
As animals faced adversity in an ever changing world, they need to adapt to their surrounding to survive. From habitat destruction to climate change and even poachers, the animal kingdom will continue to do what it has always done best, adapt and eventually thrive.
Rapid Development

These adaptations have only been seen over millions of years, but in the modern era, we’re starting to see a rapid development of traits that animals may need in the years ahead to survive. These modern-day marvels are evolving right before our eyes.
Elephants
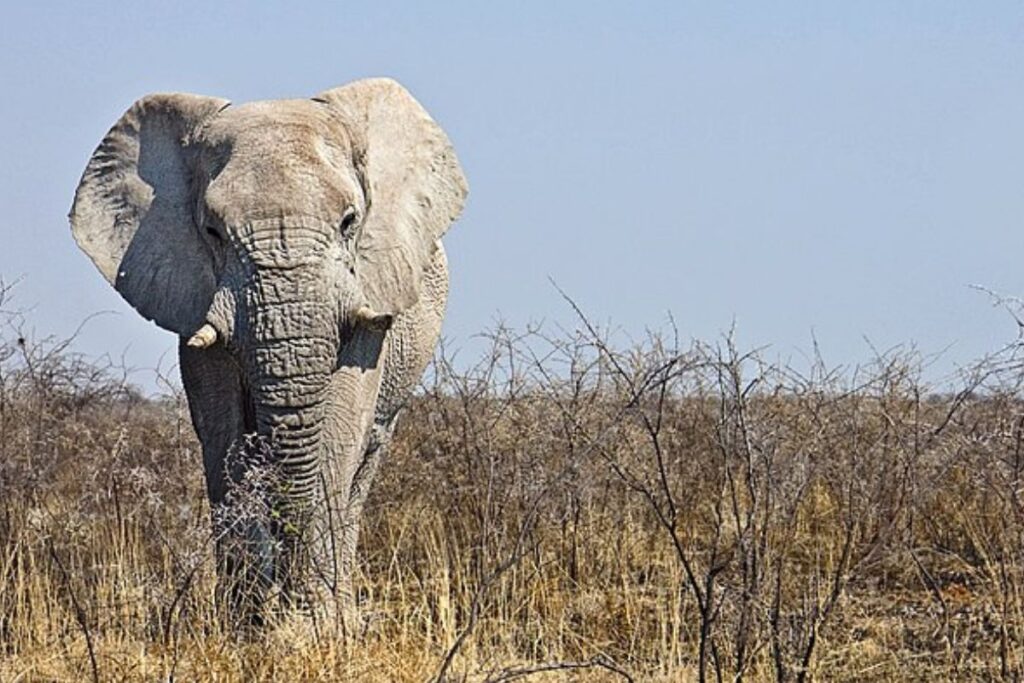

It’s no secret that elephant populations are a shadow of what they used to be for a variety of factors. Loss of habitat has played a part, but by far, the biggest factor is poaching. Their tusks are in high demand in illegal markets. But recently, new elephants have been born with surprising adaptations. Five to ten percent of Asian elephants are now being born without tusks, and up to thirty-eight percent of African elephants are also being born with adaptation. This could be through selective mating.
