
It can be pretty scary when NASA announces they’ve found a growing anomaly, especially because so much remains unknown. This finding in the magnetic field has researchers on high alert and leaves them scratching their heads about what could possibly cause this.
Often described by NASA as a “dent” or “pothole” in the planet’s magnetic shield, the South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA) allows high-energy solar particles to penetrate closer to Earth than usual, posing unique risks to satellites, spacecraft, and even the International Space Station as they pass through the affected zone.
What Is the South Atlantic Anomaly?
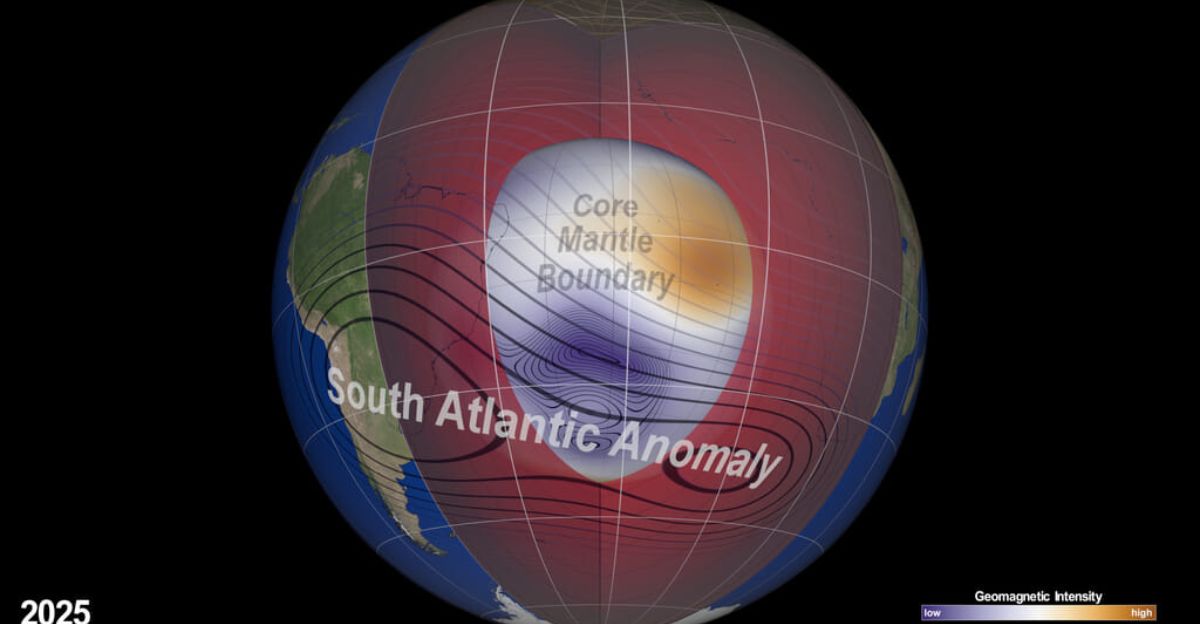
The South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA) is a vast region over South America and the South Atlantic Ocean where Earth’s magnetic field is significantly weaker than elsewhere. This allows high-energy particles from the Sun to penetrate much closer to the planet’s surface. This anomaly occurs because the inner Van Allen radiation belt, normally held at bay by Earth’s magnetic field, dips down to an altitude of about 124 miles in this area.
While the SAA does not affect daily life on the surface, it poses significant challenges to space technology. It often requires satellite operators to shut down sensitive systems when passing through the region to avoid malfunctions or permanent damage.
