) at the University of Aveiro in Portugal.
The “Alien” Ecosystem

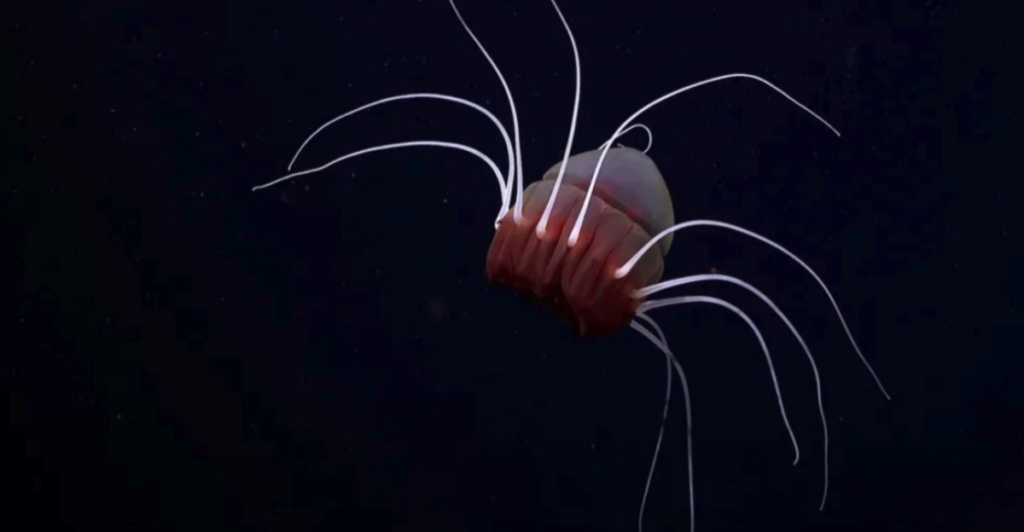
The term “alien” describes the unique nature of this ecosystem. Because it has been isolated from sunlight and the atmosphere for thousands of years, the life forms that have evolved here are unlike anything seen elsewhere.
The research team spent eight days surveying the ocean floor and went as deep as 4,265 feet below the ocean’s surface. “We were expecting quite an impoverished ecosystem because it’s not receiving food from the surface, like in a normal deep-sea setting in which you have photosynthesis happening in the surface,” said Patricia Esquete, a deep-sea ecologist with the University of Aveiro, Portugal.
Diverse Marine Life Discovered
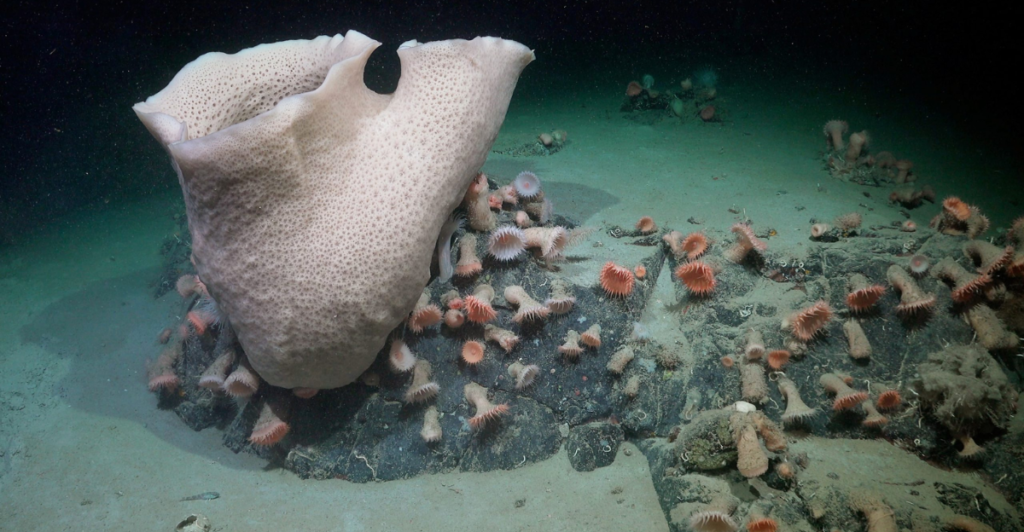

