
Capybaras are amazing animals that call South America’s wetlands home. They can inhabit a large range of biomes because of their semi-aquatic lifestyle, from marshlands to flooded savannas. Capybaras are the largest rodents in the modern world and play a critical role in their ecosystems.
Controlling Populations

Capybaras play an important role in controlling vegetation populations through their diet. They feed on plants and grass found in aquatic environments. This ensures that no single species of plant dominates the landscape and gives an opportunity for more biodiversity.
Ecological Niches

As Capybaras consume grass and other vegetation, they create ecological niches for other animals to thrive. Their grazing also ensures that tall grass doesn’t block out sun rays, which are important for the life of other plants and animals.
Water Quality

The consumption of vegetation has a knock-on effect that creates better water quality in the environment. Water clarity improves, and algae don’t overpopulate, which helps local populations that are sensitive to changes in the water.
Microbiomes

Although Capybaras do not make burrows to take shelter in like many other rodents, they do still dig in the soil to wallow. This helps with skin irritation and keeps them cool. The resulting wallow is the perfect microenvironment for amphibians and insects.
Soil Health

Their digging also aerates the soil. This helps to promote healthier soil, from making it more fertile and further spreading seeds. This also affects plant growth and vegetation quality, which attracts more grazers seeking sources of food.
A Food Source

Capybaras, being herbivores, also play an essential role in their ecosystem as prey. They are an important food source for predators such as jaguars and caimans. This keeps the balance of the food chain in their ecosystem.
Seasonal Adaptations

While food scarcity can be a huge problem in many ecosystems, Capybaras have adapted to seasonal changes where vegetation becomes unavailable or in small quantities. They absorb more nutrients from less rich food, which keeps them and their predators sated in harsher seasons.
Ecotourism
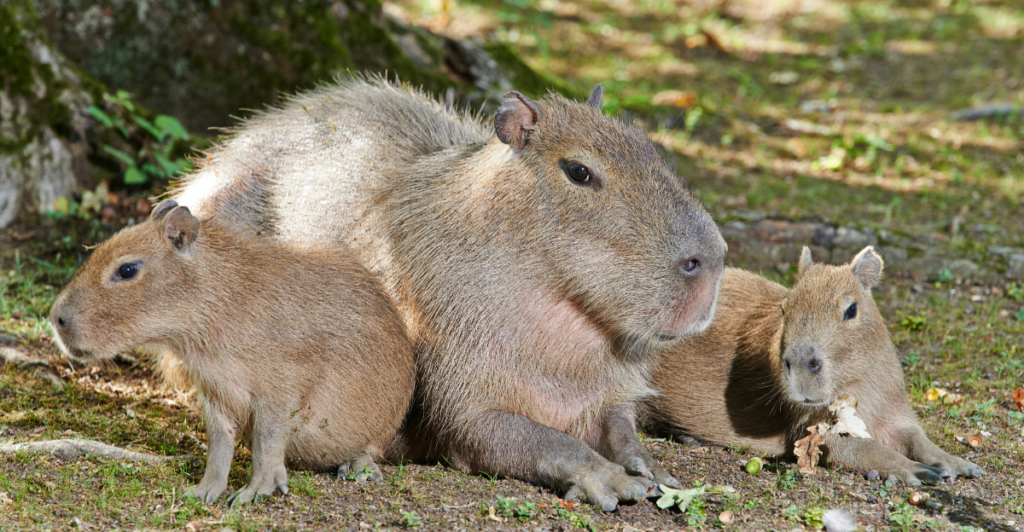

In placed like Columbia, capybaras contribute to local ecotourism and have a significant cultural presence. Through attracting ecotourists, they aid in spreading awareness about environment conservation, which will ultimately help combat habitat mitigation and climate change factors.
Nutrient Cycling
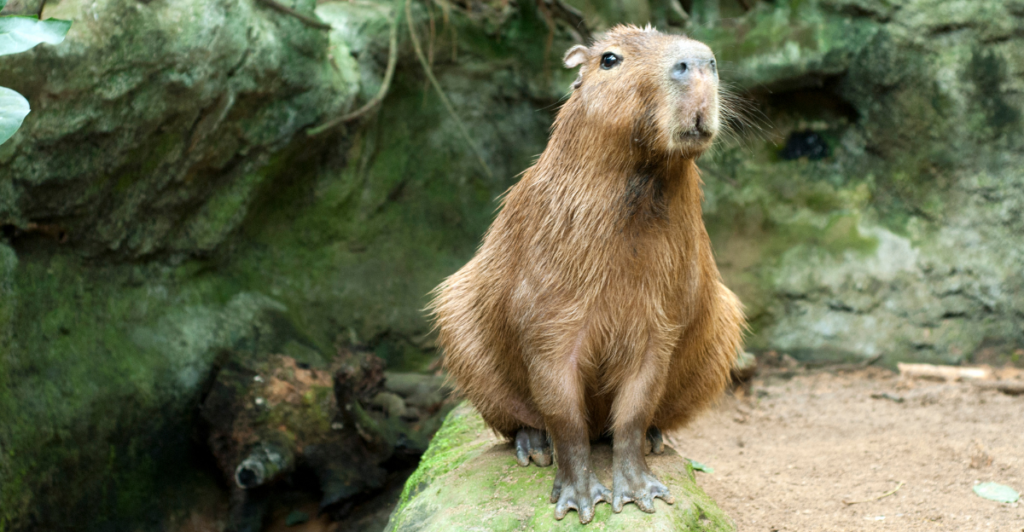