Salmon
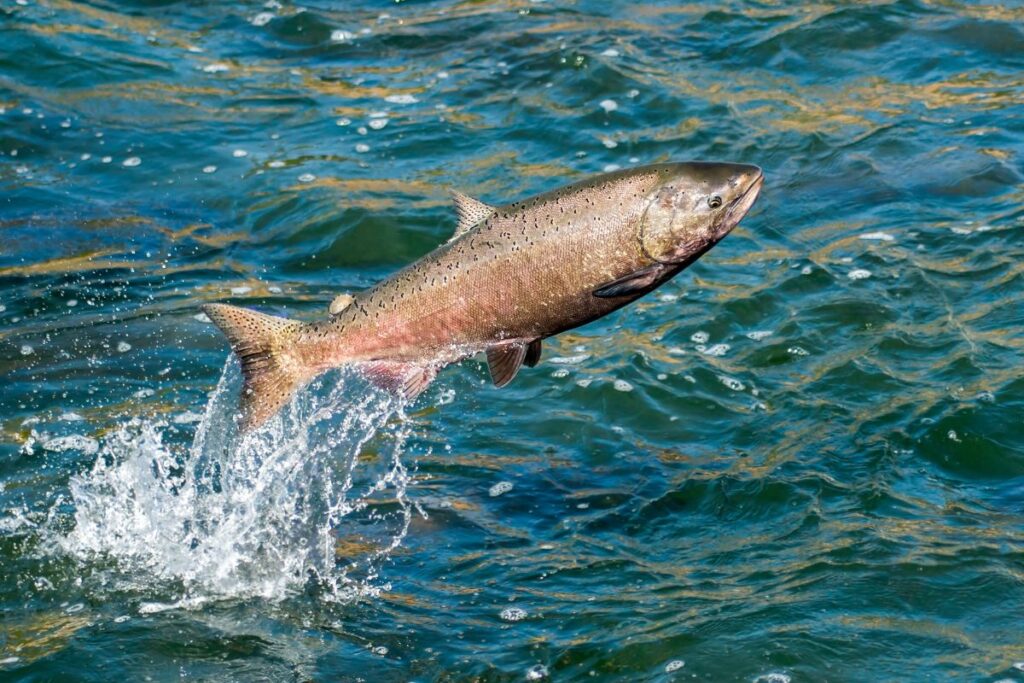

Salmon have been seen migrating earlier and earlier to adapt to climate change. Due to the water getting hotter sooner in the year, the salmon now migrate two weeks earlier than in the 1980s. This may keep increasing as the global temperature increases. It’s also been noted that salmon that migrate earlier have a higher survival rate, meaning natural selection is taking place.
Coyotes And Wolves
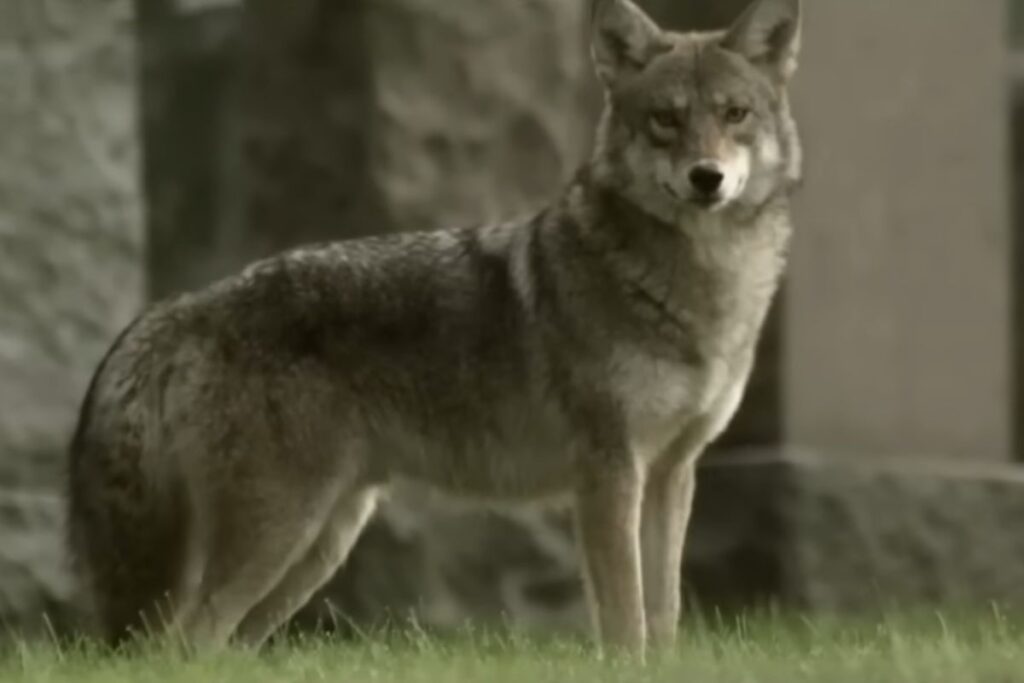

Coyotes and wolves have always clashed in shared territory. But as wolf numbers took a decline in the last one hundred years, they found a clever solution. Coyotes, who would normally stay clear of wolves, was let into the territory so that the wolves could have more breeding partners. This means that relatively new interbred species of coyote and wolf exists. It is much bigger than its coyote ancestry and roams the Eastern Coast.