The Science Behind Earth’s Magnetic Field
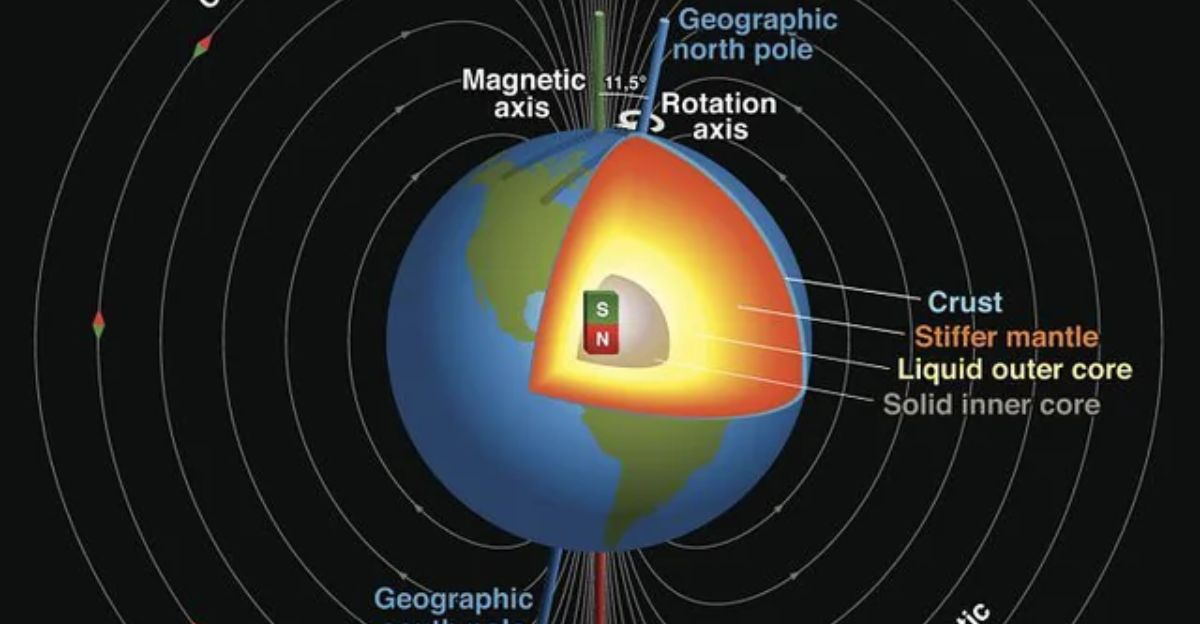
Earth’s magnetic field is a protective barrier that is generated deep within the Earth’s core through a process called the geodynamo. At the heart of this mechanism lies the movement of molten iron and nickel in the outer core, which, driven by heat from the inner core and the planet’s rotation, creates powerful electric currents. These currents, in turn, generate and sustain the magnetic field, forming a continuous feedback loop.
How NASA Discovered the Anomaly

The SAA was discovered in 1958 when early satellite missions first detected unusual radiation levels over the South Atlantic. Modern monitoring intensified with specialized missions like SAMPEX, which mapped radiation belts and revealed the anomaly’s northwest drift using two decades of particle data.
Satellite malfunctions, from Hubble’s UV detector shutdowns to the catastrophic 2016 failure of Japan’s Hitomi X-ray observatory, which spun out of control after SAA-induced system errors, helped spot this anomaly even more.
Why Is the Anomaly Expanding?

These changes are driven by constant changes deep within Earth’s core, where the planet’s magnetic field is generated. As molten metals in the outer core shift and flow, they alter the structure and strength of the magnetic field, leading to the anomaly’s gradual weakening and westward drift. As the field weakens, the inner Van Allen radiation belt dips closer to Earth’s surface over the South Atlantic, causing the affected region to grow larger and, in recent years, even split into two distinct lobes.
“The observed SAA can also be interpreted as a consequence of weakening dominance of the dipole field in the region,” said Weijia Kuang, a geophysicist and mathematician in Goddard’s Geodesy and Geophysics Laboratory. “More specifically, a localized field with reversed polarity grows strongly in the SAA region, thus making the field intensity very weak, weaker than that of the surrounding regions.”
Impacts on Satellites and Spacecraft

The South Atlantic Anomaly is an ongoing challenge for satellites and spacecraft operating in low-Earth orbit. As these vehicles pass through the region of weakened magnetic fields, they are exposed to much higher levels of ionizing radiation than elsewhere. This radiation can disrupt onboard computers, corrupt data, and even cause permanent damage to sensitive electronic components.
