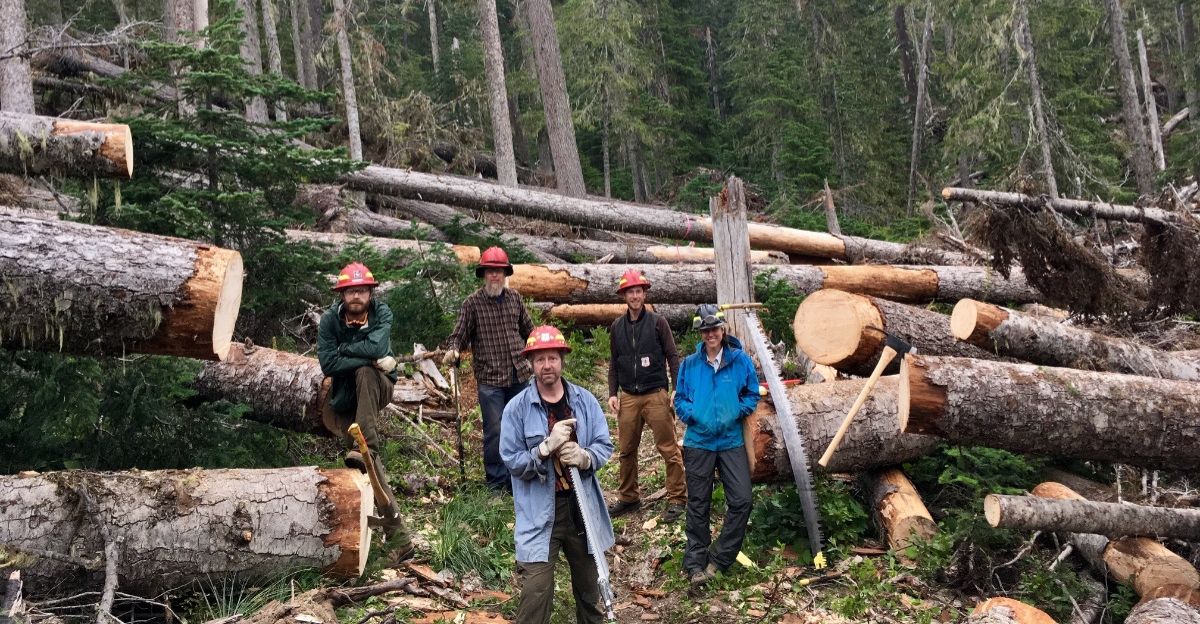

The Alaska Forest Association (AFA) has initiated legal action against the U.S. Forest Service (USFS), alleging failure to uphold timber sale commitments in the Tongass National Forest. This lawsuit underscores ongoing tensions between industry stakeholders and federal agencies over resource management and environmental conservation in Alaska.
Background: The Tongass National Forest
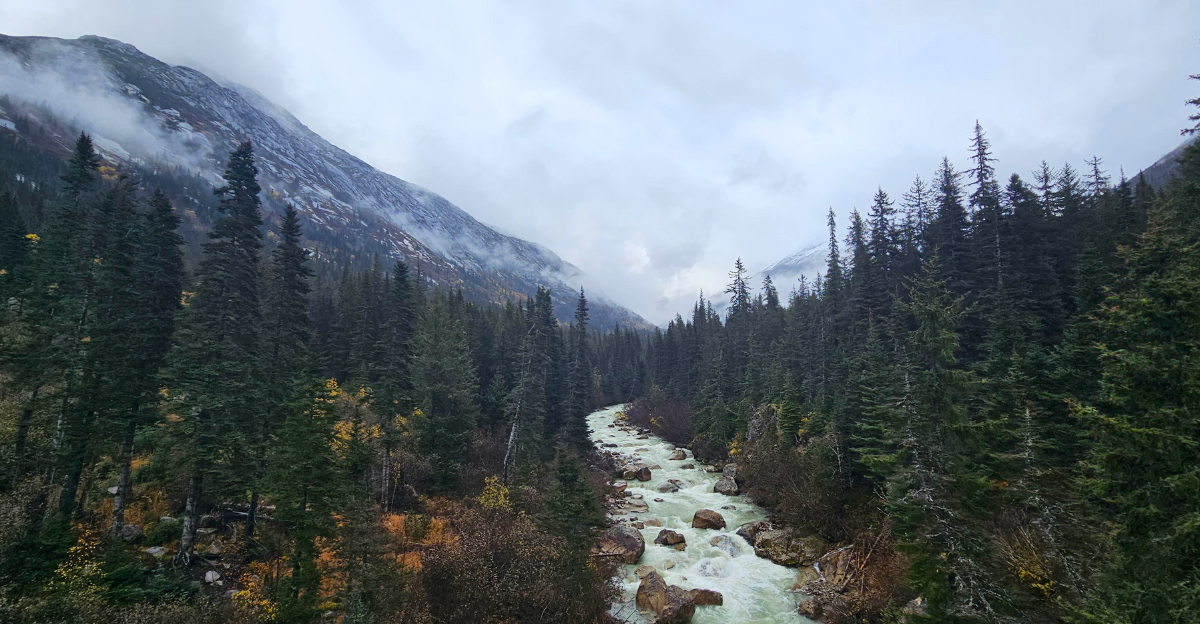

