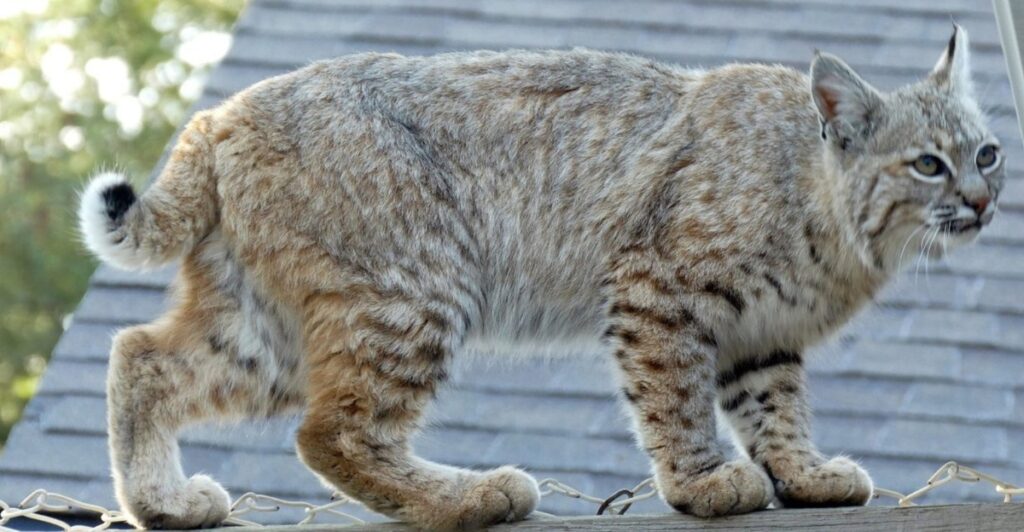

Bobcats, the small and stealthy wildcats of North America, have made a remarkable recovery after facing near extinction. This resurgence is not only good news for wildlife but also for humans. These predators play an essential role in ecosystems, including reducing the spread of diseases. Here’s everything you need to know about bobcats and how they’re helping protect us.
Wild, Elusive, and Adaptable

Bobcats are masters of survival, skillfully blending into their environments. With tufted ears, reddish coats, and their signature stubby tails, these cats are perfectly equipped for life in the wild. They can be found across North America, from the snowy forests of Canada to the deserts of Mexico. Their ability to thrive in diverse conditions—including urban fringes—makes them one of the continent’s most adaptable predators. Yet, their elusive nature means they’re rarely seen, even when nearby, earning them an almost mythical status among wildlife enthusiasts.
Recovering After Centuries of Decline
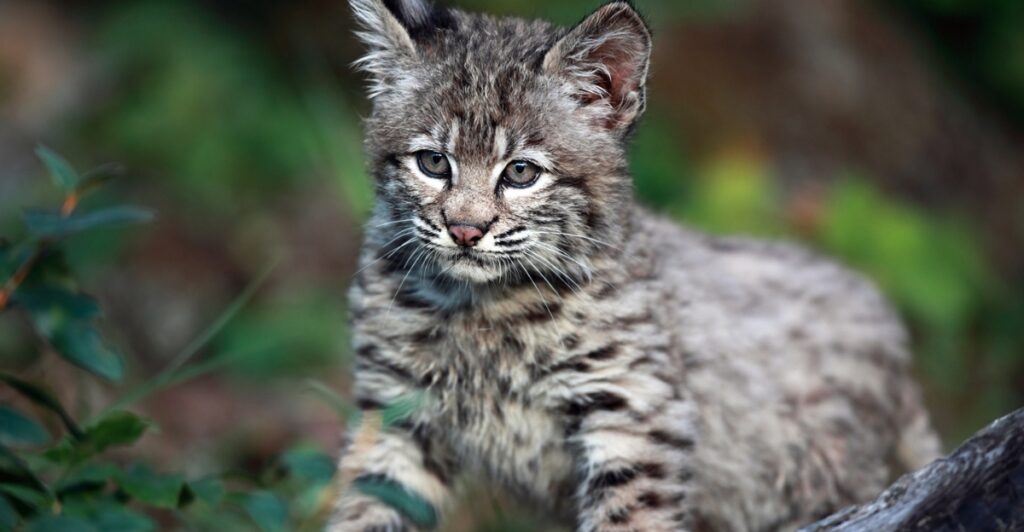