Satellite operators usually shut down non-essential systems during SAA transits to minimize the risk of malfunctions or mission failure.
The Anomaly’s Rapid Expansion
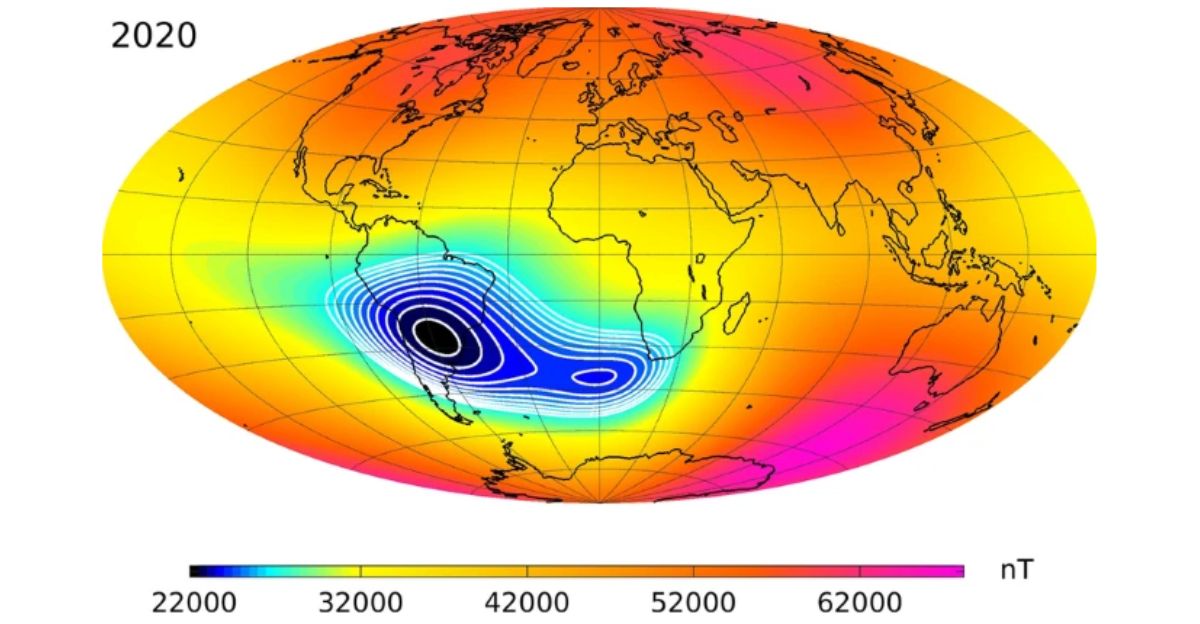
Since 2020, the SAA has expanded by over seven percent and now covers an area of approximately 4.3 million square miles. The anomaly grows and splits, creating dual centers of weakened magnetic intensity.
“Even though the SAA is slow-moving, it is going through some change in morphology, so it’s also important that we keep observing it by having continued missions,” said Terry Sabaka, a geophysicist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center. “Because that’s what helps us make models and predictions.”