Crustaceans
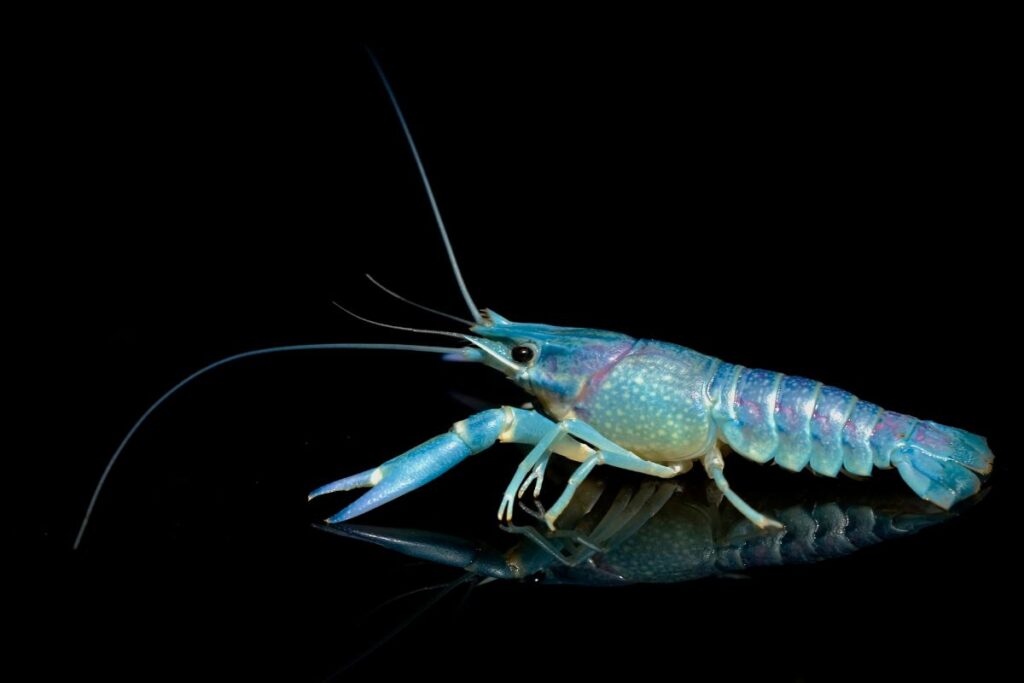

Crustaceans that live deep below the surface of the ocean in caves where there’s no light whatsoever are slowly losing one of their senses, and one day, it will probably be completely gone. The crustaceans have no use for vision where there is no light, and their eye stalks are getting smaller and smaller. The part of their brain for sight is also getting smaller.