Once hunted for their fur and targeted as pests, bobcats were nearly wiped out by the 1900s. Habitat loss added to their struggles, but conservation efforts and legal protections have allowed their populations to rebound. Today, there are several million bobcats spread across the U.S., Canada, and Mexico. While their numbers are strongest in the West, these predators are gradually reclaiming territories in the East and South. Their resurgence is a hopeful sign for biodiversity, demonstrating the impact of sustained conservation action.
A Diverse Habitat
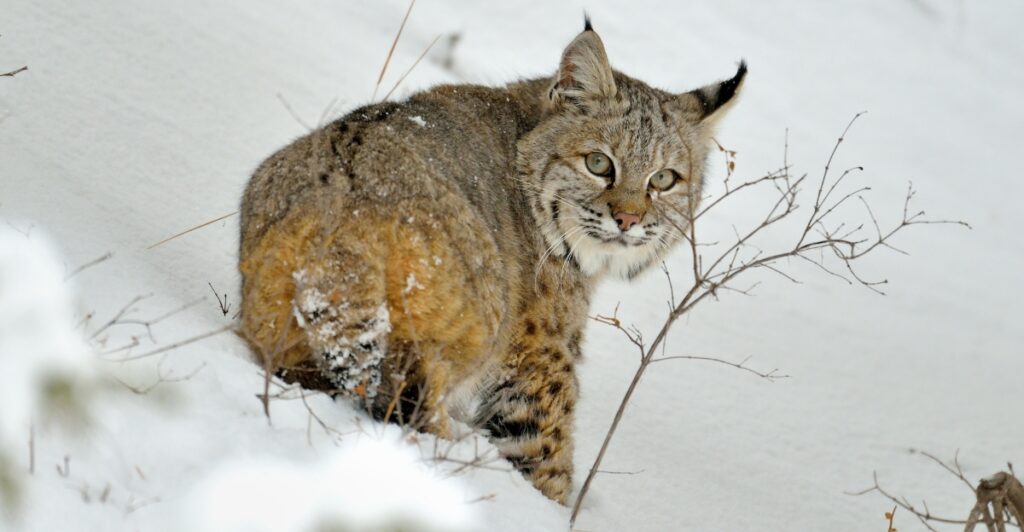

Bobcats thrive in varied landscapes, including dense woodlands, open grasslands, and rugged deserts. They’ve also learned to navigate the edges of human development, using hiking trails, suburban backyards, and even urban parks as part of their territory. However, these human-dominated areas bring risks: road collisions, exposure to rodent poison, and shrinking connectivity between wild spaces. To support bobcats’ survival, conservationists emphasize the importance of wildlife corridors that allow safe movement between fragmented habitats—not just for bobcats but for many species dependent on large territories.
Keeping Rodents in Check
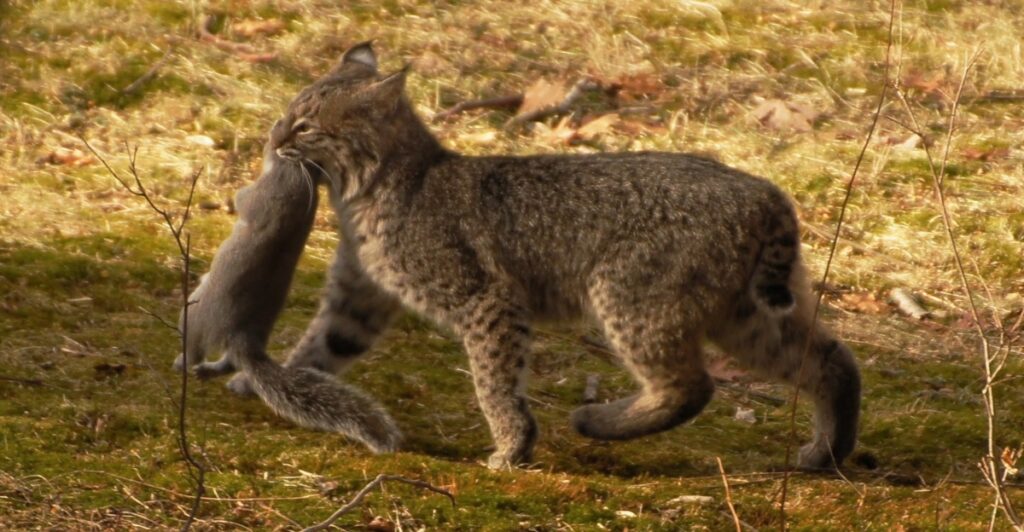