Monitoring and Predicting the Anomaly’s Future
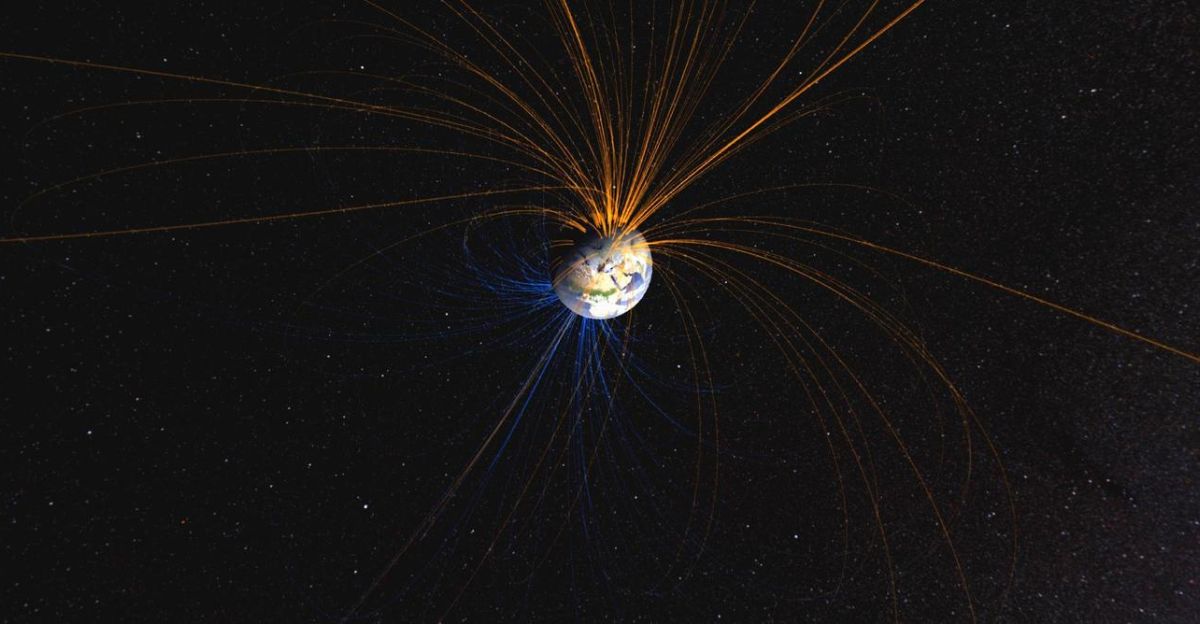
Observing this anomaly is a top priority for researchers, given its expanding footprint and the risks it poses to satellites and astronauts. Using a combination of ground-based observatories and advanced satellites, scientists collect real-time data on the strength and movement of Earth’s magnetic field.
NASA’s geomagnetic and geophysical research groups employ sophisticated models to forecast how the anomaly will evolve, including its westward drift and the recent split into two distinct lobes. These models are continually refined with new observations, allowing researchers to anticipate changes that could impact space missions and to develop strategies for mitigating potential hazards.
Risks to U.S. Infrastructure and Technology
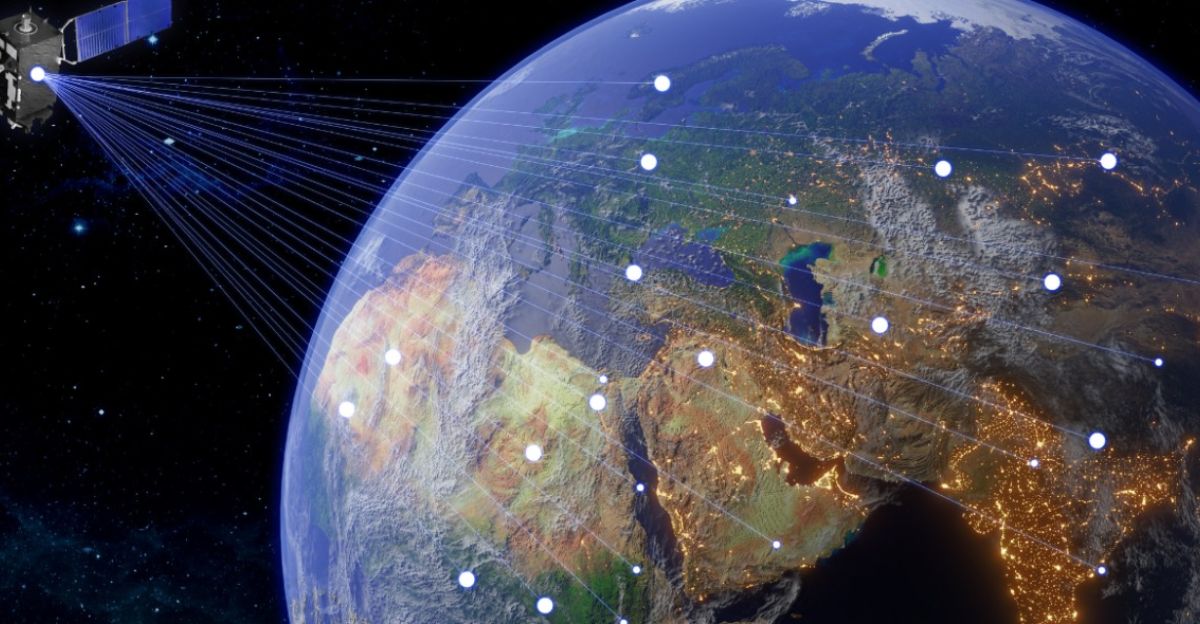
As the anomaly weakens Earth’s magnetic shield, it can potentially threaten communications and technology on the surface. This heightened vulnerability can disrupt satellite communications, GPS navigation, and Earth observation systems that underpin vital services in the United States, including telecommunications, weather forecasting, and defense operations.