The ecosystem is home to a variety of marine organisms. Sponges, sea anemones, starfish, and other invertebrates carpet the seafloor, creating a colorful and diverse habitat. “We found a well-established ecosystem,” Esquete said. “We have several new species, that’s for sure — of fish, of crustaceans and polychaete worms,”
These creatures have adapted to the cold, dark conditions and limited food supply. Researchers suspect that deep, strong ocean currents are providing the much-needed nutrients for this ecosystem to thrive.
Unique Adaptations to Extreme Conditions
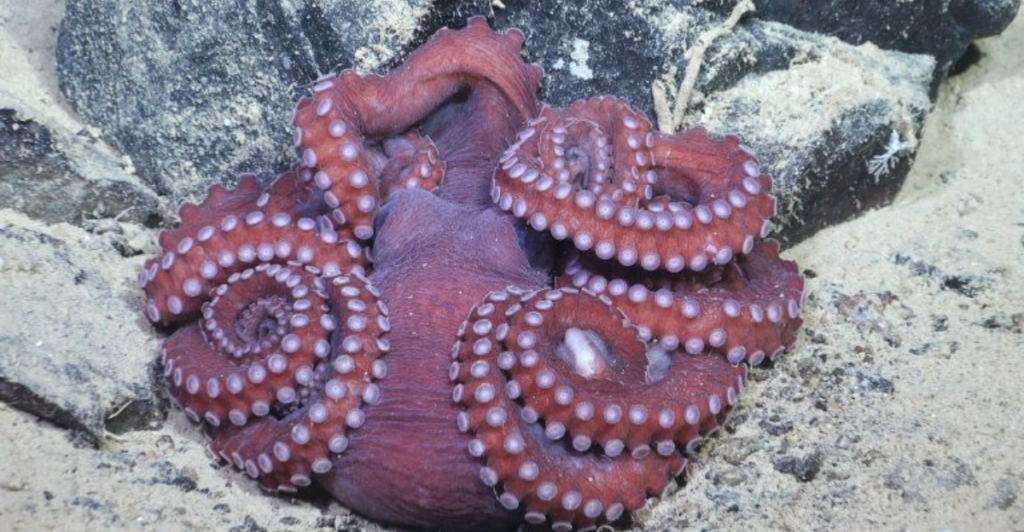

Life in this environment requires extraordinary adaptations. Organisms have developed specialized strategies to survive without sunlight, relying on alternative food sources such as chemosynthesis or organic matter that drifts down from the surface. Their metabolisms are also adapted to the frigid temperatures.
“Based on the size of the animals, the communities we observed have been there for decades, maybe even hundreds of years,” Esquete said. “Now we know that under ice shelves, at least in the first 15 kilometers from the front, there are diverse, well-established ecosystems.”
Research Methods and Technologies
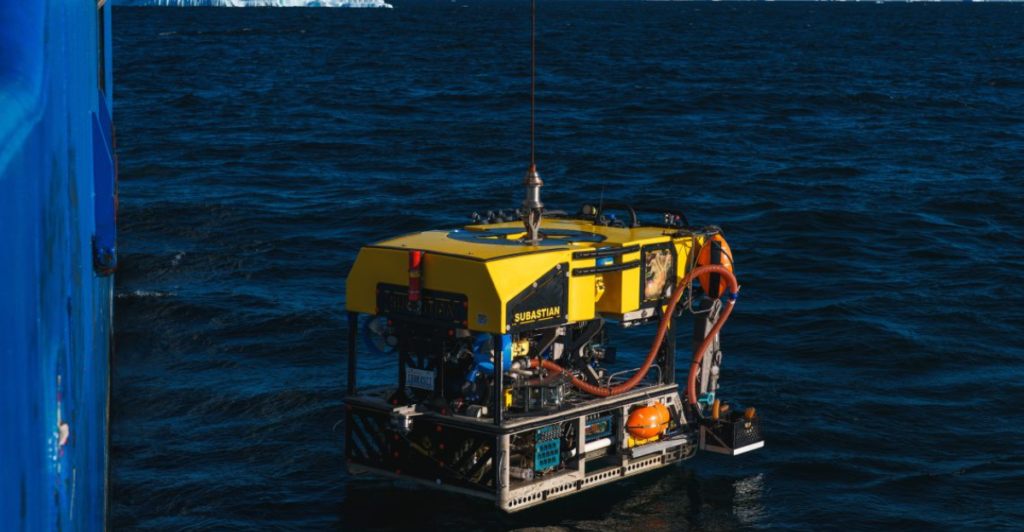

Exploring this hidden world requires cutting-edge technology. Researchers study the seafloor using remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) equipped with cameras, sensors, and sampling tools. These ROVs can navigate the challenging underwater terrain and collect data without disturbing the delicate ecosystem.
This is also the first time an ROV survey has been done so thoroughly, allowing researchers to document as much of the seafloor as possible.
Implications for Climate Change Research

This discovery has significant implications for climate change research. Understanding how these ecosystems respond to environmental changes can provide valuable insights into the broader impacts of global warming on marine environments.
“The ice loss from the Antarctic Ice Sheet is a major contributor to sea level rise worldwide,” said Sasha Montelli of University College London. “Our work is critical for providing longer-term context of these recent changes, improving our ability to make projections of future change.”
Future Research Directions

“We thought we might see some life there, but it was surprising to see the degree to which life thrived in such a hostile environment. And it wasn’t just existing there but had been sustained for a long time,” said Montelli. Further research is needed to fully understand this hidden world’s biodiversity, ecology, and resilience.
Scientists plan to conduct more detailed studies of the organisms, their adaptations, and their environmental interactions. This research will provide valuable insights into Antarctica’s marine ecosystems’ past, present, and future.
A Call For Change

The discovery of this “alien” seafloor ecosystem serves as a reminder of the hidden wonders of our planet and the importance of protecting them. By taking action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote conservation, we can help preserve these unique environments for future generations.
Climate change is drastically affecting the world around us, and if we don’t come together, we might lose opportunities like these for good. “Being right there when this iceberg calved from the ice shelf presented a rare scientific opportunity. Serendipitous moments are part of the excitement of research at sea – they offer the chance to be the first to witness the untouched beauty of our world,” noted Schmidt Ocean Institute’s executive director, Jyotika Virmani.
Explore more of our trending stories and hit Follow to keep them coming to your feed!

Don’t miss out on more stories like this! Hit the Follow button at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest news. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!