Rodents are more than just pests; they’re vectors for zoonotic diseases, such as Lyme disease. With their sharp hunting skills, bobcats help control populations of mice, rats, and other small mammals. This natural form of pest management reduces the spread of pathogens carried by rodents, benefiting both human and animal communities. By maintaining balanced ecosystems, bobcats indirectly safeguard public health. Their role as top predators highlights the interconnectedness of healthy wildlife populations and human well-being.
The Dilution Effect
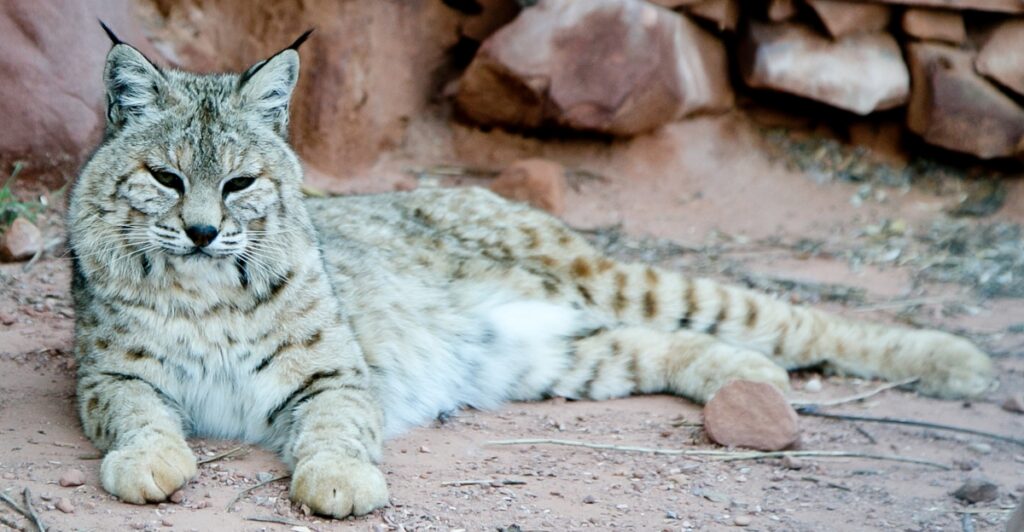