Peppered Moth
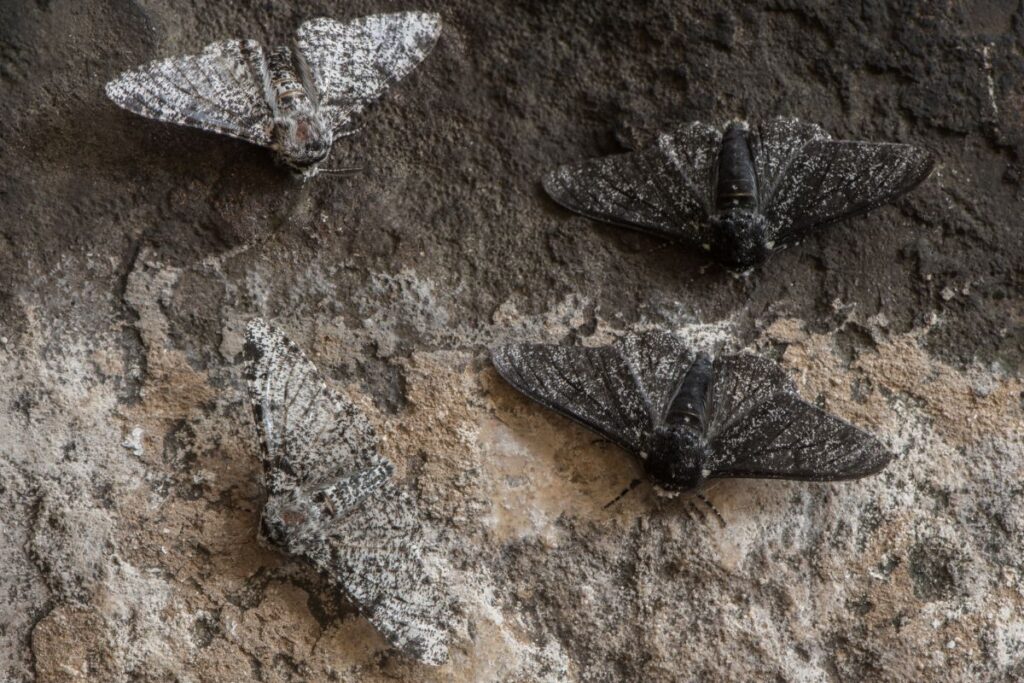

Before the Industrial Revolution, peppered moths were white with little specks of black, but as coal became a dominant resource used in industry, they started to adapt to their environment. The pale moths were easier to see and eaten by predators, while slightly darker ones weren’t. Eventually, in just 50 years, almost all peppered moths were black.
Humans
Modern medicine is a marvel, but it has also reversed natural selection in humans. No longer are the genes for survival the only ones that are passed down. A perfect example is pelvises in females. Since the 1960s, 20% more women with narrower pelvises have been born. This is because c-sections are now common and lifesaving.