Capybaras consume a lot of vegetation, which ends up playing an important role in nutrient cycling – which is the cycle of nutrients moving from the environment and into organisms. This method helps to maintain the health and productivity of the wetland habitats that they call home.
Combating Climate Change
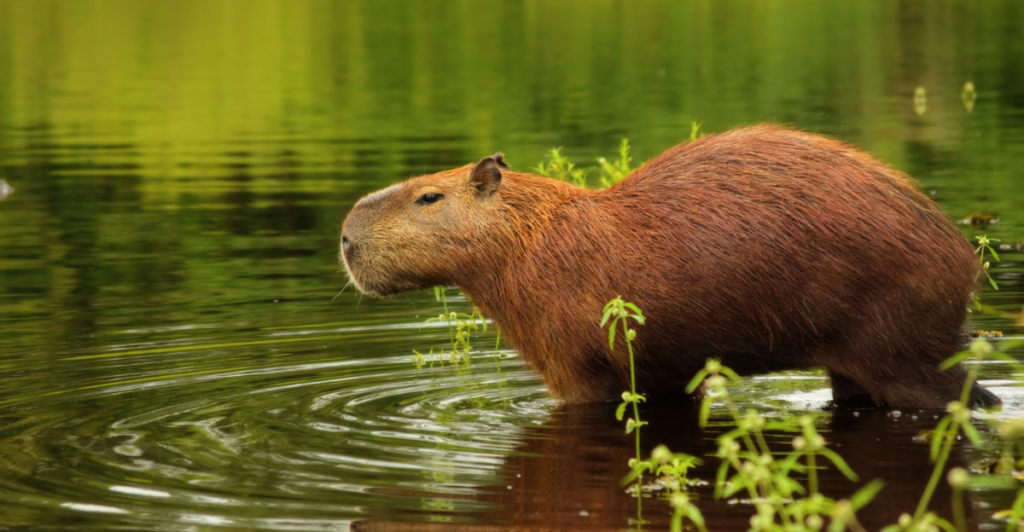

Capybaras are quite resilient to climate change factors, while many species are sensitive to it. Changes in water levels don’t affect their species since they’ve adapted a semi-aquatic nature. This ensures their survival and the survival of their predator population.
Important Adaptations
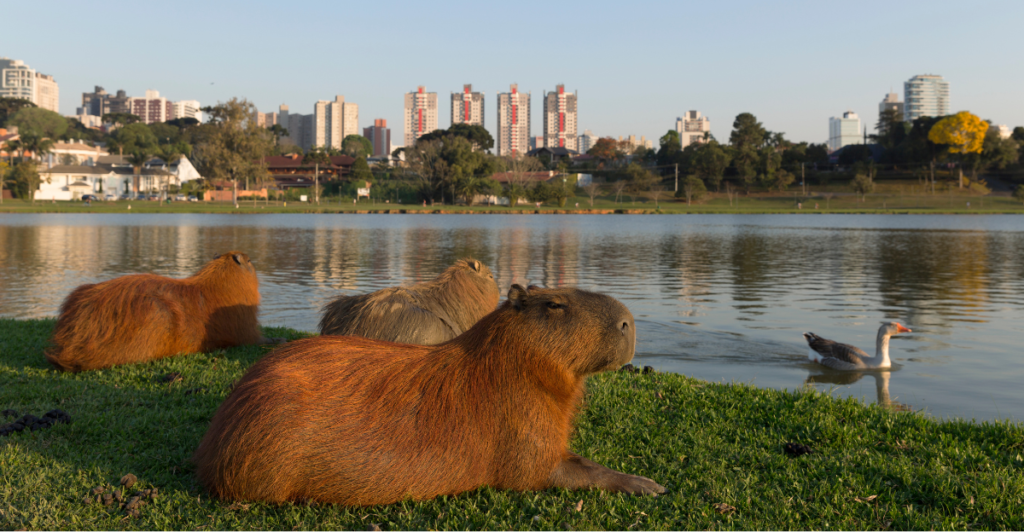

Capybaras have unique evolutionary adaptations that allow them to thrive in wetlands. Their eyes, ears, and nostrils are positioned high up on their head, similar to hippos, so that they can submerge as much of their body as possible to avoid predators. They also have webbed toes, which make them great swimmers.
Conservation Efforts
Although they are an amazing and resilient species, capybaras do face threats from hunting habitat shrinkage. Conservation efforts are the key in safeguarding them and the species in their habitat that make up a balanced ecosystem.