Bobcats play a surprising role in reducing disease transmission. As “poor hosts” for many pathogens, including the bacteria that cause Lyme disease, they help disrupt the cycle of infection. Ticks that feed on bobcats are far less likely to carry Lyme-causing bacteria than ticks that feed on rodents like white-footed mice. This phenomenon, called the dilution effect, illustrates how predators like bobcats keep ecosystems balanced by limiting the number of disease-carrying hosts. When predator diversity is high, disease risks for humans and other animals decrease significantly.
Taming the Tick Problem
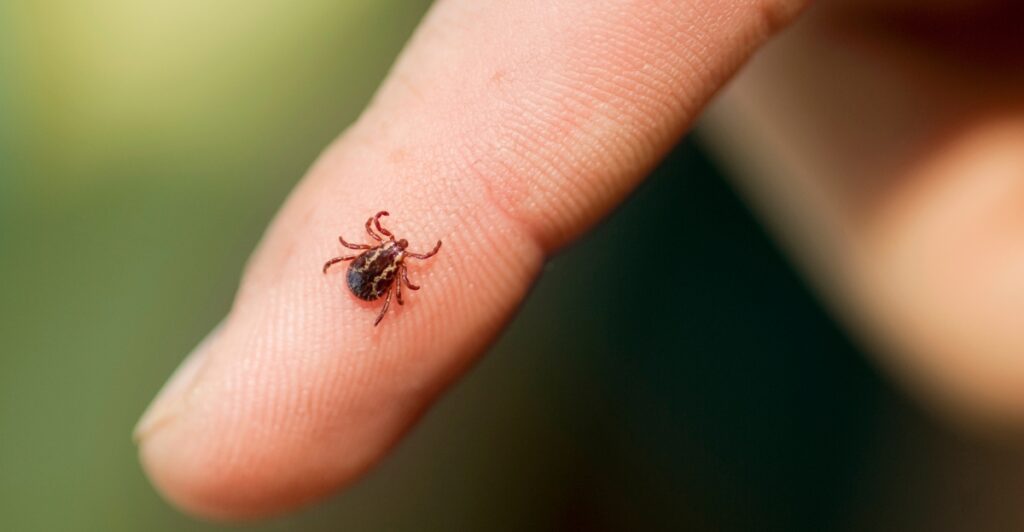

Ticks thrive in ecosystems overrun by rodents, their primary hosts. Without predators like bobcats to keep rodent populations in check, ticks multiply rapidly and spread diseases like Lyme. Bobcats indirectly reduce tick populations by feeding on rodents and fostering biodiversity. While no single species can solve the tick problem entirely, bobcats are a critical piece of the puzzle, acting as frontline defenders against outbreaks in rodent-dominated landscapes.
Why Biodiversity Matters for Disease Prevention
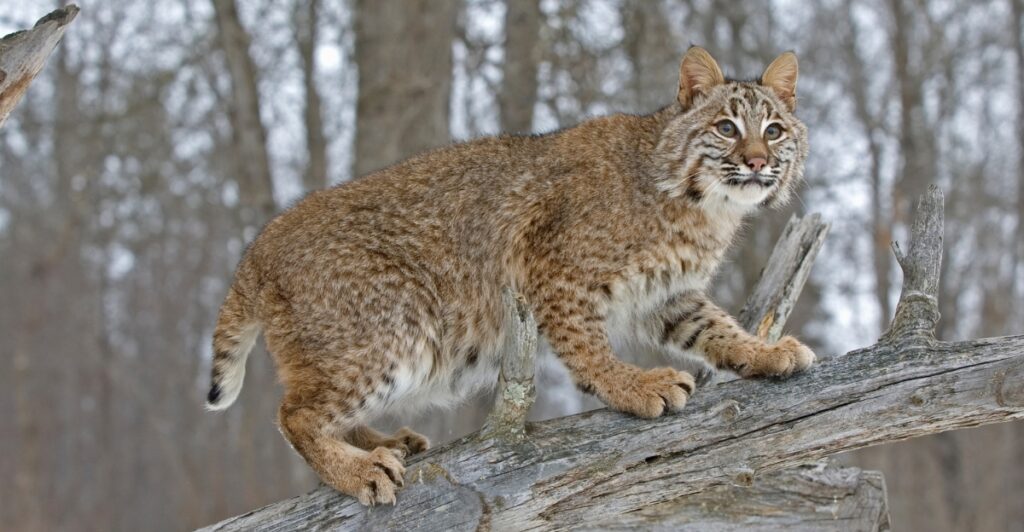