Fish In The Hudson
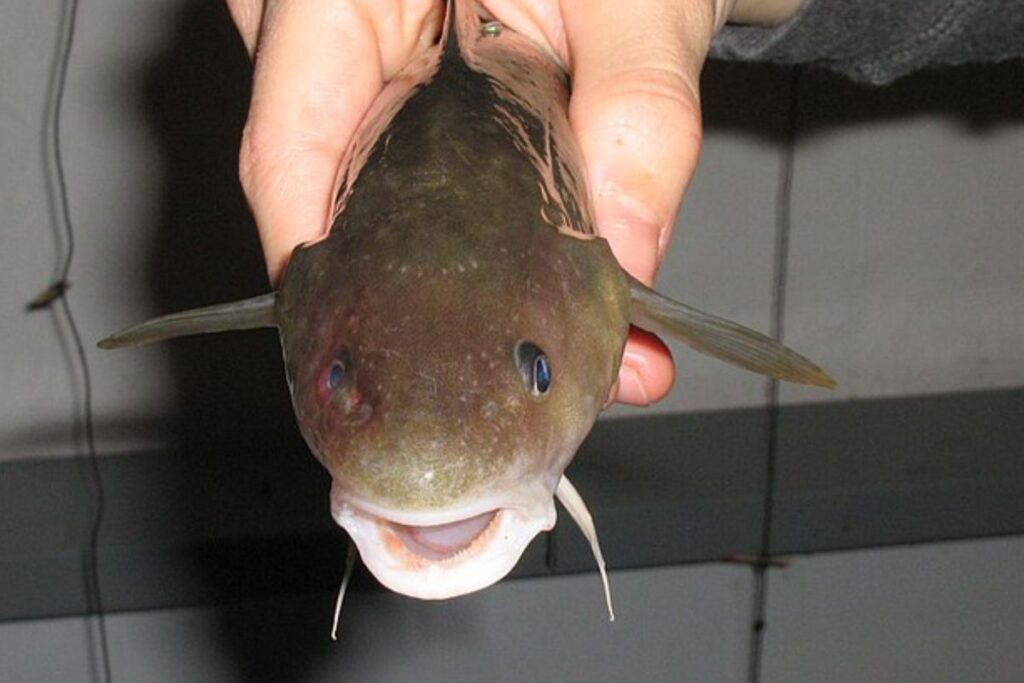

The Hudson river has seen its fair share of chemical pollution. In the 20th century, PBCs polluted the water, killing a lot of the local fish population. The tomcod, however, managed to overcome fate and changed some of the DNA so that the chemicals in the water couldn’t bind to them.
Rat’s Tail
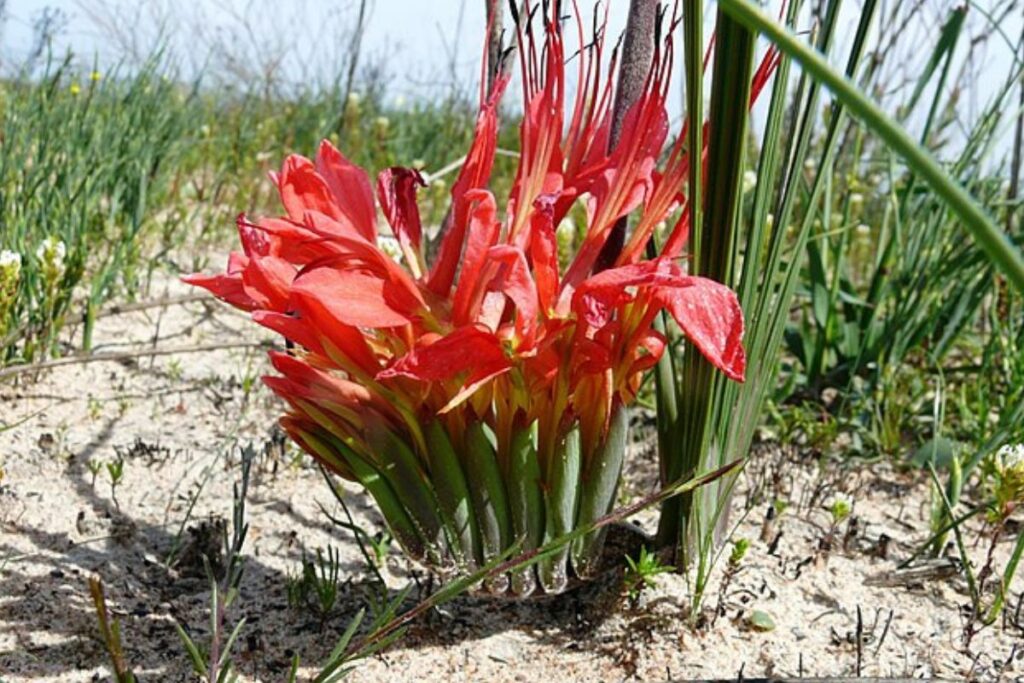

The rat’s tail is a plant that grows on the ground, where most predators frequent. Because of this, its flower wouldn’t get much attention from birds and couldn’t be pollinated. Thankfully, the plant adapted and started growing a perch for birds to sit on so they wouldn’t be so vulnerable to predators.