As the SAA expands, the risk of it affecting technology becomes more profound, prompting researchers to develop advanced shielding.
A Call for Vigilance
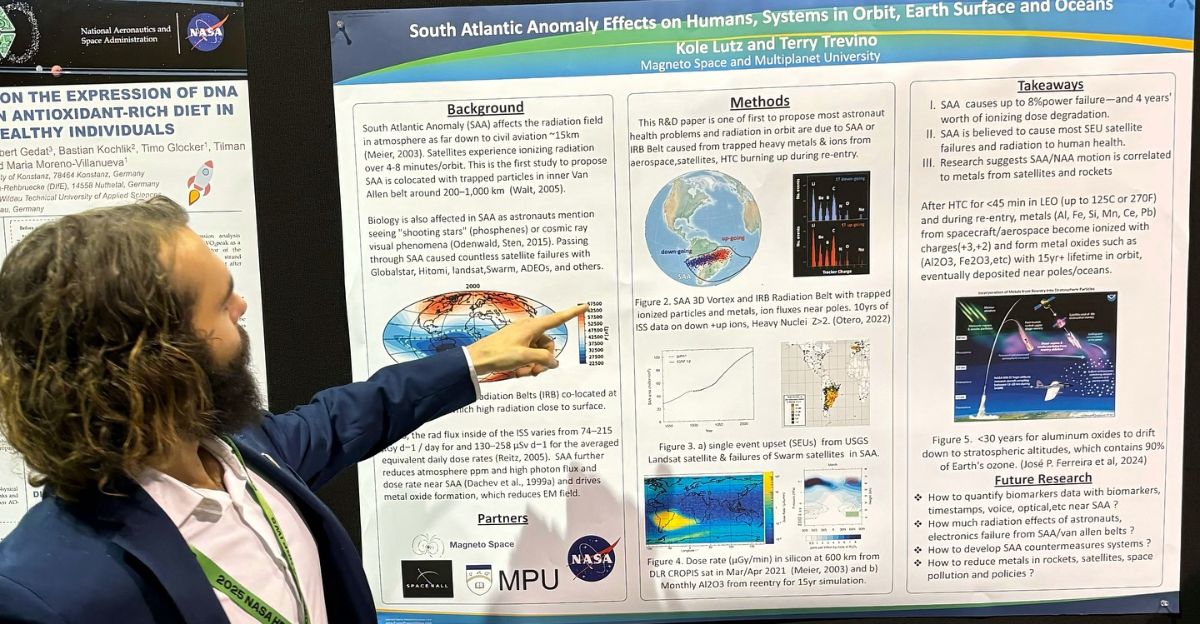
The SAA constantly evolves, forcing researchers to monitor and adapt to these changes that could impact the world. Scientists, engineers, and policymakers must work together to ensure that monitoring systems remain robust and that predictive models are continually refined to anticipate future changes.
Investments in research, satellite hardening, and international collaboration are essential to mitigate the risks posed by this anomaly and protect the critical systems society depends on daily.
Explore more of our trending stories and hit Follow to keep them coming to your feed!
Don’t miss out on more stories like this! Hit the Follow button at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest news. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!