The Tongass National Forest, encompassing approximately 16.7 million acres, is the largest national forest in the United States. It is renowned for its old-growth temperate rainforests, diverse wildlife habitats, and significant ecological value. The forest also supports various industries, including timber, fishing, and tourism, making its management a subject of complex debate.
AFA’s Allegations Against USFS

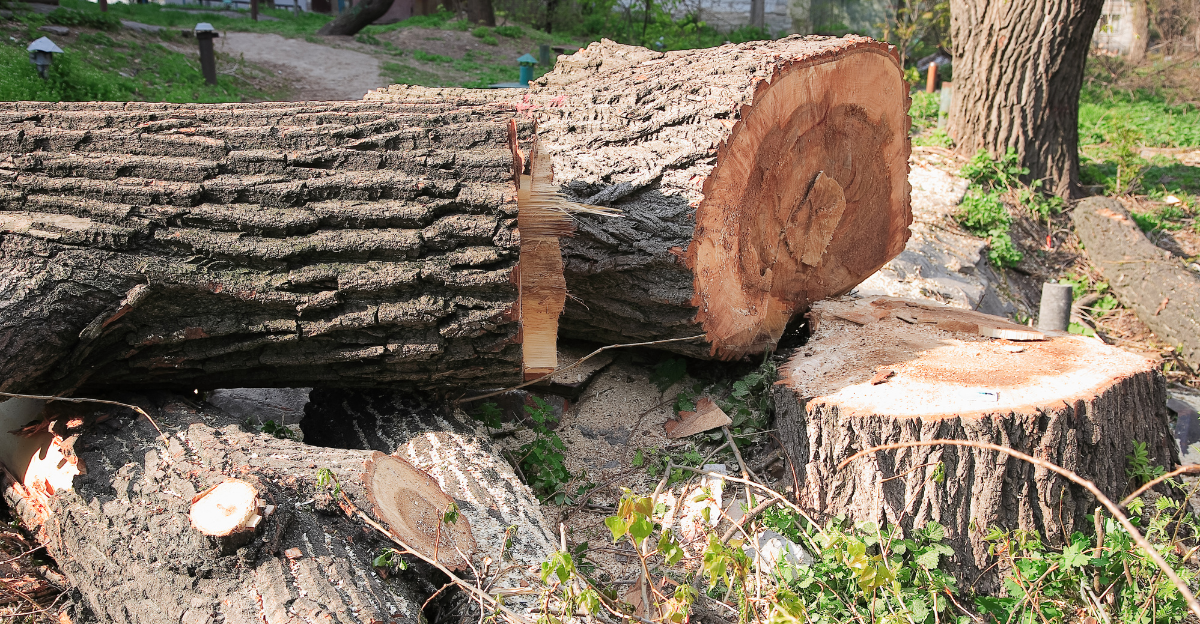
The AFA contends that the USFS has not fulfilled its obligations to offer sufficient timber sales, particularly of young-growth timber, following the cessation of old-growth sales in 2021. According to the AFA, this alleged shortfall has adversely affected the local timber industry, leading to job losses and economic decline in communities dependent on forestry.
Economic Impact on the Timber Industry
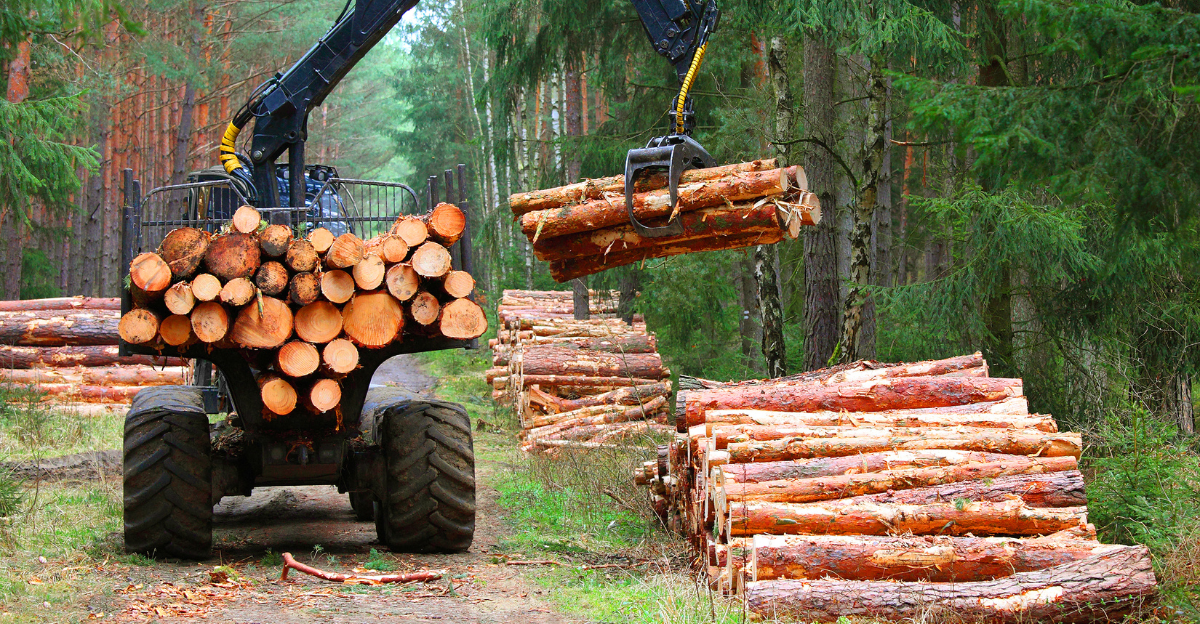