Mice
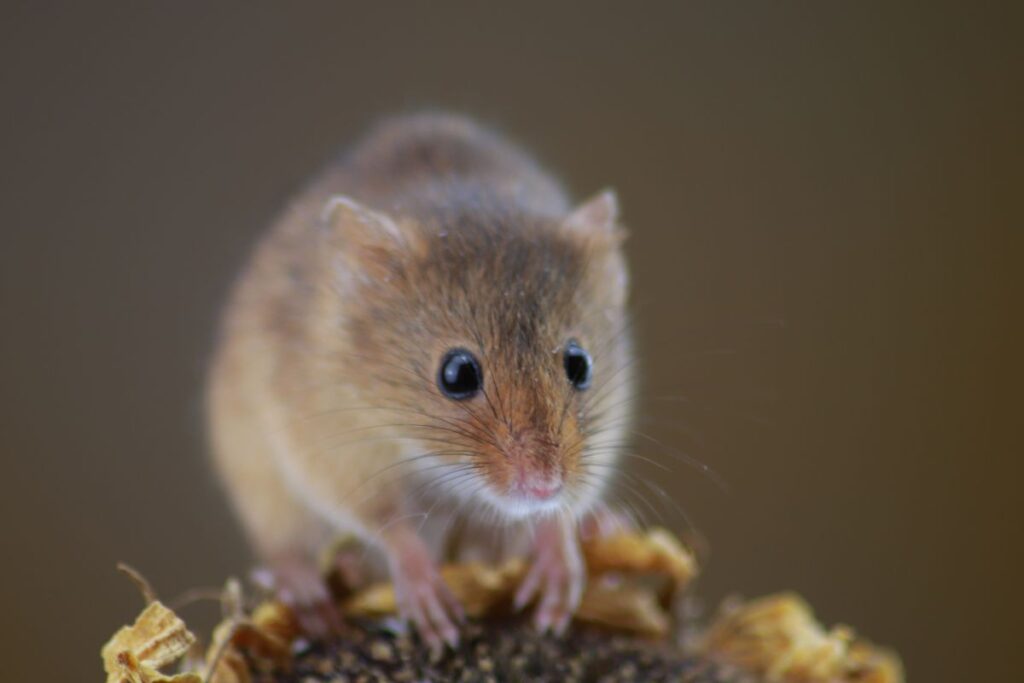

Mice have been a pest for many businesses for centuries. A poison called warfarin is used to get rid of the mice, but they’ve recently shown us that they shouldn’t be underestimated so easily. Mice have slowly become immune to the poison, and are now they’re starting to thrive in Germany.
Tawny Owls
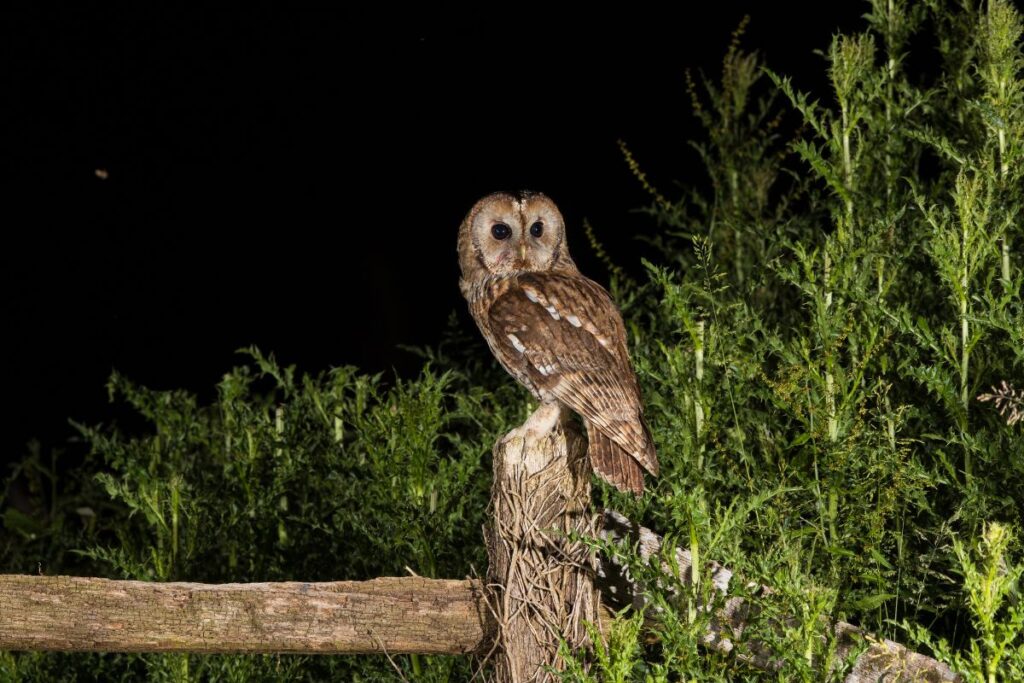

Tawny Owls have been lighter in Finland due to the snow. They would camouflage more easily compared to the darker members of their species. With climate change and