The connection between bobcats and disease prevention illustrates a broader principle: Ecosystems with diverse species are less likely to harbor outbreaks. In degraded habitats where predators are absent, rodents often dominate, leading to a spike in disease transmission. By reintroducing and protecting predators like bobcats, ecosystems regain balance. This balance reduces the prevalence of disease vectors and creates healthier conditions for all species, including humans. Preserving biodiversity is as much about our health as it is about wildlife conservation.
Rodenticides: Another Threat to Bobcats
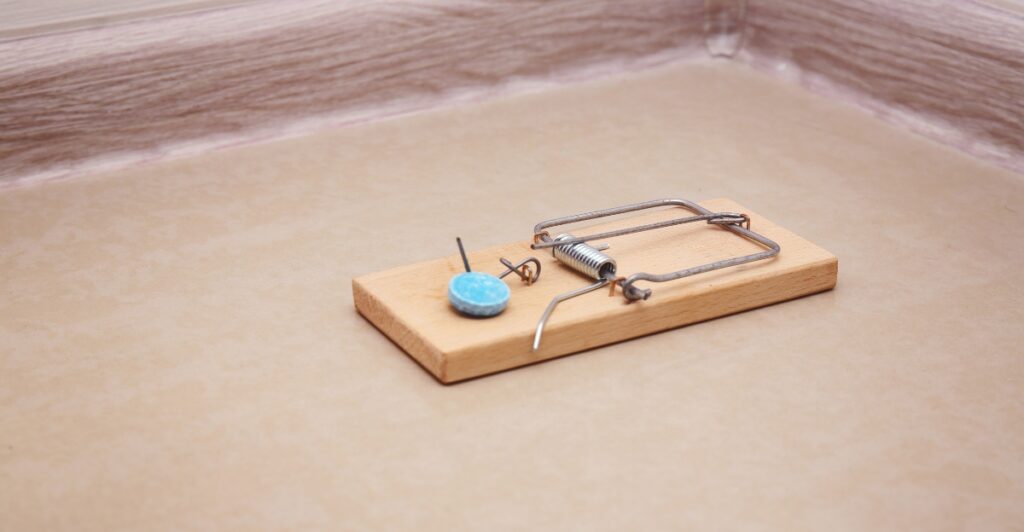

Rodent poison may seem like a quick fix for pest control, but its impact ripples through the food chain. Bobcats often consume poisoned rodents, leading to severe health issues and even death. These poisons weaken bobcats’ immune systems, making them more vulnerable to disease and reducing their populations. California’s recent ban on certain rodenticides represents a major step in protecting big predators. Safer, non-toxic pest control methods can help ensure these essential hunters continue their ecological role.
The Balancing Act of Coexistence
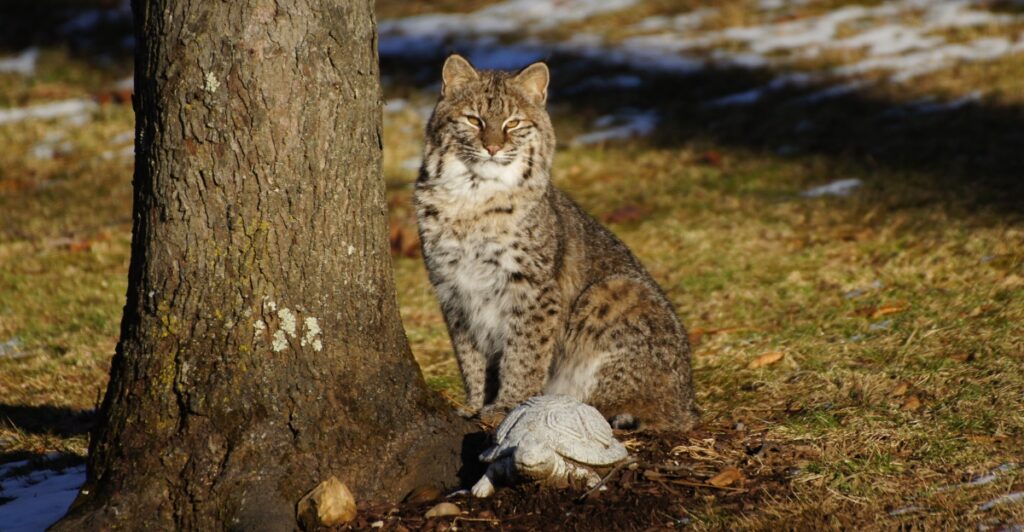