Historically, the timber industry in Southeast Alaska provided over 4,000 jobs. However, due to reduced timber sales and increased restrictions, employment has dwindled to approximately 300 positions. The AFA argues that the USFS’s policies have contributed to this decline, emphasizing the need for a balanced approach to forest management that supports environmental and economic interests.
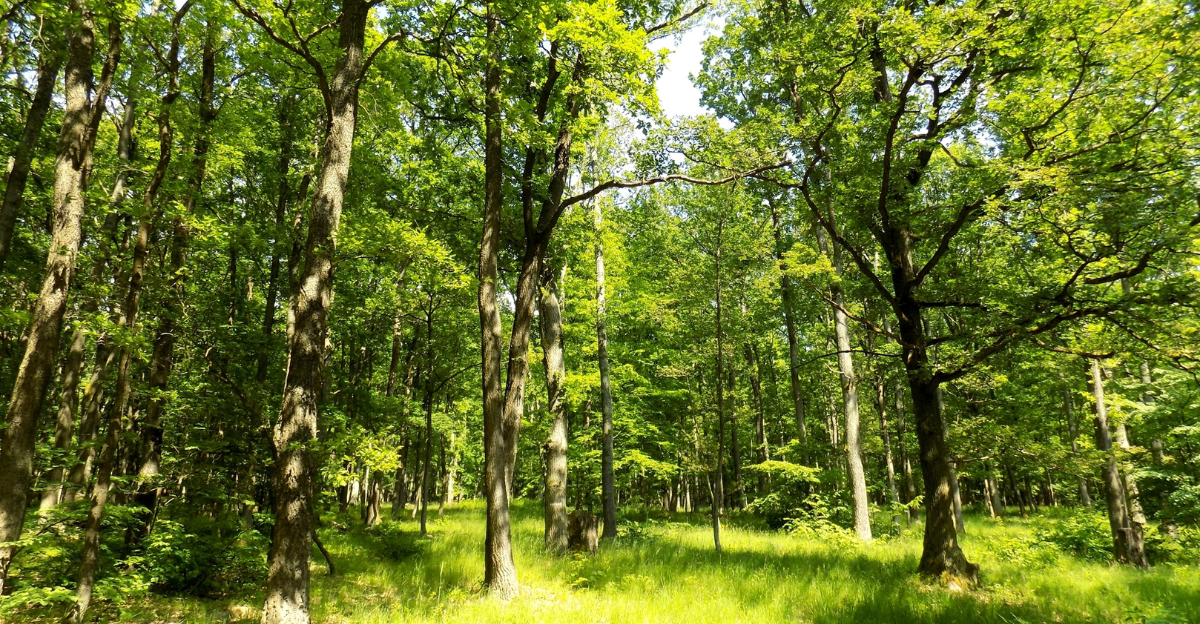
Environmental Concerns and Conservation Efforts

Environmental organizations advocate for preserving old-growth forests in the Tongass, citing their critical role in carbon sequestration, biodiversity, and ecosystem health. These groups support the USFS’s shift away from old-growth logging, emphasizing sustainable practices and the protection of wildlife habitats.
Legal Framework Governing Forest Management