hotter winters, the ice isn’t as widespread, meaning that darker brown, tawny owls have made a resurgence in recent years.
Lizards
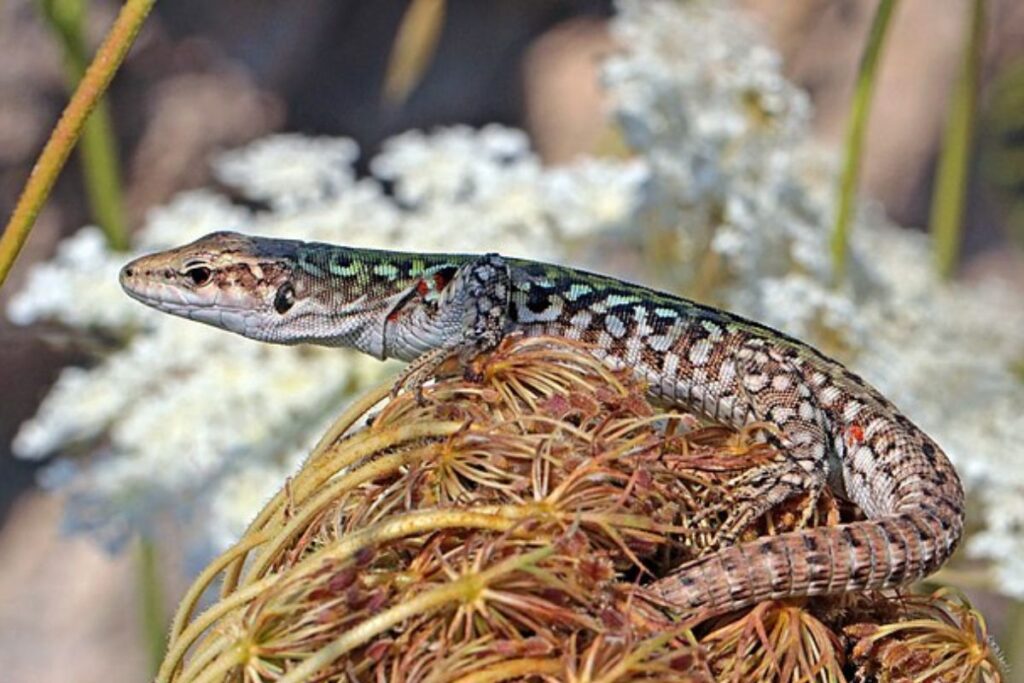

A group of lizards were dropped off at an island in Croatia and were left there for nearly 40 years. At that time, they had adapted from being complete carnivores to eating mostly plants. This genetically changed their stomachs and the way they process foods.
Source:
Humans Are Driving a New Kind of Evolution in Animals
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