As human populations continue to expand, bobcats are increasingly sharing spaces with us. From suburban gardens to rural farmlands, these wildcats are adapting to life near people. However, coexistence requires effort. Minimizing habitat destruction, reducing roadkill risks, and avoiding rodenticides are all steps humans can take to create a safer environment for bobcats. Supporting conservation initiatives that prioritize connectivity between wild spaces can further help these predators thrive while maintaining ecological balance.
Conservation Successes and Challenges
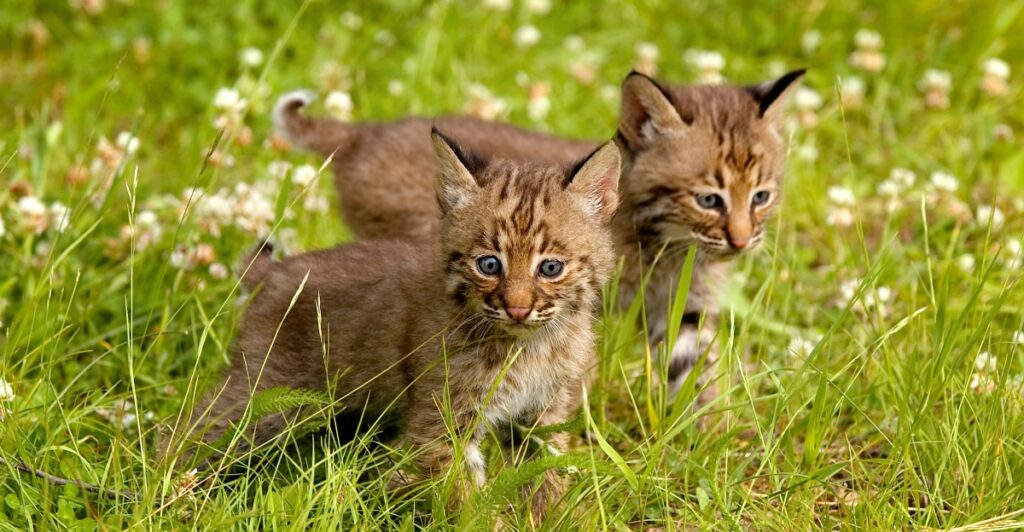

Bobcats’ recovery is a conservation triumph, but challenges remain. Hunting is still legal in most U.S. states, and proposals to reinstate it in California could threaten progress. Habitat loss and fragmentation continue to pose risks, along with the lingering effects of poisons and vehicle collisions. Protecting bobcats requires ongoing commitment from policymakers, researchers, and communities. By valuing their role in ecosystems, we can help ensure their populations remain strong for future generations.
How You Can Make a Difference
Protecting bobcats starts with small, meaningful actions. Avoiding rodenticides is a critical step, as these chemicals harm predators when they consume poisoned prey. Supporting wildlife organizations, volunteering for habitat restoration projects, and advocating for protective legislation can all make a tangible impact. For those living in areas frequented by bobcats, creating wildlife-friendly gardens with native plants and securing attractants like trash or pet food can foster peaceful coexistence.
Where to Spot a Bobcat
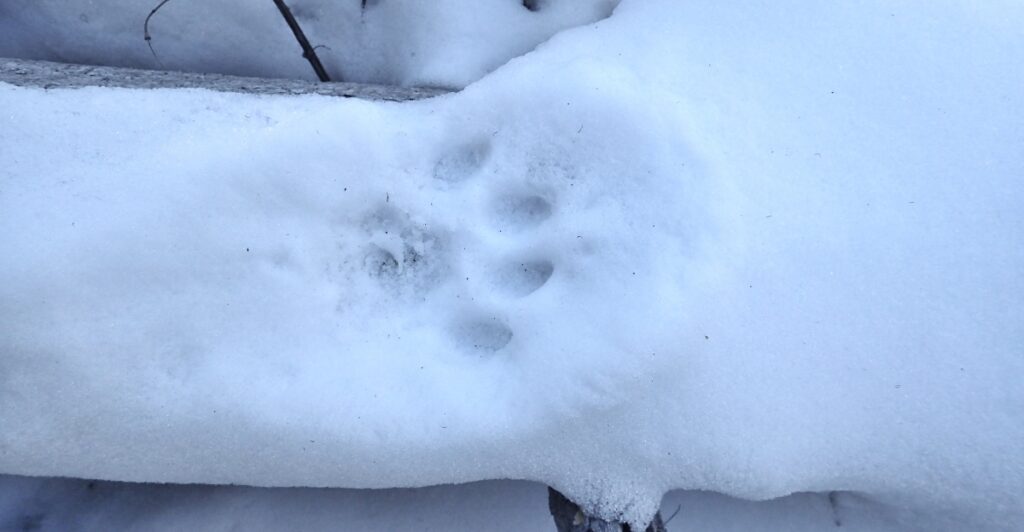