Forest management in the Tongass is guided by federal laws, including the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) and specific forest plans. The USFS must balance multiple forest uses, including recreation, habitat preservation, and resource extraction, while ensuring environmental sustainability.
Previous Legal Disputes Involving the Tongass

The Tongass has been at the center of numerous legal battles. For instance, environmental groups have previously sued the USFS over large-scale timber sales, arguing violations of NEPA and inadequate consideration of ecological impacts. These disputes highlight the ongoing challenges in managing the forest’s resources.
The Role of the Southeast Alaska Conservation Council (SEACC)

The SEACC is a prominent environmental organization protecting Southeast Alaska’s wild lands and waters. They have actively advocated for sustainable forest management practices in the Tongass, often opposing large-scale logging operations to preserve ecological integrity.
USFS’s Perspective on Timber Sales

The USFS has faced criticism from industry and environmental groups regarding its management practices. While aiming to transition from old-growth to young-growth timber harvesting, the agency must navigate complex regulatory, ecological, and economic factors to meet diverse stakeholder expectations.
Community Impacts and Perspectives

Forest management decisions deeply affect communities in Southeast Alaska. While some residents rely on the timber industry for their livelihoods, others depend on tourism and fishing, which benefit from intact ecosystems. Balancing these interests is crucial for regional sustainability and social well-being.
Alternative Economic Opportunities

In response to declining timber industry jobs, there is a growing emphasis on alternative economic opportunities, such as tourism, fishing, and renewable energy projects. These sectors aim to provide sustainable livelihoods while preserving the ecological value of the Tongass.
Future of Forest Management in the Tongass

The outcome of the AFA’s lawsuit could influence future forest management policies in the Tongass. It may prompt reevaluating timber sale strategies, stakeholder engagement processes, and the balance between conservation and resource utilization.
Navigating Complex Interests
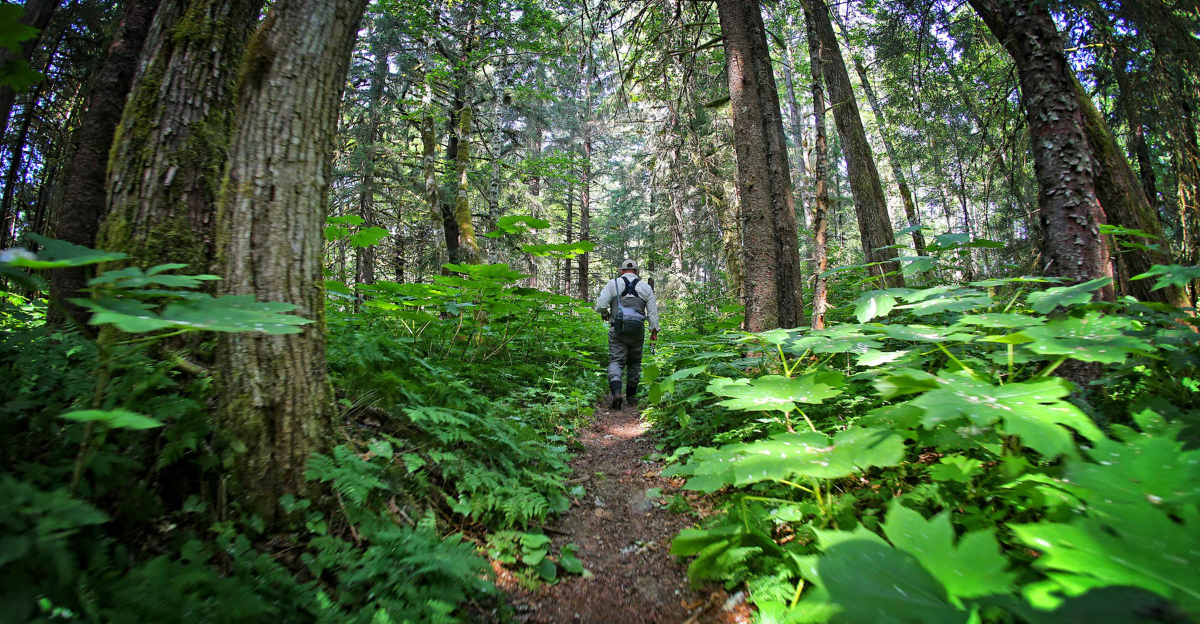

The legal challenge by the AFA against the USFS underscores the complexities inherent in managing the Tongass National Forest. Achieving a harmonious balance between economic development and environmental conservation requires collaborative efforts, transparent decision-making, and adaptive management strategies that consider the diverse interests of all stakeholders.
Explore more of our trending stories and hit Follow to keep them coming to your feed!
Don’t miss out on more stories like this! Hit the Follow button at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest news. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!