Seeing a bobcat in the wild is an extraordinary experience, but it requires patience and luck. These solitary animals are most active during dawn and dusk when they hunt for prey in the cover of low light. National parks and remote trails are prime locations for observing them, as these areas provide the quiet habitats they prefer. While rare, sightings can be enhanced by knowing their habitats, such as looking for tracks or listening for their distinctive calls. Observing bobcats from a distance ensures their safety and yours.
A Shared Future
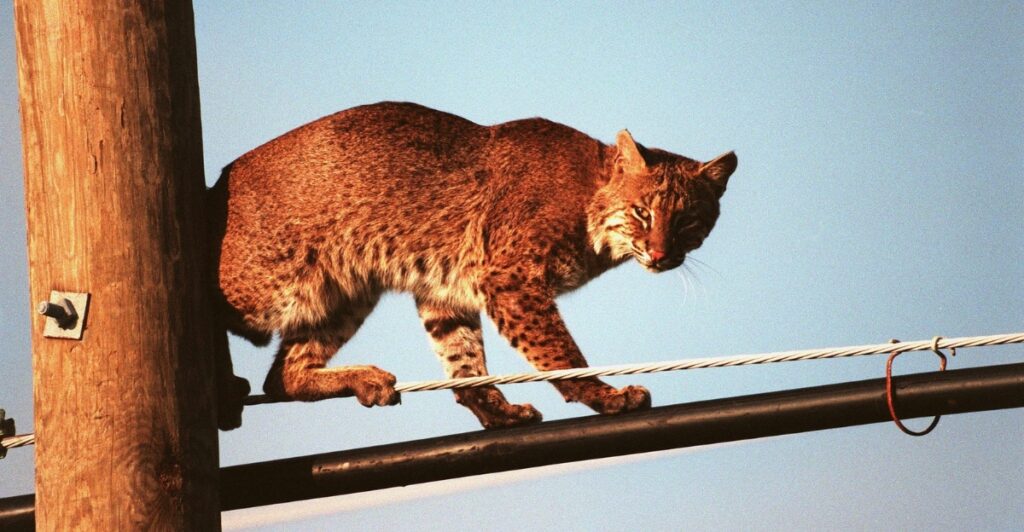

The presence of bobcats in our landscapes reminds us of nature’s resilience and our role in protecting it. These predators play a crucial part in maintaining ecological health, which ultimately benefits human populations by reducing disease risks and promoting biodiversity. Ensuring their future requires a commitment to conservation, including habitat preservation and reducing conflicts. By supporting policies and practices that value both humans and wildlife, we can create environments where bobcats and other species continue to thrive.
Resources:
- Mongabay: Bobcats are back, and they’re helping protect people from zoonotic disease
- Felidae Conservation Fund: Taking a Bite Out of Disease: How Bobcats Protect Us from Zoonoses
- Project Coyote: Bobcat (Lynx rufus)
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







